Programmed Cell Death-1 Receptor (PD-1)-Mediated Regulation of Innate Lymphoid Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Programmed Death-1 (PD-1)
2.1. PD-1 Function in T Cells
2.2. PD-1 Structure
2.3. PD-1 Signalling in T Cells
3. Innate Lymphoid Cells
Types of ILCs
4. PD-1 and ILCs
4.1. PD-1 in ILC Development
4.2. PD-1 Modulation of ILC Function
4.3. PD-1 Signalling in ILCs
4.4. PD-1 Modulation of ILC in Cancer
5. Conclusions
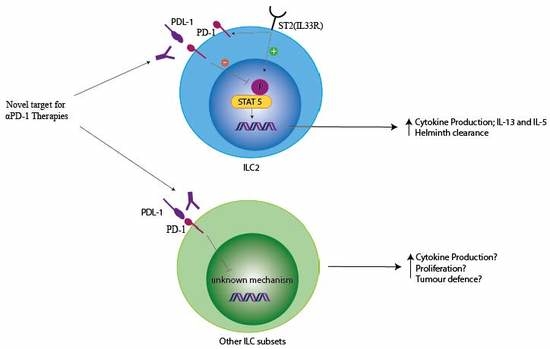
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agata, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Nishimura, H.; Ishida, Y.; Tsubata, T.; Yagita, H.; Honjo, T. Expression of the pd-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse t and b lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 1996, 8, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, T.; Akiba, H.; Iwai, H.; Matsuda, H.; Aoki, M.; Tanno, Y.; Shin, T.; Tsuchiya, H.; Pardoll, D.M.; Okumura, K.; et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine t cells and apc. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5538–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. Pd-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Tsang, J.C.; Wang, C.; Clare, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Brandt, C.; Kane, L.; Campos, L.S.; Lu, L.; et al. Single-cell rna-seq identifies a pd-1(hi) ilc progenitor and defines its development pathway. Nature 2016, 539, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seillet, C.; Mielke, L.A.; Amann-Zalcenstein, D.B.; Su, S.; Gao, J.; Almeida, F.F.; Shi, W.; Ritchie, M.E.; Naik, S.H.; Huntington, N.D.; et al. Deciphering the innate lymphoid cell transcriptional program. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.; Huang, Y.; Mallett, G.; Stathopoulou, C.; Felizardo, T.C.; Sun, M.A.; Martin, E.L.; Zhu, N.; Woodward, E.L.; Elias, M.S.; et al. Pd-1 regulates klrg1(+) group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, P.; Pesce, S.; Greppi, M.; Fulcheri, E.; Munari, E.; Olive, D.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, A.; Moretta, L.; Marcenaro, E. Pd-1 is expressed by and regulates human group 3 innate lymphoid cells in human decidua. Mucosal. Immunol. 2019, 12, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, H.; Honjo, T. Pd-1: An inhibitory immunoreceptor involved in peripheral tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemnitz, J.M.; Parry, R.V.; Nichols, K.E.; June, C.H.; Riley, J.L. Shp-1 and shp-2 associate with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary human t cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents t cell activation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovas, C.; Casazza, J.P.; Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Gostick, E.; Adams, W.C.; Precopio, M.L.; Schacker, T.; Roederer, M.; Douek, D.C.; et al. Pd-1 is a regulator of virus-specific cd8+ t cell survival in hiv infection. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, M.; Kuylenstierna, C.; Gonzalez, V.D.; Andersson, S.K.; Bosnjak, L.; Sonnerborg, A.; Quigley, M.F.; Sandberg, J.K. Severe functional impairment and elevated pd-1 expression in cd1d-restricted nkt cells retained during chronic hiv-1 infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tivol, E.A.; Borriello, F.; Schweitzer, A.N.; Lynch, W.P.; Bluestone, J.A.; Sharpe, A.H. Loss of ctla-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of ctla-4. Immunity 1995, 3, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, L.M.; Salinas, V.H.; Brown, K.E.; Vanguri, V.K.; Freeman, G.J.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Sharpe, A.H. Pd-l1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory t cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, D.L.; Wherry, E.J.; Masopust, D.; Zhu, B.; Allison, J.P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R. Restoring function in exhausted cd8 t cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 2006, 439, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, C.; Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Amadei, B.; Di Vincenzo, P.; Giuberti, T.; Laccabue, D.; Zerbini, A.; Cavalli, A.; Missale, G.; et al. Characterization of hepatitis b virus (hbv)-specific t-cell dysfunction in chronic hbv infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velu, V.; Kannanganat, S.; Ibegbu, C.; Chennareddi, L.; Villinger, F.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R.; Amara, R.R. Elevated expression levels of inhibitory receptor programmed death 1 on simian immunodeficiency virus-specific cd8 t cells during chronic infection but not after vaccination. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5819–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, S.; Amadei, B.; Tola, D.; Massari, M.; Schivazappa, S.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C. Pd-1 expression in acute hepatitis c virus (hcv) infection is associated with hcv-specific cd8 exhaustion. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11398–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprowicz, V.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Kuntzen, T.; Nolan, B.E.; Longworth, S.; Berical, A.; Blum, J.; McMahon, C.; Reyor, L.L.; Elias, N.; et al. High level of pd-1 expression on hepatitis c virus (hcv)-specific cd8+ and cd4+ t cells during acute hcv infection, irrespective of clinical outcome. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3154–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streeck, H.; Brumme, Z.L.; Anastario, M.; Cohen, K.W.; Jolin, J.S.; Meier, A.; Brumme, C.J.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Alter, G.; Allen, T.M.; et al. Antigen load and viral sequence diversification determine the functional profile of hiv-1-specific cd8+ t cells. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphorst, A.O.; Wieland, A.; Nasti, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Barber, D.L.; Konieczny, B.T.; Daugherty, C.Z.; Koenig, L.; Yu, K.; et al. Rescue of exhausted cd8 t cells by pd-1-targeted therapies is cd28-dependent. Science 2017, 355, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreich, K.J.; Yoon, H.; Ahmed, R.; Boss, J.M. Nfatc1 regulates pd-1 expression upon t cell activation. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4832–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Seo, S.K.; Choi, I.W.; Choi, I.; Lee, S.W. Interferon-sensitive response element (isre) is mainly responsible for ifn-alpha-induced upregulation of programmed death-1 (pd-1) in macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1779, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Schwartz, J.C.; Guo, X.; Bhatia, S.; Cao, E.; Lorenz, M.; Cammer, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Edidin, M.A.; et al. Structural and functional analysis of the costimulatory receptor programmed death-1. Immunity 2004, 20, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, E.; Cheung, J.; Zhu, J.; Su, X.; Taylor, M.J.; Wallweber, H.A.; Sasmal, D.K.; Huang, J.; Kim, J.M.; Mellman, I.; et al. T cell costimulatory receptor cd28 is a primary target for pd-1-mediated inhibition. Science 2017, 355, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, J.L. Pd-1 signaling in primary t cells. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, G.J.; Long, A.J.; Iwai, Y.; Bourque, K.; Chernova, T.; Nishimura, H.; Fitz, L.J.; Malenkovich, N.; Okazaki, T.; Byrne, M.C.; et al. Engagement of the pd-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel b7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchman, Y.; Wood, C.R.; Chernova, T.; Chaudhary, D.; Borde, M.; Chernova, I.; Iwai, Y.; Long, A.J.; Brown, J.A.; Nunes, R.; et al. Pd-l2 is a second ligand for pd-1 and inhibits t cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar-Molnar, E.; Gacser, A.; Freeman, G.J.; Almo, S.C.; Nathenson, S.G.; Nosanchuk, J.D. The pd-1/pd-l costimulatory pathway critically affects host resistance to the pathogenic fungus histoplasma capsulatum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2658–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; Gittis, A.G.; Su, H.P.; Mikami, B.; Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T.; Minato, N.; Garboczi, D.N. The pd-1/pd-l1 complex resembles the antigen-binding fv domains of antibodies and t cell receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, T.; Maeda, A.; Nishimura, H.; Kurosaki, T.; Honjo, T. Pd-1 immunoreceptor inhibits b cell receptor-mediated signaling by recruiting src homology 2-domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2 to phosphotyrosine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13866–13871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, K.A.; Fitz, L.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benander, C.; George, J.A.; Wooters, J.; Qiu, Y.; Jussif, J.M.; Carter, L.L.; Wood, C.R.; et al. Pd-1 inhibits t-cell receptor induced phosphorylation of the zap70/cd3zeta signalosome and downstream signaling to pkctheta. FEBS Lett. 2004, 574, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, R.V.; Chemnitz, J.M.; Frauwirth, K.A.; Lanfranco, A.R.; Braunstein, I.; Kobayashi, S.V.; Linsley, P.S.; Thompson, C.B.; Riley, J.L. Ctla-4 and pd-1 receptors inhibit t-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9543–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fife, B.T.; Pauken, K.E.; Eagar, T.N.; Obu, T.; Wu, J.; Tang, Q.; Azuma, M.; Krummel, M.F.; Bluestone, J.A. Interactions between pd-1 and pd-l1 promote tolerance by blocking the tcr-induced stop signal. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, M.; Tocheva, A.S.; Sandigursky, S.; Nayak, S.; Philips, E.A.; Nichols, K.E.; Strazza, M.; Azoulay-Alfaguter, I.; Askenazi, M.; Neel, B.G.; et al. Affinity purification mass spectrometry analysis of pd-1 uncovers sap as a new checkpoint inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E468–E477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathopoulou, C.; Gangaplara, A.; Mallett, G.; Flomerfelt, F.A.; Liniany, L.P.; Knight, D.; Samsel, L.A.; Berlinguer-Palmini, R.; Yim, J.J.; Felizardo, T.C.; et al. Pd-1 inhibitory receptor downregulates asparaginyl endopeptidase and maintains foxp3 transcription factor stability in induced regulatory t cells. Immunity 2018, 49, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarnath, S.; Costanzo, C.M.; Mariotti, J.; Ullman, J.L.; Telford, W.G.; Kapoor, V.; Riley, J.L.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H.; Fong, T.; et al. Regulatory t cells and human myeloid dendritic cells promote tolerance via programmed death ligand-1. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarnath, S.; Chen, H.; Foley, J.E.; Costanzo, C.M.; Sennesh, J.D.; Solomon, M.A.; Fowler, D.H. Host-based th2 cell therapy for prolongation of cardiac allograft viability. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, D.; Paroli, M.; Francavilla, V.; Videtta, M.; Morrone, S.; Labbadia, G.; Cerino, A.; Mondelli, M.U.; Barnaba, V. Pd-l1 negatively regulates cd4+cd25+foxp3+ tregs by limiting stat-5 phosphorylation in patients chronically infected with hcv. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spits, H.; Artis, D.; Colonna, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Eberl, G.; Koyasu, S.; Locksley, R.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Mebius, R.E.; et al. Innate lymphoid cells—A proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, R.; Klein, E.; Pross, H.; Wigzell, H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. Ii. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur. J. Immunol. 1975, 5, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebius, R.E.; Rennert, P.; Weissman, I.L. Developing lymph nodes collect cd4+cd3- ltbeta+ cells that can differentiate to apc, nk cells, and follicular cells but not t or b cells. Immunity 1997, 7, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernink, J.H.; Krabbendam, L.; Germar, K.; de Jong, E.; Gronke, K.; Kofoed-Nielsen, M.; Munneke, J.M.; Hazenberg, M.D.; Villaudy, J.; Buskens, C.J.; et al. Interleukin-12 and -23 control plasticity of cd127(+) group 1 and group 3 innate lymphoid cells in the intestinal lamina propria. Immunity 2015, 43, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes, F.; Bald, T.; Ng, S.S.; Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Rautela, J.; Straube, J.; Waddell, N.; Blake, S.J.; et al. Tumor immunoevasion by the conversion of effector nk cells into type 1 innate lymphoid cells. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonarbourg, C.; Mortha, A.; Bui, V.L.; Hernandez, P.P.; Kiss, E.A.; Hoyler, T.; Flach, M.; Bengsch, B.; Thimme, R.; Holscher, C.; et al. Regulated expression of nuclear receptor rorgammat confers distinct functional fates to nk cell receptor-expressing rorgammat(+) innate lymphocytes. Immunity 2010, 33, 736–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernink, J.H.; Peters, C.P.; Munneke, M.; te Velde, A.A.; Meijer, S.L.; Weijer, K.; Hreggvidsdottir, H.S.; Heinsbroek, S.E.; Legrand, N.; Buskens, C.J.; et al. Human type 1 innate lymphoid cells accumulate in inflamed mucosal tissues. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupedo, T.; Crellin, N.K.; Papazian, N.; Rombouts, E.J.; Weijer, K.; Grogan, J.L.; Fibbe, W.E.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Spits, H. Human fetal lymphoid tissue-inducer cells are interleukin 17-producing precursors to rorc+ cd127+ natural killer-like cells. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, T.Y.; MacLaren, A.; Romanish, M.T.; Gold, M.J.; McNagny, K.M.; Takei, F. Retinoic-acid-receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor alpha is required for natural helper cell development and allergic inflammation. Immunity 2012, 37, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyler, T.; Klose, C.S.; Souabni, A.; Turqueti-Neves, A.; Pfeifer, D.; Rawlins, E.L.; Voehringer, D.; Busslinger, M.; Diefenbach, A. The transcription factor gata-3 controls cell fate and maintenance of type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Immunity 2012, 37, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, K.; Yamada, T.; Tanabe, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Ikawa, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Furusawa, J.; Ohtani, M.; Fujii, H.; Koyasu, S. Innate production of t(h)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-kit(+)sca-1(+) lymphoid cells. Nature 2010, 463, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.E.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Bando, J.K.; Sullivan, B.M.; Ho, I.C.; Locksley, R.M. Divergent expression patterns of il-4 and il-13 define unique functions in allergic immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 13, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjosberg, J.M.; Trifari, S.; Crellin, N.K.; Peters, C.P.; van Drunen, C.M.; Piet, B.; Fokkens, W.J.; Cupedo, T.; Spits, H. Human il-25- and il-33-responsive type 2 innate lymphoid cells are defined by expression of crth2 and cd161. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz, S.A.; Siracusa, M.C.; Monticelli, L.A.; Ziegler, C.G.; Kim, B.S.; Brestoff, J.R.; Peterson, L.W.; Wherry, E.J.; Goldrath, A.W.; Bhandoola, A.; et al. Il-25 simultaneously elicits distinct populations of innate lymphoid cells and multipotent progenitor type 2 (mpptype2) cells. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, L.A.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Abt, M.C.; Alenghat, T.; Ziegler, C.G.; Doering, T.A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Laidlaw, B.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Sathaliyawala, T.; et al. Innate lymphoid cells promote lung-tissue homeostasis after infection with influenza virus. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cella, M.; Fuchs, A.; Vermi, W.; Facchetti, F.; Otero, K.; Lennerz, J.K.; Doherty, J.M.; Mills, J.C.; Colonna, M. A human natural killer cell subset provides an innate source of il-22 for mucosal immunity. Nature 2009, 457, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh-Takayama, N.; Lesjean-Pottier, S.; Vieira, P.; Sawa, S.; Eberl, G.; Vosshenrich, C.A.; Di Santo, J.P. Il-7 and il-15 independently program the differentiation of intestinal cd3-nkp46+ cell subsets from id2-dependent precursors. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, S.; Ahern, P.P.; Uhlig, H.H.; Ivanov, II.; Littman, D.R.; Maloy, K.J.; Powrie, F. Innate lymphoid cells drive interleukin-23-dependent innate intestinal pathology. Nature 2010, 464, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villanova, F.; Flutter, B.; Tosi, I.; Grys, K.; Sreeneebus, H.; Perera, G.K.; Chapman, A.; Smith, C.H.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. Characterization of innate lymphoid cells in human skin and blood demonstrates increase of nkp44+ ilc3 in psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenberg, G.F.; Monticelli, L.A.; Elloso, M.M.; Fouser, L.A.; Artis, D. Cd4(+) lymphoid tissue-inducer cells promote innate immunity in the gut. Immunity 2011, 34, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepworth, M.R.; Monticelli, L.A.; Fung, T.C.; Ziegler, C.G.; Grunberg, S.; Sinha, R.; Mantegazza, A.R.; Ma, H.L.; Crawford, A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; et al. Innate lymphoid cells regulate cd4+ t-cell responses to intestinal commensal bacteria. Nature 2013, 498, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, C.J.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Walker, J.A.; Salimi, M.; Wong, S.H.; Brewer, J.M.; Englezakis, A.; Barlow, J.L.; Hams, E.; Scanlon, S.T.; et al. Mhcii-mediated dialog between group 2 innate lymphoid cells and cd4(+) t cells potentiates type 2 immunity and promotes parasitic helminth expulsion. Immunity 2014, 41, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepworth, M.R.; Fung, T.C.; Masur, S.H.; Kelsen, J.R.; McConnell, F.M.; Dubrot, J.; Withers, D.R.; Hugues, S.; Farrar, M.A.; Reith, W.; et al. Immune tolerance. Group 3 innate lymphoid cells mediate intestinal selection of commensal bacteria-specific cd4(+) t cells. Science 2015, 348, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maazi, H.; Patel, N.; Sankaranarayanan, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Rigas, D.; Soroosh, P.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H.; Akbari, O. Icos:Icos-ligand interaction is required for type 2 innate lymphoid cell function, homeostasis, and induction of airway hyperreactivity. Immunity 2015, 42, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, M.; Coyle, A.J.; Schmitz, N.; Barner, M.; Oxenius, A.; Gallimore, A.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Bachmann, M.F. Inducible costimulator protein (icos) controls t helper cell subset polarization after virus and parasite infection. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo, J.A.; Tian, J.; Delaney, T.; Corcoran, J.; Rottman, J.B.; Lora, J.; Al-garawi, A.; Kroczek, R.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Coyle, A.J. Icos is critical for t helper cell-mediated lung mucosal inflammatory responses. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, A.J.; Lehar, S.; Lloyd, C.; Tian, J.; Delaney, T.; Manning, S.; Nguyen, T.; Burwell, T.; Schneider, H.; Gonzalo, J.A.; et al. The cd28-related molecule icos is required for effective t cell-dependent immune responses. Immunity 2000, 13, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenhove, G.; Boucquey, E.; Taquin, A.; Acolty, V.; Bonetti, L.; Ryffel, B.; Le Bert, M.; Englebert, K.; Boon, L.; Moser, M. Pd-1 is involved in the dysregulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cells in a murine model of obesity. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2053–2060.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, C.; Khan, A.R.; Floudas, A.; Saunders, S.P.; Hams, E.; Rodewald, H.R.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Fallon, P.G. Ilc2s regulate adaptive th2 cell functions via pd-l1 checkpoint control. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2507–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrier, D.E.; Serafini, N.; Di Santo, J.P. Innate lymphoid cell development: A t cell perspective. Immunity 2018, 48, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchinovich, G.; Ganter, S.; Barenwaldt, A.; Finke, D. Nkp46 calibrates tumoricidal potential of type 1 innate lymphocytes by regulating trail expression. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 3762–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Wang, R.; Yao, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Chang, X.; Fan, P.; Dong, T.; Ogg, G. Activated innate lymphoid cell populations accumulate in human tumour tissues. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumino, N.; Martini, S.; Munari, E.; Scordamaglia, F.; Besi, F.; Mariotti, F.R.; Bogina, G.; Mingari, M.C.; Vacca, P.; Moretta, L. Presence of innate lymphoid cells in pleural effusions of primary and metastatic tumors: Functional analysis and expression of pd-1 receptor. Int. J. Cancer 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchberger, S.; Royston, D.J.; Boulard, O.; Thornton, E.; Franchini, F.; Szabady, R.L.; Harrison, O.; Powrie, F. Innate lymphoid cells sustain colon cancer through production of interleukin-22 in a mouse model. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, D.W.; Stefanski, H.E.; Vincent, B.G.; Dant, T.A.; Reisdorf, S.; Bommiasamy, H.; Serody, D.A.; Wilson, J.E.; McKinnon, K.P.; Shlomchik, W.D.; et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells treat and prevent acute gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Group | Subsets | Transcription Factor Expression | Co-receptor Expression | Cytokine/Alarmins Stimulation | Effector Cytokine Profile | Role Within the Immune System |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 ILC | NK Cells (CD49b+) ILC1(Lin−CD127+/-CD49a+) | Tbet+EOMES+ Tbet+ | PD-1 CTLA4 | IL-15 IL-12 IL-18 | IFNγ TNFα Perforin and granzyme (NK cells) | Viral defence Anti-Tumour defence Intestinal inflammation |
| Group 2 ILC | Natural (ST2+, IL33R+) Inflammatory (KLRG1+) Mature (ST2+KLRG1+) | GATA3+ | PD-1 CTLA4 ICOS (PDL-1) (OX40L) | IL-25 IL-33 TSLP | IL-4 IL-5 IL-13 Amphregulin | Helminth defence Thermogenesis Tissue repair Allergy Atopic dermatitis |
| Group 3 ILC | NCR+ (Nkp46+/Nkp44+) NCR− (Nkp46−/Nkp44−) LTi | RORγt+ | PD-1 CTLA4 | IL-23 IL-1β | IL-17 IL-22 GM-CSF | Intestinal homeostasis Bacterial defence Colitis Psorasis Colon Cancer |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallett, G.; Laurence, A.; Amarnath, S. Programmed Cell Death-1 Receptor (PD-1)-Mediated Regulation of Innate Lymphoid Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112836
Mallett G, Laurence A, Amarnath S. Programmed Cell Death-1 Receptor (PD-1)-Mediated Regulation of Innate Lymphoid Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(11):2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112836
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallett, Grace, Arian Laurence, and Shoba Amarnath. 2019. "Programmed Cell Death-1 Receptor (PD-1)-Mediated Regulation of Innate Lymphoid Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 11: 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112836
APA StyleMallett, G., Laurence, A., & Amarnath, S. (2019). Programmed Cell Death-1 Receptor (PD-1)-Mediated Regulation of Innate Lymphoid Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112836