Carbon Nanomaterials and LED Irradiation as Antibacterial Strategies against Gram-Positive Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
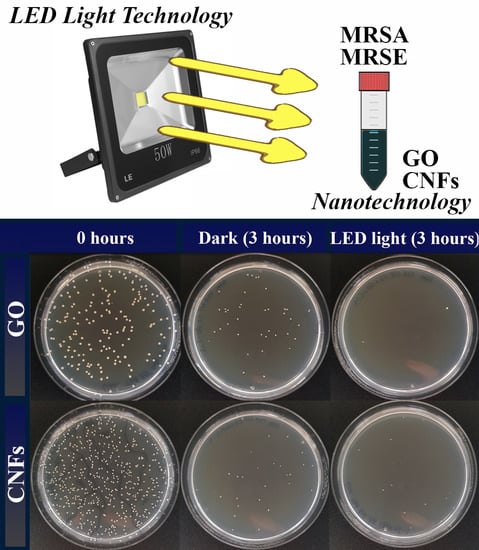
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Carbon Nanomaterials
3.2. Electron Microscopy
3.3. Raman Spectroscopy
3.4. Antibacterial Test
3.5. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay for GO and CNFs
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LED | Light-emitting diode |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| CNFs | Carbon nanofibers |
| CNMs | Carbon nanomaterials |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MRSE | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis |
| AR | Antibiotic resistance |
| AMPs | Antimicrobial peptides |
| HR-TEM | High-resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| EDS | Energy-disperse X-ray spectroscopy |
| CFUs | Colony-forming units |
| QAC | Quaternary ammonium compounds |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| LV | Loss of viability |
References
- Fernández, J.; Bert, F.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H. The challenges of multi-drug-resistance in hepatology. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance Found Worldwide, New Data Shows. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2018/antibiotic-resistance-found/en/ (accessed on 22 July 2019).
- O’neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. In The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust and HM Government: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, H.; Parashar, V.; Parashar, R.; Prakash, R.; Ramteke, P.W.; Pandey, A.C. Controlled drug release characteristics and enhanced antibacterial effect of graphene nanosheets containing gentamicin sulfate. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4104–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Excellent antimicrobial properties of mesoporous anatase TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 composite films. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 114, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Shi, L.; Shi, Z.; Ren, L.; Wang, Y. The promotion of antimicrobial activity on silicon substrates using a “click” immobilized short peptide. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mant, C.T.; Farmer, S.W.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Vasil, M.L.; Hodges, R.S. Rational design of alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced activities and specificity/therapeutic index. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12316–12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, E.A.; Wang, X.; Lee, H.S.; Weisblum, B.; Gellman, S.H. Non-haemolytic beta-amino-acid oligomers. Nature 2000, 404, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chongsiriwatana, N.P.; Patch, J.A.; Czyzewski, A.M.; Dohm, M.T.; Ivankin, A.; Gidalevitz, D.; Zuckermann, R.N.; Barron, A.E. Peptoids that mimic the structure, function, and mechanism of helical antimicrobial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2794–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, Z.; Shen, D.; Xu, W. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 333, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, V.W.L.; Chan, J.M.W.; Sardon, H.; Ono, R.J.; García, J.M.; Yang, Y.Y.; Hedrick, J.L. Antimicrobial hydrogels: A new weapon in the arsenal against multidrug-resistant infections. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 78, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Siddiqui, M.K.J. Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegstad, K.; Langsrud, S.; Lunestad, B.T.; Scheie, A.A.; Sunde, M.; Yazdankhah, S.P. Does the Wide Use of Quaternary Ammonium Compounds Enhance the Selection and Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance and Thus Threaten Our Health? Microb. Drug Resist. 2010, 16, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, D.T.F.; Lundy, F.T.; Timson, D.J. IQ-motif peptides as novel anti-microbial agents. Biochimie 2013, 95, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelgrift, R.Y.; Friedman, A.J. Nanotechnology as a therapeutic tool to combat microbial resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seil, J.T.; Webster, T.J. Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: Methods and literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2767–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Blecher, K.; Nasir, A.; Friedman, A. The growing role of nanotechnology in combating infectious disease. Virulence 2011, 2, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of the Antimicrobial Activities of Graphene Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegou, E.; Magana, M.; Katsogridaki, A.E.; Ioannidis, A.; Raptis, V.; Jordan, S.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; Chatzandroulis, S.; Ornelas, C.; Tegos, G.P. Terms of endearment: Bacteria meet graphene nanosurfaces. Biomaterials 2016, 89, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, M.; Frígols, B.; Salesa, B.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Calcium alginate/graphene oxide films: Reinforced composites able to prevent Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis infections with no cytotoxicity for human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salesa, B.; Martí, M.; Frígols, B.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Carbon Nanofibers in Pure Form and in Calcium Alginate Composites Films: New Cost-Effective Antibacterial Biomaterials against the Life-Threatening Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Polymers 2019, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, M.; Palmieri, V.; Bugli, F.; De Spirito, M.; Sanguinetti, M.; Ciancico, C.; Braidotti, M.C.; Gentilini, S.; Angelani, L.; Conti, C. Biomimetic antimicrobial cloak by graphene-oxide agar hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.M.; Tria, M.C.R.; Vergara, R.A.M.V.; Ahmed, F.; Advincula, R.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Antimicrobial graphene polymer (PVK-GO) nanocomposite films. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8892–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, M.; Dadashpour, M.; Hejazi, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Behnam, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Shadjou, N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Anti-bacterial activity of graphene oxide as a new weapon nanomaterial to combat multidrug-resistance bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Faria, A.F.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Meira, S.M.M.; de Moraes, A.C.M.; Brandelli, A.; Filho, A.G.S.; Alves, O.L. Anti-adhesion and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide sheets. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, O.N.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Wang, B.; Brown, N.A.; Luo, P.G.; McNamara, N.D.; Vangsness, M.; Sun, Y.P.; Bunker, C.E. Graphene oxide: A nonspecific enhancer of cellular growth. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8100–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Mittal, S.; Shukla, R.K.; Pandey, A.K.; Dhakate, S.R.; Pasricha, R.; Dhawan, A. Toxicity of graphene in normal human lung cells (BEAS-2B). J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, R.; Yang, X.; Ji, T.; Gu, Z.; Yin, J.J.; Gao, X.; Nie, G. Deciphering the underlying mechanisms of oxidation-state dependent cytotoxicity of graphene oxide on mammalian cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 237, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreault, F.; Tousley, M.E.; Elimelech, M. Thin-Film Composite Polyamide Membranes Functionalized with Biocidal Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2013, 1, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, M.; Verre, A.F.; Iliut, M.; Peiris-Pagés, M.; Ozsvari, B.; Gandara, R.; Cappello, A.R.; Sotgia, F.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Lisanti, M.P. Graphene oxide selectively targets cancer stem cells, across multiple tumor types: Implications for non-toxic cancer treatment, via “differentiation-based nano-therapy”. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3553–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Nanoparticle-mediated combination therapy: Two-in-one approach for cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, A.C.M.; Lima, B.A.; de Faria, A.F.; Brocchi, M.; Alves, O.L. Graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite as a promising biocidal agent against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6847–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanchanapally, R.; Nellore, B.P.V.; Sinha, S.S.; Pedraza, F.; Jones, S.J.; Pramanik, A.; Chavva, S.R.; Tchounwou, C.; Shi, Y.; Vangara, A.; et al. Antimicrobial peptide-conjugated graphene oxide membrane for efficient removal and effective killing of multiple drug resistant bacteria. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 18881–18887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stout, D.A.; Basu, B.; Webster, T.J. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid): Carbon nanofiber composites for myocardial tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3101–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorens-Gámez, M.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Low-Cost Advanced Hydrogels of Calcium Alginate/Carbon Nanofibers with Enhanced Water Diffusion and Compression Properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P. Carbon Fibers and Their Composites, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gardea, F.; Naraghi, M.; Lagoudas, D. Effect of thermal interface on heat flow in carbon nanofiber composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Ruiz-Pividal, J.F.; Llorens-Gámez, M. Enhancement of water diffusion and compression performance of crosslinked alginate with a minuscule amount of graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Deb, S. Synthesis of irregular graphene oxide tubes using green chemistry and their potential use as reinforcement materials for biomedical applications. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Iskandar, L.; Deb, S. Green synthetic routes to alginate-graphene oxide composite hydrogels with enhanced physical properties for bioengineering applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 103, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Correa, F.; Vidaurre-Agut, C.; Serrano-Aroca, A.; Campillo-Fernández, A.J. Poly(2-hydroxyethyl acrylate) hydrogels reinforced with graphene oxide: Remarkable improvement of water diffusion and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frígols, B.; Martí, M.; Salesa, B.; Hernández-Oliver, C.; Aarstad, O.; Ulset, A.S.T.; Sætrom, G.I.; Aachmann, F.L.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Graphene oxide in zinc alginate films: Antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity, zinc release, water sorption/diffusion, wettability and opacity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, E.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Leung, C.W.T.; Hong, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Light-enhanced bacterial killing and wash-free imaging based on AIE fluorogen. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7180–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Mao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Pan, H.; Chu, P.K.; Wu, S. Synergistic Bacteria Killing through Photodynamic and Physical Actions of Graphene Oxide/Ag/Collagen Coating. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26417–26428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Nikaido, H.; Williams, K.E. Silver-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli display active efflux of Ag+ and are deficient in porins. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 6127–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Y.; Ge, C.; Fang, G.; Wu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chai, Z.; Chen, C.; Yin, J.J. Light-Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Graphene Oxide, Mainly via Accelerated Electron Transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10154–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, N.G.; Wu, C.H.; Cheng, T.C. Light-emitting diodes-Their potential in biomedical applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, N.; Thrivikraman, G.; Athirasala, A.; Tahayeri, A.; França, C.M.; Ferracane, J.L.; Bertassoni, L.E. Photopolymerization of cell-laden gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels using a dental curing light for regenerative dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.H.; Monk, I.R.; Gonçalves da Silva, A.; Seemann, T.; Chua, K.Y.L.; Kearns, A.; Hill, R.; Woodford, N.; Bartels, M.D.; Strommenger, B.; et al. Global spread of three multidrug-resistant lineages of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, K.C.; Benjamin, D.K. Clinical Pharmacology of Anti-Infective Drugs. In Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 1160–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00020-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chessa, D.; Ganau, G.; Spiga, L.; Bulla, A.; Mazzarello, V.; Campus, G.V.; Rubino, S. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis Virulence Strains as Causative Agents of Persistent Infections in Breast Implants. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speziale, P.; Geoghegan, J.A. Biofilm Formation by Staphylococci and Streptococci: Structural, Functional and Regulatory Aspects and Implications for Pathogenesis; Frontiers Media SA: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zefirov, Y.V.; Zorky, P.M. New applications of van der Waals radii in chemistry. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1995, 64, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; Li, F. Graphene Oxide: Physics and Applications; Springer: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, C.; Wang, J. Raman spectra of carbon nanotubes and nanofibers prepared by ethanol flames. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cançado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Ferreira, E.H.M.; Stavale, F.; Achete, C.A.; Capaz, R.B.; Moutinho, M.V.O.; Lombardo, A.; Kulmala, T.S.; Ferrari, A.C. Quantifying defects in graphene via Raman spectroscopy at different excitation energies. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3190–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, T.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; et al. Comparative study of methylene blue dye adsorption onto activated carbon, graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, G.D.; Bisno, A.L.; Parisi, J.T.; McLaughlin, B.; Hester, M.G.; Luther, R.W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann. Int. Med. 1982, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.R.; Fouts, D.E.; Archer, G.L.; Mongodin, E.F.; DeBoy, R.T.; Ravel, J.; Paulsen, I.T.; Kolonay, J.F.; Brinkac, L.; Beanan, M.; et al. Insights on evolution of virulence and resistance from the complete genome analysis of an early methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain and a biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí, M.; Frígols, B.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Antimicrobial Characterization of Advanced Materials for Bioengineering Applications. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 138, e57710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoob, J.; Naz, S.; Awan, S.; Abbas, Z.; Jafri, W.; Hamid, S.; Jafri, F.; Usman, M.W. Comparison of Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Chloride and Bismuth Subsalicylate Against Clinical Isolates of Helicobacter pylori. Microb. Drug Resist. 2013, 20, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straccia, M.C.; Romano, I.; Oliva, A.; Santagata, G.; Laurienzo, P. Crosslinker effects on functional properties of alginate/N-succinylchitosan based hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elias, L.; Taengua, R.; Frígols, B.; Salesa, B.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Carbon Nanomaterials and LED Irradiation as Antibacterial Strategies against Gram-Positive Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143603
Elias L, Taengua R, Frígols B, Salesa B, Serrano-Aroca Á. Carbon Nanomaterials and LED Irradiation as Antibacterial Strategies against Gram-Positive Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143603
Chicago/Turabian StyleElias, Lisa, Rafael Taengua, Belén Frígols, Beatriz Salesa, and Ángel Serrano-Aroca. 2019. "Carbon Nanomaterials and LED Irradiation as Antibacterial Strategies against Gram-Positive Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143603
APA StyleElias, L., Taengua, R., Frígols, B., Salesa, B., & Serrano-Aroca, Á. (2019). Carbon Nanomaterials and LED Irradiation as Antibacterial Strategies against Gram-Positive Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143603