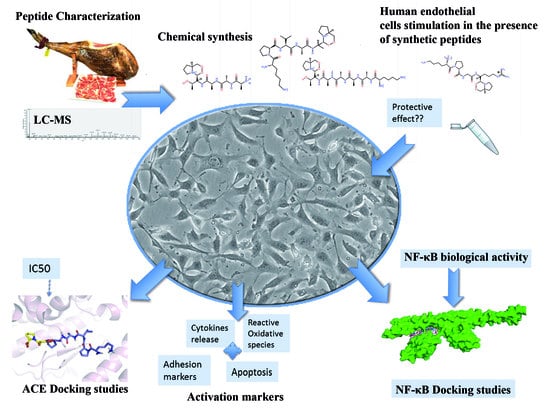
Multifunctional Peptides from Spanish Dry-Cured Pork Ham: Endothelial Responses and Molecular Modeling Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Peptides with Human in Vitro ACE Inhibitory Activity
2.2. Peptides Penetrate in the Catalytic Active Site of ACE
2.3. Peptide Effects in Inflammatory Conditions
2.3.1. Peptides Affect Gene Expression in Inflammatory Conditions
2.3.2. Peptides Affect Protein Expression in Inflammatory Conditions
2.4. Effect of Peptides in Oxidative Conditions
2.4.1. Peptides Do Not Affect Cell Viability and Apoptosis after Treatment with H2O2
2.4.2. Peptides Slightly Affect the Oxidative Status
2.5. Peptides Decrease NF-κB Activity
2.6. Peptides Bind to the Subunit NEMO
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Peptides
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Human ACE Inhibition Assay
4.4. TNF-α and H2O2 Stimulation
4.5. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. NF-κB Activity
4.8. Molecular Modelling
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme |
| BP | Bioactive Peptide |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| DMEM | Dulbecco Modified Eagle Medium |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| HA | Hippuric Acid |
| HHL | Hippuryl Histidyl Leucine |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 |
| IKK | IκB kinase |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor-κB |
| OD | Optic Density |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffer Saline |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Difluoride |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular Adhesion Molecule-1 |
| TNF- α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
References
- Vanhoutte, P.M.; Shimokawa, H.; Feletou, M.; Tang, E.H. Endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease—A 30th anniversary update. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2017, 219, 22–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehnert, B.; Burkhardt, H.; Wessels, J.T.; Schröder, A.; May, M.J.; Vestweber, D.; Zwerina, J.; Warnatz, K.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Schett, G.; et al. NF-κB inhibitor targeted to activated endothelium demonstrates a critical role of endothelial NF-κB in immune-mediated diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16556–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solt, L.A.; Madge, L.A.; May, M.J. NEMO-binding domains of both IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulate IkappaB kinase complex assembly and classical NF-kappaB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27596–27608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Deng, P.; Liu, Y. Recent Advances in Protein Kinase Activity Analysis Based on Nanomaterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Guo, Y.; Qi, X. Ubiquitination-Mediated Inflammasome Activation during Bacterial Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leo, F.; Panarese, S.; Gallerani, R.; Ceci, L.R. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides: Production and implementation of functional food. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 3622–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, E.B.; Ofosu, F.K.; Chelliah, R.; Park, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, D.H. Development of a Soy Protein Hydrolysate with an Antihypertensive Effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Slama-Ben Salem, R.; Ktari, N.; Bkhairia, I.; Nasri, R.; Mora, L.; Kallel, R.; Hamdi, S.; Jamoussi, K.; Boudaouara, T.; El-Feki, A.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-diabetic and anti-hyperlipidemic effects of protein hydrolysates from Octopus vulgaris in alloxanic rats. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides in Human Health: Challenges and Opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, E.; Aristoy, M.C.; Nishimura, H.; Arihara, K.; Toldrá, F. Antihypertensive effect and antioxidant activity of peptide fractions extracted from Spanish dry-cured ham. Meat. Sci. 2012, 91, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, M.; Grootaert, C.; Mora, L.; Aristoy, M.C.; Van Camp, J.; Toldrá, F. Transepithelial transport of dry-cured ham peptides with ACE inhibitory activity through a Caco-2 cell monolayer. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanchez, S.M.; Minguela, A.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Zafrilla-Rentero, M.P.; Abellan-Aleman, J.; Montoro-Garcia, S. The Effect of Regular Intake of Dry-Cured Ham Rich in Bioactive Peptides on Inflammation, Platelet and Monocyte Activation Markers in Humans. Nutrients 2017, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuyer, G.; Schwager, S.L.; Sturrock, E.D.; Isaac, R.E.; Acharya, K.R. Molecular recognition and regulation of human angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) activity by natural inhibitory peptides. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seto, S.W.; Chang, D.; Ko, W.M.; Zhou, X.; Kiat, H.; Bensoussan, A.; Lee, S.M.; Hoi, M.P.; Steiner, G.Z.; Liu, J. Sailuotong Prevents Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)-Induced Injury in EA.hy926 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mats, L.; Liu, R.; Deng, Z.; Mine, Y.; Tsao, R. Anti-inflammatory Effect and Cellular Uptake Mechanism of Peptides from Common Bean. J. Agric. Food Chem 2019, 67, 8370–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, R.; Liu, X.; Qu, Z. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone Protects an Endothelial Cell Line from H2O2 Damage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Long, M.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z. Curcumin activates autophagy and attenuates oxidative damage in EA.hy926 cells via the Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz-Pérez, F.; Mulero, V.; Cayuela, M.L. Application of the dual-luciferase reporter assay to the analysis of promoter activity in Zebrafish embryos. BMC Biotechnol. 2008, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.C.; Lin, S.C.; Rospigliosi, C.C.; Conze, D.B.; Wu, C.J.; Ashwell, J.D.; Eliezer, D.; Wu, H. Structural basis for recognition of diubiquitins by NEMO. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, E.; Mora, L.; Toldrá, F. Stability of ACE inhibitory ham peptides against heat treatment and in vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escudero, E.; Mora, L.; Fraser, P.D.; Aristoy, M.C.; Arihara, K.; Toldrá, F. Purification and Identification of antihypertensive peptides in Spanish dry-cured ham. J. Proteomics 2013, 78, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamamoto, N. Study of the mechanism of antihypertensive peptides VPP and IPP in spontaneously hypertensive rats by DNA microarray analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 620, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Chakrabarti, S.; Majumder, K.; Jiang, Y.; Davidge, S.T.; Wu, J. Egg-derived peptide IRW inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress in endothelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10840–10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Wu, J. Milk-derived tripeptides IPP (Ile-Pro-Pro) and VPP (Val-Pro-Pro) promote adipocyte differentiation and inhibit inflammation in 3T3-F442A cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gräbner, R.; Till, U.; Heller, R. Flow cytometric determination of E-selectin, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 in formaldehyde-fixed endothelial cell monolayers. Cytometry 2000, 40, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen-Heininger, Y.M.; Poynter, M.E.; Baeuerle, P.A. Recent advances towards understanding redox mechanisms in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, E.; Mora, L.; Fraser, P.D.; Aristoy, M.C.; Toldrá, F. Identification of novel antioxidant peptides generated in Spanish dry-cured ham. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meram, C.; Wu, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of egg yolk livetins (α, β, and γ-livetin) fraction and its enzymatic hydrolysates in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Cai, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Min, T.; Wu, H. Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity of a Novel Peptide, ECFSTA, from Wheat Germ Globulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5561–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ea, C.K.; Deng, L.; Xia, Z.P.; Pineda, G.; Chen, Z.J. Activation of IKK by TNFalpha requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, F.; Sakata, S.; Saeki, Y.; Satomi, Y.; Kirisako, T.; Kamei, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Kato, M.; Murata, S.; Yamaoka, S.; et al. Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF-kappaB activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaravalli, J.; Fontan, E.; Fsihi, H.; Coic, Y.M.; Baleux, F.; Véron, M.; Agou, F. Direct inhibition of NF-κB activation by peptide targeting the NOA ubiquitin binding domain of NEMO. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agou, F.; Courtois, G.; Chiaravalli, J.; Baleux, F.; Coïc, Y.M.; Traincard, F.; Israël, A.; Véron, M. Inhibition of NF-kappa B activation by peptides targeting NF-kappa B essential modulator (nemo) oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 54248–54257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.S.; Windshügel, B. LEADS-PEP: A Benchmark Data Set for Assessment of Peptide Docking Performance. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delano, W.L.; LAM, J.W. PyMOL: A communications tool for computational models. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 230, U1371–U1372. [Google Scholar]
- Vincendeau, M.; Hadian, K.; Messias, A.C.; Brenke, J.K.; Halander, J.; Griesbach, R.; Greczmiel, U.; Bertossi, A.; Stehle, R.; Nagel, D.; et al. Inhibition of Canonical NF-κB Signaling by a Small Molecule Targeting NEMO-Ubiquitin Interaction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetényi, C.; van der Spoel, D. Blind docking of drug-sized compounds to proteins with up to a thousand residues. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1447–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapia-Abellán, A.; Angosto-Bazarra, D.; Martínez-Banaclocha, H.; de Torre-Minguela, C.; Cerón-Carrasco, J.P.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Arostegui, J.I.; Pelegrin, P. MCC950 closes the active conformation of NLRP3 to an inactive state. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Bioactive Peptide | Sequence | Source of Protein | IC50 (µM) | Interaction Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEPTIDE 1 (BP1) | KPVAAP | Myosin-XV | 59.22 ± 3.8 | −8.1 |
| PEPTIDE 2 (BP2) | KAAAATP | PR domain Zinc Finger Protein 2 | >1000 | −7.1 |
| PEPTIDE 3 (BP3) | KPGRP | Titin | 485.50 ± 43.47 | −8.2 |
| PEPTIDE 4 (BP4) | AAATP | PR domain Zinc Finger Protein 2 | >1000 | −7.1 |
| ICAM-1 MFI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 71.36 ± 8.31 | |
| TNFα | 1271.91 ± 158.54 | 0.0003 |
| TNFα + BP1 | 1151.37 ± 59.53 | 0.03 |
| TNFα + BP2 | 1064.42 ± 32.02 | 0.009 |
| TNFα + BP3 | 1203.01 ± 279. 89 | 0.09 |
| TNFα + BP4 | 926.01 ± 152.46 | 0.04 |
| A | Ligand | PDB Code | Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic |
| BP1 | 4BWN | ALA314A, GLU315A, GLN317A | ALA314A, ALA318A | |
| BP2 | 4BWN | ASP311A, GLN313A, ALA314A, GLU315A, GLN317A | PHE312B | |
| BP3 | 4BWN | ASP311A, GLU315A, LYS326B, GLU327B | ALA314A, LYS325A | |
| BP4 | 4BWN | ALA314A, GLN317A | ||
| iNUB | 4BWN | LYS326B, GLU327B | LYS321A, ALA323B | |
| UBI peptide | 4BWN | GLU315B, GLN317A, ARG319A, GLU320A, LYS321A, | GLN317A, ALA318A, GLU320A, LYS321A, ALA323A | |
| B | Ligand | PDB Code | Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic |
| BP1 | 3JSV | THR55A, SER57A, ASP58A, ASN60A | ||
| BP2 | 3JSV | ASP39A, GLY76A | PRO37A | |
| BP3 | 3JSV | LYS63B, SER65B | ||
| BP4 | 3JSV | GLU18B, LYS63B, ARG74A, ARG312D | ||
| iNUB | 3JSV | ARG312D | ALA311C, LEU315C, VAL316D, LYS319D | |
| UBI peptide | 3JSV | GLU24A, ASN25A, ASP39A, ARG42A, LEU50A, ASP52A, GLY53A, GLN62B, GLU64B | THR22A, GLU 24A, PRO38A, GLY53A, THR55A, GLU64B |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Sánchez, S.M.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Antonio Gabaldón, J.; Abellán-Alemán, J.; Montoro-García, S. Multifunctional Peptides from Spanish Dry-Cured Pork Ham: Endothelial Responses and Molecular Modeling Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174204
Martínez-Sánchez SM, Pérez-Sánchez H, Antonio Gabaldón J, Abellán-Alemán J, Montoro-García S. Multifunctional Peptides from Spanish Dry-Cured Pork Ham: Endothelial Responses and Molecular Modeling Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174204
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Sánchez, Sara María, Horacio Pérez-Sánchez, José Antonio Gabaldón, José Abellán-Alemán, and Silvia Montoro-García. 2019. "Multifunctional Peptides from Spanish Dry-Cured Pork Ham: Endothelial Responses and Molecular Modeling Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174204
APA StyleMartínez-Sánchez, S. M., Pérez-Sánchez, H., Antonio Gabaldón, J., Abellán-Alemán, J., & Montoro-García, S. (2019). Multifunctional Peptides from Spanish Dry-Cured Pork Ham: Endothelial Responses and Molecular Modeling Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174204