Ursolic Acid Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
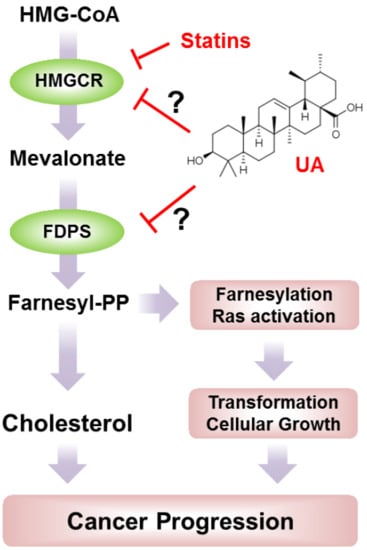
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. UA Identified as A SREBP2 Activator
2.2. UA Induces the Expression of Cholesterol Biosynthesis-Related Genes and Enzymes
2.3. UA Attenuates Growth-Signaling Pathways in A Cholesterol-Dependent Manner
2.4. UA Decreases Viability of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Cells
2.5. UA Promotes Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Death in HCC Cells
2.6. Anti-Cancer Effect of UA in HCC Cells is Diminished by Cholesterol Supplementation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Antibodies
3.2. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
3.3. Western Blotting
3.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
3.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.6. Apoptosis Assays
3.7. Luciferase Assay
3.8. Measurement of Intracellular Cholesterol
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Oh, T.I.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kan, S.Y.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.M.; Yim, W.J.; et al. Emodin Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to the Anti-Cancer Effect of Sorafenib through Suppression of Cholesterol Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2012, 379, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, T.F.; Korangy, F.; Manns, M.P.; Malek, N.P. Molecular therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniak, Ł.; Skąpska, S.; Marszałek, K. Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities. Molecules 2015, 20, 20614–20641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.R.; Prasad, S.; Sung, B.; Kannappan, R.; Aggarwal, B.B. Targeting Inflammatory Pathways by Triterpenoids for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Toxins 2010, 2, 2428–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, J.S.; Zhou, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z.S.; Sun, H.; Wang, S.M. Ursolic Acid Attenuates TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in NSCLC by Targeting Integrin αVβ5/MMPs Signaling. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 27, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, M.; Qi, X.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L. Ursolic acid sensitizes radioresistant NSCLC cells expressing HIF-1α through reducing endogenous GSH and inhibiting HIF-1α. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Pi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Song, F. Reversal of multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells by a combination of ursolic acid with doxorubicin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 165, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehri, J.M.; Kalafatis, M. Ursolic Acid Promotes the Sensitization of rhTRAIL-resistant Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6789–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lin, Z.M.; Ge, N.; Zhang, D.L.; Huang, J.; Kong, F. Ursolic Acid Induces Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1471–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shin, E.A.; Jung, J.H.; Park, J.E.; Kim, D.S.; Shim, B.S.; Kim, S.H. Ursolic Acid Induces Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells Partially via Upregulation of MicroRNA-4500 and Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 Phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, V.R.; Sung, B.; Reuter, S.; Kannappan, R.; Deorukhkar, A.; Diagaradjane, P.; Wei, C.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Krishnan, S.; et al. Ursolic acid inhibits growth and metastasis of human colorectal cancer in an orthotopic nude mouse model by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways: Chemosensitization with capecitabine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4942–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Ma, H.; Shi, W.; Duan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Lin, J.; Lv, J. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway by ursolic acid suppresses growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yie, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Wu, J.; Yang, L. Ursolic acid inhibited growth of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through AMPKα-mediated reduction of DNA methyltransferase 1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 402, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.C.; Li, X.L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Sun, W.H. Cyclooxygenase-2 mediated synergistic effect of ursolic acid in combination with paclitaxel against human gastric carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92770–92777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Junco, J.J.; Cho, J.; Mancha, A.; Malik, G.; Wei, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Liang, H.; DiGiovanni, J.; Slaga, T.J. Role of AMPK and PPARα in the anti-skin cancer effects of ursolic acid. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.T.; Ho, C.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ferraro, T.; Lou, Y.R.; Stauber, K.; Ma, W.; Georgiadis, C.; Laskin, J.D.; Conney, A.H. Inhibition of skin tumorigenesis by rosemary and its constituents carnosol and ursolic acid. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 701–708. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, C.; Lankadasari, M.B.; Aranjani, J.M.; Harikumar, K. Targeting oncogenic transcription factors by polyphenols: A novel approach for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Manu, K.A.; Ong, T.H.; Ramachandran, L.; Surana, R.; Bist, P.; Lim, L.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Hui, K.M. Inhibition of CXCR4/CXCL12 signaling axis by ursolic acid leads to suppression of metastasis in transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate model. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvente-Poirot, S.; Poirot, M. Cholesterol and Cancer, in the Balance. Science 2014, 343, 1445–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T. Cholesterol lowering: Role in cancer prevention and treatment. Boil. Chem. 2015, 396, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Lin, J.; Lu, M.L.; Solomon, K.R.; Freeman, M.R. Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts mediate akt-regulated survival in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2227–2231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Kim, J.; Adam, R.M.; Solomon, K.R.; Freeman, M.R. Cholesterol targeting alters lipid raft composition and cell survival in prostate cancer cells and xenografts. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullen, P.J.; Yu, R.; Longo, J.; Archer, M.C.; Penn, L.Z. The interplay between cell signalling and the mevalonate pathway in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvergne, B.; Michalik, L.; Wahli, W. Transcriptional Regulation of Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 465–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.F.; Zheng, L.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, C.S.; Cai, D.Q.; Wu, Z.; Qin, J.W.; Yu, Y.H.; Kim, S.K. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors induce apoptosis of lymphoma cells by promoting ROS generation and regulating Akt, Erk and p38 signals via suppression of mevalonate pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Yu, Z.; Gao, X.; Gong, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, F. Simvastatin induces breast cancer cell death through oxidative stress up-regulating miR-140-5p. Aging 2019, 11, 3198–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotamraju, S.; Willams, C.L.; Kalyanaraman, B. Statin-Induced Breast Cancer Cell Death: Role of Inducible Nitric Oxide and Arginase-Dependent Pathways. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7386–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Q.; Tong, Z.; et al. Cholesterol Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer Cells by Suppressing Degradation of EGFR through APMAP. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Rong, X.; Palladino, E.N.; Wang, J.; Fogelman, A.M.; Martin, M.G.; Alrefai, W.A.; Ford, D.A.; Tontonoz, P. Phospholipid Remodeling and Cholesterol Availability Regulate Intestinal Stemness and Tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehmsen, S.; Pedersen, M.H.; Wang, G.; Terp, M.G.; Arslanagic, A.; Hood, B.L.; Conrads, T.P.; Leth-Larsen, R.; Ditzel, H.J. Increased Cholesterol Biosynthesis Is a Key Characteristic of Breast Cancer Stem Cells Influencing Patient Outcome. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3927–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansourian, P.G.; Yoneda, M.; Rao, M.K.; Martinez, F.J.; Thomas, E.; Schiff, E.R. Effects of Statins on the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Manthravadi, S.; Shrestha, A.; Madhusudhana, S. Impact of statin use on cancer recurrence and mortality in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Divine, G.W.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Engel, L.S.; Vanslooten, A.; Wells, K.; Yood, M.U.; Alford, S.H. Statin use and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a U.S. population. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nayan, M.; Punjani, N.; Juurlink, D.N.; Finelli, A.; Austin, P.C.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Uleryk, E.; Hamilton, R.J. Statin use and kidney cancer survival outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 52, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardwell, C.R.; Mc Menamin, Ú.; Hughes, C.M.; Murray, L.J. Statin Use and Survival from Lung Cancer: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alfaqih, M.A.; Allott, E.H.; Hamilton, R.J.; Freeman, M.R.; Freedland, S.J. The current evidence on statin use and prostate cancer prevention: Are we there yet? Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.T.; Coleman, H.G.; Hughes, C.; Murray, L.J.; Cardwell, C.R. Statin use and survival in colorectal cancer: Results from a population-based cohort study and an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.Y.; Li, C.H.; Lin, C.L.; Liang, J.A. Long-term statin use in patients with lung cancer and dyslipidemia reduces the risk of death. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42208–42215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, S.F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Bojesen, S.E. Statin Use and Reduced Cancer-Related Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Colletti, A. An update on the safety of nutraceuticals and effects on lipid parameters. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2018, 17, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaró, C.; Ortiz, J.A.; Ramos, M.M.; Haro, D.; Hegardt, F.G. Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein-Mediated Effect of Fluvastatin on Cytosolic 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Synthase Transcription. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 374, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, E.; Murthy, S.; Mathur, S.N.; Field, F.J. Regulation of Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Proteins in Hamster Intestine by Changes in Cholesterol Flux. J. Boil. Chem. 2001, 276, 17576–17583. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.G.; Zhang, C.J.; Xu, X.E.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, P.F. Ursolic acid derivative ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabestic bone deleterious effects in mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 3681–3690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, A.; Radhiga, T.; Pugalendi, K.V. Effect of ursolic acid and Rosiglitazone combination on hepatic lipid accumulation in high fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtiari, N.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Soleimani, M.; Hemmati, R.; Noori-Zadeh, A.; Javan, M.; Tashakor, A. Short-term ursolic acid promotes skeletal muscle rejuvenation through enhancing of SIRT1 expression and satellite cells proliferation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 78, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmi, I.; Afzal, M.; Rahman, S.; Iqbal, M.; Imam, F.; Anwar, F. Antiobesity potential of ursolic acid stearoyl glucoside by inhibiting pancreatic lipase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 709, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; Li, H.; Hou, J.; Li, D. Ursolic acid prevents augmented peripheral inflammation and inflammatory hyperalgesia in high-fat diet-induced obese rats by restoring downregulated spinal PPARα. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5309–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Meng, F.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Meng, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Therapeutic Role of Ursolic Acid on Ameliorating Hepatic Steatosis and Improving Metabolic Disorders in High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Q.; Ding, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.M. Protective effects of ursolic acid in an experimental model of liver fibrosis through Nrf2/ARE pathway. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2015, 39, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.L.; DeBose-Boyd, R.A.; Brown, M.S. Protein Sensors for Membrane Sterols. Cell 2006, 124, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Li, H.; Tang, J.J.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.K.; Shi, X.J.; Cui, H.W.; Tang, J.; et al. Discovery of a potent HMG-CoA reductase degrader that eliminates statin-induced reductase accumulation and lowers cholesterol. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabitova, L.; Gorin, A.; Astsaturov, I. Molecular pathways: Sterols and receptor signaling in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, F.; Fan, Y.; Ni, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Hao, W.; Yue, H.; Wu, R.; Kang, X. Ursolic Acid Reverses the Chemoresistance of Breast Cancer Cells to Paclitaxel by Targeting MiRNA-149-5p/MyD88. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Dai, C.; Shen, L. Ursolic Acid Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the Axl/NF-κB Pathway in Gastric Cancer Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 2474805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremmel, L.; Rho, O.; Slaga, T.J.; DiGiovanni, J. Inhibition of skin tumor promotion by TPA using a combination of topically applied ursolic acid and curcumin. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Hao, Y.; Du, D.; Xie, S.; Hong, L.; Gu, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Fan, D.; Kung, H.F. Ursolic acid promotes cancer cell death by inducing Atg5-dependent autophagy. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Xuan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S. Ursolic acid synergistically enhances the therapeutic effects of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.W.; Kandutsch, A.A.; Waymouth, C. Inhibition of cell growth by oxygenated derivatives of cholesterol. Nature 1974, 251, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity and inhibition of growth of human fibroblasts by 7-ketocholesterol. J. Boil. Chem. 1974, 249, 7306–7314. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; He, G.; Tang, D.; Xiong, L.; Wen, Y.; Miao, X.; Hong, Z.; Yao, H.; Chen, C.; Yan, S.; et al. Lovastatin Inhibits Cancer Stem Cells and Sensitizes to Chemo- and Photodynamic Therapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.J.; Cheng, A.C.; Lee, M.F.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chen, M.; Cheng, A.; Lee, M.; Hsu, Y. Simvastatin induces G1 arrest by up-regulating GSK3β and down-regulating CDK4/cyclin D1 and CDK2/cyclin E1 in human primary colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4618–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, D.; Tsubaki, M.; Tomonari, Y.; Koumoto, Y.I.; Sakaguchi, K.; Nishida, S.; Takeda, T. Statins induce apoptosis through inhibition of Ras signaling pathways and enhancement of Bim and p27 expression in human hematopoietic tumor cells. Tumor Boil. 2017, 39, 1010428317734947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Tseng, J.H.; Liou, J.J.; Horng, S.; Wen, H.C.; Fan, Y.C.; Zhong, W.B.; Hsu, S.P. Simvastatin Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Migration in Human Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.R.; Osborne, T.F.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Gil, G. Multiple sterol regulatory elements in promoter for hamster 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A synthase. J. Boil. Chem. 1988, 263, 18480–18487. [Google Scholar]






| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| HMGCS1 | TGGCAGGGAGTCTTGGTA | TCCCACTCCAAATGATGACA |
| HMGCR | GATGGGAGGCCACAAAGAG | TTCGGTGGCCTCTAGTGAGA |
| MVD | TTAACTGGTCCTGGTGCAGA | AACATCGCGGTCATCAAGTA |
| FDPS | TCCATGATGTCATCTGCCAC | AGCCAAGGAAACAGGATG |
| SREBP1a | GCACCCACTCCATTGAAGAT | GGCACTGACTCTTCCTTGATAC |
| SREBP1c | ACAGTGACTTCCCTGGCCTAT | GCATGGACGGGTACATCTTCA |
| SREBP2 | AACGGTCATTCACCCAGGTC | GGCTGAAGAATAGGAGTTGCC |
| LDL-R | AACTGCCATTGTCGTCTTTA | ACATACCCATCAACGACAAG |
| 36B4 | CATGTTGCTGGCCAATAAGG | TGGTGATACCTAAAGCCTGGAA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.-H.; Kan, S.-Y.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Ko, H.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, J.-H. Ursolic Acid Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194767
Kim G-H, Kan S-Y, Kang H, Lee S, Ko HM, Kim JH, Lim J-H. Ursolic Acid Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194767
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Geon-Hee, Sang-Yeon Kan, Hyeji Kang, Sujin Lee, Hyun Myung Ko, Ji Hyung Kim, and Ji-Hong Lim. 2019. "Ursolic Acid Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194767
APA StyleKim, G.-H., Kan, S.-Y., Kang, H., Lee, S., Ko, H. M., Kim, J. H., & Lim, J.-H. (2019). Ursolic Acid Suppresses Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4767. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194767