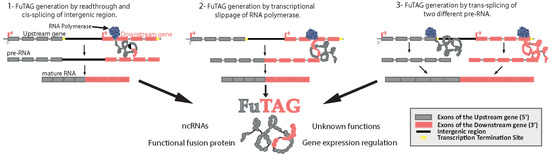
Fusion Transcripts of Adjacent Genes: New Insights into the World of Human Complex Transcripts in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The History of FuTAGs
3. Functions of FuTAGs
4. Databases for Fusion Transcripts
Analysis of FuTAGs in Public Databases
5. FuTAGs Expression in Normal Tissues and Cancer
6. FuTAG’s Parent Genes: RNAseq and Transcriptome Microarray (HTA 2.0) Data
7. Downstream of Gene Containing Transcripts and cis-SAGes
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Akt | Akt (Protein Kinase B) |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| cis-SAGe | cis-Splicing between Adjacent Genes |
| Co-TIFE | Co-Transcription-Induced First Exon |
| CTCF | CCCTC-Binding Factor |
| DOG | Downstream of Gene Containing Transcript |
| EST | Expressed Sequence Tag |
| FuTAG | Fusion Transcript of Adjacent Gene |
| HGF | Hepatocyte Growth Factor |
| IP3 | Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate |
| ISP | Intergenic Splicing Pattern |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| PAP smear | Papanicolaou Test is a Method of Cervical Screening |
| SHS | Short Homology Region |
| ss | Splicing Site |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TIC | Transcription-Induced Chimera |
| TIGF | Transcription Induced Gene Fusion |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| Trans-FT | Trans-Tusion Transcript |
References
- Pray, L.A. Eukaryotic genome complexity. Nat. Edu. 2008, 1, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Chwalenia, K.; Facemire, L.; Li, H. Chimeric RNAs in cancer and normal physiology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Qin, F.; Li, H. Chimeric RNAs and their implications in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 48, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, G.; Reymond, A.; Dabbouseh, N.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Castelo, R.; Thomson, T.M.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Guigó, R. Tandem chimerism as a means to increase protein complexity in the human genome. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greger, L.; Su, J.; Rung, J.; Ferreira, P.G.; Lappalainen, T.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Brazma, A. Tandem RNA chimeras contribute to transcriptome diversity in human population and are associated with intronic genetic variants. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, F.; Johansson, B.; Fioretos, T.; Mitelman, F. The emerging complexity of gene fusions in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Facemire, L.; Frierson, H.; Li, H. Role of CTCF in regulating SLC45A3-ELK4 chimeric RNA. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiva, P.; Toporik, A.; Edelheit, S.; Peretz, Y.; Diber, A.; Shemesh, R.; Novik, A.; Sorek, R. Transcription-mediated gene fusion in the human genome. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Han, Y.; Zellmer, L.; Yang, W.; Guan, Z.; Yu, W.; Huang, H.; Liao, D.J. It is imperative to establish a pellucid definition of chimeric RNA and to clear up a lot of confusion in the relevant research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Yuan, H.; Park, H.G.; Frierson, H.F.; Li, H. Chimeric transcript generated by cis-splicing of adjacent genes regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yang, S.; Singh, S.; Qin, F.; Kumar, S.; Wang, L.; Ma, D.; Li, H. The landscape and implications of chimeric RNAs in cervical cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Wu, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Mu, S. Abundant and broad expression of transcription-induced chimeras and protein products in mammalian genomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grosso, A.R.; Leite, A.P.; Carvalho, S.; Matos, M.R.; Martins, F.B.; Vítor, A.C.; Desterro, J.M.P.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; de Almeida, S.F. Pervasive transcription readthrough promotes aberrant expression of oncogenes and RNA chimeras in renal carcinoma. eLife 2015, 4, e09214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Li, Y.; Malek, S.N.; Kim, Y.C.; Xu, J.; Chen, P.; Xiao, F.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.; Xuan, Z.; et al. New fusion transcripts identified in normal karyotype acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, H.; Wang, W. Short homologous sequences are strongly associated with the generation of chimeric RNAs in eukaryotes. J. Mol. Evol. 2009, 68, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradet-Balade, B.; Medema, J.P.; López-Fraga, M.; Lozano, J.C.; Kolfschoten, G.M.; Picard, A.; Martínez-A, C.; Garcia-Sanz, J.A.; Hahne, M. An endogenous hybrid mRNA encodes TWE-PRIL, a functional cell surface TWEAK-APRIL fusion protein. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5711–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, T.M.; Lozano, J.J.; Loukili, N.; Carrió, R.; Serras, F.; Cormand, B.; Valeri, M.; Díaz, V.M.; Abril, J.; Burset, M.; et al. Fusion of the human gene for the polyubiquitination coeffector UEV1 with Kua, a newly identified gene. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M. A new function evolved from gene fusion. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, R.T.; Green, R.E.; Brenner, S.E. An unappreciated role for RNA surveillance. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwalenia, K.; Qin, F.; Singh, S.; Tangtrongstittikul, P.; Li, H. Connections between transcription downstream of genes and cis-SAGe chimeric RNA. Genes 2017, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilborg, A.; Sabath, N.; Wiesel, Y.; Nathans, J.; Levy-Adam, F.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A.; Shalgi, R. Comparative analysis reveals genomic features of stress-induced transcriptional readthrough. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8362–E8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.; Kumar, S.; Li, H. Absence of correlation between chimeric RNA and aging. Genes 2017, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Razzaq, S.K.; Vo, A.D.; Gautam, M.; Li, H. Identifying fusion transcripts using next generation sequencing. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 7, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Lee, K.; Yu, N.; Jang, I.; Choi, I.; Kim, P.; Jang, Y.E.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; et al. ChimerDB 3.0: An enhanced database for fusion genes from cancer transcriptome and literature data mining. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D784–D789. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prakash, T.; Sharma, V.K.; Adati, N.; Ozawa, R.; Kumar, N.; Nishida, Y.; Fujikake, T.; Takeda, T.; Taylor, T.D. Expression of conjoined genes: Another mechanism for gene regulation in eukaryotes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.N.; Kim, A.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Nam, S.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, D.-W.; Kang, A.; Kim, M.-Y.; Park, K.-H.; et al. Novel mechanism of conjoined gene formation in the human genome. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2012, 12, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorohovski, A.; Tagore, S.; Palande, V.; Malka, A.; Raviv-Shay, D.; Frenkel-Morgenstern, M. ChiTaRS-3.1-the enhanced chimeric transcripts and RNAseq database matched with protein-protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D790–D795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, S.; Yuan, L.-L.; Li, T. dbCRID: A database of chromosomal rearrangements in human diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D895–D900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, F.J.; de Mendíbil, I.O.; Vizmanos, J.L. TICdb: A collection of gene-mapped translocation breakpoints in cancer. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitelman, F.; Johansson, B.; Mertens, F. The impact of translocations and gene fusions on cancer causation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Wang, Q.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Zheng, S.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Verhaak, R.G.W. The landscape and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated transcript fusions. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4845–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Q.; Tang, M.; Barthel, F.; Amin, S.; Yoshihara, K.; Lang, F.M.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Lee, S.H.; Zheng, S.; et al. TumorFusions: An integrative resource for cancer-associated transcript fusions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1144–D1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.; Zhou, X. FusionGDB: Fusion gene annotation DataBase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D994–D1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Liang, W.-W.; Foltz, S.M.; Mutharasu, G.; Jayasinghe, R.G.; Cao, S.; Liao, W.-W.; Reynolds, S.M.; Wyczalkowski, M.A.; Yao, L.; et al. Driver fusions and their implications in the development and treatment of human cancers. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Løvf, M.; Carm, K.T.; Bakken, A.C.; Hoff, A.M.; Skotheim, R.I. Novel transcription-induced fusion RNAs in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49133–49143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varley, K.E.; Gertz, J.; Roberts, B.S.; Davis, N.S.; Bowling, K.M.; Kirby, M.K.; Nesmith, A.S.; Oliver, P.G.; Grizzle, W.E.; Forero, A.; et al. Recurrent readthrough fusion transcripts in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, L.; Bourachot, B.; Mateescu, B.; Reyal, F.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F. Regulation of miR-200c/141 expression by intergenic DNA-looping and transcriptional readthrough. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, I.; Wang, C.-Y. A novel readthrough transcript JMJD7-PLA2G4B regulates head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and survival. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Singh, S.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, J.; Lin, T.; Li, H. The landscape of chimeric RNAs in bladder urothelial carcinoma. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 110, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-E.; Kim, H.-P.; Han, S.-W.; Jang, H.; Lee, S.-H.; Song, S.-H.; Bang, D.; Kim, T.-Y. NFATC3-PLA2G15 fusion transcript identified by RNA sequencing promotes tumor invasion and proliferation in colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiceanu, M.; Qin, F.; Xie, Z.; Jia, Y.; Lopez, K.; Janus, N.; Facemire, L.; Kumar, S.; Pang, Y.; Qi, Y.; et al. Recurrent chimeric fusion RNAs in non-cancer tissues and cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2859–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, F.; Song, Z.; Babiceanu, M.; Song, Y.; Facemire, L.; Singh, R.; Adli, M.; Li, H. Discovery of CTCF-sensitive Cis-spliced fusion RNAs between adjacent genes in human prostate cells. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005001. [Google Scholar]
- Pintarelli, G.; Dassano, A.; Cotroneo, C.E.; Galvan, A.; Noci, S.; Piazza, R.; Pirola, A.; Spinelli, R.; Incarbone, M.; Palleschi, A.; et al. Read-through transcripts in normal human lung parenchyma are down-regulated in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27889–27898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magrangeas, F.; Pitiot, G.; Dubois, S.; Bragado-Nilsson, E.; Chérel, M.; Jobert, S.; Lebeau, B.; Boisteau, O.; Lethé, B.; Mallet, J.; et al. Cotranscription and intergenic splicing of human galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase and interleukin-11 receptor alpha-chain genes generate a fusion mRNA in normal cells. Implication for the production of multidomain proteins during evolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16005–16010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Portal. Available online: https://gtexportal.org/home/ (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Kowalski, P.E.; Freeman, J.D.; Mager, D.L. Intergenic splicing between a HERV-H endogenous retrovirus and two adjacent human genes. Genomics 1999, 57, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Communi, D.; Suarez-Huerta, N.; Dussossoy, D.; Savi, P.; Boeynaems, J.M. Cotranscription and intergenic splicing of human P2Y11 and SSF1 genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16561–16566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeneCards-Human Genes|Gene Database|Gene Search. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/ (accessed on 8 September 2019).
- Dreisig, K.; Kornum, B.R. A critical look at the function of the P2Y11 receptor. Purinergic Signal. 2016, 12, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PPAN-P2RY11 Gene-GeneCards|A0A0B4J1V8 Protein|A0A0B4J1V8 Antibody. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=PPAN-P2RY11 (accessed on 17 April 2019).
- Kato, M.; Khan, S.; Gonzalez, N.; O’Neill, B.P.; McDonald, K.J.; Cooper, B.J.; Angel, N.Z.; Hart, D.N.J. Hodgkin’s lymphoma cell lines express a fusion protein encoded by intergenically spliced mRNA for the multilectin receptor DEC-205 (CD205) and a novel C-type lectin receptor DCL-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34035–34041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Sinha, C.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. SLC45A3-ELK4 chimera in prostate cancer: Spotlight on cis-splicing. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.A.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Cao, X.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Han, B.; Jing, X.; Sam, L.; Barrette, T.; Palanisamy, N.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Transcriptome sequencing to detect gene fusions in cancer. Nature 2009, 458, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rickman, D.S.; Pflueger, D.; Moss, B.; VanDoren, V.E.; Chen, C.X.; de la Taille, A.; Kuefer, R.; Tewari, A.K.; Setlur, S.R.; Demichelis, F.; et al. SLC45A3-ELK4 is a novel and frequent erythroblast transformation-specific fusion transcript in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2734–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, G.; Yun, H.; Sun, C.-H.; Park, I.; Lee, S.; Kwon, J.; Do, I.; Hong, M.E.; Van Vrancken, M.; Lee, J.; et al. Integrated genomic analyses identify frequent gene fusion events and VHL inactivation in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6538–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zheng, J.; Li, H.; Deng, J.; Hu, M.; Wu, H.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Lan, X.; Lu, J.; et al. Identification of chimeric TSNAX-DISC1 resulting from intergenic splicing in endometrial carcinoma through high-throughput RNA sequencing. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2687–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-S.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.-H.; Goh, S.-H. Overexpression of KLHL23 protein from readthrough transcription of PHOSPHO2-KLHL23 in gastric cancer increases cell proliferation. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, F.; Brueschke, A.; Sonenberg, N. Gene fusion and overlapping reading frames in the mammalian genes for 4E-BP3 and MASK. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52290–52297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Lin, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zou, B.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Feng, D.; Song, Z.; et al. lncINS-IGF2 promotes cell proliferation and migration by promoting G1/S transition in lung cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.; Tran Quang, C.; Hypolite, G.; Belhocine, M.; Bergon, A.; Cordonnier, G.; Ghysdael, J.; Macintyre, E.; Boissel, N.; Spicuglia, S.; et al. Novel intergenically spliced chimera, NFATC3-PLA2G15, is associated with aggressive T-ALL biology and outcome. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2018, 16, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qin, F.; Liu, A.; Li, H. Recurrent fusion RNA DUS4L-BCAP29 in non-cancer human tissues and cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31415–31423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McElroy, S.L.; Winham, S.J.; Cuellar-Barboza, A.B.; Colby, C.L.; Ho, A.M.-C.; Sicotte, H.; Larrabee, B.R.; Crow, S.; Frye, M.A.; Biernacka, J.M. Bipolar disorder with binge eating behavior: A genome-wide association study implicates PRR5-ARHGAP8. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflueger, D.; Mittmann, C.; Dehler, S.; Rubin, M.A.; Moch, H.; Schraml, P. Functional characterization of BC039389-GATM and KLK4-KRSP1 chimeric readthrough transcripts which are up-regulated in renal cell cancer. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, D.F.; Privitera, A.P.; Barresi, V. Chromosomal density of cancer up-regulated genes, aberrant enhancer activity and cancer fitness genes are associated with transcriptional Cis-Effects of broad copy number gains in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barresi, V.; Castorina, S.; Musso, N.; Capizzi, C.; Luca, T.; Privitera, G.; Condorelli, D.F. Chromosomal instability analysis and regional tumor heterogeneity in colon cancer. Cancer Genet. 2017, 210, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condorelli, D.F.; Spampinato, G.; Valenti, G.; Musso, N.; Castorina, S.; Barresi, V. Positive caricature transcriptomic effects associated with broad genomic aberrations in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barresi, V.; Valenti, G.; Spampinato, G.; Musso, N.; Castorina, S.; Rizzarelli, E.; Condorelli, D.F. Transcriptome analysis reveals an altered expression profile of zinc transporters in colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 9707–9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barresi, V.; Trovato-Salinaro, A.; Spampinato, G.; Musso, N.; Castorina, S.; Rizzarelli, E.; Condorelli, D.F. Transcriptome analysis of copper homeostasis genes reveals coordinated upregulation of SLC31A1,SCO1 and COX11 in colorectal cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodtkorb, M.; Lingjaerde, O.C.; Huse, K.; Troen, G.; Hystad, M.; Hilden, V.I.; Myklebust, J.H.; Leich, E.; Rosenwald, A.; Delabie, J.; et al. Whole-genome integrative analysis reveals expression signatures predicting transformation in follicular lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilborg, A.; Passarelli, M.C.; Yario, T.A.; Tycowski, K.T.; Steitz, J.A. Widespread inducible transcription downstream of human genes. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Li, M.; Vilborg, A.; Lee, N.; Shu, M.-D.; Yartseva, V.; Šestan, N.; Steitz, J.A. Mammalian 5′-capped microRNA precursors that generate a single microRNA. Cell 2013, 155, 1568–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwalenia, K.; Qin, F.; Singh, S.; Li, H. A cell-based splicing reporter system to identify regulators of cis-splicing between adjacent genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jividen, K.; Li, H. Chimeric RNAs generated by intergenic splicing in normal and cancer cells. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacu, S.; Yuan, W.; Kan, Z.; Bhatt, D.; Rivers, C.S.; Stinson, J.; Peters, B.A.; Modrusan, Z.; Jung, K.; Seshagiri, S.; et al. Deep RNA sequencing analysis of readthrough gene fusions in human prostate adenocarcinoma and reference samples. BMC Med. Genomics 2011, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-P.; Cho, G.-A.; Han, S.-W.; Shin, J.-Y.; Jeong, E.-G.; Song, S.-H.; Lee, W.-C.; Lee, K.-H.; Bang, D.; Seo, J.-S.; et al. Novel fusion transcripts in human gastric cancer revealed by transcriptome analysis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5434–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| N. | FuTAG | Upstream Gene | Downstream Gene | Position (Chr) | Tissue/Cell Type | Normal Tissue Expression (GTEx) | NM, NR | ISP Mechanism in According to Lu et al., [12] | Ensembl Code | Structure | Junction Exon Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GALT-IL11Rα | GALT | IL11Rα | 9p13 | Normal human cell- T cell clones and fetal bone marrow | Colon, adipocytes, ovary and testis | N.D. | Type I | ENSG00000258728 | ex10-ex2 (ex11-ex1 removed) | GAGCAG-ATGAGC | Magrangeas et al., [44] |
| 2 | HHLA1-OC90 | HHLA1 | OC-90 | 8q24.1–24.3 | Tera1 and NTera2D1 cell lines | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | Kowalski et al., [46] |
| 3 | P2Y11 (PPAN)-SSF1 | P2Y11 | SSF1 (PPAN) | 19p13.1 | HL-60 cell lines | Heart, thyroid, adrenal gland, ovary, prostate and testis | NM_001040664; NM_001198690 | Type III | ENSG00000243207 | ex12partial-ex2 (ex12partial-ex1 removed) | ATCGAG-GTGCCA | Communi et al., [47] |
| 4 | TWE-PRIL (TNFSF12-TNFSF13) | TWEAK (TNFSF12) | APRIL (TNFSF13) | 17P13.1 | T lymphocytes and monocytes cell lines | Kidney, liver and breast | NM_172089 | Type I | ENSG00000248871 | ex6-ex2 (ex7-ex1 removed) | TGTCAG-AGTTCC | Pradet-Balade et al., [16] |
| 5 | SLC45A3-ELK4 | SLC45A3 | ELK4 | 1q32 | LNCaP and PC3 prostate cancer cell lines | N.D. | N.D. | Type II | N.D. | N.D | N.D | Kumar et al., [52] |
| 6 | DEC205-DCL1 (or LY75-CD302) | DEC205 (LY75) | DCL1 (CD302) | 2q24 | Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells | White blood cells, skeletal muscle, thyroid, adrenal gland | NM_001198759 | Type I | ENSG00000248672 | ex34-ex2 (ex35-ex1 removed) | CTCTGG-ACTGTC | Kato et al., [51] |
| 7 | SCNN1A-TNFRSF1A | SCNN1A | TNFRSF1A | 12p13.31 | Breast cancer cell lines | N.D. | N.D. | Type I | N.D. | ex12-ex2 (ex13-ex1 removed) | GTCACG-GTGCTC | Varley et al., [36] |
| 8 | CTSD-IFITM10 | CTSD | IFITM10 | 11p15.5 | Breast cancer cell lines | N.D. | N.D. | Type I | N.D. | ex8-ex2 (ex9-ex1 removed) | CTCAAG-GCCCAG | Varley et al., [36] |
| 9 | STX16-NPEPL1 | STX16 | NPEPL1 | 20q13.32 | Acute myeloid leukemia and gastrointestinal stromal tumors | Whole blood, lymph node, brain, cortex, cerebellum, spinal cord, heart, artery, skeletal muscle, small intestine, colon, adipocyte, kidney, liver, lung, spleen, stomach, esophagus, bladder, pancreas, thyroid, salivary gland, adrenal gland, pituitary, breast, skin, ovary, uterus, placenta, prostate, testis. | NR_037945.1 | Type IV | ENSG00000254995 | ex8- ex1(addictional intergenic exon)- ex2(addictional intergenic exon)- ex3(addictional intergenic exon)-ex2-6- ex1(addictional intron exon) -ex7-12 (ex9-ex1 removed) | CACAAG-GACTTC_CACACT-TGCCTG_GGGAAG-GCTGGT_ATGGAG-CTCTGG_GGGAAG-AGGGCA_GGGGGT-ACTACC | Wen et al. [14]; Kang et al. [55] |
| 10 | JMJD7-PLA2G4B | JMJD7 | PLA2G4B | 15q15.1 | human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines | White blood cells, lymph node, brain, heart, colon, adipocyte, kidney, liver, lung, thyroid, adrenal gland, breast, ovary, prostate, testis. | NM_001198588; NM_005090 | N.D. | ENSG00000168970 | ex6-ex2 (ex7-ex1 removed) | GAGAAG-GCAGAG | Cheng et al., [38] |
| 11 | miR-200c/141-PTPN6 | miR-200c/141 | PTPN6 | N.D. | Ovarian tumorigenesis | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D | N.D | Batista et al., [37] |
| 12 | DUS4L-BCAP29 | DUS4L | BCAP29 | 7q22.3 | gastric and prostate cancer tissues | N.D. | N.D. | Type I | N.D. | ex7-ex2 (ex8-ex1 removed) | CAGATG-GTGTGA | Tang et al., [61] |
| 13 | TSNAX-DISC1 | TSNAX | DISC1 | 1q42.2 | endometrial carcinoma tissues | Whole blood, brain, cortex, cerebellum, spinal cord, tibial nerve, heart, artery, skeletal muscle, small intestine, colon, adipocyte, kidney, liver, lung, spleen, stomach, esophagus, bladder, pancreas, thyroid, salivary gland, adrenal gland, pituitary, breast, skin, ovary, uterus, prostate, testis. | NR_028393; NR_028394; NR_028395; NR_028396; NR_028397; NR_028398; NR_028399; NR_028400 | Type IV | ENSG00000270106 | ex4-ex(addictional intergenic exon)-ex2 (ex5/6-ex1 removed) | ACTACA-AAGTTT_TATTTG-GCAGCC | Li et al., [56] |
| 14 | PHOSPHO2-KLHL23 | PHOSPHO2 | KLHL23 | 2q31.1 | Gastric cancer cell lines and tissues | N.D. | NM_001199290; NR_144936 | Type I | ENSG00000213160 | ex3-ex2 (ex4-ex1 removed) | AGTTGG-CCATGG | Choi et al., [57] |
| 15 | RPL17-C18orf32 | RPL17 | C18orf32 | 18q21.1 | Gastric cancer cell lines and tissues | N.D. | NM_001199355; NM_001199356 | Type I | ENSG00000215472 | ex6-ex2 (ex7-ex1 removed) | AAAAAG-TTGAGG | Choi et al., [57] |
| 16 | PRR5-ARHGAP8 | PRR5 | ARHGAP8 | 22q13.31 | Gastric cancer cell lines and tissues and bipolar disorder | White blood cells, brain, colon, adipocyte, kidney, lung, thyroid, adrenal gland, breast, ovary, prostate, testis. | NM_181334 | N.D. | ENSG00000248405 | ex4-ex2 (ex5–8-ex1 removed) | ATGAGG-AGCTGC | Choi et al., [57]; McElroy et al., [62] |
| 17 | Kua-UVE1 (TMEM189-UBE2V1) | Kua | UVE1 | 20q13.2 | Colon cancer cell lines | Liver, thyroid, adrenal gland, breast, testis. | NM_199203 | Type I | ENSG00000124208 | ex5-ex2 (ex6-ex1 removed) | CCACAG-GAGTAA | Thomson et al., [17] |
| 18 | MASK-BP3 (ANKHD1-EIFAEBP3) | MASK | EIF4EBP3 | 5q31.3 | ? | White blood cells, lymph node, brain, heart, skeletal muscle, colon, adipocyte, kidney, liver, lung thyroid, adrenal gland, breast, ovary, prostate testis. | NM_020690 | Type IV | ENSG00000254996 | ex33-ex(addictional intergenic exon)-ex2 (ex34-ex1 removed) | CAGCAG-GCCAGT_CCAGAG-GCACCA | Poulin et al., [58] |
| 19 | CTSC-RAB38 | CTSC | RAB38 | 11q14.2 | Clear renal cell carcinoma | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D | N.D | Grosso et al., [13] |
| 20 | BC039389-GATM (WRB-SH3BGR or KLK4-KRSP1 ) | WRB | SH3BGR | 21q22.2 | Kidney cancer | N.D. | NM_001317744; NM_001350300 | N.D. | ENSG00000285815 | N.D | N.D | Pflueger et al., [63] |
| 21 | LHX6-NDUFA8 | LHX6 | NDUFA8 | N.D. | Cervical cancer tissues (PAP smear) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | Variant.1- ex8-ex2 (ex9–10-ex1 removed) Variant.2- ex8-ex3 (ex9/10-ex1/2 removed) | ACTTGA-GTGAAA ACTTGA-GCAGAT | Wu et al., [11] |
| 22 | SLC2A11-MIF | SLC2A11 | MIF | N.D. | Cervical cancer tissues (PAP smear) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | ex9-ex2 (ex10–13-ex1 removed) | GTTAGT-TACATC | Wu et al., [11] |
| 23 | INS-IGF2 | INS | IGF2 | 11q15.5 | NSCLC tissues | Whole blood, brain, cortex, cerebellum, spinal cord, tibial nerve, heart, artery, skeletal muscle, colon, adipocyte, kidney, liver, lung, stomach, esophagus, pancreas, thyroid, salivary gland, adrenal gland, pituitary, breast, ovary, testis. | NM_001042376; NR_003512 | N.D. | ENSG00000129965 | ex2-ex1partial (ex3-ex1partial removed) | TGCAGG-CCTCAG | Gao et al., [34] |
| 24 | NFATC3-PLA2G15 | NFATC3 | PLA2G15 | 16q22.1 | T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia and Colon rectal cancer | N.D. | N.D. | Type I | N.D. | ex9-ex2 (ex10-ex1 removed) | ATGATG-TCCCTG | Bond et al., [60]; Jang et al., [40] |
| 25 | BCL2L2-PABPN1 | BCL2L2 | PABPN1 | 14q11.2 | Bladder urothelial carcinoma tissues and cell line. | Whole blood, brain, cortex, cerebellum, spinal cord, tibial nerve, heart, artery, skeletal muscle, small intestine, colon, adipocyte, kidney, liver, lung, spleen, stomach, esophagus, bladder, pancreas, thyroid, salivary gland, adrenal gland, pituitary, breast, skin, ovary, uterus, prostate, testis. | NM_001199864 | Type I | ENSG00000258643 | ex3-ex2 (ex4-ex1 removed) | GGCTGG-GAGCTG | Zhu et al., [39] |
| 26 | CHFR-GOLGA3 | CHFR | GOLGA3 | 12q24.33 | Bladder urothelial carcinoma tissues and cell line. | N.D. | N.D. | Type I | N.D. | N.D | N.D | Zhu et al., [39] |
| Conjoined Genes (ConjoinG ID and Name) | Omics Technologies | Alias | Upstream Gene | Downstream Gene | Readthrough | RNA* | Known Hybrid Protein* | Chr | Band |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC ** | FC ** | FC ** | |||||||
| CGHSA0796 NFS1-CPNE1 | RNAseq | 1.58 | 3.36 | N/A | NO | NO | 20 | q11.22 | |
| HTA2.0 | 4.52 | 1.53 | 4.52 | ||||||
| CGHSA0023 TGIF2-C20orf24 | RNAseq | N/A | N/A | 2.08 | YES | CDS Predicted | 20 | q11.23 | |
| HTA2.0 | 1.11 | 2.13 | N/A | ||||||
| CGHSA0579 TP53RK-SLC13A3 | RNAseq | 2.39 | 20.324 | N/A | YES | NO | 20 | q13.12 | |
| HTA2.0 | 1.29 | −1.25 | N/A | ||||||
| CGHSA0573 SPINLW1-WFDC6 | RNAseq | EPPIN-WFDC6 | 7.69 | 2.97 | 1.45 | NO | NO | 20 | q13.12 |
| HTA2.0 | −1.69 | −1.9 | −1.69 | ||||||
| CGHSA0217 Kua-UBE2V1 | RNAseq | TMEM189-UBE2V1 | 1.59 | 1.42 | 1.24 | YES | YES | 20 | q13.13 |
| HTA2.0 | 1.72 | 1.41 | 1.72 | ||||||
| CGHSA0215 STX16-NPEPL1 | RNAseq | 2.07 | 2.54 | 3.05 | YES | YES | 20 | q13.32 | |
| HTA2.0 | 1.85 | 1.1 | 1.51 | ||||||
| CGHSA0738 SLMO2-ATP5E | RNAseq | PRELID3B-ATP5F1E | 1.36 | 1.33 | N/A | YES | NO | 20 | q13.32 |
| HTA2.0 | 3.13 | 2.79 | 7.11 | ||||||
| CGHSA0212 ZGPAT-LIME1 | RNAseq | 1.42 | 3.08 | N/A | YES | CDS Predicted | 20 | q13.33 | |
| HTA2.0 | 1.1 | −1.08 | N/A | ||||||
| CGHSA0570 LIME1-SLC2A4RG | RNAseq | 3.08 | 1.32 | N/A | NO | NO | 20 | q13.33 | |
| HTA2.0 | −1.08 | 1.03 | N/A | ||||||
| CGHSA0214 MYT1-PCMTD2 | RNAseq | 2.22 | 2.23 | N/A | YES | YES | 20 | q13.33 | |
| HTA2.0 | −1.57 | 2.7 | N/A | ||||||
| CGHSA0577 TPD52L2-DNAJC5 | RNAseq | 1.93 | 1.07 | N/A | Not Attempted Experimentally | NO | 20 | q13.33 | |
| HTA2.0 | 2.32 | 1.09 | N/A |
| Transcript Cluster ID | FC > 1.5 (CRCvs.MU) GSE73360 and GSE84984 [66,67,68] | FDR p-Value (CRC VS. MU) | Chr Position | Gene Symbol | Description (Contain Readthrough Word) | FuTAG Reported in Table 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC02005002.hg.1 | 1.57 | 2 × 10−6 | 2q31.1 | KLHL23; PHOSPHO2-KLHL23 | kelch-like family member 23; PHOSPHO2-KLHL23 readthrough; NULL | [57] |
| TC02005005.hg.1 | 2 | 1.7 × 10−7 | 2q33.1 | MOB4; HSPE1-MOB4 | MOB family member 4, phocein; HSPE1-MOB4 readthrough; NULL | |
| TC02002467.hg.1 | 2.32 | 2 × 10−6 | 2q24.2 | LY75-CD302; CD302; LY75 | LY75-CD302 readthrough; CD302 molecule; lymphocyte antigen 75; NULL | [51] |
| TC05000726.hg.1 | 2.61 | 1.2 × 10−7 | 5q31.3 | EIF4EBP3; ANKHD1; ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 3; ankyrin repeat and KH domain containing 1; ANKHD1-EIF4EBP3 readthrough; NULL | [58] |
| TC05001690.hg.1 | 1.67 | 2 × 10−6 | 5q22.3 | TMED7-TICAM2; TICAM2; TMED7 | TMED7-TICAM2 readthrough; toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 2; transmembrane emp24 protein transport domain containing 7; NULL | [69] |
| TC07003311.hg.1 | 1.75 | 1.4 × 10−5 | 7q11.23 | DTX2P1-UPK3BP1-PMS2P11; LOC100132832 | DTX2P1-UPK3BP1-PMS2P11 readthrough transcribed pseudogene; PMS2 postmeiotic segregation increased 2 (S. cerevisiae) pseudogene | |
| TC0X002317.hg.1 | 1.64 | 1 × 10−10 | Xq22.1 | RPL36A; RPL36A-HNRNPH2 | ribosomal protein L36a; RPL36A-HNRNPH2 readthrough; NULL | |
| TC0X002316.hg.1 | 4.2 | 4.1 × 10−12 | Xq22.1 | HNRNPH2; RPL36A-HNRNPH2 | heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H2 (H’); RPL36A-HNRNPH2 readthrough; NULL | |
| TC10002935.hg.1 | 2.17 | 5.4 × 10−9 | 10p12.2 | BMI1; COMMD3-BMI1 | BMI1 polycomb ring finger oncogene; COMMD3-BMI1 readthrough; NULL | |
| TC11000477.hg.1 | 2.26 | 1.7 × 10−8 | 11q12.1 | CNTF; ZFP91; ZFP91-CNTF | ciliary neurotrophic factor; ZFP91 zinc finger protein; ZFP91-CNTF readthrough (NMD candidate); zinc finger protein 91 homolog (mouse); ZFP91-CNTF readthrough (non-protein coding); NULL | |
| TC11000673.hg.1 | 1.58 | 6.5 × 10−13 | 11q13.2 | RBM14; RBM4; RBM14-RBM4; LOC101059993 | RNA binding motif protein 14; RNA binding motif protein 4; RBM14-RBM4 readthrough; uncharacterized LOC101059993; NULL | |
| TC11002132.hg.1 | 1.72 | 7.6 × 10−8 | 11q14.1 | NDUFC2-KCTD14; NDUFC2; KCTD14 | NDUFC2-KCTD14 readthrough; NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1, subcomplex unknown, 2, 14.5kDa; potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 14; NULL | |
| TC12001797.hg.1 | 3.66 | 1.9 × 10−12 | 12q21.33 | POC1B; POC1B-GALNT4; GALNT4 | POC1 centriolar protein homolog B (Chlamydomonas); POC1B-GALNT4 readthrough; UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 4 (GalNAc-T4) | |
| TC13001721.hg.1 | 1.7 | 8.3 × 10−9 | 13q33.1 | ERCC5; BIVM-ERCC5 | excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 5; BIVM-ERCC5 readthrough; NULL | |
| TC14001267.hg.1 | 2.85 | 5.9 × 10−10 | 14q24.2 | SYNJ2BP-COX16; COX16; SYNJ2BP | SYNJ2BP-COX16 readthrough; COX16 cytochrome c oxidase assembly homolog (S. cerevisiae); synaptojanin 2 binding protein | |
| TC17000082.hg.1 | 1.83 | 3 × 10−11 | 17p13.1 | RNASEK; C17orf49; RNASEK-C17orf49 | ribonuclease, RNase K; chromosome 17 open reading frame 49; RNASEK-C17orf49 readthrough | |
| TC17002881.hg.1 | 1.74 | 1 × 10−10 | 17q21.33 | NME2; NME1-NME2 | NME/NM23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 2; NME1-NME2 readthrough; NULL | |
| TC18001003.hg.1 | 9.48 | 3 × 10−10 | 18q21.1 | SNORD58B; RPL17; RPL17-C18orf32 | small nucleolar RNA, C/D box 58B; ribosomal protein L17; RPL17-C18orf32 readthrough | |
| TC20001752.hg.1 | 1.72 | 4.3 × 10−9 | 20q13.13 | TMEM189; TMEM189-UBE2V1; UBE2V1 | transmembrane protein 189; TMEM189-UBE2V1 readthrough; ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 variant 1; NULL | [17] |
| TC6_apd_hap1000079.hg.1 | 4.49 | 1.8 × 10−13 | 6p21.33 | DDX39B; ATP6V1G2-DDX39B; OTTHUMG00000148789; BAT1 | DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 39B; ATP6V1G2-DDX39B readthrough (NMD candidate); NULL |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barresi, V.; Cosentini, I.; Scuderi, C.; Napoli, S.; Di Bella, V.; Spampinato, G.; Condorelli, D.F. Fusion Transcripts of Adjacent Genes: New Insights into the World of Human Complex Transcripts in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215252
Barresi V, Cosentini I, Scuderi C, Napoli S, Di Bella V, Spampinato G, Condorelli DF. Fusion Transcripts of Adjacent Genes: New Insights into the World of Human Complex Transcripts in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(21):5252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215252
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarresi, Vincenza, Ilaria Cosentini, Chiara Scuderi, Salvatore Napoli, Virginia Di Bella, Giorgia Spampinato, and Daniele Filippo Condorelli. 2019. "Fusion Transcripts of Adjacent Genes: New Insights into the World of Human Complex Transcripts in Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 21: 5252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215252
APA StyleBarresi, V., Cosentini, I., Scuderi, C., Napoli, S., Di Bella, V., Spampinato, G., & Condorelli, D. F. (2019). Fusion Transcripts of Adjacent Genes: New Insights into the World of Human Complex Transcripts in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(21), 5252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215252