Inhibition of the Adenosinergic Pathway in Cancer Rejuvenates Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The ADO Pathway
2.1. Enzymes
2.2. Receptors
3. ADO in Cancer
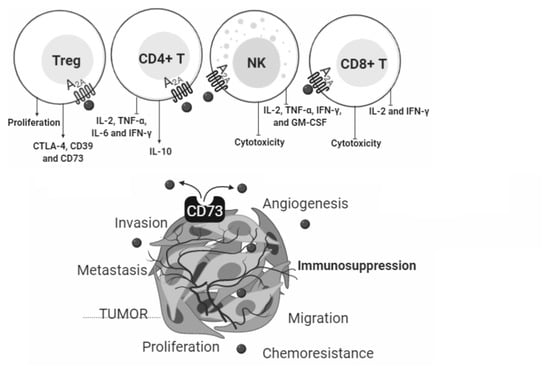
4. ADO in the Immune System
4.1. ADO in Macrophages
4.2. ADO in Lymphocytes
4.2.1. CD4+ T Cells and NK
4.2.2. T Regulatory Cells
4.2.3. CD8+ T Cells
5. ADO in Exosomes
6. ADO Pathway in Cancer Therapy
6.1. Targeting ADO Receptors in Cancer Cells
6.1.1. A1R
6.1.2. A2AR
6.1.3. A2BR
6.1.4. A3R
6.2. CD73
6.3. CD38
6.4. Combined Therapies
6.4.1. Radiotherapy
6.4.2. Chemotherapy
6.4.3. Immunotherapies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | adenosine deaminase |
| ADO | adenosine |
| AdoK | Adenosine kinase |
| ADP | adenosine diphosphate |
| ADPR | ADP-ribose |
| ALPs | alkaline phosphatases |
| AMID | factor-homologous mitochondrion-associated inducer of death |
| AMP | adenosine monophosphate |
| APCs | antigen presenting cells |
| ATP | Adenosine 5’-triphosphate |
| cAMP | intracellular cyclic AMP |
| CD39 | E-NTPDase1 |
| CD73 | ecto-5’-nucleotidase |
| CD73 inhibitor | adenosine 5’-α,β-methylene-diphosphate |
| CNTs | concentrative nucleoside transporters |
| CTLA-4 | anti- cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| E-NPP | ecto-pyrophosphate-phosphodiesterases |
| ENT | nucleoside equilibrative transporters |
| E-NTPDases | ecto-nucleoside triphosphate-diphosphohydrolases |
| ErbB2 | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 2 |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| HIF-1alpha | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| IFNγ | Interferon gamma |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IL-13 | Interleukin 13 |
| IL-2 | Interleukin 2 |
| IL-4 | Interleukin 4 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin 8 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MDSCs | myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| MIP-α | Human macrophage inflammatory protein alpha |
| NAD+ | adenine dinucleotide |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NSCLC | Non-small Cell Lung Cancer |
| PD-1 | programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PIP3 | Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate |
| Rap1 | Ras-proximate-1 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| Th1 | T helper 1 cells |
| Th2 | helper 2 cells |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TMZ | Temozolomide |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TRAIL | TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand mediated apoptosis |
| Treg | regulatory T cell |
| UDP | uridine diphosphate |
| UTP | Uridine-5’-triphosphate |
| VEGF | Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladanyi, A.; Timar, J. Immunologic and immunogenomic aspects of tumor progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic Signalling and Endothelium. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 14, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Di Virgilio, F. Purinergic signalling and cancer. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 491–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signalling: Past, present and future. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2009, 42, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic Signalling and Neurological Diseases: An Update. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic Mechanisms and Pain. Adv. Pharmacol. 2016, 75, 91–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic Signaling in the Cardiovascular System. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Dale, N. Purinergic signalling during development and ageing. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 11, 277–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, D.F.; Bernardes, V.M.; da Silva, J.L.G.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Leal, D.B.R. Adenosine signaling and adenosine deaminase regulation of immune responses: Impact on the immunopathogenesis of HIV infection. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, D.; Chrobak, P.; Allard, B.; Messaoudi, N.; Stagg, J. Targeting the CD73-adenosine axis in immuno-oncology. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, B.; Turcotte, M.; Stagg, J. CD73-generated adenosine: Orchestrating the tumor-stroma interplay to promote cancer growth. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 485156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.; Mittal, D.; Stagg, J.; Smyth, M.J. Targeting cancer-derived adenosine: New therapeutic approaches. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Boeynaems, J.M. Purinergic signalling and immune cells. Purinergic Signal. 2014, 10, 529–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, R.D.; Emens, L.A. Targeting adenosine for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer 2018, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Fan, J.; Wang, L.; Thompson, L.F.; Liu, A.; Daniel, B.J.; Shin, T.; Curiel, T.J.; Zhang, B. CD73 on tumor cells impairs antitumor T-cell responses: A novel mechanism of tumor-induced immune suppression. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigano, S.; Alatzoglou, D.; Irving, M.; Menetrier-Caux, C.; Caux, C.; Romero, P.; Coukos, G. Targeting Adenosine in Cancer Immunotherapy to Enhance T-Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sek, K.; Molck, C.; Stewart, G.D.; Kats, L.; Darcy, P.K.; Beavis, P.A. Targeting Adenosine Receptor Signaling in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, A.N.; Szent-Gyorgyi, A. The physiological activity of adenine compounds with especial reference to their action upon the mammalian heart. J. Physiol. 1929, 68, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.L.; Sarti, A.C.; Di Virgilio, F. Extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides as signalling molecules. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signalling in the reproductive system in health and disease. Purinergic Signal. 2014, 10, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnstock, G. Blood cells: An historical account of the roles of purinergic signalling. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 11, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, H.; Zebisch, M.; Strater, N. Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 437–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, E.; Horenstein, A.L.; Canzonetta, C.; Costa, F.; Morandi, F. Canonical and non-canonical adenosinergic pathways. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: The State of the Art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Varani, K.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine receptors in health and disease. Adv. Pharmacol. 2011, 61, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S. The A3 adenosine receptor: History and perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 74–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Dalpiaz, A.; Varani, K.; Gessi, S.; Gilli, G. Binding thermodynamics at A1 and A2A adenosine receptors. Life Sci. 1996, 59, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayah, A.; Kanellopoulos, J.M.; Di Virgilio, F. P2 receptors and immunity. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F. P2X receptors and inflammation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, K.H.; Thompson, L.F.; Kaufmann, M.; Moller, P. Expression of ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73) in normal mammary gland and in breast carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 1991, 63, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bavaresco, L.; Bernardi, A.; Braganhol, E.; Cappellari, A.R.; Rockenbach, L.; Farias, P.F.; Wink, M.R.; Delgado-Canedo, A.; Battastini, A.M. The role of ecto-5’-nucleotidase/CD73 in glioma cell line proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 319, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Song, B.; Wang, X.; Chang, X.S.; Pang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yin, K.; Fang, G.E. The expression and clinical significance of CD73 molecule in human rectal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5459–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadej, R.; Skladanowski, A.C. Dual, enzymatic and non-enzymatic, function of ecto-5’-nucleotidase (eN, CD73) in migration and invasion of A375 melanoma cells. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.X.; Chen, Y.T.; Feng, B.; Mao, X.B.; Yu, B.; Chu, X.Y. Expression and clinical significance of CD73 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.; Bavaresco, L.; Braganhol, E.; Rockenbach, L.; Farias, P.F.; Wink, M.R.; Azambuja, A.A.; Barrios, C.H.; Morrone, F.B.; Oliveira Battastini, A.M. Differential ectonucleotidase expression in human bladder cancer cell lines. Urol. Oncol. 2010, 28, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Xu, X.; Qiao, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, F.; Gao, G.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of NT5E/CD73 expression and its prognostic significance in distinct types of cancers. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Adinolfi, E. Extracellular purines, purinergic receptors and tumor growth. Oncogene 2017, 36, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Novitskiy, S.V.; Sachsenmeier, K.F.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Hasko, G. Switching off CD73: A way to boost the activity of conventional and targeted antineoplastic therapies. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavis, P.A.; Stagg, J.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J. CD73: A potent suppressor of antitumor immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Beavis, P.A.; Darcy, P.K.; Stagg, J. Immunosuppressive activities of adenosine in cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannone, R.; Miele, L.; Maiolino, P.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. Blockade of A2b adenosine receptor reduces tumor growth and immune suppression mediated by myeloid-derived suppressor cells in a mouse model of melanoma. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, A.; Joachims, M.L.; Thompson, L.F.; Miller, A.D.; Canoll, P.D.; Bynoe, M.S. CD73 Promotes Glioblastoma Pathogenesis and Enhances Its Chemoresistance via A2B Adenosine Receptor Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 4387–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azambuja, J.H.; Gelsleichter, N.E.; Beckenkamp, L.R.; Iser, I.C.; Fernandes, M.C.; Figueiro, F.; Battastini, A.M.O.; Scholl, J.N.; de Oliveira, F.H.; Spanevello, R.M.; et al. CD73 Downregulation Decreases In Vitro and In Vivo Glioblastoma Growth. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3260–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quezada, C.; Garrido, W.; Oyarzun, C.; Fernandez, K.; Segura, R.; Melo, R.; Casanello, P.; Sobrevia, L.; San Martin, R. 5’-ectonucleotidase mediates multiple-drug resistance in glioblastoma multiforme cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, A.; Sokolovskaya, A.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Amdahl, H.; West, A.; Yagita, H.; Lahesmaa, R.; Thompson, L.F.; Jalkanen, S.; Blokhin, D.; et al. CD73 participates in cellular multiresistance program and protects against TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turcotte, M.; Allard, D.; Mittal, D.; Bareche, Y.; Buisseret, L.; Jose, V.; Pommey, S.; Delisle, V.; Loi, S.; Joensuu, H.; et al. CD73 Promotes Resistance to HER2/ErbB2 Antibody Therapy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5652–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lv, M.; Qiao, B.; Li, X. Blockade pf CD73/adenosine axis improves the therapeutic efficacy of docetaxel in epithelial ovarian cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 299, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, S.; Pommey, S.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Beavis, P.A.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J.; Stagg, J. CD73 promotes anthracycline resistance and poor prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11091–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dastjerdi, M.N.; Rarani, M.Z.; Valiani, A.; Mahmoudieh, M. The effect of adenosine A1 receptor agonist and antagonist on p53 and caspase 3, 8, and 9 expression and apoptosis rate in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, D.F.; Kondo, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Niu, D.F.; Mochizuki, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Yamane, T.; Katoh, R. Hypoxia-inducible adenosine A2B receptor modulates proliferation of colon carcinoma cells. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchio, E.A.; Tan, C.Y.; Gregory, K.J.; Christopoulos, A.; White, P.J.; May, L.T. Ligand-Independent Adenosine A2B Receptor Constitutive Activity as a Promoter of Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 357, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Costanzi, S.; Balasubramanian, R.; Gao, Z.G.; Jacobson, K.A. A2B adenosine receptor blockade inhibits growth of prostate cancer cells. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasama, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kasamatsu, A.; Okamoto, A.; Koyama, T.; Minakawa, Y.; Ogawara, K.; Yokoe, H.; Shiiba, M.; Tanzawa, H.; et al. Adenosine A2b receptor promotes progression of human oral cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koszalka, P.; Golunska, M.; Urban, A.; Stasilojc, G.; Stanislawowski, M.; Majewski, M.; Skladanowski, A.C.; Bigda, J. Specific Activation of A3, A2A and A1 Adenosine Receptors in CD73-Knockout Mice Affects B16F10 Melanoma Growth, Neovascularization, Angiogenesis and Macrophage Infiltration. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.R.; Deng, W.W.; Liu, J.F.; Mao, L.; Yu, G.T.; Bu, L.L.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.F.; Sun, Z.J. Blockade of adenosine A2A receptor enhances CD8(+) T cells response and decreases regulatory T cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediavilla-Varela, M.; Luddy, K.; Noyes, D.; Khalil, F.K.; Neuger, A.M.; Soliman, H.; Antonia, S.J. Antagonism of adenosine A2A receptor expressed by lung adenocarcinoma tumor cells and cancer associated fibroblasts inhibits their growth. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Madore, J.; Reinhardt, J.; Landsberg, J.; Chitsazan, A.; Rautela, J.; Bald, T.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Ahern, E.; et al. Targeting Adenosine in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Reduces Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4684–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaji, W.; Tanaka, S.; Tsukimoto, M.; Kojima, S. Adenosine A(2B) receptor antagonist PSB603 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting induction of regulatory T cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.J.; Min, H.Y.; Chung, H.J.; Park, E.J.; Shin, D.H.; Jeong, L.S.; Lee, S.K. A novel adenosine analog, thio-Cl-IB-MECA, induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Woo, J.S. The adenosine A3 receptor agonist Cl-IB-MECA induces cell death through Ca(2)(+)/ROS-dependent down regulation of ERK and Akt in A172 human glioma cells. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 2667–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaei, M.; Panjehpour, M.; Karami-Tehrani, F.; Salami, S. Molecular mechanisms of A3 adenosine receptor-induced G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in androgen-dependent and independent prostate cancer cell lines: Involvement of intrinsic pathway. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.M.; Joshaghani, H.R.; Panjehpour, M.; Aghaei, M. A2B adenosine receptor agonist induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in breast cancer stem cells via ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Cell. Oncol. (Dordr.) 2018, 41, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaya, H.; Gotoh, A.; Kanno, T.; Nishizaki, T. A3 adenosine receptor mediates apoptosis in in vitro RCC4-VHL human renal cancer cells by up-regulating AMID expression. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, T.; Nakano, T.; Fujita, Y.; Gotoh, A.; Nishizaki, T. Adenosine induces apoptosis in SBC-3 human lung cancer cells through A(3) adenosine receptor-dependent AMID upregulation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Targa, M.; Paradiso, B.; Parrilli, A.; Fini, M.; Lanza, G.; Borea, P.A. The stimulation of A(3) adenosine receptors reduces bone-residing breast cancer in a rat preclinical model. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellari, A.R.; Pillat, M.M.; Souza, H.D.; Dietrich, F.; Oliveira, F.H.; Figueiro, F.; Abujamra, A.L.; Roesler, R.; Lecka, J.; Sevigny, J.; et al. Ecto-5’-Nucleotidase Overexpression Reduces Tumor Growth in a Xenograph Medulloblastoma Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Simioni, C.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Mirandola, P.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A. A(2B) and A(3) adenosine receptors modulate vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8 expression in human melanoma cells treated with etoposide and doxorubicin. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beavis, P.A.; Divisekera, U.; Paget, C.; Chow, M.T.; John, L.B.; Devaud, C.; Dwyer, K.; Stagg, J.; Smyth, M.J.; Darcy, P.K. Blockade of A2A receptors potently suppresses the metastasis of CD73+ tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14711–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledderose, C.; Hefti, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Bao, Y.; Seier, T.; Li, L.; Woehrle, T.; Zhang, J.; Junger, W.G. Adenosine arrests breast cancer cell motility by A3 receptor stimulation. Purinergic Signal. 2016, 12, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merighi, S.; Benini, A.; Mirandola, P.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Simioni, C.; Leung, E.; Maclennan, S.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A. Caffeine inhibits adenosine-induced accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor, and interleukin-8 expression in hypoxic human colon cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Ramirez, A.S.; Diaz-Munoz, M.; Battastini, A.M.; Campos-Contreras, A.; Olvera, A.; Bergamin, L.; Glaser, T.; Jacintho Moritz, C.E.; Ulrich, H.; Vazquez-Cuevas, F.G. Cellular Migration Ability Is Modulated by Extracellular Purines in Ovarian Carcinoma SKOV-3 Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 4468–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Zhi, X.; Zhou, T.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Yin, L.; Shao, Z.; Ou, Z. Overexpression of Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73) promotes T-47D human breast cancer cells invasion and adhesion to extracellular matrix. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stagg, J.; Divisekera, U.; McLaughlin, N.; Sharkey, J.; Pommey, S.; Denoyer, D.; Dwyer, K.M.; Smyth, M.J. Anti-CD73 antibody therapy inhibits breast tumor growth and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lokshin, A.; Raskovalova, T.; Huang, X.; Zacharia, L.C.; Jackson, E.K.; Gorelik, E. Adenosine-mediated inhibition of the cytotoxic activity and cytokine production by activated natural killer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7758–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszalka, P.; Pryszlak, A.; Golunska, M.; Kolasa, J.; Stasilojc, G.; Skladanowski, A.C.; Bigda, J.J. Inhibition of CD73 stimulates the migration and invasion of B16F10 melanoma cells in vitro, but results in impaired angiogenesis and reduced melanoma growth in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Z.; Li, X.; Kang, N.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, T.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X. A Novel Specific Anti-CD73 Antibody Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Motility by Regulating Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.L.; Shen, M.N.; Hu, B.; Wang, B.L.; Yang, W.J.; Lv, L.H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, A.L.; Sun, Y.F.; et al. CD73 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling by inducing Rap1-mediated membrane localization of P110beta and predicts poor prognosis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azambuja, J.H.; Schuh, R.S.; Michels, L.R.; Gelsleichter, N.E.; Beckenkamp, L.R.; Iser, I.C.; Lenz, G.S.; de Oliveira, F.H.; Venturin, G.; Greggio, S.; et al. Nasal Administration of Cationic Nanoemulsions as CD73-siRNA Delivery System for Glioblastoma Treatment: A New Therapeutical Approach. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.W.; Wang, H.P.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Long, M.; Zhang, H.Z.; Dong, K. CD73 promotes proliferation and migration of human cervical cancer cells independent of its enzyme activity. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Sarti, A.C.; Grassi, F. Modulation of innate and adaptive immunity by P2X ion channels. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 52, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Hasko, G. Adenosine signaling and the immune system: When a lot could be too much. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Hasko, G. Immunity, inflammation and cancer: A leading role for adenosine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, M.H.; Raoofi Mohseni, S.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Anvari, E.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2032–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreckler, L.M.; Wan, T.C.; Ge, Z.D.; Auchampach, J.A. Adenosine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha release from mouse peritoneal macrophages via A2A and A2B but not the A3 adenosine receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regateiro, F.S.; Cobbold, S.P.; Waldmann, H. CD73 and adenosine generation in the creation of regulatory microenvironments. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 171, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, N.E.; Sanmarco, L.M.; Eberhardt, N.; Garcia, M.C.; Rivarola, H.W.; Cano, R.C.; Aoki, M.P. CD73 Inhibition Shifts Cardiac Macrophage Polarization toward a Microbicidal Phenotype and Ameliorates the Outcome of Experimental Chagas Cardiomyopathy. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasko, G.; Pacher, P. Regulation of macrophage function by adenosine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, S.; Pluddemann, A.; Martinez Estrada, F. Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: Phenotypic diversity and functions. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 262, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, F.O.; Helming, L.; Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages: An immunologic functional perspective. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasko, G.; Kuhel, D.G.; Chen, J.F.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Deitch, E.A.; Mabley, J.G.; Marton, A.; Szabo, C. Adenosine inhibits IL-12 and TNF-[alpha] production via adenosine A2a receptor-dependent and independent mechanisms. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnholt, K.E.; Kota, R.S.; Aung, H.H.; Rutledge, J.C. Adenosine blocks IFN-gamma-induced phosphorylation of STAT1 on serine 727 to reduce macrophage activation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6767–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabo, C.; Scott, G.S.; Virag, L.; Egnaczyk, G.; Salzman, A.L.; Shanley, T.P.; Hasko, G. Suppression of macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha production and collagen-induced arthritis by adenosine receptor agonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasko, G.; Pacher, P.; Deitch, E.A.; Vizi, E.S. Shaping of monocyte and macrophage function by adenosine receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasko, G.; Szabo, C.; Nemeth, Z.H.; Kvetan, V.; Pastores, S.M.; Vizi, E.S. Adenosine receptor agonists differentially regulate IL-10, TNF-alpha, and nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages and in endotoxemic mice. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 4634–4640. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante, C.J.; Pinhal-Enfield, G.; Elson, G.; Cronstein, B.N.; Hasko, G.; Outram, S.; Leibovich, S.J. The adenosine-dependent angiogenic switch of macrophages to an M2-like phenotype is independent of interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Ralpha) signaling. Inflammation 2013, 36, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciaraffia, E.; Riccomi, A.; Lindstedt, R.; Gesa, V.; Cirelli, E.; Patrizio, M.; De Magistris, M.T.; Vendetti, S. Human monocytes respond to extracellular cAMP through A2A and A2B adenosine receptors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 96, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanin, R.F.; Braganhol, E.; Bergamin, L.S.; Campesato, L.F.; Filho, A.Z.; Moreira, J.C.; Morrone, F.B.; Sevigny, J.; Schetinger, M.R.; de Souza Wyse, A.T.; et al. Differential macrophage activation alters the expression profile of NTPDase and ecto-5’-nucleotidase. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montalban Del Barrio, I.; Penski, C.; Schlahsa, L.; Stein, R.G.; Diessner, J.; Wockel, A.; Dietl, J.; Lutz, M.B.; Mittelbronn, M.; Wischhusen, J.; et al. Adenosine-generating ovarian cancer cells attract myeloid cells which differentiate into adenosine-generating tumor associated macrophages - a self-amplifying, CD39- and CD73-dependent mechanism for tumor immune escape. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergamin, L.S.; Braganhol, E.; Figueiro, F.; Casali, E.A.; Zanin, R.F.; Sevigny, J.; Battastini, A.M. Involvement of purinergic system in the release of cytokines by macrophages exposed to glioma-conditioned medium. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azambuja, J.H.; da Silveira, E.F.; de Carvalho, T.R.; Oliveira, P.S.; Pacheco, S.; do Couto, C.T.; Beira, F.T.; Stefanello, F.M.; Spanevello, R.M.; Braganhol, E. Glioma sensitive or chemoresistant to temozolomide differentially modulate macrophage protumor activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 2652–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekic, C.; Day, Y.J.; Sag, D.; Linden, J. Myeloid expression of adenosine A2A receptor suppresses T and NK cell responses in the solid tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7250–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cekic, C.; Linden, J. Adenosine A2A receptors intrinsically regulate CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7239–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiedel, A.C.; Lacher, S.K.; Linnemann, C.; Knolle, P.A.; Muller, C.E. Antiproliferative effects of selective adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists on human lymphocytes: Evidence for receptor-independent mechanisms. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, A.; Kini, R.; Ohta, A.; Subramanian, M.; Madasu, M.; Sitkovsky, M. The development and immunosuppressive functions of CD4(+) CD25(+) FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells are under influence of the adenosine-A2A adenosine receptor pathway. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdmann, A.A.; Gao, Z.G.; Jung, U.; Foley, J.; Borenstein, T.; Jacobson, K.A.; Fowler, D.H. Activation of Th1 and Tc1 cell adenosine A2A receptors directly inhibits IL-2 secretion in vitro and IL-2-driven expansion in vivo. Blood 2005, 105, 4707–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, E.; Zubiaga, A.M.; Merrow, M.; Sauter, N.P.; Huber, B.T. Cholera toxin discriminates between T helper 1 and 2 cells in T cell receptor-mediated activation: Role of cAMP in T cell proliferation. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lappas, C.M.; Day, Y.J.; Marshall, M.A.; Engelhard, V.H.; Linden, J. Adenosine A2A receptor activation reduces hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting CD1d-dependent NKT cell activation. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, A.; Kjaergaard, J.; Sharma, S.; Mohsin, M.; Goel, N.; Madasu, M.; Fradkov, E.; Ohta, A.; Sitkovsky, M. In vitro induction of T cells that are resistant to A 2 adenosine receptor-mediated immunosuppression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kjaergaard, J.; Hatfield, S.; Jones, G.; Ohta, A.; Sitkovsky, M. A2A adenosine receptor gene-deletion or synthetic A2A antagonist liberate tumor-reactive CD8+ T-cells from tumor-induced immunosuppression. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Conrad, D.M.; Butler, J.J.; Zhao, C.; Blay, J.; Hoskin, D.W. Adenosine acts through A2 receptors to inhibit IL-2-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT5 in T lymphocytes: Role of cyclic adenosine 3’,5’-monophosphate and phosphatases. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minguet, S.; Huber, M.; Rosenkranz, L.; Schamel, W.W.; Reth, M.; Brummer, T. Adenosine and cAMP are potent inhibitors of the NF-kappa B pathway downstream of immunoreceptors. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, D.L.; Yerian, L.; Schauer, P.; Kashyap, S.R.; Lopez, R.; Hazen, S.L.; Feldstein, A.E. Cytokeratin 18 fragment levels as a noninvasive biomarker for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in bariatric surgery patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S.; Cattabriga, E.; Avitabile, A.; Gavioli, R.; Fortini, C.; Leung, E.; Mac Lennan, S.; Borea, P.A. Expression of A3 adenosine receptors in human lymphocytes: Up-regulation in T cell activation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priebe, T.; Platsoucas, C.D.; Nelson, J.A. Adenosine receptors and modulation of natural killer cell activity by purine nucleosides. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 4328–4331. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, A.M.; Wang, J.; Lupo, K.B.; Yu, H.; Atallah Lanman, N.M.; Matosevic, S. Adenosinergic Signaling Alters Natural Killer Cell Functional Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Lin, G.; Field, J.J.; Linden, J. Induction of antiinflammatory purinergic signaling in activated human iNKT cells. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffe, F.; Stegmann, K.A.; Broelsch, F.; Manns, M.P.; Cornberg, M.; Wedemeyer, H. Adenosine and IFN-{alpha} synergistically increase IFN-gamma production of human NK cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, F.; Horenstein, A.L.; Chillemi, A.; Quarona, V.; Chiesa, S.; Imperatori, A.; Zanellato, S.; Mortara, L.; Gattorno, M.; Pistoia, V.; et al. CD56brightCD16- NK Cells Produce Adenosine through a CD38-Mediated Pathway and Act as Regulatory Cells Inhibiting Autologous CD4+ T Cell Proliferation. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuldova, M.; Svoboda, J.; Kovaru, F.; Vannucci, L.; Kovaru, H.; Fiserova, A. NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity modulation by A(2) adenosine receptor agonist in different mammalian species. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2009, 54, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Gao, Y.; Patch, A.M.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Messaoudene, M.; Lin, G.; Coudert, J.D.; Stannard, K.A.; Zitvogel, L.; et al. A2AR Adenosine Signaling Suppresses Natural Killer Cell Maturation in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harish, A.; Hohana, G.; Fishman, P.; Arnon, O.; Bar-Yehuda, S. A3 adenosine receptor agonist potentiates natural killer cell activity. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 23, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, K.M.; Hanidziar, D.; Putheti, P.; Hill, P.A.; Pommey, S.; McRae, J.L.; Winterhalter, A.; Doherty, G.; Deaglio, S.; Koulmanda, M.; et al. Expression of CD39 by human peripheral blood CD4+ CD25+ T cells denotes a regulatory memory phenotype. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horenstein, A.L.; Chillemi, A.; Zaccarello, G.; Bruzzone, S.; Quarona, V.; Zito, A.; Serra, S.; Malavasi, F. A CD38/CD203a/CD73 ectoenzymatic pathway independent of CD39 drives a novel adenosinergic loop in human T lymphocytes. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e26246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, T.L.; Jackson, E.K. Adenosine and prostaglandin e2 production by human inducible regulatory T cells in health and disease. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gennaro, P.; Gerlini, G.; Caporale, R.; Sestini, S.; Brandani, P.; Urso, C.; Pimpinelli, N.; Borgognoni, L. T regulatory cells mediate immunosuppresion by adenosine in peripheral blood, sentinel lymph node and TILs from melanoma patients. Cancer Lett. 2018, 417, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.; Gorelik, E.; Prasad, S.J.; Ronchese, F.; Lukashev, D.; Wong, M.K.K.; Huang, X.; Caldwell, S.; Liu, K.; Smith, P.; et al. A2A adenosine receptor protects tumors from antitumor T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13132–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, T.L. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes and tumor-mediated immune suppression. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morandi, F.; Marimpietri, D.; Horenstein, A.L.; Bolzoni, M.; Toscani, D.; Costa, F.; Castella, B.; Faini, A.C.; Massaia, M.; Pistoia, V.; et al. Microvesicles released from multiple myeloma cells are equipped with ectoenzymes belonging to canonical and non-canonical adenosinergic pathways and produce adenosine from ATP and NAD\r+\r. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1458809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clayton, A.; Al-Taei, S.; Webber, J.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z. Cancer exosomes express CD39 and CD73, which suppress T cells through adenosine production. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimu, J.; Webber, J.; Gurney, M.; Al-Taei, S.; Clayton, A.; Tabi, Z. Dominant immunosuppression of dendritic cell function by prostate-cancer-derived exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1368823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theodoraki, M.N.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Jackson, E.K.; Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes in HNSCC plasma as surrogate markers of tumour progression and immune competence. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 194, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smyth, L.A.; Ratnasothy, K.; Tsang, J.Y.; Boardman, D.; Warley, A.; Lechler, R.; Lombardi, G. CD73 expression on extracellular vesicles derived from CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ T cells contributes to their regulatory function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puhan, M.A.; Chandra, D.; Mosenifar, Z.; Ries, A.; Make, B.; Hansel, N.N.; Wise, R.A.; Sciurba, F. National Emphysema Treatment Trial Research, G., The minimal important difference of exercise tests in severe COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tong, L.; Chu, X.; Deng, F.; Tang, J.; Tang, Y.; Dai, Y. The Adenosine A1 Receptor Antagonist DPCPX Inhibits Tumor Progression via the ERK/JNK Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Sult, E.; Hay, C.; Blake, S.J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Takeda, K.; Teng, M.W.L.; et al. Co-inhibition of CD73 and A2AR Adenosine Signaling Improves Anti-tumor Immune Responses. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beavis, P.A.; Henderson, M.A.; Giuffrida, L.; Mills, J.K.; Sek, K.; Cross, R.S.; Davenport, A.J.; John, L.B.; Mardiana, S.; Slaney, C.Y.; et al. Targeting the adenosine 2A receptor enhances chimeric antigen receptor T cell efficacy. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beavis, P.A.; Milenkovski, N.; Henderson, M.A.; John, L.B.; Allard, B.; Loi, S.; Kershaw, M.H.; Stagg, J.; Darcy, P.K. Adenosine Receptor 2A Blockade Increases the Efficacy of Anti-PD-1 through Enhanced Antitumor T-cell Responses. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, S.; Kheshtchin, N.; Ajami, M.; Ashurpoor, M.; Safvati, A.; Namdar, A.; Mirzaei, R.; Mousavi Niri, N.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Ghahremani, M.H.; et al. Increased efficacy of a dendritic cell-based therapeutic cancer vaccine with adenosine receptor antagonist and CD73 inhibitor. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317695021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molck, C.; Ryall, J.; Failla, L.M.; Coates, J.L.; Pascussi, J.M.; Heath, J.K.; Stewart, G.; Hollande, F. The A2b adenosine receptor antagonist PSB-603 promotes oxidative phosphorylation and ROS production in colorectal cancer cells via adenosine receptor-independent mechanism. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekic, C.; Sag, D.; Li, Y.; Theodorescu, D.; Strieter, R.M.; Linden, J. Adenosine A2B receptor blockade slows growth of bladder and breast tumors. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanno, T.; Gotoh, A.; Fujita, Y.; Nakano, T.; Nishizaki, T. A(3) adenosine receptor mediates apoptosis in 5637 human bladder cancer cells by G(q) protein/PKC-dependent AIF upregulation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjehpour, M.; Karami-Tehrani, F. An adenosine analog (IB-MECA) inhibits anchorage-dependent cell growth of various human breast cancer cell lines. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, S.; Sorrentino, R.; Porta, A.; Forte, G.; Popolo, A.; Petrella, A.; Pinto, A. Cl-IB-MECA enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis via the modulation of NF-kappaB signalling pathway in thyroid cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 221, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Ohana, G.; Barer, F.; Ochaion, A.; Erlanger, A.; Madi, L. An agonist to the A3 adenosine receptor inhibits colon carcinoma growth in mice via modulation of GSK-3 beta and NF-kappa B. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2465–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhi, X.; Chen, S.; Zhou, P.; Shao, Z.; Wang, L.; Ou, Z.; Yin, L. RNA interference of ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73) inhibits human breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2007, 24, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terp, M.G.; Olesen, K.A.; Arnspang, E.C.; Lund, R.R.; Lagerholm, B.C.; Ditzel, H.J.; Leth-Larsen, R. Anti-human CD73 monoclonal antibody inhibits metastasis formation in human breast cancer by inducing clustering and internalization of CD73 expressed on the surface of cancer cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iannone, R.; Miele, L.; Maiolino, P.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. Adenosine limits the therapeutic effectiveness of anti-CTLA4 mAb in a mouse melanoma model. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Atyabi, F.; Rastegari, A.; Kheshtchin, N.; Arab, S.; Hassannia, H.; Ajami, M.; Mirsanei, Z.; Habibi, S.; Masoumi, F.; et al. CD73 specific siRNA loaded chitosan lactate nanoparticles potentiate the antitumor effect of a dendritic cell vaccine in 4T1 breast cancer bearing mice. J. Control. Release 2017, 246, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Atyabi, F.; Rastegari, A.; Mollarazi, E.; Kiani, M.; Razavi, A.; Yousefi, M.; Kheshtchin, N.; Hassannia, H.; Hadjati, J.; et al. Downregulation of CD73 in 4T1 breast cancer cells through siRNA-loaded chitosan-lactate nanoparticles. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8403–8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Donk, N. Reprint of “Immunomodulatory effects of CD38-targeting antibodies”. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejcik, J.; Casneuf, T.; Nijhof, I.S.; Verbist, B.; Bald, J.; Plesner, T.; Syed, K.; Liu, K.; van de Donk, N.W.; Weiss, B.M.; et al. Daratumumab depletes CD38+ immune regulatory cells, promotes T-cell expansion, and skews T-cell repertoire in multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Leve, S.; Wirsdorfer, F.; Jendrossek, V. Targeting the Immunomodulatory CD73/Adenosine System to Improve the Therapeutic Gain of Radiotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hay, C.M.; Sult, E.; Huang, Q.; Mulgrew, K.; Fuhrmann, S.R.; McGlinchey, K.A.; Hammond, S.A.; Rothstein, R.; Rios-Doria, J.; Poon, E.; et al. Targeting CD73 in the tumor microenvironment with MEDI9447. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1208875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, D.; Young, A.; Stannard, K.; Yong, M.; Teng, M.W.; Allard, B.; Stagg, J.; Smyth, M.J. Antimetastatic effects of blocking PD-1 and the adenosine A2A receptor. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model | Main Result | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| P1R antagonism | ||
| Melanoma in vivo | Inhibition of A2BR enhanced efficacy of dacarbazine | Reversed immune suppression in the TME [42] |
| Glioblastoma in vivo | Inhibition of A2BR enhanced efficacy of TMZ | A2BR [43] |
| CD73 inhibition | ||
| Glioblastoma in vitro | CD73 KO increased efficacy of TMZ | ADO production [44] |
| Glioblastoma in vitro | CD73 KO reversed the MDR phenotype | A3R [45] |
| Leukemia in vitro | CD73 KO restored TRAIL sensitivity | Independent of CD73enzymatic activity [46] |
| Breast cancer in vivo | Anti-CD73 mab therapy enhanced efficacy of anti-ErbB2 mAb | Association of CD73 expression with TGF-β, EMT and HIF-1 [47] |
| Ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo | Anti-CD73 mab therapy enhanced docetaxel response | Reverse the immunosuppression [48] |
| Breast cancer in vivo | CD73 inhibitor therapy enhanced efficacy of doxorubicin | Activation of immune response mediated by A2AR [49] |
| Model | Main Result | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| P1R antagonism | ||
| Breast cancer in vitro | Inhibition of A1R induced apoptosis | Upregulation of p53 and caspases [50] |
| Colon carcinoma in vitro | Inhibition of A2BR suppressed tumor growth | A2BR [51] |
| Prostate cancer in vitro | Inhibition of A2BR suppressed tumor growth | A2BR [52,53] |
| Oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro | Inhibition of A2BR suppressed tumor growth | A2BR [54] |
| Melanoma in vivo | Activation of P1R inhibited melanoma growth | Enhance immune killing of tumors [55] |
| HNSCC in vivo | Inhibition of A2AR suppressed tumor growth | Reduced Tregs population and enhanced the anti-tumor response of CD8+ T cells [56] |
| Lung adenocarcinoma in vivo | Inhibition of A2AR suppressed tumor growth | Prevented negative signaling in T cells and inhibited angiogenesis [57] |
| Melanoma in vivo | Inhibition of A2AR suppressed tumor growth | NK activation [58] |
| Melanoma in vivo | Inhibition of A2BR suppressed tumor growth | Reduced Tregs population and increased in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells [59] |
| P1R agonism | ||
| Leukemia in vitro | Activation of A3R induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | Modulation of Wnt, β-catenin, GSK-β and AKT [60] |
| Bladder cancer in vitro | Activation of A3R induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | ERK and JNK activation [61] |
| Cancer cell lines | Activation of A3R induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | Downregulation of CDK4, cyclin D1 and upregulation of p53 [62] |
| Ovarian cancer in vitro | Activation of A3R reduced cell viability and induced cell cycle arrest | Downregulation of Cyclin D1 and CDK4 [63] |
| Renal cancer in vitro | Activation of A3R induced apoptosis | AMID upregulation [64] |
| Glioblastoma in vitro | Activation of A3R induced cell death | ERK and AKT downregulation [62] |
| Lung cancer in vitro | Activation of A3R induced cell death | Mediated by caspases upregulation [65] |
| Breast cancer in vivo | Activation of A3R inhibited tumor proliferation | Not reported [66] |
| CD73 inhibition | ||
| Glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo | Knockdown of CD73 decreased glioma growth | Stimulation of AKT/NF-kB pathways [44] |
| CD73 overexpression | ||
| Medulloblastoma in vitro and in vivo | Reduced proliferation and vascularization | Mediated by A1R [67] |
| Model | Main Result | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| P1R antagonism | ||
| Melanoma in vitro | Reduced angiogenesis | A2BR blockade impairs IL-8 production, whereas blocking A3R decreases VEGF [68] |
| Breast cancer and melanoma in vivo | A2AR blockade reduced metastasis | Enhanced NK cell maturation and cytotoxicity [69] |
| P1R agonism | ||
| Breast cancer in vitro | Activation of A3R induced migration | Not reported [70] |
| Colon cancer in vitro | Enhanced migration | A2BR and A3R activation and regulation HIF-1alpha/VEGF/IL-8 via ERK1/2, p38, and AKT [71] |
| CD73 inhibition | ||
| Ovarian Carcinoma in vitro | CD73 inhibitor blocked migration | Not reported [72] |
| Glioblastoma in vitro | CD73 KO decreased migration and invasion | Altered MMP-2 and Vimentin expression [44] |
| Breast cancer in vitro | Anti-CD73 mab therapy inhibited migration, invasion and adhesion | EGFR and IL-8 [73] |
| Breast cancer in vivo | Anti-CD73 mab therapy decreased lung metastases | Activation of NK cells, CD8+ T and IFNγ by A2BR [74,75] |
| Melanoma in vitro and in vivo | CD73 inhibitor decreased adherence of cells and enhanced migration and invasion | Via P1R [76] |
| Breast cancer in vitro and in vivo | Anti-CD73 mab therapy inhibited migration metastasis in vivo | CD73 expression promoted autophagy [77] |
| Hepatocellular cancer in vitro and in vivo | CD73 KO inhibited migration, invasion and metastasis | A2AR activates Rap1, P110β, and PIP3 production by AKT [78] |
| Glioblastoma in vivo | CD73 KO inhibited angiogenesis | Not reported [79] |
| CD73 overexpression | ||
| Cervical cancer in vitro | Promoted migration; and high concentration inhibited migration. | Upregulation of EGFR, VEGF, and AKT [80] |
| NCT Number | Phase | Year | Type of Cancer | Drug Name | Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00879775 | Phase 2 | 2009 | Cancer | Caffeine | P1R antagonist |
| NCT024031093 | Phase 1/2 | 2015 | Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) | PBF-509 | A2AR antagonist |
| NCT02655822 | Phase 1 | 2016 | Advanced Cancers | CPI-444 | A2AR antagonist |
| NCT03274479 | Phase 1 | 2018 | Locally Advanced or Metastatic NSCLC | PBF-1129 | A2BR antagonist |
| NCT00790218 | Phase 1/2 | 2009 | Hepatocellular Carcinoma | CF102 | A3R antagonist |
| NCT01987999 | Phase 2 | 2013 | Prostate Cancer | Acetogenins | ATP inhibitor |
| NCT02503774 | Phase 1 | 2015 | Solid Tumors | MEDI9447 | CD73 |
| NCT03267589 | Phase 2 | 2017 | Relapsed Ovarian Cancer | MEDI9447 | CD73 |
| NCT03616886 | Phase 1/2 | 2018 | Triple Negative Breast Cancer | MEDI9447 | CD73 |
| NCT03549000 | Phase 1 | 2018 | Advanced Malignancies | NZV930 | CD73 |
| NCT03381274 | Phase 1/2 | 2018 | NSCLC | MEDI9447 | CD73 |
| NCT03454451 | Phase 1 | 2018 | Cancer | CPI-006 | CD73 |
| NCT03835949 | Phase 1 | 2019 | Advanced or Metastatic Cancer | TJ004309 | CD73 |
| NCT03875573 | Phase 2 | 2019 | Luminal B Breast Cancer | oleclumab | CD73 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azambuja, J.H.; Ludwig, N.; Braganhol, E.; Whiteside, T.L. Inhibition of the Adenosinergic Pathway in Cancer Rejuvenates Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225698
Azambuja JH, Ludwig N, Braganhol E, Whiteside TL. Inhibition of the Adenosinergic Pathway in Cancer Rejuvenates Innate and Adaptive Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225698
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzambuja, Juliana Hofstätter, Nils Ludwig, Elizandra Braganhol, and Theresa L. Whiteside. 2019. "Inhibition of the Adenosinergic Pathway in Cancer Rejuvenates Innate and Adaptive Immunity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225698
APA StyleAzambuja, J. H., Ludwig, N., Braganhol, E., & Whiteside, T. L. (2019). Inhibition of the Adenosinergic Pathway in Cancer Rejuvenates Innate and Adaptive Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225698