The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
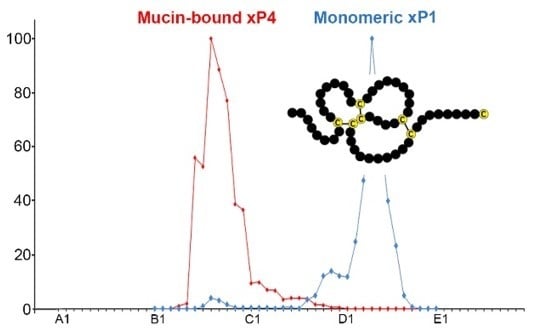
2.1. Characterzation of xP1 and xP4 in X. Laevis Gastric Extracts by SEC and Western Blot Analysis
2.2. Binding of 125I-Labeled Porcine TFF2 to X. Laevis Gastric Mucin In Vitro (Overlay Assay)
3. Discussion
3.1. xP1 Mainly Occurs in An Unusual Monomeric Form: Possible Functional Implications
3.2. xP4 is Mucin-Associated: Interaction with the Ortholog of MUC6
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extraction of Proteins and Purification by SEC
4.2. SDS-PAGE, Agarose Gel Electrophoresis, and Western Blot Analysis
4.3. TFF2 Binding Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgGE | Agarose gel electrophoresis |
| PAS | Periodic acid-Schiff |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| TFF | Trefoil factor family |
References
- Hauser, F.; Hoffmann, W. xP1 and xP4. P-domain peptides expressed in Xenopus laevis stomach mucosa. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 21306–21309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W.; Jagla, W. Cell type specific expression of secretory TFF peptides: Colocalization with mucins and synthesis in the brain. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 147–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides: Regulators of mucosal regeneration and repair, and more. Peptides 2004, 25, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W.; Hauser, F. The P-domain or trefoil motif: A role in renewal and pathology of mucous epithelia? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993, 18, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagla, W.; Wiede, A.; Kolle, S.; Hoffmann, W. Differential expression of the TFF-peptides xP1 and xP4 in the gastrointestinal tract of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res. 1998, 291, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Session, A.M.; Uno, Y.; Kwon, T.; Chapman, J.A.; Toyoda, A.; Takahashi, S.; Fukui, A.; Hikosaka, A.; Suzuki, A.; Kondo, M.; et al. Genome evolution in the allotetraploid frog Xenopus laevis. Nature 2016, 538, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzler, C.; Oertel, M.; Hinz, M.; Hoffmann, W. Structure of the Xenopus laevis TFF-gene xP4.1, differentially expressed to its duplicated homolog xP4.2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1489, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF Peptides. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 2nd ed.; Kastin, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1338–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Ribieras, S.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. The pS2/TFF1 trefoil factor, from basic research to clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1378, F61–F77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westley, B.R.; Griffin, S.M.; May, F.E. Interaction between TFF1, a gastric tumor suppressor trefoil protein, and TFIZ1, a brichos domain-containing protein with homology to SP-C. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7967–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Laubinger, W.; Kalbacher, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W. Biosynthesis of gastrokine-2 in the human gastric mucosa: Restricted spatial expression along the antral gland axis and differential interaction with TFF1, TFF2 and mucins. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Pleiotropic effects of Trefoil Factor 1 deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, O.; Chenard, M.P.; Masson, R.; Linares, J.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Wendling, C.; Tomasetto, C.; Chambon, P.; Rio, M.C. Gastric mucosa abnormalities and tumorigenesis in mice lacking the pS2 trefoil protein. Science 1996, 274, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutto, M.; Saleh, M.; Arredouani, M.S.; Piazuelo, B.; Belkhiri, A.; El-Rifai, W. Loss of Tff1 Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype with Increase in the Levels of RORγt+ T Lymphocytes and Il-17 in Mouse Gastric Neoplasia. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2424–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saukkonen, K.; Tomasetto, C.; Narko, K.; Rio, M.C.; Ristimaki, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and effect of celecoxib in gastric adenomas of trefoil factor 1-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3032–3036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karam, S.M.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Trefoil factor 1 is required for the commitment programme of mouse oxyntic epithelial progenitors. Gut 2004, 53, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, S.M.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Amplification and invasiveness of epithelial progenitors during gastric carcinogenesis in trefoil factor 1 knockout mice. Cell Prolif. 2008, 41, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, E.P.; Ali, T.; Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; O’Kennedy, R.; May, F.E.B.; Westley, B.R.; Josenhans, C.; Rust, M.; Suerbaum, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide interacts with TFF1 in a pH-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, M.; May, F.E.B. The Interaction of Helicobacter pylori with TFF1 and Its Role in Mediating the Tropism of the Bacteria Within the Stomach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thim, L. Trefoil peptides: From structure to function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thim, L.; Madsen, F.; Poulsen, S.S. Effect of trefoil factors on the viscoelastic properties of mucus gels. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellev, S.; Nexo, E.; Thim, L.; Poulsen, S.S. Systemically administered trefoil factors are secreted into the gastric lumen and increase the viscosity of gastric contents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Hayama, M.; Momose, M.; El-Zimaity, H.M.; Matsuda, K.; Sano, K.; Maruta, F.; Okumura, N.; Katsuyama, T. Co-localization of TFF2 with gland mucous cell mucin in gastric mucous cells and in extracellular mucous gel adherent to normal and damaged gastric mucosa. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 126, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF2, a MUC6-binding lectin stabilizing the gastric mucus barrier and more. Int. J. Oncool. 2015, 47, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, J.I.; Newton, J.; Westley, B.; May, F. Dramatic diurnal variation in the concentration of the human trefoil peptide TFF2 in gastric juice. Gut 2001, 48, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, F.E.; Semple, J.I.; Newton, J.L.; Westley, B.R. The human two domain trefoil protein, TFF2, is glycosylated in vivo in the stomach. Gut 2000, 46, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisch, F.G.; Ragge, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Human gastric TFF2 peptide contains an N-linked fucosylated N,N’-diacetyllactosediamine (LacdiNAc) oligosaccharide. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisch, F.G.; Bonar, D.; Schloerer, N.; Schroten, H. Human trefoil factor 2 is a lectin that binds α-GlcNAc-capped mucin glycans with antibiotic activity against Helicobacter pylori. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27363–27375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oinuma, T.; Ide, S.; Kawano, J.; Suganuma, T. Purification and immunohistochemistry of Griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin-II-binding mucus glycoprotein in rat stomach. Glycobiology 1994, 4, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Kurihara, M.; Goso, Y.; Urata, T.; Ota, H.; Katsuyama, T.; Hotta, K. Peripheral α-linked N-acetylglucosamine on the carbohydrate moiety of mucin derived from mammalian gastric gland mucous cells: Epitope recognized by a newly characterized monoclonal antibody. Biochem. J. 1996, 318, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, M.; Ito, Y.; Okimura, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sakura, K.; Kasama, S.; Fukuda, M.N.; Fukuda, M.; Katsuyama, T.; Nakayama, J. Natural antibiotic function of a human gastric mucin against Helicobacter pylori infection. Science 2004, 305, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Ge, Z.; Ohtani, M.; Jones, E.K.; Wang, T.C. Accelerated progression of gastritis to dysplasia in the pyloric antrum of TFF2-/- C57BL6 x Sv129 Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albert, T.K.; Laubinger, W.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Human intestinal TFF3 forms disulfide-linked heteromers with the mucus-associated FCGBP protein and is released by hydrogen sulfide. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemer, J.; Bulleid, N.; Herrmann, J.M. Disulfide formation in the ER and mitochondria: Two solutions to a common process. Science 2009, 324, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.; Sparvoli, A.; Fagioli, C.; Fassina, G.; Sitia, R. Formation of reversible disulfide bonds with the protein matrix of the endoplasmic reticulum correlates with the retention of unassembled Ig light chains. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuzawa, M.; Yasumasu, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Iuchi, I. Cloning and expression of xP1-L, a new marker gene for larval surface mucous cells of tadpole stomach in Xenopus laevis. Gene Expr. Patterns 2007, 8, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, H.F. Molecular and cellular aspects of thiol-disulfide exchange. In Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology; Meister, A., Ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1963; Volume 63, pp. 69–172. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, L.B. The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, J.; Clavreul, N.; Sethuraman, M.; Adachi, T.; Cohen, R.A. Thiol oxidation in signaling and response to stress: Detection and quantification of physiological and pathophysiological thiol modifications. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, L.F.; Karam, S.M.; Wendling, C.; Chenard, M.P.; Kershenobich, D.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Trefoil factor 1 (TFF1/pS2) deficiency activates the unfolded protein response. Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grasberger, H.; El-Zaatari, M.; Dang, D.T.; Merchant, J.L. Dual oxidases control release of hydrogen peroxide by the gastric epithelium to prevent Helicobacter felis infection and inflammation in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennett, E.C.; Chuang, C.Y.; Degendorfer, G.; Whitelock, J.M.; Davies, M.J. Mechanisms and consequences of oxidative damage to extracellular matrix. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Mogami, S.; Hibi, T. Roles of oxidative stress in stomach disorders. J. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 50, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, N.A.; Poulsom, R.; Stamp, G.W.H.; Hall, P.A.; Jeffery, R.E.; Longcroft, J.M.; Rio, M.-C.; Tomasetto, C.; Chambon, P. Epidermal growth factor (EGF/URO) induces expression of regulatory peptides in damaged human gastrointestinal tissues. J. Pathol. 1990, 162, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rio, M.-C.; Chenard, M.-P.; Wolf, C.; Marcellin, L.; Tomasetto, C.; Lathe, R.; Bellocq, J.-P.; Chambon, P. Induction of pS2 and hSP genes as markers of mucosal ulceration of the digestive tract. Gastroenterology 1991, 100, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.P.A.; Hoffmann, J.; Haeckel, C.; Rutkowski, K.; Schmid, R.M.; Wagner, M.; Adler, G.; Schulz, H.U.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W.; et al. Induction of TFF1 gene expression in pancreas overexpressing transforming growth factor α. Gut 1999, 45, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Chwieralski, C.E.; Bälder, R.; Hinz, M.; Braun, A.; Krug, N.; Hoffmann, W. Induced trefoil factor family 1 expression by trans-differentiating Clara cells in a murine asthma model. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Guttek, K.; Händel, U.; Reinhold, D.; Hoffmann, W. Increased cerebral Tff1 expression in two murine models of neuroinflammation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Salm, F.; Händel, U.; Hoffmann, W. Transcriptional responses in the murine spleen after Toxoplasma gondii infection: Inflammasome und mucus-associated genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Wu, Z.; Nuding, S.; Groscurth, S.; Marcinowski, M.; Beisner, J.; Buchner, J.; Schaller, M.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Reduction of disulphide bonds unmasks potent antimicrobial activity of human β-defensin 1. Nature 2011, 469, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Hoffmann, W. Porcine gastric TFF2 is a mucus constituent and differs from pancreatic TFF2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Hoffmann, W. Commercial Porcine Gastric Mucin Preparations, also Used as Artificial Saliva, are a Rich Source for the Lectin TFF2: In Vitro Binding Studies. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Klasson, S.; Larsson, E.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C.; Samuelsson, T. Searching the evolutionary origin of epithelial mucus protein components—mucins and FCGBP. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, J. Dual roles of gastric gland mucin-specific O-glycans in prevention of gastric cancer. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jørgensen, K.H.; Thim, L.; Jacobsen, H.E. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): I. Preparation and initial chemical characterization of a new polypeptide from porcine pancreas. Regul. Pept. 1982, 3, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga Emidio, N.; Hoffmann, W.; Brierly, S.M.; Muttenthaler, M. Trefoil factor family: Unresolved questions and clinical perspectives. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stürmer, R.; Reising, J.; Hoffmann, W. The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052
Stürmer R, Reising J, Hoffmann W. The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052
Chicago/Turabian StyleStürmer, René, Jana Reising, and Werner Hoffmann. 2019. "The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052
APA StyleStürmer, R., Reising, J., & Hoffmann, W. (2019). The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236052