Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6′-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
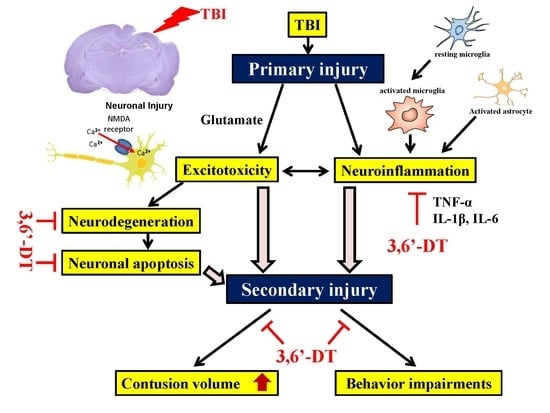
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. 3,6′-DT Lowers Markers of Inflammation in Cellular Studies
2.2. Post-Injury 3,6′-DT Treatment Significantly Reduced Contusion Volume
2.3. Post-Injury Treatment Reduced TBI-Induced Neurodegeneration
2.4. 3,6′-DT Administered at 5 h Post-Injury Improved Functional Outcomes as Revealed by Behavioral Evaluation at 24 h after CCI
2.5. Treatment with 3,6′-DT Reduced Apoptotic Neurons in the Cortical Contusion Regions after TBI
2.6. Treatment with 3,6′-DT Suppressed Microglia Activation
2.7. 3,6′-DT Administered at 5 h Post-Injury Downregulates Injury-Induced Cytokine mRNA Expression at 8 h after CCI
2.8. 3,6′-DT Reduced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Protein Expression at 8 h after TBI in the Ipsilateral Hemisphere
2.9. Treatment with 3,6′-DT Reduces CCI-Induced Oxidative Damage in the Cortical Contusion Regions after CCI
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cellular Studies
4.2. In Vivo Studies
4.3. Drug Administration
4.4. Behavioral Evaluation of Neurological Outcomes
4.5. Contusion Volume
4.6. Fluoro-Jade C (FJC) Staining
4.7. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.9. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) or Double Immunofluorescence
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maas, A.I.; Stocchetti, N.; Bullock, R. Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, A.; Carpenter, K.L.; Menon, D.K.; Pickard, J.D.; Hutchinson, P.J. The cytokine response to human traumatic brain injury: Temporal profiles and evidence for cerebral parenchymal production. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.C.; Liao, Y.E.; Yang, L.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Tweedie, D.; Karnati, H.K.; Greig, N.H. Neuroinflammation in animal models of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 272, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozano, D.; Gonzales-Portillo, G.S.; Acosta, S.; de la Pena, I.; Tajiri, N.; Kaneko, Y.; Borlongan, C.V. Neuroinflammatory responses to traumatic brain injury: Etiology, clinical consequences, and therapeutic opportunities. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tansey, M.G. Inflammation in neuropsychiatric disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 91–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodcock, T.; Morganti-Kossmann, M.C. The role of markers of inflammation in traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frugier, T.; Morganti-Kossmann, M.C.; O’Reilly, D.; McLean, C.A. In situ detection of inflammatory mediators in post mortem human brain tissue after traumatic injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shohami, E.; Gallily, R.; Mechoulam, R.; Bass, R.; Ben-Hur, T. Cytokine production in the brain following closed head injury: Dexanabinol (HU-211) is a novel TNF-alpha inhibitor and an effective neuroprotectant. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 72, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Goh, S.J.; Tang, P.Y.; Deng, Y.Y.; Ling, E.A.; Moochhala, S. Systemic inflammatory response following acute traumatic brain injury. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 3795–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; You, Z.; Kim, H.H.; Hwang, S.K.; Khuman, J.; Guo, S.; Lo, E.H.; Whalen, M.J. Genetic analysis of the role of tumor necrosis factor receptors in functional outcome after traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, L.; Perego, C.; Ortolano, F.; Aresi, S.; Fumagalli, S.; Zanier, E.R.; Stocchetti, N.; de Simoni, M.G. Tumor necrosis factor in traumatic brain injury: Effects of genetic deletion of p55 or p75 receptor. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 82–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Pecoraro, R.; Pinto, A. Studies of selective TNF inhibitors in the treatment of brain injury from stroke and trauma: A review of the evidence to date. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 2221–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Cui, X.; Barochia, A.; Li, Y.; Natanson, C.; Eichacker, P.Q. The evolving experience with therapeutic TNF inhibition in sepsis: Considering the potential influence of risk of death. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaltonen, K.J.; Virkki, L.M.; Malmivaara, A.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Nordstrom, D.C.; Blom, M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of existing TNF blocking agents in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordas, I.; Mould, D.R.; Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J. Anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease: Pharmacokinetics-based dosing paradigms. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 91, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eger, K.; Jalalian, M.; Verspohl, E.J.; Lupke, N.P. Synthesis, central nervous system activity and teratogenicity of a homothalidomide. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1990, 40, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Hsieh, T.C.; Wu, J.M.; Wu, E. Thalidomide—A notorious sedative to a wonder anticancer drug. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 4102–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, T.L.; McHugh, S.M.; Deighton, J.; Ewan, P.W.; Dearman, R.J.; Kimber, I. Selective down-regulation of T cell- and non-T cell-derived tumour necrosis factor alpha by thalidomide: Comparisons with dexamethasone. Immunol. Lett. 1999, 68, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, T.L.; McHugh, S.M.; Deighton, J.; Dearman, R.J.; Ewan, P.W.; Kimber, I. Differential regulation by thalidomide and dexamethasone of cytokine expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Immunopharmacology 1998, 40, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.L.; Sampaio, E.P.; Zmuidzinas, A.; Frindt, P.; Smith, K.A.; Kaplan, G. Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA degradation. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.K.; Jantaratnotai, N.; McLarnon, J.G. Thalidomide inhibition of vascular remodeling and inflammatory reactivity in the quinolinic acid-injected rat striatum. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decourt, B.; Drumm-Gurnee, D.; Wilson, J.; Jacobson, S.; Belden, C.; Sirrel, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Shill, H.; Powell, J.; Walker, A.; et al. Poor safety and tolerability hamper reaching a potentially therapeutic dose in the use of thalidomide for Alzheimer’s disease: Results from a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Giordano, T.; Yu, Q.S.; Holloway, H.W.; Perry, T.A.; Lahiri, D.K.; Brossi, A.; Greig, N.H. Thiothalidomides: Novel isosteric analogues of thalidomide with enhanced TNF-alpha inhibitory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 5222–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, N.H.; Giordano, T.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Q.S.; Perry, T.A.; Holloway, H.W.; Brossi, A.; Rogers, J.T.; Sambamurti, K.; Lahiri, D.K. Thalidomide-based TNF-alpha inhibitors for neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2004, 64, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tweedie, D.; Luo, W.; Short, R.G.; Brossi, A.; Holloway, H.W.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.S.; Greig, N.H. A cellular model of inflammation for identifying TNF-alpha synthesis inhibitors. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 183, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratz, R.; Tweedie, D.; Rubovitch, V.; Luo, W.; Yoon, J.S.; Hoffer, B.J.; Greig, N.H.; Pick, C.G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis inhibitor, 3,6′-dithiothalidomide, reverses behavioral impairments induced by minimal traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 1032–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belarbi, K.; Jopson, T.; Tweedie, D.; Arellano, C.; Luo, W.; Greig, N.H.; Rosi, S. TNF-alpha protein synthesis inhibitor restores neuronal function and reverses cognitive deficits induced by chronic neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tweedie, D.; Ferguson, R.A.; Fishman, K.; Frankola, K.A.; Van Praag, H.; Holloway, H.W.; Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Caracciolo, L.; Russo, I.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis inhibitor 3,6’-dithiothalidomide attenuates markers of inflammation, Alzheimer pathology and behavioral deficits in animal models of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Tweedie, D.; Mughal, M.R.; Chigurupati, S.; Greig, N.H.; Mattson, M.P. 3,6′-dithiothalidomide improves experimental stroke outcome by suppressing neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 91, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baratz, R.; Tweedie, D.; Wang, J.Y.; Rubovitch, V.; Luo, W.; Hoffer, B.J.; Greig, N.H.; Pick, C.G. Transiently lowering tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis ameliorates neuronal cell loss and cognitive impairments induced by minimal traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedie, D.; Frankola, K.A.; Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Greig, N.H. Thalidomide Analogues Suppress Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Synthesis of TNF-alpha and Nitrite, an Intermediate of Nitric Oxide, in a Cellular Model of Inflammation. Open Biochem. J. 2011, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhery, M.S.; Khan, M.; Mahmood, R.; Mehmood, A.; Khan, S.N.; Riazuddin, S. Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells from aged mice have reduced wound healing, angiogenesis, proliferation and anti-apoptosis capabilities. Cell Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, A.E.; Pioro, E.P.; Sasse, M.E.; Kostenko, V.; Cardona, S.M.; Dijkstra, I.M.; Huang, D.; Kidd, G.; Dombrowski, S.; Dutta, R.; et al. Control of microglial neurotoxicity by the fractalkine receptor. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, S.T.; Longhi, L.; Saatman, K.E.; Conte, V.; Stocchetti, N.; McIntosh, T.K. Motor and cognitive function evaluation following experimental traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blach-Olszewska, Z.; Leszek, J. Mechanisms of over-activated innate immune system regulation in autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frankola, K.A.; Greig, N.H.; Luo, W.; Tweedie, D. Targeting TNF-alpha to elucidate and ameliorate neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2011, 10, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, S.M.; Rothwell, N.J. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti-Kossmann, M.C.; Rancan, M.; Stahel, P.F.; Kossmann, T. Inflammatory response in acute traumatic brain injury: A double-edged sword. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2002, 8, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.T.; Wang, Y.W.; Yang, J.T.; Yang, Y.L.; Chen, H.I. Effect of interleukin-1 on traumatic brain injury-induced damage to hippocampal neurons. J. Neurotrauma 2005, 22, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohami, E.; Bass, R.; Wallach, D.; Yamin, A.; Gallily, R. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) activity in rat brain is associated with cerebroprotection after closed head injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1996, 16, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoblach, S.M.; Fan, L.; Faden, A.I. Early neuronal expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha after experimental brain injury contributes to neurological impairment. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 95, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.K.; Tansey, M.G. TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: Implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, E.N. Inflammatory cytokines within the central nervous system: Sources, function, and mechanism of action. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263, C1–C16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasturk, A.E.; Gokce, E.C.; Yilmaz, E.R.; Horasanli, B.; Evirgen, O.; Hayirli, N.; Gokturk, H.; Erguder, I.; Can, B. Therapeutic evaluation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist etanercept against traumatic brain injury in rats: Ultrastructural, pathological, and biochemical analyses. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gourin, C.G.; Shackford, S.R. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta by human cerebral microvascular endothelium after percussive trauma. J. Trauma 1997, 42, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.A.; Halliday, M.I.; Campbell, G.C.; Byrnes, D.P.; Rowlands, B.J. The presence of tumour necrosis factor in CSF and plasma after severe head injury. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 8, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbita, S.P.; Srivastava, M.K.; Eslami, P.; Johnson, M.F.; Kobritz, N.K.; Tweedie, D.; Greig, N.H.; Zemlan, F.P.; Sharma, S.P.; Harris-White, M.E. Early intervention with a small molecule inhibitor for tumor necrosis factor-alpha prevents cognitive deficits in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Shuaib, A. Involvement of inflammatory cytokines in central nervous system injury. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 67, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Wang, C.C.; Cheong, C.U.; Chao, C.M.; Cheng, B.C.; Yang, C.Z.; Chang, C.P. Etanercept attenuates traumatic brain injury in rats by reducing early microglial expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, M.A.; Uysal, O.; Cikriklar, H.I.; Ozbek, Z.; Turgut Cosan, D.; Baydemir, C.; Kazanci, B.; Hafizoglu, D. Effect of etanercept and lithium chloride on preventing secondary tissue damage in rats with experimental diffuse severe brain injury. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tobinick, E. Perispinal etanercept advances as a neurotherapeutic. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2018, 18, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.N.; Gibson, T.R.; Thompson, B.M.; Deng, Y.; Hall, E.D. Relationship of calpain-mediated proteolysis to the expression of axonal and synaptic plasticity markers following traumatic brain injury in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 201, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.E.; Kaup, A.; Kirby, K.A.; Byers, A.L.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Yaffe, K. Traumatic brain injury and risk of dementia in older veterans. Neurology 2014, 83, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greig, N.H.; Tweedie, D.; Rachmany, L.; Li, Y.; Rubovitch, V.; Schreiber, S.; Chiang, Y.H.; Hoffer, B.J.; Miller, J.; Lahiri, D.K.; et al. Incretin mimetics as pharmacologic tools to elucidate and as a new drug strategy to treat traumatic brain injury. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, S62–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, L.E.; Fisher, A.M.; Tagge, C.A.; Zhang, X.L.; Velisek, L.; Sullivan, J.A.; Upreti, C.; Kracht, J.M.; Ericsson, M.; Wojnarowicz, M.W.; et al. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in blast-exposed military veterans and a blast neurotrauma mouse model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 134ra60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.N.; Yang, L.Y.; Greig, N.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Lai, C.C.; Wang, J.Y. Neuroprotective effects of pifithrin-alpha against traumatic brain injury in the striatum through suppression of neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, autophagy, and apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.Y.; Chu, Y.H.; Tweedie, D.; Yu, Q.S.; Pick, C.G.; Hoffer, B.J.; Greig, N.H.; Wang, J.Y. Post-trauma administration of the pifithrin-alpha oxygen analog improves histological and functional outcomes after experimental traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 269, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.Y.; Greig, N.H.; Huang, Y.N.; Hsieh, T.H.; Tweedie, D.; Yu, Q.S.; Hoffer, B.J.; Luo, Y.; Kao, Y.C.; Wang, J.Y. Post-traumatic administration of the p53 inactivator pifithrin-alpha oxygen analogue reduces hippocampal neuronal loss and improves cognitive deficits after experimental traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 96, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Huang, Y.N.; Chiu, C.C.; Tweedie, D.; Luo, W.; Pick, C.G.; Chou, S.Y.; Luo, Y.; Hoffer, B.J.; Greig, N.H.; et al. Pomalidomide mitigates neuronal loss, neuroinflammation, and behavioral impairments induced by traumatic brain injury in rat. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feeney, D.M.; Boyeson, M.G.; Linn, R.T.; Murray, H.M.; Dail, W.G. Responses to cortical injury: I. Methodology and local effects of contusions in the rat. Brain Res. 1981, 211, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Raghupathi, R.; Saatman, K.E.; Smith, D.H.; Stutzmann, J.M.; Wahl, F.; McIntosh, T.K. Riluzole attenuates cortical lesion size, but not hippocampal neuronal loss, following traumatic brain injury in the rat. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 52, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batsaikhan, B.; Wang, J.-Y.; Scerba, M.T.; Tweedie, D.; Greig, N.H.; Miller, J.P.; Hoffer, B.J.; Lin, C.-T.; Wang, J.-Y. Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6′-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030502
Batsaikhan B, Wang J-Y, Scerba MT, Tweedie D, Greig NH, Miller JP, Hoffer BJ, Lin C-T, Wang J-Y. Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6′-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(3):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030502
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatsaikhan, Buyandelger, Jing-Ya Wang, Michael T. Scerba, David Tweedie, Nigel H. Greig, Jonathan P. Miller, Barry J. Hoffer, Chih-Tung Lin, and Jia-Yi Wang. 2019. "Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6′-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 3: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030502
APA StyleBatsaikhan, B., Wang, J.-Y., Scerba, M. T., Tweedie, D., Greig, N. H., Miller, J. P., Hoffer, B. J., Lin, C.-T., & Wang, J.-Y. (2019). Post-Injury Neuroprotective Effects of the Thalidomide Analog 3,6′-Dithiothalidomide on Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(3), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030502