Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Transcriptional Alterations in Growth- and Development-Related Genes in Sweet Potato Plants Infected and Non-Infected by SPFMV, SPV2, and SPVG
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
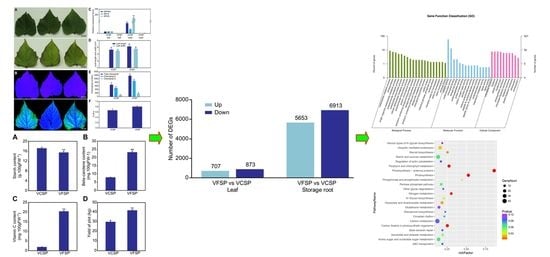
2.1. Phenotypes and Growth Indexes of VCSP and VFSP
2.2. Gene Expression Profiles of Leaves and Storage Roots in VCSP and VFSP
2.3. GO Classification of Differential Expression Genes
2.4. Pathway Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.5. Validation of differentially expressed candidate genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Measurement of Leaf Length (LL) and Width (LW)
4.3. Determination of Chlorophyll Contents
4.4. Assay of Maximal Photochemical Efficiency (Fv/Fm)
4.5. Assay of Starch Content
4.6. HPLC Analysis of Vitamin C
4.7. Assay of Total Beta-Carotene
4.8. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
4.9. Verification of RNA-Seq Data by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGO | argonaut |
| BL | brassinolide |
| BRs | brassinosteroids |
| CAT | catalase |
| CKs | cytokinins |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| JA | jasmonic acid |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| POD | peroxidase |
| RBSDV | rice black-streaked dwarf virus |
| RPKM | reads per kilobase per million reads |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time PCR |
| SPCDV | Sweet potato chlorosis dwarf virus |
| SPCFV | Sweet potato chlorotic fleck virus |
| SPCSV | Sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus |
| SPFMV | Sweet potato feathery mottle virus |
| SPMMV | Sweet potato mild mottle virus |
| SPV2 | Sweet potato virus Y |
| SPVD | Sweet potato virus disease |
| SPVG | Sweet potato virus G |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| TMV | Tobacco mosaic virus |
| VCSP | sweet potato plants infected with SPFMV, SPV2, and SPVG |
| VFSP | sweet potato plants non-infected with SPFMV, SPV2, and SPVG |
References
- FAOSTAT. FAO Statistical Databases. 2014. Available online: http://apps.fao.org/faostat/en/ (accessed on 18 February 2017).
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, H. Research progress on the tip meristem culture of sweet potato. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2005, 21, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Qin, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y. Serological and molecular detection of viruses infecting sweet potato in China. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2012, 42, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Karyeija, R.F.; Kreuze, J.F.; Gibson, R.W.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Synergistic interactions of a potyvirus and a phloem-limited crinivirus in sweet potato plants. Virology 2000, 269, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untiveros, M.; Fuentes, S.; Salazar, L.F. Synergistic interaction of sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus(Crinivirus) with carla-, cucumo-, ipomo-, and potyviruses infecting sweet potato. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Z. Methodology for identification of disease resistance of sweet potato cultivars to sweet potato virus disease and yield loss estimation. J. Plant Prot. 2014, 41, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Loebenstein, G. Chapter Two—Control of Sweet potato Virus Diseases. Adv. Virus Res. 2015, 91, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tugume, A.K.; Mukasa, S.B.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Mixed infections of four viruses, the incidence and phylogenetic relationships of sweet potato chlorotic fleck virus (Betaflexiviridae) isolates in wild species and sweetpotatoes in Uganda and evidence of distinct isolates in East Africa. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xie, L.; Wu, B.; Xin, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J. Identification and genetic diversity analysis on sweet potato viruses in Shandong Province. J. Plant Prot. 2017, 44, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z. Comparison test of detoxified sweet potato and common sweet potato planting. Jiangxi Agric. Sci. Technol. 1999, 3, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhuang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, F. Physiological characteristics of yield-increasing of virus-free sweet potato. Res. Agric. Modernization. 2003, 24, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, R. Analysis of Purple Sweet Potato Virus-Free Technology and Its Physiological and Biochemical Indexes. Master’s Thesis, Jilin Normal University, Siping City, Jilin Province, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Mao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y. Analysis on the growth habit and physiological characteristics of virus-free sweet potato. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2000, 16, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Duan, C.G.; Hou, W.N.; Du, Q.S.; Lv, D.Q.; Fang, R.X. Satellite RNA-derived small interfering RNA satsiR-12 targeting the 3’ untranslated region of cucumber mosaic virus triggers viral RNAs for degradation. J. Virol. 2011, 5, 13384–13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, P.; Jackel, J.N.; Li, S.; Heard, I.M.; Bisaro, D.M. Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA binding protein DRB3 participates in methylation-mediated defense against geminiviruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, P.; Sanville, B.C.; Buchmann, R.C.; Bisaro, D.M. Viral genome methylation as an epigenetic defense against geminiviruses. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8997–9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Yan, B.; Lou, X.; Ma, H.; Ruan, S. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the transcriptional alterations in heat-resistant and heat-sensitive sweet maize (Zea mays L.) varieties under heat stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Burklew, C.E.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, B. De novo sequencing and a comprehensive analysis of purple sweet potato (Impomoea batatas L.) transcriptome. Planta 2012, 236, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Li, A.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, A. Transcriptome sequencing of the sweet potato progenitor (Ipomoea trifida (H.B.K.) G. Don.) and discovery of drought tolerance genes. Trop. Plant Biol. 2016, 9, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coruzzi, G.; Bush, D.R. Nitrogen and carbon nutrient and metabolite signaling in plants. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thum, K.E.; Shasha, D.E.; Lejay, L.V.; Coruzzi, G.M. Light- and carbon-signaling pathways. Modeling circuits of interactions. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanczyk-Wochniak, E.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolic profiling reveals altered nitrogen nutrient regimes have diverse effects on the metabolism of hydroponically-grown tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, R.A.; Lejay, L.V.; Dean, A.; Chiaromonte, F.; Shasha, D.E.; Coruzzi, G.M. Qualitative network models and genome-wide expression data define carbon/nitrogen-responsive molecular machines in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clouse, S.D.; Sasse, J.M. BRASSINOSTEROIDS: Essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Nitta, T.; Asami, T.; Fujioka, S.; Arai, Y. Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. Plant J. 2003, 33, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.W.; Deng, X.G.; Fu, F.Q.; Lin, H.H. Induction of plant virus defense response by brassinosteroids and brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2015, 241, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Hong, G.; Zhu, Q. Jasmonic acid-mediated defense suppresses brassinosteroid-mediated susceptibility to rice black streaked dwarf virus infection in rice. New Phytol. 2016, 214, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porra, R.J.; Thompson, W.A.; Kriedemann, P.E. Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: Verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1989, 975, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Zhao, L.; Yan, B.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, H.; Chen, W.; Ruan, S. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Transcriptional Alterations in Growth- and Development-Related Genes in Sweet Potato Plants Infected and Non-Infected by SPFMV, SPV2, and SPVG. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051012
Shi J, Zhao L, Yan B, Zhu Y, Ma H, Chen W, Ruan S. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Transcriptional Alterations in Growth- and Development-Related Genes in Sweet Potato Plants Infected and Non-Infected by SPFMV, SPV2, and SPVG. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051012
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jiang, Lin Zhao, Baiyuan Yan, Yueqing Zhu, Huasheng Ma, Wenyue Chen, and Songlin Ruan. 2019. "Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Transcriptional Alterations in Growth- and Development-Related Genes in Sweet Potato Plants Infected and Non-Infected by SPFMV, SPV2, and SPVG" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051012
APA StyleShi, J., Zhao, L., Yan, B., Zhu, Y., Ma, H., Chen, W., & Ruan, S. (2019). Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Transcriptional Alterations in Growth- and Development-Related Genes in Sweet Potato Plants Infected and Non-Infected by SPFMV, SPV2, and SPVG. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051012