Effect of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Coating based on Whey Protein Nanofibrils with TiO2 Nanotubes on the Quality and Shelf Life of Chilled Meat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
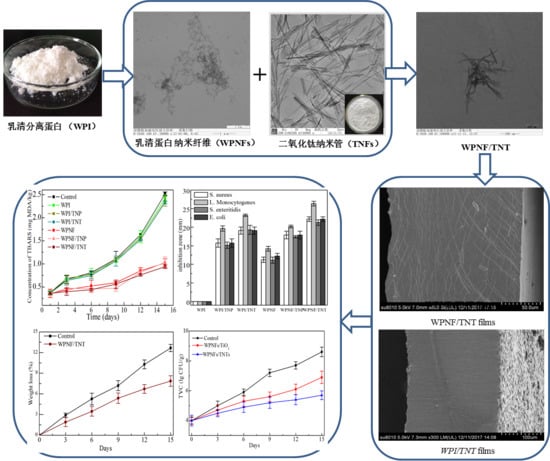
2. Results
2.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Micrographs of the Coating Solution
2.2. Texture Profile Analysis
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of the Microstructure of Films
2.2.2. Light Transmission and Film Transparency
2.2.3. Physical Properties of Nanocomposite Films
Mechanical Properties
Moisture Content (MC), Solubility in Water, Transparency, and Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
2.2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
2.3. Functional Properties of the Ecs on the Preservation of Chilled Meat
2.3.1. Lipid Oxidation
2.3.2. DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activity
2.3.3. Antimicrobial Activity
2.3.4. Weight Loss
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of WPNFs
4.3. Preparation of the Edible Coating Emulsions
4.4. Characterization and Physical Properties of Nanocomposite Films
4.4.1. Negative Stain Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4.3. Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
4.4.4. Physical Properties of Nanocomposite Films
Thickness Measurement
Mechanical Properties
MC Measurement
Measurement of Solubility in Water
Transparency Measurement
Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
Antibacterial Activity Analysis
4.5. Meat Quality Assessment
4.5.1. Preparation of Meat Samples and Treatments
4.5.2. Measurement of Lipid Oxidation
4.5.3. Measurement of Antioxidant Activity with DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activity
4.5.4. Microbiological Analyses
4.5.5. Weight Loss
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WPI | whey protein isolates |
| WPNFs | whey protein nanofibrils |
| TNTs | titanium dioxide nanotubes |
| TNPs | titanium dioxide nanoparticles |
| ECs | edible coatings |
| EFCs | edible films and coatings |
| TiO2 | titanium dioxide |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| UV | ultraviolet spectroscopy |
| TS | tensile strength |
| EB | elongation at break |
| MC | moisture content |
| WVP | water vapor permeability |
| TBARS | thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| TBA | 2-Thiobarbituric acid |
| TCA | trichloroacetic acid |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
References
- Pimonpan Kaewprachu, S.R. Mechanical and physico-chemical properties of biodegradable protein—Based films: A comparative study. Food Appl. Biosci. J. 2014, 2, 14–29. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M. Properties of Cast Films Made from Different Ratios of Whey Protein Isolate, Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate and Glycerol. Materials 2013, 6, 3254–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limchoowong, N.; Sricharoen, P.; Techawongstien, S.; Chanthai, S. An iodine supplementation of tomato fruits coated with an edible film of the iodide-doped chitosan. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundes, C.; Perez-Gago, M.B.; Monteiro, A.R.; Palou, L. Antifungal activity of food additives in vitro and as ingredients of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-lipid edible coatings against Botrytis cinerea and Alternaria alternata on cherry tomato fruit. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y.; Weiss, J. Structural design principles for delivery of bioactive components in nutraceuticals and functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 577–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umaraw, P.; Verma, A.K. Comprehensive review on application of edible film on meat and meat products: An eco-friendly approach. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.; Karboune, S. Natural Antimicrobial/Antioxidant Agents in Meat and Poultry Products as Well as Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernándezpan, I.; Carrióngranda, X.; Maté, J.I. Antimicrobial efficiency of edible coatings on the preservation of chicken breast fillets. Food Control 2014, 36, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Baraniak, B. Effects of plasticizers, pH and heating of film-forming solution on the properties of pea protein isolate films. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Krochta, J.M. Accelerated Shelf Life Testing of Whey-Protein-Coated Peanuts Analyzed by Static Headspace Gas Chromatography. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.; Pastor, C.; Chiralt, A.; McClements, D.J.; Gonzalez-Martinez, C. Recent advances in edible coatings for fresh and minimally processed fruits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodpran, T.; Benjakul, S.; Artharn, A. Properties and microstructure of protein-based film from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi) muscle as affected by palm oil and chitosan incorporation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 41, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loveday, S.M.; Su, J.; Rao, M.A.; Anema, S.G.; Singh, H. Whey protein nanofibrils: Kinetic, rheological and morphological effects of group IA and IIA cations. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 26, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, X. Edible coating based on whey protein isolate nanofibrils for antioxidation and inhibition of product browning. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajh, T.; Nedeljkovic, J.M.; Chen, L.X.; Poluektov, O.; Thurnauer, M.C. Improving Optical and Charge Separation Properties of Nanocrystalline TiO2 by Surface Modification with Vitamin C. J. Phys. Chem. 1999, 103, 3515–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawengkijwanich, C.; Hayata, Y. Development of TiO2 powder-coated food packaging film and its ability to inactivate Escherichia coli in vitro and in actual tests. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 123, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F.; Ren, F.; Zhao, G.; Leng, X. Fabrication and characterization of TiO2/whey protein isolate nanocomposite film. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, R.A.; Furtado, G.D.F.; Netto, F.M.; Cunha, R.L. Assessing the potential of whey protein fibril as emulsifier. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, C.; Zhu, K.; Fan, Z. TiO2 nanotubes infiltrated with nanoparticles for dye sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 235402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernshøj, K.D.; Hassing, S. Analysis of reflectance and transmittance measurements on absorbing and scattering small samples using a modified integrating sphere setup. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 63, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synak, R.; Lipinski, W.; Pawelczak, M. Roughness evaluation of very smooth surfaces using a novel method of scatter measurement. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, San Diego, CA, USA, 15 October 2012; Volume 8495, p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Food applications of emulsion-based edible films and coatings. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejdan, A.; Ojagh, S.M.; Adeli, A.; Abdollahi, M. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the physico-mechanical and ultraviolet light barrier properties of fish gelatin/agar bilayer film. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Gunasekaran, S. Preparation and characterization of whey protein film incorporated with TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, N50–N56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolfi, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Mousavi, M.; Hashemi, M. Development and characterization of the kefiran-whey protein isolate-TiO2 nanocomposite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, M.M.; Nute, G.R.; Hughes, S.I.; Enser, M.; Wood, J.D.; Richardson, R.I. Flavour perception of oxidation in beef. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Lin, H.; Zou, L.; Brody, A.L.; Li, Z.; Qazi, I.M.; Pavase, T.R.; Lv, L. A comprehensive review on the application of active packaging technologies to muscle foods. Food Control 2017, 82, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y. Rapid detection of total viable count (TVC) in pork meat by hyperspectral imaging. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, R.A.; Fattori, J.; Michelon, M.; Cunha, R.L. Formation and pH-stability of whey protein fibrils in the presence of lecithin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenares, J.C.; Luque, R.; Campelo, J.M.; Colmenares, F.; Karpiński, Z.; Romero, A.A. Nanostructured Photocatalysts and Their Applications in the Photocatalytic Transformation of Lignocellulosic Biomass: An Overview. Materials 2009, 2, 2228–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Vanamu, G.; Nie, Z.; Konishi, H.; Yeredla, R.; Phillips, J.; Wang, Y. Photocatalytic Oxidation of a Volatile Organic Component of Acetaldehyde Using Titanium Oxide Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2006, 2006, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.J.; Skibsted, L.H. Oxidative stability of frozen pork patties. Effect of light and added salt. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolder, S.G.; Vasbinder, A.J.; Sagis, L.M.C.; van der Linden, E. Heat-induced whey protein isolate fibrils: Conversion, hydrolysis, and disulphide bond formation. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Jiménez, A.; Atarés, L.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Effect of Fatty acids and beeswax addition on properties of sodium caseinate dispersions and films. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chai, Z.; Leng, X. Study of the physical properties of whey protein isolate and gelatin composite films. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5100–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajinipriya, M.; Nagalakshmaiah, M.; Robert, M.; Elkoun, S. Homogenous and transparent nanocellulosic films from carrot. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 118, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Huang, Y.; Lin, B.; Wang, S. A nanocomposite film fabricated with simultaneously extracted protein-polysaccharide from a marine alga and TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 29, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soazo, M.; Pérez, L.M.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of freezing on physical properties of whey protein emulsion films. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, Ó.L.; Reinas, I.; Silva, S.I.; Fernandes, J.C.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A.A.; Poças, M.F.; Pintado, M.E.; Malcata, F.X. Effect of whey protein purity and glycerol content upon physical properties of edible films manufactured therefrom. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mchugh, T.H.; Avena-Bustillos, R.; Krochta, J.M. Hydrophilic Edible Films: Modified Procedure for Water Vapor Permeability and Explanation of Thickness Effects. J. Food Sci. 2010, 58, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussalah, M.; Caillet, S.; Salmiéri, S.; Saucier, L.; Lacroi, M. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Effects of Milk Protein-Based Film Containing Essential Oils for the Preservation of Whole Beef Muscle. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5598–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlieghere, F.; Vermeulen, A.; Debevere, J. Chitosan: Antimicrobial activity, interactions with food components and applicability as a coating on fruit and vegetables. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Film | Thickness (mm) | TS (MPa) | EB (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 0.147 ± 0.023a | 9.53 ± 0.33a | 4.95 ± 0.07b |
| WPI/TNPs | 0.139 ± 0.037a | 11.42 ± 0.33c | 4.26 ± 0.07a |
| WPI/TNTs | 0.141 ± 0.042a | 13.45 ± 0.41d | 4.96 ± 0.66b |
| WPNFs | 0.142 ± 0.034a | 10.49 ± 0.35b | 5.88 ± 0.66d |
| WPNFs/ TNPs | 0.144 ± 0.035a | 14.73 ± 0.31e | 5.36 ± 0.70c |
| WPNFs/TNTs | 0.147 ± 0.051a | 15.49 ± 0.35f | 5.83 ± 0.09d |
| Film | MC (%) | Solubility in Water (%) | Transparency (%) | WVP (10 −11gm/m2sPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 33.1 ± 1.1d | 42.2 ± 0.9f | 30.4 ± 1.1c | 8.1 ± 0.21f |
| WPI/TNP | 34.3 ± 1.1e | 35.2 ± 1.3e | 25.4 ± 2.1a | 5.7 ± 0.21d |
| WPI/TNT | 35.6 ± 1.7f | 34.6 ± 1.4d | 27.5 ± 2.2b | 4.9 ± 0.32c |
| WPNF | 24.1 ± 1.1a | 29.2 ± 1.3c | 53.1 ± 0.9f | 6.2 ± 0.32e |
| WPNF/TNP | 27.6 ± 2.1c | 27.6 ± 2.1b | 40.1 ± 3.1d | 4.4 ± 0.22b |
| WPNF/TNT | 24.3 ± 0.7b | 26.3 ± 1.5a | 48.6 ± 1.2e | 3.7 ± 0.13a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, G.; Liu, C.; Jiang, B.; Xu, J. Effect of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Coating based on Whey Protein Nanofibrils with TiO2 Nanotubes on the Quality and Shelf Life of Chilled Meat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051184
Feng Z, Li L, Wang Q, Wu G, Liu C, Jiang B, Xu J. Effect of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Coating based on Whey Protein Nanofibrils with TiO2 Nanotubes on the Quality and Shelf Life of Chilled Meat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051184
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Zhibiao, Lele Li, Qiannan Wang, Guangxin Wu, Chunhong Liu, Bin Jiang, and Jing Xu. 2019. "Effect of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Coating based on Whey Protein Nanofibrils with TiO2 Nanotubes on the Quality and Shelf Life of Chilled Meat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051184
APA StyleFeng, Z., Li, L., Wang, Q., Wu, G., Liu, C., Jiang, B., & Xu, J. (2019). Effect of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Coating based on Whey Protein Nanofibrils with TiO2 Nanotubes on the Quality and Shelf Life of Chilled Meat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051184