Actin Cytoskeleton as Actor in Upstream and Downstream of Calcium Signaling in Plant Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Actin Cytoskeleton Adjusts Calcium Homeostasis
3. The Actin Cytoskeleton Acts a Potential Downstream of Calcium Signaling
3.1. Calcium Directly Binds to ABPs to Regulate Their Activity and Effect on Actin Dynamics
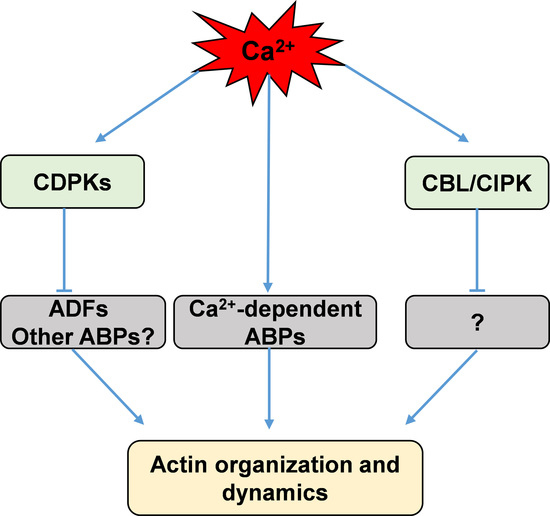
3.2. Calcium Indirectly Regulates the Actin Dynamics Via Calcium-Stimulated Protein Kinases, CDPKs
3.3. ROP GTPase Signaling Mediates Actin Cytoskeleton Regulation by Calcium
4. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABA | abscisic acid |
| ABPs | actin-binding proteins |
| ADF | actin-depolymerizing factor |
| CB | cytochalasin B |
| CBL | calcineurin B-like protein |
| CD | cytochalasin D |
| CDPKs | calcium-dependent protein kinases |
| CIPKs | CBL-interacting protein kinases |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| F-actin | filamentous actin |
| G-actin | globular actin |
| Jas | jasplakinolide |
| Lat A | latrunculin A |
| Lat B | latrunculin B |
| MAP18 | MICROTUBULE-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN18 |
| MDP25 | MICROTUBULE-DESTABILIZING PROTEIN25 |
| MS | mechanosensitive |
| MT | microtubule |
| PA | phosphatidic acid |
| PM | plasma membrane |
| PIP2 | phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate |
| ROP GTPases | The rho family of small GTPases |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SA | stretch-activated |
| VLN | VILLIN |
| Y2H | yeast two-hybrid |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | linear dichroism |
References
- Hepler, P.K. Calcium: A central regulator of plant growth and development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2142–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, A.N.; Kudla, J.; Sanders, D. The language of calcium signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 593–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.; Roux, S.J. Role of Ca2+ in mediating plant responses to extracellular ATP and ADP. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, C.; Oldroyd, G.E. Plant signalling in symbiosis and immunity. Nature 2017, 543, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldon, D.; Mbengue, M.; Mazars, C.; Galaud, J.P. Calcium signalling in plant biotic interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, K.; Kudla, J. Calcium decoding mechanisms in plants. Biochimie 2011, 93, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranty, B.; Aldon, D.; Cotelle, V.; Galaud, J.P.; Thuleau, P.; Mazars, C. Calcium sensors as key hubs in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudla, J.; Becker, D.; Grill, E.; Hedrich, R.; Hippler, M.; Kummer, U.; Parniske, M.; Romeis, T.; Schumacher, K. Advances and current challenges in calcium signaling. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staiger, C.J.; Blanchoin, L. Actin dynamics: Old friends with new stories. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, T.; Sano, T.; Hasezawa, S. Actin microfilament dynamics and actin side-binding proteins in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Signaling to actin stochastic dynamics. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hussey, P.J.; Ren, H. ACTIN BINDING PROTEIN 29 from Lilium pollen plays an important role in dynamic actin remodeling. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1930–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perico, C.; Sparkes, I. Plant organelle dynamics: Cytoskeletal control and membrane contact sites. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y. The cytoskeleton in the pollen tube. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 28, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, S. Organization and regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in the pollen tube. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Kong, S.G. Actin-mediated movement of chloroplasts. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, 210310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smertenko, A.P.; Jiang, C.J.; Simmons, N.J.; Weeds, A.G.; Davies, D.R.; Hussey, P.J. Ser6 in the maize actin-depolymerizing factor, ZmADF3, is phosphorylated by a calcium-stimulated protein kinase and is essential for the control of functional activity. Plant J. 1998, 14, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allwood, E.G.; Smertenko, A.P.; Hussey, P.J. Phosphorylation of plant actin-depolymerising factor by calmodulin-like domain protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 2001, 499, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smertenko, A.P.; Deeks, M.J.; Hussey, P.J. Strategies of actin reorganisation in plant cells. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 3019–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.F.; Fan, L.M.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhang, W.; Wu, W.H. Ca2+-permeable channels in the plasma membrane of Arabidopsis pollen are regulated by actin microfilaments. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3892–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, L.; Vidali, L.; Domínguez, J.; Pérez, H.; Sánchez, F.; Hepler, P.K.; Quinto, C. Rearrangement of actin microfilaments in plant root hairs responding to Rhizobium etli nodulation signals. Plant Physiol. 1998, 116, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, L.; Lovy-Wheeler, A.; Kunkel, J.G.; Hepler, P.K. Pollen tube growth oscillations and intracellular calcium levels are reversibly modulated by actin polymerization. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Baluska, F.; Samaj, J.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q. Disruption of actin filaments induces mitochondrial Ca2+ release to the cytoplasm and [Ca2+]c changes in Arabidopsis root hairs. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Huang, S.; Yuan, M.; Schumaker, K.S.; et al. The actin-related Protein2/3 complex regulates mitochondrial-associated calcium signaling during salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4544–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.H.; Acharya, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. Interaction between calcium and actin in guard cell and pollen signaling networks. Plants 2013, 2, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, T.V.; Evans, M.J.; Woolfenden, H.C.; Morris, R.J. Towards the physics of calcium signalling in plants. Plants 2013, 2, 541–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidchik, V.; Shabala, S.; Isayenkov, S.; Cuin, T.; Pottosin, I. Calcium transport across plant membranes: Mechanisms and functions. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurusu, T.; Kuchitsu, K.; Nakano, M.; Nakayama, Y.; Iida, H. Plant mechanosensing and Ca2+ transport. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Navazio, L.; Szabo, I. The contribution of organelles to plant intracellular calcium signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 4175–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwiebert, E.M.; Mills, J.W.; Stanton, B.A. Actin-based cytoskeleton regulates a chloride channel and cell volume in a renal cortical collecting duct cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7081–7089. [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello, H.F. Role of actin filament organization in cell volume and ion channel regulation. J. Exp. Zool. 1997, 279, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmey, P. The cytoskeleton and cell signaling: Component localization and mechanical coupling. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fan, L.M. Actin dynamics regulates voltage-dependent calcium-permeable channels of the vicia faba guard cell plasma membrane. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2009, 51, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazars, C.; Thion, L.; Thuleau, P.; Graziana, A.; Knight, M.R.; Moreau, M.; Ranjeva, R. Organization of cytoskeleton controls the changes in cytosolic calcium of cold-shocked Nicotiana plumbaginifolia protoplasts. Cell Calcium 1997, 22, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvar, B.L.; Sangwan, V.; Omann, F.; Dhindsa, R.S. Early steps in cold sensing by plant cells: The role of actin cytoskeleton and membrane fluidity. Plant J. 2000, 23, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka-Postupolska, D.; Clark, G. Annexins as overlooked regulators of membrane trafficking in plant cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, J.M.; Massa, G.D.; Gilroy, S. Ionic signaling in plant responses to gravity and touch. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2002, 21, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushart, T.J.; Cannon, A.; Clark, G.; Roux, S.J. Structure and function of CrACA1, the major PM-type Ca2+-ATPase, expressed at the peak of the gravity-directed trans-cell calcium current in spores of the fern Ceratopteris richardii. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, M.; Furuichi, T.; Tatsumi, H.; Sokabe, M. Cytoplasmic calcium increases in response to changes in the gravity vector in hypocotyls and petioles of Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, H.; Furuichi, T.; Nakano, M.; Toyota, M.; Hayakawa, K.; Sokabe, M.; Iida, H. Mechanosensitive channels are activated by stress in the actin stress fibres, and could be involved in gravity sensing in plants. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, V.; Moss, S.E. Annexins: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 331–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, V.; Creutz, C.E.; Moss, S.E. Annexins: Linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2005, 6, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.M. Annexin-mediated calcium signalling in plants. Plants (Basel) 2014, 3, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, J.; Clark, G.; Roux, S.J. ANN1 and ANN2 function in post-phloem sugar transport in root tips to affect primary root growth. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, K. A cotton annexin protein AnxGb6 regulates fiber elongation through its interaction with actin 1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; Yuan, S.; Qian, D.; Nan, Q.; An, L.; Xiang, Y. Annexin5 plays a vital role in Arabidopsis pollen development via Ca2+-dependent membrane trafficking. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldogh, I.R.; Yang, H.C.; Nowakowski, W.D.; Karmon, S.L.; Hays, L.G.; Yates, J.R.; Pon, L.A. Arp2/3 complex and actin dynamics are required for actin-based mitochondrial motility in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3162–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacRobbie, E.A.; Kurup, S. Signalling mechanisms in the regulation of vacuolar ion release in guard cells. New Phytol. 2007, 175, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, T.; Liu, X.M.; Li, J.J.; Sun, J.B.; Song, L.N.; Mao, T.L. Arabidopsis microtubule-destabilizing protein25 functions in pollen tube growth by severing actin filaments. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Nan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bai, Q.; Zhang, P.; An, L.; Xiang, Y. Gelsolin-like domain 3 plays vital roles in regulating the activities of the lily villin/gelsolin/fragmin superfamily. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, G.; Yang, Z. Rop GTPase-dependent dynamics of tip-localized F-actin controls tip growth in pollen tubes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.U.; Gu, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Yang, Z. Oscillatory ROP GTPase activation leads the oscillatory polarized growth of pollen tubes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5385–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.; Parrotta, L.; Cresti, M. Organelle trafficking, the cytoskeleton, and pollen tube growth. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, D.; Staiger, C.J. The actin cytoskeleton: Functional arrays for cytoplasmic organization and cell shape control. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, D.; Liu, Q.; Lisboa, S.; Scherer, G.E.; Quader, H.; Malho, R. Phosphoinositides and phosphatidic acid regulate pollen tube growth and reorientation through modulation of [Ca2+]c and membrane secretion. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Xu, G.; Yang, Z.B. Calcium participates in feedback regulation of the oscillating ROP1 Rho GTPase in pollen tubes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22002–22007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bascom, B.C., Jr.; Winship, L.J.; Bezanilla, M. Simultaneous imaging and functional studies reveal a tight correlation between calcium and actin networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2869–E2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Xiang, Y. The function of actin-binding proteins in pollen tube growth. Protoplasma 2007, 230, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y. The actin cytoskeleton and signaling network during pollen tube tip growth. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Z. Signaling in pollen tube growth: Crosstalk, feedback, and missing links. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Wan, A.R.; Jauh, G.Y. An actin-binding protein, LlLIM1, mediates calcium and hydrogen regulation of actin dynamics in pollen tubes. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiang, Y.; Hou, J.; Ren, H.Y. ABP41 is involved in the pollen tube development via fragmenting actin filaments. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qu, X.L.; Bao, C.C.; Khurana, P.; Wang, Q.N.; Xie, Y.R.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, N.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J.; et al. Arabidopsis VILLIN5, an actin filament bundling and severing protein, is necessary for normal pollen tube growth. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2749–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuga, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Dieterle, M.; Moes, D.; Moreau, F.; Tholl, S.; Steinmetz, A.; Thomas, C. Arabidopsis LIM proteins: A family of actin bundlers with distinct expression patterns and modes of regulation. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3034–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, E.; Xu, Q.; Wang, M.; Rui, Y.; Liu, B.; Yuan, M.; Fu, Y. MAP18 regulates the direction of pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis by modulating F-actin organization. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.R.; Wang, J.; Chen, N.Z.; Huang, S.J. Arabidopsis villins promote actin turnover at pollen tube tips and facilitate the construction of actin collars. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, R.; Huang, S.; Fu, Y. Arabidopsis RIC1 severs actin filaments at the apex to regulate pollen tube growth. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1140–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro, S.; Kameyama, K.; Kanzawa, N.; Tamiya, T.; Mabuchi, I.; Tsuchiya, T. The gelsolin/fragmin family protein identified in the higher plant Mimosa pudica. J. Biochem. 2001, 130, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Du, F.; Cao, L.; Dong, H.; Ren, H. Arabidopsis VILLIN4 is involved in root hair growth through regulating actin organization in a Ca2+-dependent manner. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Wu, F.; Sheng, P.; Wang, J.; et al. VLN2 regulates plant architecture by affecting microfilament dynamics and polar auxin transport in rice. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2829–2845. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayasu, T.; Yokota, E.; Shimmen, T. Purification of an actin-binding protein composed of 115-kDa polypeptide from pollen tubes of lily. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 249, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, E.; Vidali, L.; Tominaga, M.; Tahara, H.; Orii, H.; Morizane, Y.; Hepler, P.K.; Shimmen, T. Plant 115-kDa actin filament bundling protein, P-115-ABP, is a homologue of plant villin and is widely distributed in cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidali, L.; Yokota, E.; Cheung, A.Y.; Shimmen, T.; Hepler, P.K. The 135 kDa actin-bundling protein from Lilium longiflorum pollen is the plant homologue of villin. Protoplasma 1999, 209, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, E.; Shimmen, T. The 135-kDa actin-bundling protein from lily pollen tubes arranges F-actin into bundles with uniform polarity. Planta 1999, 209, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Hou, J.; Chen, X.; Chaudhry, F.; Staiger, C.J.; Ren, H. Identification and characterization of a Ca2+-dependent actin filament-severing protein from lily pollen. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Qin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, M.; et al. MDP25, a novel calcium regulatory protein, mediates hypocotyl cell elongation by destabilizing cortical microtubules in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 4411–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, D.; Hayashi, A.; Temmei, Y.; Kanzawa, N.; Tsuchiya, T. Biochemical and immunohistochemical characterization of Mimosa annexin. Planta 2004, 219, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, E.; Muto, S.; Shimmen, T. Inhibitory regulation of higher-plant myosin by Ca2+ ions. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, C.M.; Gant, S.J.; Bowles, D.J. Tomato annexins p34 and p35 bind to F-actin and display nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity inhibited by phospholipid binding. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Blanchoin, L.; Chaudhry, F.; Franklin-Tong, V.E.; Staiger, C.J. A gelsolin-like protein from Papaver rhoeas pollen (PrABP80) stimulates calcium-regulated severing and depolymerization of actin filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 23364–23375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giehl, K.; Valenta, R.; Rothkegel, M.; Ronsiek, M.; Mannherz, H.G.; Jockusch, B.M. Interaction of plant profilin with mammalian actin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 226, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelroizen, I.; Didry, D.; Christensen, H.; Chua, N.H.; Carlier, M.F. Role of nucleotide exchange and hydrolysis in the function of profilin in actin assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12302–12309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovar, D.R.; Drøbak, B.K.; Staiger, C.J. Maize profilin isoforms are functionally distinct. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, P.; Henty, J.L.; Huang, S.; Staiger, A.M.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis VILLIN1 and VILLIN3 have overlapping and distinct activities in actin bundle formation and turnover. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2727–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S. Arabidopsis VILLIN2 and VILLIN3 act redundantly in sclerenchyma development via bundling of actin filaments. Plant J. 2012, 71, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.Q.; Yamamoto, M.; Mejillano, M.; Yin, H.L. Gelsolin, a multifunctional actin regulatory protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33179–33182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Qu, X.; Zhang, R. Plant villins: Versatile actin regulatory proteins. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, S.; Larsson, M.; Robinson, R.C.; Burtnick, L.D. Gelsolin: The tail of a molecular gymnast. Cytoskeleton 2013, 70, 360–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burtnick, L.D.; Koepf, E.K.; Grimes, J.; Jones, E.Y.; Stuart, D.I.; McLaughlin, P.J.; Robinson, R.C. The crystal structure of plasma gelsolin: Implications for actin severing, capping, and nucleation. Cell 1997, 90, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmirski, S.L.; Isaacson, R.L.; An, C.; Buckle, A.; Johnson, C.M.; Daggett, V.; Fersht, A.R. Loss of a metal-binding site in gelsolin leads to familial amyloidosis-Finnish type. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Robinson, R.C.; Gao, L.Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Brunet, A.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Arabidopsis VILLIN1 generates actin filament cables that are resistant to depolymerization. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, H.; Burtnick, L.D.; Mejillano, M.; Yin, H.L.; Robinson, R.C.; Choe, S. The calcium activation of gelsolin: Insights from the 3A˚ structure of the G4-G6/actin complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 324, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Meng, D.; Gu, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, T. Apple S-RNase interacts with an actin-binding protein, MdMVG, to reduce pollen tube growth by inhibiting its actin-severing activity at the early stage of self-pollination induction. Plant J. 2018, 95, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Hoffman, L.M.; Beckerle, M.C. LIM proteins in actin cytoskeleton mechanoresponse. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moes, D.; Gatti, S.; Hoffmann, C.; Dieterle, M.; Moreau, F.; Neumann, K.; Schumacher, M.; Diederich, M.; Grill, E.; Shen, W.H.; et al. A LIM domain protein from tobacco involved in actin-bundling and histone gene transcription. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Hoffmann, C.; Dieterle, M.; Van Troys, M.; Ampe, C.; Steinmetz, A. Tobacco WLIM1 is a novel F-actin binding protein involved in actin cytoskeleton remodeling. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2194–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Moreau, F.; Dieterle, M.; Hoffmann, C.; Gatti, S.; Hofmann, C.; Van Troys, M.; Ampe, C.; Steinmetz, A. The LIM domains of WLIM1 define a new class of actin bundling modules. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 33599–33608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Xiao, Y.H.; Hou, L.; Luo, X.Y.; Li, D.M.; Pei, Y. Cloning and expression analysis of a LIM-domain protein gene from cotton (Gossypium hirsuturm L.). Yi Chuan Xue Bao 2003, 30, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, N.N.; Li, D.D.; Li, X.B. A cotton LIM domain-containing protein (GhWLIM5) is involved in bundling actin filaments. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 66, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.B.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Wu, X.M.; Li, C.L.; Luo, M.; Wu, S.J.; Kong, Z.S.; Pei, Y.; Jiao, G.L.; et al. The dual functions of WLIM1a in cell elongation and secondary wall formation in developing cotton fibers. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4421–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, Y.; Nagasaki, N.; Tomioka, R.; Suito, M.; Kamiya, T.; Maeshima, M. Molecular properties of a novel, hydrophilic cation-binding protein associated with the plasma membrane. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasaki, N.; Tomioka, R.; Maeshima, M. A hydrophilic cation-binding protein of Arabidopsis thaliana, AtPCaP1, is localized to plasma membrane via N-myristoylation and interacts with calmodulin and the phosphatidylinositol phosphates PtdIns (3,4,5) P (3) and PtdIns (3,5) P (2). FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2267–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, B.Q.; Wang, C.; Jin, L.F.; Zhao, Q.; Yuan, M. Arabidopsis MICROTUBULE-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN18 functions in directional cell growth by destabilizing cortical microtubules. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Nagasaki-Takeuchi, N.; Ide, Y.; Maeshima, M. An Arabidopsis hydrophilic Ca2+-binding protein with a PEVK-rich domain, PCaP2, is associated with the plasma membrane and interacts with calmodulin and phosphatidylinositol phosphates. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, E.; Yuan, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, L. PCaP2 regulates nuclear positioning in growing Arabidopsis thaliana root hairs by modulating filamentous actin organization. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wasteneys, G.; Yang, Z. Arabidopsis interdigitating cell growth requires two antagonistic pathways with opposing action on cell morphogenesis. Cell 2005, 120, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhu, L.; Wen, M.; Yang, Z. A ROP GTPase signaling pathway controls cortical microtubule ordering and cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, L.; Ehrhardt, D.; Yang, Z.; Fu, Y. Rho GTPase signaling activates microtubule severing to promote microtubule ordering in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, S.; Ren, H. Profilin as a regulator of the membrane-actin cytoskeleton interface in plant cells. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Henty-Ridilla, J.L.; Blanchoin, L.; Staiger, C.J. Profilin-dependent nucleation and assembly of actin filaments controls cell elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 220–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, M.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Huang, S. Profilin regulates apical actin polymerization to control polarized pollen tube growth. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1694–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.; Zhai, H.; Shi, W.; Wang, J.; Jia, H.; Xiang, Y.; An, L. Overexpression of profilin 3 affects cell elongation and F-actin organization in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Qiao, Z.; Chua, K.P.; Tursic, A.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.G.; Mu, Y.; Hou, X.; Miao, Y. Profilin Negatively regulates formin-mediated actin assembly to modulate PAMP-triggered plant immunity. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1882–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guhathakurta, P.; Prochniewicz, E.; Thomas, D.D. Actin-Myosin interaction: Structure, function and drug discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.D.; Cooper, J.A. Actin, a central player in cell shape and movement. Science 2009, 326, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Haigler, H.T. Characterization of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding and phosphorylation of lipocortin I. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 6931–6937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khanna, N.C.; Helwig, E.D.; Ikebuchi, N.W.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Bajwa, R.; Waisman, D.M. Purification and characterization of annexin proteins from bovine lung. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 4852–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traverso, V.; Morris, J.F.; Flower, R.J.; Buckingham, J. Lipocortin 1 (annexin 1) in patches associated with the membrane of a lung adenocarcinoma cell line and in the cell cytoplasm. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babiychuk, E.B.; Palstra, R.J.; Schaller, J.; Kämpfer, U.; Draeger, A. Annexin VI participates in the formation of a reversible, membrane-cytoskeleton complex in smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35191–35195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzima, E.; Trotter, P.J.; Orchard, M.A.; Walker, J.H. Annexin V relocates to the platelet cytoskeleton upon activation and binds to a specific isoform of actin. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 4720–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrazzini, E.; Vitale, A. Protein biosynthesis and maturation in the ER. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1675, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Arsova, B.; Watt, M.; Usadel, B. Monitoring of plant protein post-translational modifications using targeted proteomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K. Signaling mechanisms and functional roles of cofilin phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Tipakornsaowapak, T.; Zheng, L.; Mu, Y.; Lewellyn, E. Phospho-regulation of intrinsically disordered proteins for actin assembly and endocytosis. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2762–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, C.; Romanowsky, S.M.; Barron, Y.D.; Garg, S.; Azuse, C.L.; Curran, A.; Davis, R.M.; Hatton, J.; Harmon, A.C.; Harper, J.F. Calcium-dependent protein kinases regulate polarized tip growth in pollen tubes. Plant J. 2009, 59, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Li, S.; Asim, M.; Mao, J.; Xu, D.; Ullah, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H. The Arabidopsis Calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) and their roles in plant growth regulation and abiotic stress responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam-Evans, C.; Harmon, A.C.; Palevitz, B.A.; Fechheimer, M.; Cormier, M.J. Calcium-dependent protein kinase is localized with F-actin in plant cells. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 1989, 12, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, E.W.; Patharkar, O.R.; Hegeman, A.D.; Taybi, T.; Cushman, J.C. Autophosphorylation and subcellular localization dynamics of a salt- and water deficit-induced calcium-dependent protein kinase from ice plant. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1430–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlier, M.F.; Santolini, J.; Lanrent, V.; Melki, R.; Didry, D.; Hong, Y.; Xia, G.X.; Chua, N.H.; Pantolni, D. Actin depolymerizing factor (ADF/cofilin) enhances the rate of filament turnover: Implication in actin-based motility. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 136, 1307–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkin, V.E.; Orlova, A.; Kudryashov, D.S.; Solodukhin, A.; Reisler, E.; Schröder, G.F.; Egelman, E.H. Remodeling of actin filaments by ADF/cofilin proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20568–20572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.; Roland, J.; Boujemaa-Paterski, R.; Kang, H.; McCullough, B.R.; Reymann, A.C.; Guérin, C.; Martiel, J.L.; De la Cruz, E.M.; Blanchoin, L. Cofilin tunes the nucleotide state of actin filaments and severs at bare and decorated segment boundaries. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Q.; Qian, D.; Niu, Y.; He, Y.X.; Tong, S.F.; Niu, Z.M.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; An, L.; Wan, D.; et al. Plant actin depolymerizing factors possess opposing biochemical properties arising from key amino acid changes throughout evolution. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.J.; Weeds, A.G.; Hussey, P.J. The maize actin depolymerizing factor, ZmADF3, redistributes to the growing tip of elongating root hairs and can be induced to translocate into the nucleus with actin. Plant J. 1997, 12, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.H.; Xia, G.X.; Hong, Y.; Ramachandran, S.; Kost, B.; Chua, N.H. ADF proteins are involved in the control of flowering and regulate F-actin organization, cell expansion, and organ growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Cheung, A.Y.; Wu, H.M. Actin-depolymerizing factor mediates Rac/Rop GTPase-regulated pollen tube growth. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, R.C.; Vidali, L.; Kleinman, K.P.; Bezanilla, M. Actin depolymerizing factor is essential for viability in plants, and its phosphoregulation is important for tip growth. Plant J. 2008, 54, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uno, Y.; Rodriguez, M.M.A.; Maher, E.; Cushman, J.C. Identification of proteins that interact with catalytically active calcium-dependent protein kinases from Arabidopsis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2009, 281, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.H.; Hong, Y. Arabidopsis CDPK6 phosphorylates ADF1 at N-terminal serine 6 predominantly. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 1715–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y. Arabidopsis SOS3 plays an important role in salt tolerance by mediating calcium-dependent microfilament reorganization. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.K.; Kanwar, P.; Samtani, H.; Kaur, K.; Jha, S.K.; Pandey, G.K. Alternative splicing of CIPK3 results in distinct target selection to propagate aba signaling in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; John, S.J.; Chen, M.; Chang, J.; Yang, G.; He, G. A CBL-interacting protein kinase TaCIPK27 confers drought tolerance and exogenous ABA sensitivity in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 123, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, K.W.; Zielinski, R.E.; Huber, S.C. Revisiting paradigms of ca2+ signaling protein kinase regulation in plants. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hao, L.; Zhu, B.; Jiang, Z. Plant calcium signaling in response to potassium deficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.Z.; Deng, M.; Li, L.; Yang, B.; Li, H.; Deng, H.; Jiang, Y.Q. Rapeseed calcineurin B-like protein CBL4, interacting with CBL-interacting protein kinase CIPK24, modulates salt tolerance in plants. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, C.; Traubenik, S.; Zanetti, M.E.; Blanco, F.A. Small GTPases in plant biotic interactions. Small GTPases 2017, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feiquelman, G.; Fu, Y.; Yalovsky, S. Rop GTPases structure-function and signaling pathyways. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascom, C.J.R.; Burkart, G.M.; Mallett, D.R.; O’Sullivan, J.E.; Tomaszewski, A.J.; Walsh, K.; Bezanilla, M. Systematic survey of the function of ROP regulators and effectors during tip growth in the moss P. patens. J. Exp. Bot. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Claes, A.R.; Grebe, T.; Hermkes, R.; Viotti, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Grebe, M. Auxin and ROP GTPase signaling of polar nuclear migration in root epidermal hair cells. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lu, H.; Li, W.; Yuan, M.; Fu, Y. A ROP2-RIC1 pathway fine-tunes microtubule reorganization for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkart, G.M.; Baskin, T.I.; Bezanilla, M. A family of ROP proteins that suppresses actin dynamics, and is essential for polarized growth and cell adhesion. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2553–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, D.; Pleskot, R.; Pejchar, P.; Potocký, M.; Trpkošová, P.; Cwiklik, L.; Vukašinovi, N.; Sternberg, H.; Yalovsky, S.; Zárský, V. Exocyst SEC3 and phosphoinositides define sites of exocytosis in pollen tube initiation and growth. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 980–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, D.; Yalovsky, S. Cell polarity signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michard, E.; Simon, A.A.; Tavares, B.; Wudick, M.M.; Feijó, J.A. Signaling with ions: The keystone for apical cell growth and morphogenesis in pollen tubes. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Gu, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, Z. A genome-wide analysis of Arabidopsis Rop-interactive CRIB motif-containing proteins that act as Rop GTPase targets. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 2841–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z. ROP/RAC GTPase: An old new master regulator for plant signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| ABPs | Species | Tissues | Activities on Actin Organization | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 115ABP | Lilium longiflorum | Pollen tube | MF nucleation, capping, and bundling | [71,72] |
| 135ABP | Lilium longiflorum | Pollen tube | MF nucleation, capping, and bundling | [73,74] |
| ABP29 | Lilium longiflorum | Pollen tube | MF nucleation, capping, and severing | [12] |
| ABP41 | Lilium davidii | Pollen tube | MF severing and capping | [62,75] |
| AnxGb6 | Gossypium barbadense | Fiber | Actin binding | [45] |
| Fragmin-like 42-kD protein | Mimosa pudica | Petiole | MF severing | [68] |
| LILIM1 | Lilium longiflorum | Pollen tube | MF bundling | [61] |
| MAP18 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Pollen tube | MF severing | [65] |
| MdMVG | Malus domestica | Pollen tube | MF severing | [75] |
| MDP25 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Pollen tube | MF severing | [49,76] |
| Mimosa annexin | Mimosa pudica | Pulvinus | MF binding | [77] |
| Myosin | Lilium longiflorum | None | MF binding | [78] |
| OsVLN2 | Oryza sativa | Roots and Shoots | MF bundling, severing, and capping | [70] |
| P34/35 | Lycopersicon esculentum | None | MF binding | [79] |
| PLIM2c | Arabidopsis thaliana | Pollen and Pollen tube | MF bundling | [64] |
| PrABP80 | Papaver rhoeas | None | MF nucleation, capping and severing | [80] |
| Profilin | Zea mays | None | Sequester G-Actin | [81,82,83] |
| RIC1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Pollen tube | MF severing and capping | [67] |
| VLN2/5 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Pollen tube | MF bundling, severing and capping | [63,66] |
| VLN2/3 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Sclerenchyma | MF bundling, severing and capping | [84,85] |
| VLN4 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Root hair | MF bundling, severing and capping | [69] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, D.; Xiang, Y. Actin Cytoskeleton as Actor in Upstream and Downstream of Calcium Signaling in Plant Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061403
Qian D, Xiang Y. Actin Cytoskeleton as Actor in Upstream and Downstream of Calcium Signaling in Plant Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061403
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Dong, and Yun Xiang. 2019. "Actin Cytoskeleton as Actor in Upstream and Downstream of Calcium Signaling in Plant Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061403
APA StyleQian, D., & Xiang, Y. (2019). Actin Cytoskeleton as Actor in Upstream and Downstream of Calcium Signaling in Plant Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061403