Structural and Computational Characterization of Disease-Related Mutations Involved in Protein-Protein Interfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structural Characterization of Proteins and Interactions in Diseases Detected in Newborn Screening
2.2. Residues Energetically Relevant for the Interaction Are More Likely to Be at the Interface Core
2.3. Pathogenic and Neutral Variants Are Differentially Distributed in Protein-Protein Interfaces
2.4. Amino Acid Substitution Susceptibility in the Interface Is Larger in Pathogenic Variants
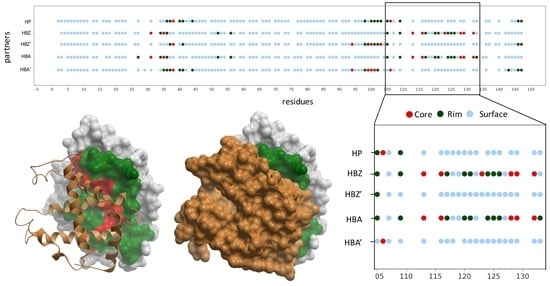
2.5. Docking-Based Interface Prediction for Further Characterization of Protein Sequence Variants: A Case Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Interaction and Mutational Data
4.2. Interacting Proteins Analysis
4.3. Experimental Protein-Protein Interfaces
4.4. Predicted Protein-Protein Interfaces
4.5. Energetic Characterization of Protein-Protein Interfaces
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| SNV | Single nucleotide variant |
| SAV | Single amino acid variant |
| PPI | Protein-protein interaction |
| HBB | Hemoglobin subunit beta |
| HBZ | Hemoglobin subunit zeta |
| HBA | Hemoglobin subunit alpha |
| HP | Haptoglobin |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| MSA | Multiple Sequence Alignment |
| ASA | Accessible Surface Area |
| NIP | Normalized Interface Propensity |
| HADHA | Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase trifunctional multienzyme complex subunit α |
References
- The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; Boerwinkle, E.; Doddapaneni, H.; Han, Y.; Korchina, V.; Lee, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Fang, X.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Muir, P.; Li, S.; Lou, S.; Wang, D.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Salichos, L.; Zhang, J.; Weinstock, G.M.; Isaacs, F.; Rozowsky, J.; et al. The real cost of sequencing: Scaling computation to keep pace with data generation. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ankala, A.; Wilcox, W.R.; Hegde, M.R. Solving the molecular diagnostic testing conundrum for Mendelian disorders in the era of next-generation sequencing: Single-gene, gene panel, or exome/genome sequencing. Genet. Med. 2014, 17, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, A.; Razali, R.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. Protein-protein interaction sites are hot spots for disease-associated nonsynonymous SNPs. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 33, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhou, H.; Skolnick, J. Insights into disease-associated mutations in the human proteome through protein structural analysis. Structure 2015, 23, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jubb, H.C.; Pandurangan, A.P.; Turner, M.A.; Ochoa-Montaño, B.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. Mutations at protein-protein interfaces: Small changes over big surfaces have large impacts on human health. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Boil. 2017, 128, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, N.; Bross, P.; Vang, S.; Christensen, J.H. Protein Misfolding and Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2006, 7, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, A.; O’Connor, T. Protein aggregation diseases: Pathogenicity and therapeutic perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennessen, J.A.; Bigham, A.W.; O’Connor, T.D.; Fu, W.; Kenny, E.E.; Gravel, S.; McGee, S.; Do, R.; Liu, X.; Jun, G.; et al. Evolution and Functional Impact of Rare Coding Variation from Deep Sequencing of Human Exomes. Science 2012, 337, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaser, R.; Adusumalli, S.; Leng, S.N.; Sikic, M.; Ng, P.C. SIFT missense predictions for genomes. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Chem. Boil. 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niroula, A.; Urolagin, S.; Vihinen, M. PON-P2: Prediction method for fast and reliable identification of harmful variants. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ferrando, V.; Gazzo, A.; De La Cruz, X.; Orozco, M.; Gelpí, J.L. PMut: A web-based tool for the annotation of pathological variants on proteins, 2017 update. Acids Res. 2017, 45, W222–W228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera, C.; Lois, S.; De La Cruz, X. Prediction of pathological mutations in proteins: The challenge of integrating sequence conservation and structure stability principles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2013, 4, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyaev, S.R. Inferring causality and functional significance of human coding DNA variants. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, R10–R17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yates, C.M.; Sternberg, M.J. The Effects of Non-Synonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (nsSNPs) on Protein–Protein Interactions. J. Mol. Boil. 2013, 425, 3949–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, A.; Sternberg, M.J. The Contribution of Missense Mutations in Core and Rim Residues of Protein–Protein Interfaces to Human Disease. J. Mol. Boil. 2015, 427, 2886–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kucukkal, T.G.; Petukh, M.; Li, L.; Alexov, E. Structural and physico-chemical effects of disease and non-disease nsSNPs on proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Boil. 2015, 32, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahni, N.; Yi, S.; Taipale, M.; Bass, J.I.F.; Coulombe-Huntington, J.; Yang, F.; Peng, J.; Weile, J.; Karras, G.I.; Wang, Y.; et al. Widespread Macromolecular Interaction Perturbations in Human Genetic Disorders. Cell 2015, 161, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agius, R.; Torchala, M.; Moal, I.H.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Bates, P.A. Characterizing Changes in the Rate of Protein-Protein Dissociation upon Interface Mutation Using Hotspot Energy and Organization. PLoS Comput. Boil. 2013, 9, e1003216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guharoy, M.; Chakrabarti, P. Conservation and relative importance of residues across protein-protein interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15447–15452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sipos, B.; Goldman, N.; Laskowski, R.A.; Parks, S.L.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Thornton, J.M. Amino acid changes in disease-associated variants differ radically from variants observed in the 1000 genomes project dataset. PLoS Comput. Boil. 2013, 9, e1003382. [Google Scholar]
- Thusberg, J.; Olatubosun, A.; Vihinen, M. Performance of mutation pathogenicity prediction methods on missense variants. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosca, R.; Ceol, A.; Aloy, P. Interactome3D: Adding structural details to protein networks. Nat. Chem. Boil. 2012, 10, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Thijssen, B.; Das, J.; Lipkin, S.M.; Yu, H. Three-dimensional reconstruction of protein networks provides insight into human genetic disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kammenga, J.E. The background puzzle: How identical mutations in the same gene lead to different disease symptoms. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3362–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas-Bautista, D.; Fernández-Recio, J. Docking-based modeling of protein-protein interfaces for extensive structural and functional characterization of missense mutations. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, O.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Hot Regions in Protein–Protein Interactions: The Organization and Contribution of Structurally Conserved Hot Spot Residues. J. Mol. Boil. 2005, 345, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teppa, E.; Zea, D.J.; Marino-Buslje, C.; Marino-Buslje, C.; Marino-Buslje, C. Protein–protein interactions leave evolutionary footprints: High molecular coevolution at the core of interfaces. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bogan, A.; Thorn, K.S. Anatomy of hot spots in protein interfaces. J. Mol. Boil. 1998, 280, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, I.S.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Hot spots-A review of the protein-protein interface determinant amino-acid residues. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 68, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.K.; Zhang, S. Computational Prediction of Protein Hot Spot Residues. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 18, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, S.; Ammari, M.; Aranda, B.; Breuza, L.; Briganti, L.; Broackes-Carter, F.; Campbell, N.H.; Chavali, G.; Chen, C.; Del-Toro, N.; et al. The MIntAct project—IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Acids Res. 2013, 42, D358–D363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Licata, L.; Briganti, L.; Peluso, D.; Perfetto, L.; Iannuccelli, M.; Galeota, E.; Sacco, F.; Palma, A.; Santonico, E.; Castagnoli, L.; et al. MINT, the molecular interaction database: 2012 update. Acids Res. 2011, 40, D857–D861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwinski, L.; Miller, C.S.; Smith, A.J.; Pettit, F.K.; Bowie, J.U.; Eisenberg, D. The Database of Interacting Proteins: 2004 update. Acids Res. 2004, 32, D449–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goll, J.; Wu, H.; Uetz, P.; Rajagopala, S.V.; Shiau, S.C.; Lamb, B.T. MPIDB: The microbial protein interaction database. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1743–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launay, G.; Salza, R.; Multedo, D.; Thierry-Mieg, N.; Ricard-Blum, S. MatrixDB, the extracellular matrix interaction database: Updated content, a new navigator and expanded functionalities. Acids Res. 2014, 43, D321–D327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, K.; Chen, C.; Sribnaia, A.; Lo, R.; Foroushani, A.K.; Laird, M.R.; Winsor, G.L.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Brinkman, F.S.L.; Lynn, D.J. InnateDB: Systems biology of innate immunity and beyond--recent updates and continuing curation. Acids Res. 2012, 41, D1228–D1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatr-Aryamontri, A.; Breitkreutz, B.-J.; Oughtred, R.; Boucher, L.; Heinicke, S.; Chen, D.; Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, A.; Kolas, N.; O’Donnell, L.; et al. The BioGRID interaction database: 2015 update. Acids Res. 2014, 43, D470–D478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isserlin, R.; A El-Badrawi, R.; Bader, G.D. The Biomolecular Interaction Network Database in PSI-MI 2.5. Database 2011, 2011, baq037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, T.S.K.; Goel, R.; Kandasamy, K.; Keerthikumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Mathivanan, S.; Telikicherla, D.; Raju, R.; Shafreen, B.; Venugopal, A.; et al. Human Protein Reference Database—2009 update. Acids Res. 2008, 37, D767–D772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, H.M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Nakamura, H.; Markley, J.L. The Protein Data Bank archive as an open data resource. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2014, 28, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bateman, A. The UniProt Consortium UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Acids Res. 2016, 45, D158–D169. [Google Scholar]
- Stenson, P.D.; Ball, E.V.; Mort, M.; Phillips, A.D.; Shaw, K.; Cooper, D.N. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) and Its Exploitation in the Fields of Personalized Genomics and Molecular Evolution. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2012, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Riera, C.; Lois, S.; Dominguez, C.; Fernandez-Cadenas, I.; Montaner, J.; Rodríguez-Sureda, V.; De La Cruz, X.; Fernández-Cadenas, I.; Rodriguez-Sureda, V. Molecular damage in Fabry disease: Characterization and prediction of alpha-galactosidase A pathological mutations. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2014, 83, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera, C.; Padilla, N.; De La Cruz, X.; La Cruz, X. The Complementarity Between Protein-Specific and General Pathogenicity Predictors for Amino Acid Substitutions. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Finn, R.D.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A.; Punta, M. Challenges in homology search: HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Acids Res. 2013, 41, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Acids Res. 2013, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, E.D. A Simple Definition of Structural Regions in Proteins and Its Use in Analyzing Interface Evolution. J. Mol. Boil. 2010, 403, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.M.; Gabb, H.; Sternberg, M.J. Rapid refinement of protein interfaces incorporating solvation: Application to the docking problem. J. Mol. Boil. 1998, 276, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.M.-K.; Blundell, T.L.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Férnandez-Recio, J. pyDock: Electrostatics and desolvation for effective scoring of rigid-body protein-protein docking. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 68, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosdidier, S.; Fernández-Recio, J. Identification of hot-spot residues in protein-protein interactions by computational docking. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]





| Disease-causing SAVs | |||||||||
| Region | All Residues 1 | Observed 2 | Expected 3 | O/E 4 | Regions | OR 5 | 95% C.I. | p-value | Adjusted p-Value |
| Buried | 6019 | 1842 | 1.548.96 | 1.19 | Buried versus Surface | 2.05 | 1.83–2.28 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 |
| Surface | 3118 | 552 | 802.40 | 0.69 | Core versus Buried | 0.94 | 0.82–1.09 | 0.441 | 1 |
| Rim | 916 | 151 | 235.73 | 0.64 | Core versus Rim | 2.11 | 1.69–2.64 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 |
| Core | 1146 | 337 | 294.92 | 1.14 | Core versus Surface | 1.94 | 1.65–2.27 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 |
| Total | 11199 | 2882 | Rim versus Surface | 0.92 | 0.75–1.12 | 0.428 | 1 | ||
| Rim versus Buried | 0.45 | 0.37–0.54 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | |||||
| Interface versus Surface | 1.44 | 1.25–1.54 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | |||||
| Neutral SAVs | |||||||||
| Region | All Residues 1 | Observed 2 | Expected 3 | O/E 4 | Regions | OR 5 | 95% C.I. | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value |
| Buried | 6019 | 524 | 834.14 | 0.63 | Buried versus Surface | 0.29 | 0.25–0.33 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 |
| Surface | 3118 | 767 | 432.10 | 1.78 | Core versus Buried | 0.82 | 0.63–1.04 | 0.105 | 0.738 |
| Rim | 916 | 178 | 126.94 | 1.40 | Core versus Rim | 0.32 | 0.24–0.43 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 |
| Core | 1146 | 83 | 158.82 | 0.52 | Core versus Surface | 0.24 | 0.19–0.30 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 |
| Total | 11199 | 1552 | Rim versus Surface | 0.74 | 0.61–0.89 | 0.001187 | 0.008209 | ||
| Rim versus Buried | 2.53 | 2.08–3.06 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | |||||
| Interface versus Surface | 0.44 | 0.38–0.52 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | |||||
| Interface Region | All Residues 1 | Observed Low-Energy Residues 2 | Expected Low-Energy Residues 3 | O/E 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rim | 916 | 201 | 298.08 | 0.67 |
| Core | 1146 | 470 | 372.92 | 1.26 |
| Total | 2062 | 671 |
| UniProt 1 (Partner) | Neutral Mutations | Pathogenic Mutations 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core 3 | Rim 3 | Core 3 | Rim 3 | |
| O95166 | D398G | A396G, K406R | - | R399 *, V412L |
| P60520 | - | D398G, K406R | - | R399 *, V412L |
| Q14164 | D398G | A396G, K406R, K519R, A596V, S654N, K734Q | - | Q358K, R399 *, V412L, R610G, Y740 * |
| Q99714 | D398G, S654N | A396G, K406R, A596V, R645S, R645N, L661I, K734Q | - | R399 *, V412L, R610G, Y740 * |
| Q9GZQ8 | D398G | V52I, V526I, N142S, L221I, E223T, I237M, A396G, K406R | - | R399 *, V412L |
| Q9H0R8 | D398G | N142S, L221I, E223T, I237M, A396G, K406R, S654N, L661I | - | R399 *, V412L |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navío, D.; Rosell, M.; Aguirre, J.; de la Cruz, X.; Fernández-Recio, J. Structural and Computational Characterization of Disease-Related Mutations Involved in Protein-Protein Interfaces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071583
Navío D, Rosell M, Aguirre J, de la Cruz X, Fernández-Recio J. Structural and Computational Characterization of Disease-Related Mutations Involved in Protein-Protein Interfaces. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(7):1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071583
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavío, Dàmaris, Mireia Rosell, Josu Aguirre, Xavier de la Cruz, and Juan Fernández-Recio. 2019. "Structural and Computational Characterization of Disease-Related Mutations Involved in Protein-Protein Interfaces" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 7: 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071583
APA StyleNavío, D., Rosell, M., Aguirre, J., de la Cruz, X., & Fernández-Recio, J. (2019). Structural and Computational Characterization of Disease-Related Mutations Involved in Protein-Protein Interfaces. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(7), 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071583