MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
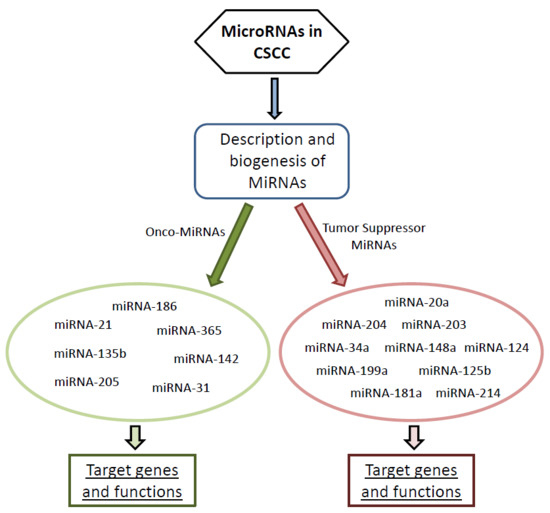
2. Onco-miRNAs Involved in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
2.1. MicroRNA-21
2.2. MicroRNA-205
2.3. MicroRNA-365
2.4. MicroRNA-31
2.5. MicroRNA-186
2.6. MicroRNA-142
2.7. MicroRNA-135b
3. Tumor Suppressor MiRNAs Involved in CSCC
3.1. MicroRNA-34a
3.2. MicroRNA-125b
3.3. MicroRNA-181a
3.4. MicroRNA-148a
3.5. MicroRNA-20a
3.6. MicroRNA-203
3.7. MicroRNA-204
3.8. MicroRNA-199a
3.9. MicroRNA-124
3.10. MicroRNA-214
4. MicroRNAs and Cancer Therapy
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Que, S.K.T.; Zwald, F.O.; Schmults, C.D. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Incidence, risk factors, diagnosis, and staging. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, A.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Bath-Hextall, F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brougham, N.D.; Dennett, E.R.; Cameron, R.; Tan, S.T. The incidence of metastasis from cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and the impact of its risk factors. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 106, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, U.; Keim, U.; Eigentler, T.; Katalinic, A.; Holleczek, B.; Martus, P.; Garbe, C. Incidence, Mortality, and Trends of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer in Germany. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karia, P.S.; Han, J.; Schmults, C.D. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Estimated incidence of disease, nodal metastasis, and deaths from disease in the United States, 2012. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brash, D.E.; Rudolph, J.A.; Simon, J.A.; Lin, A.; McKenna, G.J.; Baden, H.P.; Halperin, A.J.; Ponten, J. A role for sunlight in skin cancer: UV-induced p53 mutations in squamous cell carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10124–10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; Jonason, A.S.; Leffell, D.J.; Simon, J.A.; Sharma, H.W.; Kimmelman, J.; Remington, L.; Jacks, T.; Brash, D.E. Sunburn and p53 in the onset of skin cancer. Nature 1994, 372, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.R.; Zhou, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Drummond, J.A.; Peng, S.A.; Saade, R.E.; Tsai, K.Y.; Curry, J.L.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Lai, S.Y.; et al. Mutational landscape of aggressive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6582–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soufir, N.; Moles, J.P.; Vilmer, C.; Moch, C.; Verola, O.; Rivet, J.; Tesniere, A.; Dubertret, L.; Basset-Seguin, N. P16 UV mutations in human skin epithelial tumors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 5477–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierceall, W.E.; Goldberg, L.H.; Tainsky, M.A.; Mukhopadhyay, T.; Ananthaswamy, H.N. Ras gene mutation and amplification in human nonmelanoma skin cancers. Mol. Carcinog. 1991, 4, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratushny, V.; Gober, M.D.; Hick, R.; Ridky, T.W.; Seykora, J.T. From keratinocyte to cancer: The pathogenesis and modeling of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Pasparakis, M. Epidermal p65/NK-kappaB signalling is essential for skin carcinogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.J.; Sanborn, Z.; Arnett, K.L.; Bayston, L.J.; Liao, W.; Proby, C.M.; Leigh, I.M.; Collisson, E.A.; Gordon, P.B.; Jakkula, L.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in Notch receptors in cutaneous and lung squamous cell carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17761–17766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridd, K.; Bastian, B.C. Somatic mutation of epidermal growth factor receptor in a small subset of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M.; Calin, G.A. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 2005, 122, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Shiekhattar, R. MicroRNA biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3509–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Padgett, R.W. MicroRNAs: Small regulators with a big impact. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsburgh, S.; Fullard, N.; Roger, M.; Degnan, A.; Todryk, S.; Przyborski, S.; O’Reilly, S. MicroRNAs in the skin: Role in development, homoeostasis and regeneration. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1923–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 2001, 294, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveto, S.; Mancino, M.; Manfrini, N.; Biffo, S. Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, X.J.; Zou, Q.; Wang, S.P.; Tang, S.M.; Zhang, G.Z. Biological functions of microRNAs: A review. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 67, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or Tumor Suppressor? The Duplicity of MicroRNAs in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, N.; Greshock, J.; Megraw, M.S.; Giannakakis, A.; Liang, S.; Naylor, T.L.; Barchetti, A.; Ward, M.R.; et al. microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9136–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, A.B.; Lenarduzzi, M.; Krushel, T.; Waldron, L.; Pintilie, M.; Shi, W.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Jurisica, I.; O’Sullivan, B.; Waldron, J.; et al. Comprehensive MicroRNA profiling for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, K.; Yu, J. Inhibition of microRNA-21 upregulates the expression of programmed cell death 4 and phosphatase tensin homologue in the A431 squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darido, C.; Georgy, S.R.; Wilanowski, T.; Dworkin, S.; Auden, A.; Zhao, Q.; Rank, G.; Srivastava, S.; Finlay, M.J.; Papenfuss, A.T.; et al. Targeting of the tumor suppressor GRHL3 by a miR-21-dependent proto-oncogenic network results in PTEN loss and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bracken, C.P.; Bert, A.G.; Goodall, G.J. MicroRNAs as regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3112–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruegger, C.; Kempf, W.; Spoerri, I.; Arnold, A.W.; Itin, P.H.; Burger, B. MicroRNA expression differs in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas and healthy skin of immunocompetent individuals. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Peng, H.; Ruan, Q.; Fatima, A.; Getsios, S.; Lavker, R.M. MicroRNA-205 promotes keratinocyte migration via the lipid phosphatase SHIP2. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3950–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, W.; Ma, S.; Cao, H.; Peng, X.; Guo, L.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, L.; Guo, L.; Wan, M.; et al. A novel onco-miR-365 induces cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L. HOXA9 inhibits HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis through interacting with CRIP2 to repress cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Landen, N.X.; Meisgen, F.; Lohcharoenkal, W.; Stahle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNA-31 is overexpressed in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and regulates cell motility and colony formation ability of tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Zhou, Y.; Lian, X.; Tu, Y. MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting RhoTBT1. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Shen, R.; Yan, Y.; Deng, L. miR-186 promotes tumor growth in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting apoptotic protease activating factor-1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 4010–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, M.; Xu, J. MicroRNA-142-5p induces cancer stem cell-like properties of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via inhibiting PTEN. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasz, E.B.; Seline, L.N.; Schock, A.M.; Duncan, N.E.; Lopez, A.; Lazar, J.; Flister, M.J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, P.; Sokumbi, O.; et al. MicroRNA-135b Regulates Leucine Zipper Tumor Suppressor 1 in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luo, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-34a directly targets high-mobility group box 1 and inhibits the cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5611–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefort, K.; Brooks, Y.; Ostano, P.; Cario-Andre, M.; Calpini, V.; Guinea-Viniegra, J.; Albinger-Hegyi, A.; Hoetzenecker, W.; Kolfschoten, I.; Wagner, E.F.; et al. A miR-34a-SIRT6 axis in the squamous cell differentiation network. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2248–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, L.; Meisgen, F.; Harada, M.; Heilborn, J.; Homey, B.; Grander, D.; Stahle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNA-125b down-regulates matrix metallopeptidase 13 and inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29899–29908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, J.; Dziunycz, P.J.; Dzung, A.; Lefort, K.; Falke, M.; Denzler, R.; Freiberger, S.N.; Iotzova-Weiss, G.; Kuzmanov, A.; Levesque, M.P.; et al. miR-181a decelerates proliferation in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the proto-oncogene KRAS. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Li, W.; Zhao, T.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Role of miR-148a in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by repression of MAPK pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 583, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, R.; Luo, C.; Zhou, X.; Xia, K.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M.; Zou, Q.; Cao, P.; Cao, K. MiR-20a inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and proliferation by directly targeting LIMK1. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lohcharoenkal, W.; Harada, M.; Loven, J.; Meisgen, F.; Landen, N.X.; Zhang, L.; Lapins, J.; Mahapatra, K.D.; Shi, H.; Nissinen, L.; et al. MicroRNA-203 Inversely Correlates with Differentiation Grade, Targets c-MYC, and Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in cSCC. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toll, A.; Salgado, R.; Espinet, B.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; Hernandez-Ruiz, E.; Andrades, E.; Sandoval, J.; Esteller, M.; Pujol, R.M.; Hernandez-Munoz, I. MiR-204 silencing in intraepithelial to invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma progression. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Zhou, J.D.; He, Q.Y.; Yin, Z.Q.; Cao, K.; Luo, C.Q. MiR-199a inhibits the ability of proliferation and migration by regulating CD44-Ezrin signaling in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7131–7141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.K.; Kim, I.; Yoon, S.K. Identification of miR-199a-5p target genes in the skin keratinocyte and their expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, K.; Jinnin, M.; Etoh, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shimozono, N.; Fukushima, S.; Masuguchi, S.; Maruo, K.; Inoue, Y.; Ishihara, T.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-124/-214 in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma mediates abnormal cell proliferation via the induction of ERK. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Shu, Y. MiR-21 overexpression in human primary squamous cell lung carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.X.; Huang, X.F.; Shao, Q.; Huang, M.Y.; Deng, L.; Wu, Q.L.; Zeng, Y.X.; Shao, J.Y. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA 2008, 14, 2348–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Farhana, L.; Rajendra, S.G.; Levi, E.; Majumdar, A.P. miR-21 and miR-145 cooperation in regulation of colon cancer stem cells. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, E.; Funel, N.; Peters, G.J.; Del Chiaro, M.; Erozenci, L.A.; Vasile, E.; Leon, L.G.; Pollina, L.E.; Groen, A.; Falcone, A.; et al. MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: Correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4528–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.A.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6029–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffler, D.; Brocke-Heidrich, K.; Pfeifer, G.; Stocsits, C.; Hackermuller, J.; Kretzschmar, A.K.; Burger, R.; Gramatzki, M.; Blumert, C.; Bauer, K.; et al. Interleukin-6 dependent survival of multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood 2007, 110, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Si, M.L.; Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Mo, Y.Y. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2799–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Si, M.L.; Wu, H.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14328–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Wu, F.; Nie, D.; Sheng, S.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folini, M.; Gandellini, P.; Longoni, N.; Profumo, V.; Callari, M.; Pennati, M.; Colecchia, M.; Supino, R.; Veneroni, S.; Salvioni, R.; et al. miR-21: An oncomir on strike in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S.R.; Yang, C.H.; Pfeffer, L.M. The Role of miR-21 in Cancer. Drug Dev. Res. 2015, 76, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Tsao, C.J. Emerging role of microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Xu, J.; Liu, L.; Shen, H.; Zeng, H.; Shu, Y. A systematic-analysis of predicted miR-21 targets identifies a signature for lung cancer. Biomed. Pharm. 2012, 66, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zou, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Dulak, A.; Tomko, R.J., Jr.; Lazo, J.S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J. microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8157–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Nikolova, D.A.; Leupold, J.H.; Colburn, N.H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe-Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, L.B.; Christoffersen, N.R.; Jacobsen, A.; Lindow, M.; Krogh, A.; Lund, A.H. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, F.J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.; Hennessy, E.J.; Martin, C.; O’Leary, J.J.; Ruan, Q.; Johnson, D.S.; Chen, Y.; O’Neill, L.A. Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miR-21. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscaglia, L.E.; Li, Y. Apoptosis and the target genes of microRNA-21. Chin. J. Cancer 2011, 30, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.H.; Yue, J.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Handorf, C.R.; Pfeffer, L.M. MicroRNA miR-21 regulates the metastatic behavior of B16 melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 39172–39178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kleeman, S.; Coburn, S.B.; Fumagalli, C.; Perner, J.; Jammula, S.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Orzolek, L.; Hao, H.; Taylor, P.R.; et al. Selection and Application of Tissue microRNAs for Nonendoscopic Diagnosis of Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 771–783 e773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. Prognostic value of miR-21 in various cancers: An updating meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.B.; Herschkowitz, J.I.; Rosen, J.M. The ups and downs of miR-205: Identifying the roles of miR-205 in mammary gland development and breast cancer. RNA Biol. 2010, 7, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Lopez, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Cano, A. Role of microRNA in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis and clinical perspectives. Cancer Manag. Res. 2014, 6, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Fang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, J.; Li, M. miR-205 targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Huang, Y.; Gong, W. miR-205 promotes the growth, metastasis and chemoresistance of NSCLC cells by targeting PTEN. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2897–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Liang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, R.; Su, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Lee, M.H.; Yang, H. MiR-205 determines the radioresistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by directly targeting PTEN. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Ryan, D.G.; Getsios, S.; Oliveira-Fernandes, M.; Fatima, A.; Lavker, R.M. MicroRNA-184 antagonizes microRNA-205 to maintain SHIP2 levels in epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19300–19305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iorio, M.V.; Casalini, P.; Piovan, C.; Di Leva, G.; Merlo, A.; Triulzi, T.; Menard, S.; Croce, C.M.; Tagliabue, E. microRNA-205 regulates HER3 in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2195–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandellini, P.; Folini, M.; Longoni, N.; Pennati, M.; Binda, M.; Colecchia, M.; Salvioni, R.; Supino, R.; Moretti, R.; Limonta, P.; et al. miR-205 Exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, S.; Mo, Y.Y. Suppression of cell growth and invasion by miR-205 in breast cancer. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; O’Loughlin, E.; Wang, L.; Fan, X.; Lai, E.C.; Yi, R. MicroRNA-205 controls neonatal expansion of skin stem cells by modulating the PI(3)K pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canueto, J.; Cardenoso-Alvarez, E.; Garcia-Hernandez, J.L.; Galindo-Villardon, P.; Vicente-Galindo, P.; Vicente-Villardon, J.L.; Alonso-Lopez, D.; De Las Rivas, J.; Valero, J.; Moyano-Sanz, E.; et al. MicroRNA (miR)-203 and miR-205 expression patterns identify subgroups of prognosis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojadinovic, O.; Ramirez, H.; Pastar, I.; Gordon, K.A.; Stone, R.; Choudhary, S.; Badiavas, E.; Nouri, K.; Tomic-Canic, M. MiR-21 and miR-205 are induced in invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M. miR-365 overexpression promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ADAMTS-1 in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 262–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, H.; Mu, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Ma, S. MicroRNA-365 promotes lung carcinogenesis by downregulating the USP33/SLIT2/ROBO1 signalling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.L.; Ye, H.; Teng, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, G.; Li, X.B.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z.Z.; Yang, X. Akt-p53-miR-365-cyclin D1/cdc25A axis contributes to gastric tumorigenesis induced by PTEN deficiency. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, J.; Liu, L.; Zheng, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.; Du, X.; Han, W. microRNA-365, down-regulated in colon cancer, inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis of colon cancer cells by probably targeting Cyclin D1 and Bcl-2. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H. MicroRNA-365 inhibits growth, invasion and metastasis of malignant melanoma by targeting NRP1 expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 4913–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Xi, W.; Zhang, W.; Hu, P.; Wang, T.; Shan, L. [miR-365 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of SOSP9607 osteosarcoma cells]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi = Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 32, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Su, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chu, D.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, R. MicroRNA-365 targets multiple oncogenes to inhibit proliferation, invasion, and self-renewal of aggressive endometrial cancer cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5171–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Gan, X.; Zeng, W.; Liu, Y.; Guan, H. miR-365 induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis through targeting Bcl-2. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Ye, Q.; Ming, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, K. Prognostic significance and anti-proliferation effect of microRNA-365 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Q.; Yang, J.; Shu, Y. MicroRNA-365 suppresses cell growth and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating phosphoserine aminotransferase 1. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 4581–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ou, C.; Ding, Z. miR-365 promotes cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) through targeting nuclear factor I/B (NFIB). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Ding, Z. Loss of BAX by miR-365 Promotes Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Suppressing Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Rao, M.; Xu, S. MicroRNA-365 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma by targeting PIK3R3. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xiao, S.B.; Xu, P.; Xie, Q.; Cao, L.; Wang, D.; Luo, R.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, H.C.; Fang, L.R. miR-365, a novel negative regulator of interleukin-6 gene expression, is cooperatively regulated by Sp1 and NF-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21401–21412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Huang, Z.X.; Chen, X.W.; Deng, Q.K.; Yan, W.; Zhou, M.J.; Ou, C.S.; Ding, Z.H. Differential expression profiles of microRNAs in NIH3T3 cells in response to UVB irradiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepicheva, N.A.; Song, J.L. Function and regulation of microRNA-31 in development and disease. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2016, 83, 654–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Wu, B. MicroRNA-31 inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting RhoA in human gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.J.; Yang, F.; Ding, J.J.; Yan, D.L.; Wang, D.D.; Yang, S.J.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Ma, R.; et al. MiR-31 inhibits migration and invasion by targeting SATB2 in triple negative breast cancer. Gene 2016, 594, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekchnov, E.A.; Amelina, E.V.; Bryzgunova, O.E.; Zaporozhchenko, I.A.; Konoshenko, M.Y.; Yarmoschuk, S.V.; Murashov, I.S.; Pashkovskaya, O.A.; Gorizkii, A.M.; Zheravin, A.A.; et al. Searching for the Novel Specific Predictors of Prostate Cancer in Urine: The Analysis of 84 miRNA Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Qin, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhong, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xia, L.; et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as a tumor suppressor and increases sensitivity to mitomycin-C in urothelial bladder cancer by targeting integrin alpha5. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27445–27457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.H.; Yu, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y.Q. Elevated microRNA-31 expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene SATB2. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sempere, L.F.; Ouyang, H.; Memoli, V.A.; Andrew, A.S.; Luo, Y.; Demidenko, E.; Korc, M.; Shi, W.; Preis, M.; et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, C.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, X.; Song, Y.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, S.; Luan, L.; et al. MiR-31 promotes mammary stem cell expansion and breast tumorigenesis by suppressing Wnt signaling antagonists. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Hung, P.S.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wu, K.J.; Chiou, S.H.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-31 ablates expression of the HIF regulatory factor FIH to activate the HIF pathway in head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Shao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Shu, Y. A systematic analysis of predicted MiR-31-targets identifies a diagnostic and prognostic signature for lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Ma, P.; Wu, D.; Shu, Y.; Gao, W. Functions and mechanisms of microRNA-31 in human cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Fang, L.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, R.; Li, M. miR-186 downregulation correlates with poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma, where it interferes with cell-cycle regulation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Bai, R.; Yang, K.; Tian, Z. MiR-186 inhibited aerobic glycolysis in gastric cancer via HIF-1alpha regulation. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; He, L.; Gan, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Dai, Y.; Tan, J. MiR-186 suppresses the growth and metastasis of bladder cancer by targeting NSBP1. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, D.Q.; Yao, D.M.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.D.; Deng, Z.Q.; Wen, X.M.; Guo, H.; Ma, J.C.; et al. Down-Regulation of miR-186 Correlates with Poor Survival in de novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin. Lab. 2016, 62, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, M. MicroRNAs: Exploring new horizons in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Tavallaee, G.; Tokar, T.; Nakamura, A.; Sundararajan, K.; Weston, A.; Sharma, A.; Mahomed, N.N.; Gandhi, R.; Jurisica, I.; et al. Identification of synovial fluid microRNA signature in knee osteoarthritis: Differentiating early- and late-stage knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Shen, D.; Sohun, H.; Ge, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Rong, X.; et al. miR186, a serum microRNA, induces endothelial cell apoptosis by targeting SMAD6 in Kawasaki disease. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; She, K.; Peng, G.; Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; He, J. MicroRNA-186 suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through targeting MAP3K2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, W.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Liao, Z.; Xian, Q.; Yu, L. miR-186 inhibits cell proliferation of prostate cancer by targeting GOLPH3. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Bai, Z.H.; Wang, X.B.; Bai, L.; Miao, F.; Pei, H.H. miR-186 and 326 predict the prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and affect the proliferation and migration of cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myatt, S.S.; Wang, J.; Monteiro, L.J.; Christian, M.; Ho, K.K.; Fusi, L.; Dina, R.E.; Brosens, J.J.; Ghaem-Maghami, S.; Lam, E.W. Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Guo, F. miR-186 reverses cisplatin resistance and inhibits the formation of the glioblastoma-initiating cell phenotype by degrading Yin Yang 1 in glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, H.; Yin, X.; Long, L.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Hui, L.; Lin, X.; Fang, Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. miR-186 regulation of Twist1 and ovarian cancer sensitivity to cisplatin. Oncogene 2016, 35, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Cui, M.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, H.; Zhao, S. MiR-186 targets ROCK1 to suppress the growth and metastasis of NSCLC cells. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 8933–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, R.; Kheirollahi, A.; Davoodi, J. Apaf-1: Regulation and function in cell death. Biochimie 2017, 135, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, N.J.; Wang, W.L.; Reyes, E.Y.; Kumar, B.; Chen, C.C.; Ramakrishna, C.; Cantin, E.M.; Vonderfecht, S.L.; Taganov, K.D.; Chau, N.; et al. Altered lymphopoiesis and immunodeficiency in miR-142 null mice. Blood 2015, 125, 3720–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.Z.; Li, L.; Lodish, H.F.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004, 303, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, N.; Liu, X.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Deng, Z. MicroRNA-142-3p inhibits cell proliferation and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer via targeting sirtuin 1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 5205–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lou, K.; Chen, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, H. MicroRNA-142-5p Overexpression Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis by Regulating FOXO in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colamaio, M.; Puca, F.; Ragozzino, E.; Gemei, M.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; Aiello, C.; Bastos, A.U.; Federico, A.; Chiappetta, G.; Del Vecchio, L.; et al. miR-142-3p down-regulation contributes to thyroid follicular tumorigenesis by targeting ASH1L and MLL1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E59–E69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Xi, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. miR-142-5p regulates tumor cell PD-L1 expression and enhances anti-tumor immunity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 488, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, X.; Jia, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hong, M.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, J.; et al. An oncogenic role of miR-142-3p in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) by targeting glucocorticoid receptor-alpha and cAMP/PKA pathways. Leukemia 2012, 26, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiao, Z.; Ai, F.; Liu, F.; Chen, X.; Cao, K.; Ren, W.; Zhang, X.; Shu, P.; Zhang, D. miR-142-5p promotes development of colorectal cancer through targeting SDHB and facilitating generation of aerobic glycolysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Duan, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, T.; Qian, H.; Yang, S.; Xin, D.; He, Z.; Guo, Y. MicroRNA-142-5p promotes cell growth and migration in renal cell carcinoma by targeting BTG3. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2394–2402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Ma, S.P.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Lin, T.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, S.H.; Zhang, W.C.; Wang, X.L. miR-142-3p Suppresses Cell Growth by Targeting CDK4 in Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1969–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xu, W.; Lu, T.; Zhou, J.; Ge, X.; Hua, D. MicroRNA-142-3p Promotes Cellular Invasion of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Activation of RAC1. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818790508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, V.; Leigh, I.M. WNT Signaling in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. A Future Treatment Strategy? J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, K.; Jin, J.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.; Song, H.; Li, D.; Maskey, N.; Zhao, B.; Wu, C.; Xu, H.; et al. miR-135b, upregulated in breast cancer, promotes cell growth and disrupts the cell cycle by regulating LATS2. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Chang, Y.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, J.C.; Chen, C.C.; Pan, S.H.; Wu, C.T.; Chen, H.Y.; Yang, S.C.; Hong, T.M.; et al. MicroRNA-135b promotes lung cancer metastasis by regulating multiple targets in the Hippo pathway and LZTS1. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagel, R.; le Sage, C.; Diosdado, B.; van der Waal, M.; Oude Vrielink, J.A.; Bolijn, A.; Meijer, G.A.; Agami, R. Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135 family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Lv, P. The tumor-suppressive microRNA-135b targets c-myc in osteoscarcoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, T. Downregulation of MicroRNA-135 Promotes Sensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to Gefitinib by Targeting TRIM16. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Q. Poor expression of microRNA-135b results in the inhibition of cisplatin resistance and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through MST1-mediated MAPK signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2018, 33, 3420–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.J.; Bian, Y.; Kulkarni, A.B. MicroRNA-135b acts as a tumor promoter by targeting the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway in genetically defined mouse model of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2013, 331, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Cui, M.; Wang, Q. Down-regulation of microRNA-135b inhibited growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FOXO1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10294–10304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aakula, A.; Leivonen, S.K.; Hintsanen, P.; Aittokallio, T.; Ceder, Y.; Borresen-Dale, A.L.; Perala, M.; Ostling, P.; Kallioniemi, O. MicroRNA-135b regulates ERalpha, AR and HIF1AN and affects breast and prostate cancer cell growth. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchione, A.; Baldassarre, G.; Ishii, H.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Belletti, B.; Petrocca, F.; Zanesi, N.; Fong, L.Y.; Battista, S.; Guarnieri, D.; et al. Fez1/Lzts1 absence impairs Cdk1/Cdc25C interaction during mitosis and predisposes mice to cancer development. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Pan, W.; Lin, X.; Hu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, G.; Qiu, Y.; Chang, L.; Hua, C.; et al. MicroRNA-346 functions as an oncogene in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, M.; Hessam, S.; Amur, S.; Skrygan, M.; Bromba, M.; Stockfleth, E.; Gambichler, T.; Bechara, F.G. Expression of oncogenic miR-17-92 and tumor suppressive miR-143-145 clusters in basal cell carcinoma and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 86, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, A.; Barzilai, A.; Gur-Wahnon, D.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Glassberg, S.; Meningher, T.; Elharar, E.; Masalha, M.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Tabibian-Keissar, H.; et al. Alterations of microRNAs throughout the malignant evolution of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: The role of miR-497 in epithelial to mesenchymal transition of keratinocytes. Oncogene 2018, 37, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Knight, R.A. miR-34: From bench to bedside. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokavec, M.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Hermeking, H. The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slabakova, E.; Culig, Z.; Remsik, J.; Soucek, K. Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, G.; Su, L.; Singhal, S.; Liu, X. Emerging roles of SIRT6 on telomere maintenance, DNA repair, metabolism and mammalian aging. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 364, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchie A: First microRNA mimic enters clinic. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 577. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.K.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A.G.; Kim, S.; Hong, D.S. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.M.; Lin, K.Y.; Chen, Y.Q. Diverse functions of miR-125 family in different cell contexts. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Sun, S.; Shi, J.; Cao, F.; Han, X.; Chen, Z. MicroRNA-125a-5p plays a role as a tumor suppressor in lung carcinoma cells by directly targeting STAT3. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317697579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; An, H.; Xu, C.; Cao, W.; Yuan, W.; Ma, J. Upregulation of microRNA-125b by G-CSF promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50642–50654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, X.; Wei, K.; Lin, Z.; Cui, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B. MicroRNA-125b Suppresses Ovarian Cancer Progression via Suppression of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Pathway by Targeting the SET Protein. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzhaf-Strathmann, J.; Edbauer, D. Good guy or bad guy: The opposing roles of microRNA 125b in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, S.; Talebi, F.; Chan, W.F.; Masoumi, F.; Vojgani, M.; Power, C.; Noorbakhsh, F. MicroRNA-181 Variants Regulate T Cell Phenotype in the Context of Autoimmune Neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.H.; Bae, S.D.; Hong, H.S.; Kim, R.H.; Kang, M.K.; Park, N.H. miR-181a shows tumor suppressive effect against oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by downregulating K-ras. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Ma, R.; Cao, H.; Ji, M.; Jing, C.; Tang, J. The function role of miR-181a in chemosensitivity to adriamycin by targeting Bcl-2 in low-invasive breast cancer cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, W.; Weng, J.; Zhou, C.; Huang, K.; Tang, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, W.; et al. miR-181a-5p promotes the progression of gastric cancer via RASSF6-mediated MAPK signalling activation. Cancer Lett. 2017, 389, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduci, L.; Azzalin, G.; Gioiosa, S.; Carissimi, C.; Laudadio, I.; Fulci, V.; Macino, G. microRNA-181a enhances cell proliferation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by targeting EGR1. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nabhan, M.; Louka, M.L.; Khairy, E.; Tash, F.; Ali-Labib, R.; El-Habashy, S. MicroRNA-181a and its target Smad 7 as potential biomarkers for tracking child acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Gene 2017, 628, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, A.; Lee, C.; Joseph, P.; Marchini, S.; Baccarini, A.; Kolev, V.; Romualdi, C.; Fruscio, R.; Shah, H.; Wang, F.; et al. microRNA-181a has a critical role in ovarian cancer progression through the regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Qiao, M.; Yao, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Dong, Q.; Jia, J.; Cui, X.; Li, Z.; Xia, J.; et al. Serum-based microRNA signature predicts relapse and therapeutic outcome of adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.L.; Lin, L. MiR-155 and miR-148a reduce cardiac injury by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway during acute viral myocarditis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.X.; Wang, Z.N. The microRNA-148/152 family: Multi-faceted players. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Han, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, K.; Shen, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Prochownik, E.; Li, Y. MicroRNA-148a deficiency promotes hepatic lipid metabolism and hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Si, L.; Tian, H. MicroRNA-148a inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in lung adenocarcinoma via directly targeting transcription factor E2F3. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 5400–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Xia, J.; Zuo, J.; Jin, S.; Zhou, H.; Yao, L.; Huang, H.; Han, Z. MicroRNA-148a is silenced by hypermethylation and interacts with DNA methyltransferase 1 in gastric cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 2701–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, A.P.; Mooso, B.A.; Libertini, S.J.; Lim, R.M.; Nakagawa, R.M.; Vidallo, K.D.; Costanzo, N.C.; Ghosh, P.M.; Mudryj, M. miR-148a dependent apoptosis of bladder cancer cells is mediated in part by the epigenetic modifier DNMT1. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.R.; He, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, J. MicroRNA-148a is silenced by hypermethylation and interacts with DNA methyltransferase 1 in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, M.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Koo, J.H.; Yang, Y.M.; An, J.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, K.M.; Park, J.W.; Kim, S.G. microRNA-148a dysregulation discriminates poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with USP4 overexpression. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2792–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yu, W. MicroRNA-148a suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting ROCK1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 380, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Su, J.; Liang, H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, W. MicroRNA-148a Suppresses the Proliferation and Migration of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Down-regulating ErbB3. Pancreas 2016, 45, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Ren, X.; Hu, H.; Sheng, H.; Lai, M. MiR-148a promotes apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2 in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, A.; Zhu, C.; Peng, S.; Shuai, C.; Sun, L.; Han, Y.; Qian, Y.; Gao, S.; Su, T. Downregulation of Microrna-148a in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from Oral Cancer Promotes Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Targeting Wnt10b. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liffers, S.T.; Munding, J.B.; Vogt, M.; Kuhlmann, J.D.; Verdoodt, B.; Nambiar, S.; Maghnouj, A.; Mirmohammadsadegh, A.; Hahn, S.A.; Tannapfel, A. MicroRNA-148a is down-regulated in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting CDC25B. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mogilyansky, E.; Rigoutsos, I. The miR-17/92 cluster: A comprehensive update on its genomics, genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Zuo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, M.; Huang, W. MicroRNA-20a overexpression inhibited proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, S.T.; Lin, B.R.; Wu, T.S.; Lin, S.K.; Kuo, M.Y.; Tan, C.T. MicroRNA-17/20a functions to inhibit cell migration and can be used a prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; He, J.; Wei, X.; Wan, G.; Lao, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.; Hu, Z.; Luo, X.; et al. MicroRNA-20a-mediated loss of autophagy contributes to breast tumorigenesis by promoting genomic damage and instability. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5874–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Chen, W.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-20a Regulates Glioma Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Apoptosis by Targeting CUGBP Elav-Like Family Member 2. World Neurosurg. 2019, 121, e519–e527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Dong, J.; Luo, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, F. MicroRNA-20a regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy by targeting thrombospondin 2 in cervical cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 844, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Han, G.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; He, Q. MiRNA-20a-5p promotes the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting RUNX3. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Up-regulation of miR-20a by HPV16 E6 exerts growth-promoting effects by targeting PDCD6 in cervical carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, F.; Han, S.; Chu, P.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; et al. MiR-20a-5p suppresses tumor proliferation by targeting autophagy-related gene 7 in neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Yao, D.; Chen, J.; Ding, N.; Ren, F. MiR-20a promotes cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, B.V.; Koto, K.; Gutierrez-Hartmann, A. Nuclear and cytoplasmic LIMK1 enhances human breast cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, P.; Han, X.; Wu, L.; Li, X.; Xiong, Z. Decreased expression of microRNA-20a promotes tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 11446–11451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bo, J.; Yang, G.; Huo, K.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, Y. microRNA-203 suppresses bladder cancer development by repressing bcl-w expression. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yue, Z.; Xu, H.; Xing, C.; Liu, Z. Aberrant expression of miR-203 and its clinical significance in gastric and colorectal cancers. J. Gastrointest Surg. 2010, 15, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, K.; Fan, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.W.; Zhu, H.Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.Y.; Meng, Y.L.; Cui, P.C.; Cheng, S.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-203 leads to G1 phase cell cycle arrest in laryngeal carcinoma cells by directly targeting survivin. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Deng, Y.; Yang, G.; Xie, W. MicroRNA-203 down-regulation is associated with unfavorable prognosis in human glioma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 108, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Guo, L.; Jiang, W.; Lu, S.H. miR-203 Inhibits the Proliferation and Self-Renewal of Esophageal Cancer Stem-Like Cells by Suppressing Stem Renewal Factor Bmi-1. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 23, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Gong, D.J.; Tao, J.; Cheng, H.Z.; Huang, S.D. MicroRNA-203 inhibits cell proliferation by repressing DeltaNp63 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, Z.; Cao, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, Z.; Xin, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Z.; et al. MiR-203 suppresses tumor growth and invasion and down-regulates MiR-21 expression through repressing Ran in esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 342, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Er, K.; Mao, C.; Yan, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cui, F.; Zhao, W.; Shi, H. miR-203 suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting VEGFA in cervical cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kempen, L.C.; van den Hurk, K.; Lazar, V.; Michiels, S.; Winnepenninckx, V.; Stas, M.; Spatz, A.; van den Oord, J.J. Loss of microRNA-200a and c, and microRNA-203 expression at the invasive front of primary cutaneous melanoma is associated with increased thickness and disease progression. Virchows Arch. 2012, 461, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly, E.; Wei, T.; Pavez Lorie, E.; Suzuki, H.; Kato, M.; Torma, H.; Stahle, M.; Pivarcsi, A. Protein kinase C-dependent upregulation of miR-203 induces the differentiation of human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melar-New, M.; Laimins, L.A. Human papillomaviruses modulate expression of microRNA 203 upon epithelial differentiation to control levels of p63 proteins. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5212–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikenaga, N.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Yu, J.; Kayashima, T.; Sakai, H.; Fujita, H.; Nakata, K.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA-203 expression as a new prognostic marker of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 3120–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greither, T.; Grochola, L.F.; Udelnow, A.; Lautenschlager, C.; Wurl, P.; Taubert, H. Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 126, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viticchie, G.; Lena, A.M.; Cianfarani, F.; Odorisio, T.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Melino, G.; Candi, E. MicroRNA-203 contributes to skin re-epithelialization. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, R.; Poy, M.N.; Stoffel, M.; Fuchs, E. A skin microRNA promotes differentiation by repressing ‘stemness’. Nature 2008, 452, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Xu, C.; Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, J. MicroRNA-203 inhibits cellular proliferation and invasion by targeting Bmi1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bu, P.; Yang, P. MicroRNA-203 inhibits malignant melanoma cell migration by targeting versican. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lena, A.M.; Shalom-Feuerstein, R.; Rivetti di Val Cervo, P.; Aberdam, D.; Knight, R.A.; Melino, G.; Candi, E. miR-203 represses ‘stemness’ by repressing DeltaNp63. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, W.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, M. Loss of miR-204 expression enhances glioma migration and stem cell-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H. MicroRNA-204 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells by targeting PCNA-1 and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.; Lee, E.; Moon, H.; Kim, K.H.; Jin, M.S.; Kwon, N.H.; Kim, S.; et al. Tumor suppressor microRNA-204-5p regulates growth, metastasis, and immune microenvironment remodeling in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, J.S.; Plyler, J.R.; Bansal, H.; Prajapati, S.; Bansal, S.; Rebeles, J.; Chen, H.I.; Chang, Y.F.; Panneerdoss, S.; Zoghi, B.; et al. Genomic loss of tumor suppressor miRNA-204 promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by activating AKT/mTOR/Rac1 signaling and actin reorganization. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Lin, B.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Miao, M.; Gu, J.; Pan, H.; Yang, F.; et al. A dual yet opposite growth-regulating function of miR-204 and its target XRN1 in prostate adenocarcinoma cells and neuroendocrine-like prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7686–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Pan, H.; Li, R. The dual regulatory role of miR-204 in cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11667–11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suiqing, C.; Min, Z.; Lirong, C. Overexpression of phosphorylated-STAT3 correlated with the invasion and metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dermatol. 2005, 32, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi Gheinani, A.; Burkhard, F.C.; Rehrauer, H.; Aquino Fournier, C.; Monastyrskaya, K. MicroRNA MiR-199a-5p regulates smooth muscle cell proliferation and morphology by targeting WNT2 signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 7067–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Duan, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhao, T.; Xu, S.; Yang, L.; Li, D. microRNA-199a-3p functions as tumor suppressor by regulating glucose metabolism in testicular germ cell tumors. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lei, S.; Long, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q. MicroRNA-199a-5p inhibits tumor proliferation in melanoma by mediating HIF-1alpha. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5241–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ba, X.; Guo, Y.; Sun, D.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. MicroRNA-199a-5p promotes tumour growth by dual-targeting PIAS3 and p27 in human osteosarcoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, F.; Tian, D.; Wang, T.; Lu, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, P.; Qin, L. miR-199a-3p enhances cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells by targeting ITGB8. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Ma, J.; Tao, L.; Mo, L.; Chen, W. MiR-199a-3p enhances cisplatin sensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma cells by inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway and expression of MDR1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33621–33630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shen, J.K.; Lin, M.; Choy, E.; Cote, G.M.; Harmon, D.C.; Mankin, H.J.; Hornicek, F.J.; Duan, Z. CD44 is a direct target of miR-199a-3p and contributes to aggressive progression in osteosarcoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.D.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Dong, L.; Huang, Z.; Wu, F.; Deng, X. MiR-199a-5p Inhibits the Growth and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting ROCK1. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533034618775509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.A.; Harrison, G.; Mansel, R.E.; Jiang, W.G. The role of the CD44/ezrin complex in cancer metastasis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2003, 46, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, Z.M.; Guo, X.M.; Su, D.F.; Liu, X. An updated role of microRNA-124 in central nervous system disorders: A review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liang, Y.; Xu, M.; Xiong, J.; Wang, D.; Ding, Q. MicroRNA-124 acts as a tumor-suppressive miRNA by inhibiting the expression of Snail2 in osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4979–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.L.; Gao, H.L.; Lv, X.K.; Hei, Y.R.; Li, P.Z.; Zhang, J.X.; Lu, N. MicroRNA-124 inhibits cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by directly repressing Snail2 in gastric cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3389–3396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, W.H.; Zhao, G.F.; Li, X.H.; Wei, L.; Liu, G.B.; Huang, H. MicroRNA-124 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and suppresses tumor growth by interacting with PLCB1 and regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Liu, B.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.X. MicroRNA-124-3p suppresses cell migration and invasion by targeting ITGA3 signaling in bladder cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, C.; Chu, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhen, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lv, B.; Li, H.; et al. MicroRNA-124 suppresses proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting AKT-GLUT1/HKII. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317706215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Mao, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. MicroRNA-124-3p inhibits cell migration and invasion in bladder cancer cells by targeting ROCK1. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhai, X.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Chang, J. MiR-124 retards bladder cancer growth by directly targeting CDK4. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; He, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, B. MicroRNA-124 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting CAV1 in bladder cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Targeting ERK1/2 protein-serine/threonine kinases in human cancers. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, P.; Fu, H.; Zhao, X.; Wu, C.; Ruan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Hou, L.; Chen, P.; et al. MicroRNA-214 modulates neural progenitor cell differentiation by targeting Quaking during cerebral cortex development. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekaran, K.S.; Sathyanarayanan, A.; Karunagaran, D. MicroRNA-214 suppresses growth, migration and invasion through a novel target, high mobility group AT-hook 1, in human cervical and colorectal cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Du, J.; Jiang, R.; Li, L. MicroRNA-214 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung carcinoma cells by targeting JAK1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Geng, P.; Song, H. microRNA-214 suppresses the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting EZH2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5679–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehei, A.L.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Y.X.; Mu, W.B.; Yang, D.S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.J.; Younusi, A. MicroRNA-214 functions as an oncogene in human osteosarcoma by targeting TRAF3. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5156–5164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Fan, W.; Fan, Y.; Gao, S. MicroRNA-214 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer MKN28 cells by suppressing the expression of Dact2. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 4909–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, E.; Orso, F.; Taverna, D. miR-214 as a key hub that controls cancer networks: Small player, multiple functions. J. Investig Dermatol. 2015, 135, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.Y.; Ferrajoli, A.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Calin, G.A. microRNA Therapeutics in Cancer-An Emerging Concept. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, V.P.; Ngo, T.A.; Pernestig, A.K.; Tilevik, D.; Kant, K.; Nguyen, T.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. MicroRNA amplification and detection technologies: Opportunities and challenges for point of care diagnostics. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2019, 99, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. A review: microRNA detection methods. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 2226–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Onco-miRNAs in CSCC | |||
| MiRNA | Target Genes | Function | Ref. |
| MicroRNA-21 | PTEN, PDCD4, GRHL3 | tumor growth, invasion, antiapoptotic | [29,30] |
| MicroRNA-205 | ZEB, SHIP2 | cell proliferation, keratinocyte migration | [31,32,33] |
| MicroRNA-365 | HOXA9 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion | [34,35] |
| MicroRNA-31 | RhoBTB1 | migration, invasion | [36,37] |
| MicroRNA-186 | APAF1 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, antiapoptotic | [38] |
| MicroRNA-142 | PTEN | CSCC progression, maintenance stem cell properties | [39] |
| MicroRNA-135b | LZTS1 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion | [40] |
| Tumor suppressor miRNAs in CSCC | |||
| MiRNA | Target genes | Function | Ref |
| MicroRNA-34a | HMGB1, SIRT6 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion | [41,42] |
| MicroRNA-125b | MMP13, MMP7, MAP2K7 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, inflammation, angiogenesis | [43] |
| MicroRNA-181a | KRAS | survival | [44] |
| MicroRNA-148a | MAP3K4, MAP3K9 | metastasis | [45] |
| MicroRNA-20a | LIMK1 | cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, invasion, metastasis | [46] |
| MicroRNA-203 | c-MYC | migration, angiogenesis, invasion | [47] |
| MicroRNA-204 | SHP2 | CSCC progression | [48] |
| MicroRNA-199a | CD44, BCAM, FZD6, DDR1 | cell proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis | [49,50] |
| MicroRNA-124 | ERK2 | tumor progression | [51] |
| MicroRNA-214 | ERK1, ERK2 | cell proliferation, differentiation, survival | [51] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Sancha, N.; Corchado-Cobos, R.; Pérez-Losada, J.; Cañueto, J. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092181
García-Sancha N, Corchado-Cobos R, Pérez-Losada J, Cañueto J. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092181
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Sancha, Natalia, Roberto Corchado-Cobos, Jesús Pérez-Losada, and Javier Cañueto. 2019. "MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092181
APA StyleGarcía-Sancha, N., Corchado-Cobos, R., Pérez-Losada, J., & Cañueto, J. (2019). MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092181