Identification and Functional Characterization of IDS Gene Mutations Underlying Taiwanese Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II)
Abstract
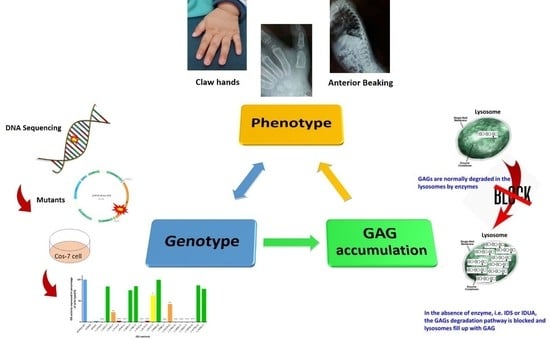
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Mutations of the IDS Gene by Sequencing Analysis
2.2. The IDS Activity in Extracts of COS-7 Cells Expressing Novel Mutant cDNA
2.3. The Quantitative Analysis of Urinary GAG-Derived Disaccharides by Liquid Chromatography /Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. DNA Isolation, Amplification, and Sequencing
4.3. Constructing Mutant DNA by Site-Directed Mutagenesis
4.4. Cell Culture and Transient Transfection
4.5. Enzyme Assay for MPS II
4.6. The Quantification of uGAG-Derived Disaccharides by Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay
4.7. MPS II Phenotype Determination
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Besley, G.T.N.; Wraith, J.E. Lysosomal disorders. Curr. Paediatr. 1997, 7, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wraith, J.E. Mucopolysaccharidoses. Curr. Paediatr. 1996, 6, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, E.; Muenzer, J. The mucopolysaccharidoses. In Scriver’s Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease; Valle, D., Beaudet, A., Vogelstein, B., Kinzler, K., Antonarakis, S., Ballabio, A., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 2465–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chuang, C.K.; Chen, M.R.; Chiu, P.C.; Ke, Y.Y.; Niu, D.M.; Tsai, F.J.; Hwu, W.L.; Lin, J.L.; Lin, S.P. Natural history and clinical assessment of Taiwanese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis IVA. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.H.; Hwang, H.Z.; Song, S.M.; Paik, K.H.; Kwon, E.K.; Moon, K.B.; Yoon, J.H.; Han, C.K.; Jin, D.K. Mutational spectrum of the iduronate 2 sulfatase gene in 25 unrelated Korean Hunter syndrome patients: Identification of 13 novel mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Kato, Z.; Kuratsubo, I.; Tanaka, N.; Ishigami, T.; Kajihara, J.; Sukegawa-Hayasaka, K.; Orii, K.; Isogai, K.; Fukao, T.; et al. Mutational and structural analysis of Japanese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 50, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lin, S.P.; Chuang, C.K.; Niu, D.M.; Chen, M.R.; Tsai, F.J.; Chao, M.C.; Chiu, P.C.; Lin, S.J.; Tsai, L.P.; et al. Incidence of the mucopolysaccharidoses in Taiwan, 1984–2004. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2009, 149, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Peracha, H.; Ballhausen, D.; Wiesbauer, A.; Rohrbach, M.; Gautschi, M.; Mason, R.W.; Giugliani, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.E.; et al. Epidemiology of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 121, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.J.; Meaney, C.A.; Hopwood, J.J.; Morris, C.P. Sequence of the human iduronate 2-sulfatase (IDS.) gene. Genomics 1993, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, K.M.; Lu, F.; Shen, Y.; Pierson, C.A.; Muzny, D.M.; Gu, Y.; Nelson, D.L.; Gibbs, R.A. 130 kb of DNA sequence reveals 2 new genes and a regional duplication distal to the human iduronate-2-sulfate sulfatase locus. Genome Res. 1995, 5, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birot, A.M.; Bouton, O.; Froissart, R.; Maire, I.; Bozon, D. IDS Gene-pseudogene exchange responsible for an intragenic deletion in a Hunter patient. Hum. Mutat. 1996, 8, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, M.L.; Malmgren, H.; Dahl, N.; Carlberg, B.M.; Pettersson, U. Presence of an IDS-related locus (IDS2) in Xq28 complicates the mutational analysis of Hunter syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 3, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.J.; Morris, C.P.; Anson, D.S.; Occhiodoro, T.; Bielicki, J.; Clements, P.R.; Hopwood, J.J. Hunter syndrome: Isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8531–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wraith, J.E.; Scarpa, M.; Beck, M.; Bodamer, O.A.; De Meirleir, L.; Guffon, N.; Meldgaard Lund, A.; Malm, G.; Van der Ploeg, A.T.; Zeman, J. Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome): A clinical review and recommendations for treatment in the era of enzyme replacement therapy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cudry, S.; Tigaud, I.; Froissart, R.; Bonnet, V.; Maire, I.; Bozon, D. MPS II in females: Molecular basis of two different cases. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 37, E29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollard, L.M.; Jones, J.R.; Wood, T.C. Molecular characterization of 355 mucopolysaccharidosis patients reveals 104 novel mutations. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Lin, S.P.; Lin, S.C.; Tseng, K.L.; Li, C.L.; Chuang, C.K.; Lee-Chen, G.J. Expression studies of mutations underlying Taiwanese Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II). Hum. Genet. 2005, 116, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, M.; Bunge, S.; Beck, M.; Kresse, H.; Tylki-Szymanska, A.; Gal, A. Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome): Mutation hot spots in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Rathmann, M.; Bunge, S.; Steglich, C.; Schwinger, E.; Gal, A. Evidence for an iduronate-sulfatase pseudogene near the functional Hunter syndrome gene in Xq27.3-q28. Hum. Genet. 1995, 95, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.; Mangas, M.; Prata, M.J.; Ribeiro, G.; Lopes, L.; Ribeiro, H.; Pinto-Basto, J.; Lima, M.R.; Lacerda, L. Molecular characterization of Portuguese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II shows evidence that the IDS gene is prone to splicing mutations. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeratichamroen, S.; Cairns, J.R.; Wattanasirichaigoon, D.; Wasant, P.; Ngiwsara, L.; Suwannarat, P.; Pangkanon, S.; Kuptanon, J.; Tanpaiboon, P.; Rujirawat, T.; et al. Molecular analysis of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in Thai patients with Hunter syndrome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31, S303–S311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafiadaki, E.; Cooper, A.; Heptinstall, L.E.; Hatton, C.E.; Thornley, M.; Wraith, J.E. Mutation analysis in 57 unrelated patients with MPS II (Hunter’s disease). Arch. Dis. Child. 1998, 79, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Kuzenkova, L.M.; Savost’anov, K.V.; Gevorkyan, A.K.; Pushkov, A.A.; Nikitin, A.G.; Vashakmadze, N.D.; Zhurkova, N.V.; Podkletnova, T.V.; Namazova-Baranova, L.S.; et al. Genetic analysis of 17 children with Hunter syndrome: Identification and functional characterization of four novel mutations in the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. J. Genet. Genom. 2014, 41, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosuga, M.; Mashima, R.; Hirakiyama, A.; Fuji, N.; Kumagai, T.; Seo, J.H.; Nikaido, M.; Saito, S.; Ohno, K.; Sakuraba, H.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of 65 families with mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome) characterized by 16 novel mutations in the IDS gene: Genetic, pathological, and structural studies on iduronate-2-sulfatase. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 118, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flomen, R.H.; Green, P.M.; Bentley, D.R.; Giannelli, F.; Green, E.P. Detection of point mutations and a gross deletion in six Hunter syndrome patients. Genomics 1992, 13, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollebregt, A.A.M.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; Kroos, M.A.; Oussoren, E.; Plug, I.; Ruijter, G.J.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; Pijnappel, W.W.M.P. Genotype-phenotype relationship in mucopolysaccharidosis II: Predictive power of IDS variants for the neuronopathic phenotype. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2017, 59, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froissart, R.; Maire, I.; Millat, G.; Cudry, S.; Birot, A.M.; Bonnet, V.; Bouton, O.; Bozon, D. Identification of iduronate sulfatase gene alterations in 70 unrelated Hunter patients. Clin. Genet. 1998, 53, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, A.; D’Avanzo, F.; Rigon, L.; Rampazzo, A.; Concolino, D.; Barone, R.; Volpi, N.; Santoro, L.; Lualdi, S.; Bertola, F.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of patients affected by mucopolysaccharidosis: A multicenter study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, P.L.; Braun, S.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Whitley, C.B. Mutation R468W of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in mild Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type II) confirmed by in vitro mutagenesis and expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1992, 1, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, C.B.; Anderson, R.A.; Aronovich, E.L.; Crotty, P.L.; Anyane-Yeboa, K.; Russo, D.; Warburton, D. Caveat to genotype-phenotype correlation in mucopolysaccharidosis type II: Discordant clinical severity of R468W and R468Q mutations of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene. Hum. Mutat. 1993, 2, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, W.; Wulff, K.; Wehnert, M.; Seidlitz, G.; Herrmann, F.H. Mutations of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS.) gene in patients with Hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis II). Hum. Mutat. 1994, 4, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhzouz, C.; Lazea, C.; Bucerzan, S.; Nascu, I.; Kiss, E.; Denes, C.L.; Grigorescu-Sido, P. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Romanian Patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. JIMD Rep. 2017, 33, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lualdi, S.; Di Rocco, M.; Corsolini, F.; Spada, M.; Bembi, B.; Cotugno, G.; Battini, R.; Stroppiano, M.; Gabriela Pittis, M.; Filocamo, M. Identification of nine new IDS alleles in mucopolysaccharidosis II. Quantitative evaluation by real-time RT-PCR of mRNAs sensitive to nonsense-mediated and nonstop decay mechanisms. Biochim. Acta 2006, 1762, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lissens, W.; Seneca, S.; Liebaers, I. Molecular analysis in 23 Hunter disease families. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1997, 20, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Bellows, A.B.; Thompson, J.N. Molecular basis of iduronate-2-sulphatase gene mutations in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome). J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uttarilli, A.; Ranganath, P.; Matta, D.; Md Nurul Jain, J.; Prasad, K.; Babu, A.S.; Girisha, K.M.; Verma, I.C.; Phadke, S.R.; Mandal, K.; et al. Identification and characterization of 20 novel pathogenic variants in 60 unrelated Indian patients with mucopolysaccharidoses type I and type II. Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Ye, J.; Han, L.; Gao, X.; Gu, X. Analysis of the IDS gene in 38 patients with Hunter syndrome: The c.879G>A (p.Gln293Gln) synonymous variation in a female create exonic splicing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagerstedt, K.; Karsten, S.L.; Carlberg, B.M.; Kleijer, W.J.; Tönnesen, T.; Pettersson, U.; Bondeson, M.L. Double-strand breaks may initiate the inversion mutation causing the Hunter syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tajima, G.; Sakura, N.; Kosuga, M.; Okuyama, T.; Kobayashi, M. Effects of idursulfase enzyme replacement therapy for Mucopolysaccharidosis type II when started in early infancy: Comparison in two siblings. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2013, 108, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.K.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Chan, M.J.; Liao, H.C.; Lo, Y.T.; Wang, L.Y.; Tu, R.Y.; Fang, Y.Y.; et al. Status of newborn screening and follow up investigations for Mucopolysaccharidoses I and II in Taiwan. Orphanet J. Rare. Dis 2018, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lee, C.L.; Lo, Y.T.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, T.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Niu, D.M.; Chuang, C.K.; Lin, S.P. The relationships between urinary glycosaminoglycan levels and phenotypes of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, R.; Pellico, A.; Pittalà, A.; Gasperini, S. Neurobehavioral phenotypes of neuronopathic mucopolysaccharidoses. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karsten, S.; Voskoboeva, E.; Tishkanina, S.; Pettersson, U.; Krasnopolskaja, X.; Bondeson, M.L. Mutational spectrum of the iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS.) gene in 36 unrelated Russian MPS II patients. Hum. Genet. 1998, 103, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonuccelli, G.; Di Natale, P.; Corsolini, F.; Villani, G.; Regis, S.; Filocamo, M. The effect of four mutations on the expression of iduronate-2-sulfatase in mucopolysaccharidosis type II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1537, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gort, L.; Chabás, A.; Coll, M.J. Hunter disease in the Spanish population: Molecular analysis in 31 families. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1998, 21, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, J.J.; Bunge, S.; Morris, C.P.; Wilson, P.J.; Steglich, C.; Beck, M.; Schwinger, E.; Gal, A. Molecular basis of mucopolysaccharidosis type II: Mutations in the iduronate-2-sulphatase gene. Hum. Mutat. 1993, 2, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voznyi, Y.V.; Keulemans, J.L.; van Diggelen, O.P. A fluorimetric enzyme assay for the diagnosis of MPS II (Hunter disease). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2001, 24, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; Filocamo, M.; Regis, S.; Corsolini, F.; Stroppiano, M.; Duca, M.D.; Gatti, R. Expression studies of two novel in CIS-mutations identified in an intermediate case of Hunter syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 120, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auray-Blais, C.; Bhérer, P.; Gagnon, R.; Young, S.P.; Zhang, H.H.; An, Y.; Clarke, J.T.; Millington, D.S. Efficient analysis of urinary glycosaminoglycans by LC-MS/MS in mucopolysaccharidoses type I., II and VI. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 102, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubaski, F.; Osago, H.; Mason, R.W.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Tsuchiya, M.; Orii, T.; Tomatsu, S. Glycosaminoglycans detection methods: Applications of mass spectrometry. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, C.K.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Liu, H.L.; Lin, S.P. A modified liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for predominant disaccharide units of urinary glycosaminoglycans in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Orphanet J. Rare. Dis 2014, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lo, Y.T.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, S.F.; Tu, R.Y.; Chen, T.L.; Lin, S.P.; Chuang, C.K. Normalization of glycosaminoglycan-derived disaccharides detected by tandem mass spectrometry assay for the diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, E.G.; Escolar, M.L.; Delaney, K.A.; Mitchell, J.J. Assessments of neurocognitive and behavioral function in the mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122S, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| No. | Missense Nucleotide Alteration | Protein Alteration | Gene Location | Phenotype Severity | IDS Activity | uGAG Tests | Known/ Novel | ACMG Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | c.137A>C | p.D46A | Exon 2 | S | 0.1 | Positive | Known [16] | |
| 2 | c.142C>T | p.R48C | Exon 2 | #NBS | 16.27 | Negative | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 3 | c.189T>G | p.N63K | Exon 2 | S | 0.21 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 4 | c.253 G>A | p.A85T | Exon 3 | A | 0.00 | Positive | Known [17,18] | |
| 5 | c.254C>T | p.A85V | Exon 3 | #NBS | 0.83 | Positive | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 6 | c.262C>T | p.R88C | Exon 3 | S | 0.43 | Positive | Known [17,19,20] | |
| 7 | c.301C>T | p.R101C | Exon 3 | #NBS | 15.4-40.8 | Negative | Known [21] | Benign |
| 8 | c.311A>T | p.D104V | Exon 3 | #NBS | 0.32 | Positive | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 9 | c.413A>G | p.H138R | Exon 3 | S | 0.18 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 10 | c.454A>C | p.S152R | Exon 4 | S | 0.11 | Positive | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 11 | c.589C>T | p.P197S | Exon 5 | #NBS | 7.8 | Negative | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 12 | c.683C>T | p.P228L | Exon 5 | A | 0.56 | Positive | Known [17,22] | |
| 13 | c.697A>G | p.R233G | Exon 5 | A | 0.71 | Positive | Known [20] | |
| 14 | c.778C>T | p.P260S | Exon 6 | #NBS | 6.47 | Negative | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 15 | c.797C>G | p.P266R | Exon 6 | A | 1.96 | Positive | Known [22] | |
| 16 | c.801 G>T | p.W267C | Exon 6 | A | 0.89 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 17 | c.817C>T | p.R273W | Exon 6 | #NBS | 0.2 | Positive | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 18 | c.851C>T | p.P284L | Exon 6 | #NBS (A) | 0.51 | Negative | Known [24] | Uncertain Significance |
| 19 | c.890G>A | p.R297H | Exon 7 | #NBS | 9.2 | Negative | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 20 | c.998C>T | p.S333L | Exon 7 | S | 0.34 | Positive | Known [25,26] | |
| 21 | c.1025A>G | p.H342R | Exon 8 | #NBS | 0.4 | Positive | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 22 | c.1039A>G | p.K347E | Exon 8 | S | 0.49 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 23 | c.1400C>T | p.P467L | Exon 9 | #NBS | 0.27 | Positive | Known [27,28] | Likely Pathogenic |
| 24 | c.1402C>T | p.R468W | Exon 9 | S | 0.04 | Positive | Known [17,29] | |
| 25 | c.1403G>A | p.R468Q | Exon 9 | S | 0.00 | Positive | Known [17,21,30] | |
| 26 | c.1454T>G | p.I485R | Exon 9 | S | 0.16 | Positive | Known [17,31] | |
| 27 | c.1466G>A | p.G489D | Exon 9 | S | 0.11 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 28 | c.1478G>A | p.R493H | Exon 9 | #NBS | 8.82–124.91 | Negative | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 29 | c.1478G>C | p.R493P | Exon 9 | S | 0.13 | Positive | Known [16,28] | |
| 30 | c.1499C>T | p.T500I | Exon 9 | #NBS | 13.2–34.5 | Negative | Novel | Benign |
| 31 | c.1513T>C | p.P505L | Exon 9 | #NBS | 5.93 | Negative | Novel | Likely Pathogenic |
| 32 | c.1600A>C | p.N534H | Exon 9 | A | 1.09 | Positive | Known [32] | |
| Nonsense | ||||||||
| 1 | c.801G>A | p.W267X | Exon 6 | S | 0.15 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 2 | c.1106C>G | p.S369X | Exon 7 | A | 0.1 | Positive | Known [33] | |
| 3 | c.1561G>T | p.E521X | Exon 9 | S | 0.24 | Positive | Known [17,34] | |
| Silent | ||||||||
| 1 | c.684A>G | p.Pro228 = | Exon 5 | #NBS | NA | NA | Novel | Benign |
| 2 | c.1122 C>T | p.Gly374 = | Exon 8 | A | 0.34–7.1 | Positive | Known [20] | |
| Splicing | ||||||||
| 1 | c.103 + 34_56dup | Intron 1 | #NBS | 0.56–14.69 | Negative | Novel | Uncertain Significance | |
| 2 | c.240 + 1G>C | False splicing; deletion of 105 AAs | Intron 2 | S | 0.68 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 3 | c.708 + 2T>G | − | Intron 5 | S | 0.48 | Positive | Known [22] | |
| 4 | c.880-2A>T | − | Intron 7 | A | 0.75 | Positive | Novel | Pathogenic |
| 5 | c.1006 + 5G>C | Splicing in 22 nucleotide | Intron 7 | A | 0.05 | Positive | Known [35] | |
| 6 | c.1180 + 184T>C | − | Intron 8 | #NBS | NA | NA | Novel | |
| Small Deletions | ||||||||
| 1 | c.231_236delCTTTGC | Loss of F78 and A79 | Exon 2 | S | 0.12 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 2 | c.1055del12 | Loss of V353-H356 | Exon 8 | S | 0.25 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 3 | c.1184delG | Frame shift, 44 altered AAs, term | Exon 9 | S | 0.19 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| 4 | c.1421delAG | Frame shift, 7 altered AAs, term | Exon 9 | S | 0.34 | Positive | Known [17] | |
| Gross deletions | ||||||||
| 1 | Exon 4–7 deletion | NA | A | 0.3 | Positive | Known [11] | ||
| 2. | c.1007-1666_c.1180 + 2113 delinsTT | NA | #NBS | 0.99 | Positive | Known [36,37] | Pathogenic | |
| 3 | Exon 8 deletion | NA | A | 0.64 | Positive | Known [37] | ||
| Complex Rearrangements | ||||||||
| 1 | IDS inversion | NA | A | 0.13–1.54 | Positive | Known [38,39] |
| No. | Missense Nucleotide Alteration/Protein Alteration | Ages (Ms) of the Test | Ages (Yrs) at last Follow up | (a)Leukocyte IDS Activity | (b)uGAG Tests | DMB/Cre Ratio | uDS (μg/mL) | uHS (μg/mL) | ACMG Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | c.142C>T; p.R48C | 1.7 | 0.3 | 16.27 | Negative | 38.73 | 0.01 | 0.75 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 2 | c.254C>T; p.A85V | 4.6 | 0.5 | 0.83 | Positive | 78.58 | 11.59 | 12.36 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 3 | c.301C>T; p.R101C | 1.7 | 3.4 | 15.4–40.8 | Negative | 5.07 | 0.2 | 0.13 | Benign |
| 4 | c.311A>T; p.D104V | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.32 | Positive | 44.6 | 45.95 | 11.43 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 5 | c.589C>T; p.P197S | 1.9 | 3 | 7.80 | Negative | 63.82 | 0.38 | 1.46 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 6 | c.778C>T; p.P260S | 2.3 | 1 | 6.47 | Negative | 12.29 | 0.12 | 0.1 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 7 | c.817C>T; p.R273W | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.20 | Positive | 65.06 | 15.78 | 16.23 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 8 | c.851C>T; p.P284L | 1.8 | 1.3 | 0.51 | Negative | 34.22 | 0.03 | 0.08 | Uncertain Significance |
| 9 | c.890G>A; p.R297H | 3 | 0.5 | 9.20 | Negative | 69.67 | 0.08 | 0.04 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 10 | c.1025A>G; p.H342R | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0.40 | Positive | 70.90 | 21.21 | 12.06 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 11 | c.1400C>T; p.P467L | 1.9 | 0.7 | 0.27 | Positive | 153.16 | 21.4 | 30.01 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 12 | c.1478G>A; p.R493H | 1.6 | 3.2 | 26.37 ± 10.98 | Negative | 40.18 | 0.04 | 0.09 | Likely Pathogenic |
| 13 | c.1499C>T; p.T500I | 1.6 | 1.9 | 17.15 ± 3.69 | Negative | 26.11 | 0.1 | 0.27 | Benign |
| 14 | c.1513T>C; p.P505L | 1.4 | 0.5 | 5.93 | Negative | 32.15 | 0.08 | 0.11 | Likely Pathogenic |
| Splicing | |||||||||
| 15 | * c.103 + 34_56dup | 1.1 | 3.8 | 3.86 ± 2.24 | Negative | 41.15 | 0.06 | 0.11 | Uncertain Significance |
| 16 | c.1180 + 184T>C | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Gross Deletions | |||||||||
| 17 | c.1007-1666_c.1180 + 2113 delinsTT (including exon 8 del) | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.99 | Positive | 177.96 | 30.77 | 203.35 | Pathogenic |
| Complex Rearrangement | |||||||||
| 18 | IDS inversion | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.13 | Positive | 44.05 | 8.72 | 37.30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-Y.; Tu, R.-Y.; Chern, S.-R.; Lo, Y.-T.; Fran, S.; Wei, F.-J.; Huang, S.-F.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-L.; et al. Identification and Functional Characterization of IDS Gene Mutations Underlying Taiwanese Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010114
Lin H-Y, Tu R-Y, Chern S-R, Lo Y-T, Fran S, Wei F-J, Huang S-F, Tsai S-Y, Chang Y-H, Lee C-L, et al. Identification and Functional Characterization of IDS Gene Mutations Underlying Taiwanese Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Hsiang-Yu, Ru-Yi Tu, Schu-Rern Chern, Yun-Ting Lo, Sisca Fran, Fang-Jie Wei, Sung-Fa Huang, Shin-Yu Tsai, Ya-Hui Chang, Chung-Lin Lee, and et al. 2020. "Identification and Functional Characterization of IDS Gene Mutations Underlying Taiwanese Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010114
APA StyleLin, H. -Y., Tu, R. -Y., Chern, S. -R., Lo, Y. -T., Fran, S., Wei, F. -J., Huang, S. -F., Tsai, S. -Y., Chang, Y. -H., Lee, C. -L., Lin, S. -P., & Chuang, C. -K. (2020). Identification and Functional Characterization of IDS Gene Mutations Underlying Taiwanese Hunter Syndrome (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010114