Resveratrol Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Prevents Mitochondrial Damage Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Resveratrol Protects Zebrafish Embryos form ZnO NP-Induced Mortality
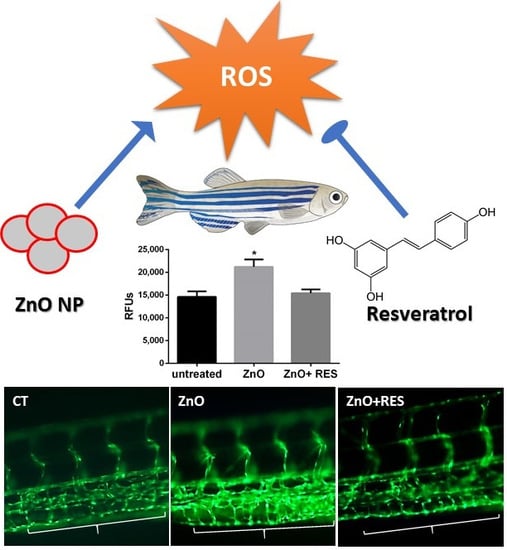
2.2. Resveratrol Decreases ZnO NP-Induced Pro-Oxidant Effect
2.3. Resveratrol Counteracts ZnO NP-Induced Mitochondrial Damage
2.4. Resveratrol Prevents ZnO NP-Induced Apoptosis and Necrosis
2.5. Resveratrol Counteracts Cardiac Vascular Modifications and Function Induced by ZnO NP
2.6. Resveratrol Ameliorates Morphological Vascular Modifications Induced by ZnO NPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. NPs Suspension Preparation
3.3. Zebrafish Husbandry
3.4. Acute Toxicity Assays
3.5. Zebrafish Embryo Imaging and Cardiotoxicity Assay
3.6. ROS Measurement
3.7. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm) Measurement
3.8. Apoptosis and Necrosis Determination
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasan, S. A review on nanoparticles: Their synthesis and types. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2015, 2277, 2502. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, P.; Von der Kammer, F.; Baalousha, M.; Hofmann, T. Nanoparticles: Structure, properties, preparation and behaviour in environmental media. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 326–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmond, M.J.; McCall, M.J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles in modern sunscreens: An analysis of potential exposure and hazard. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, O.; Juganson, K.; Ivask, A.; Kasemets, K.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to selected environmentally relevant test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: A critical review. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandebriel, R.J.; De Jong, W.H. A review of mammalian toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, L.; Shin, S.; Burnett, R.T.; Kwong, J.C.; Hystad, P.; van Donkelaar, A.; Goldberg, M.S.; Lavigne, E.; Copes, R.; Martin, R.V.; et al. Exposure to ambient air pollution and the incidence of congestive heart failure and acute myocardial infarction: A population-based study of 5.1 million Canadian adults living in Ontario. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzad, A.; Meyer, T.; Kleinsasser, N.; Hackenberg, S. Molecular mechanisms of Zinc Oxide nanoparticle-induced genotoxicity short running title: Genotoxicity of ZnO NPs. Materials 2017, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles impacts: Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, developmental toxicity, and neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.P.; Xia, Q.; Hwang, H.M.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanisms of nanotoxicity: Generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Bazhin, A.V.; Werner, J.; Karakhanova, S. Reactive oxygen species in the immune system. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 32, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Park, K. Oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory responses induced by silica nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 184, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limon-Pacheco, J.; Gonsebatt, M.E. The role of antioxidants and antioxidant-related enzymes in protective responses to environmentally induced oxidative stress. Mutat. Res. 2009, 674, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, P.; Ong, C.; Bay, B.H.; Baeg, G.H. Nanotoxicity: An interplay of oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1163–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saddick, S.; Afifi, M.; Abu Zinada, O.A. Effect of Zinc nanoparticles on oxidative stress-related genes and antioxidant enzymes activity in the brain of Oreochromis niloticus and Tilapia zillii. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Aydin, F.; Gurkan, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Ates, M.; Demir, V.; Arslan, Z. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on bioaccumulation and oxidative stress in different organs of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, H.; Nounou, H.; Shalaby, M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induced oxidative dna damage, inflammation and apoptosis in rat’s brain after oral exposure. Toxics 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkaladi, A. Vitamins E and C ameliorate the oxidative stresses induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles on liver and gills of Oreochromis niloticus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Iwahashi, H.; Endoh, S.; Nishio, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Hagihara, Y.; Horie, M. Ascorbic acid attenuates acute pulmonary oxidative stress and inflammation caused by zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Occup. Health 2015, 57, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Sil, P.C. Iron oxide nanoparticles mediated cytotoxicity via PI3K/AKT pathway: Role of quercetin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 71, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Esquivel, A.E.; Charles-Nino, C.L.; Pacheco-Moises, F.P.; Ortiz, G.G.; Jaramillo-Juarez, F.; Rincon-Sanchez, A.R. Beneficial effects of quercetin on oxidative stress in liver and kidney induced by titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonane, M.; Moin, N.; Satish, A. The role of antioxidants in attenuation of Caenorhabditis elegans lethality on exposure to TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant properties of resveratrol: A structure–activity insight. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Du, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, Q. Resveratrol ameliorates cadmium induced renal oxidative damage and inflammation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 7563–7572. [Google Scholar]
- Emsen, B.; Turkez, H. The protective role of resveratrol against zinc oxide induced nanotoxicity. Anatol. J. Bot. 2017, 1, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Eissa, I.A.M.; Abdeen, A.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Ismail, M.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Hassan, A.M. Lycopene and resveratrol ameliorate zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced oxidative stress in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 69, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Gen. 2007, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, G.K.; Zhang, Y.; Zagho, M.M.; Ismail, H.M.; Al-Khalaf, A.A.; Prieto, R.M.; Albinali, K.E.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Deng, Y. A systematic investigation of the bio-toxicity of core-shell magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres using zebrafish model. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 265, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaito, A.; Posadino, A.M.; Younes, N.; Hasan, H.; Halabi, S.; Alhababi, D.; Al-Mohannadi, A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Eid, A.H.; Nasrallah, G.K.; et al. Potential Adverse Effects of Resveratrol: A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liao, W.; Luo, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q. A review of cardiovascular toxicity of TiO2, ZnO and Ag nanoparticles (NPs). Biometals 2018, 31, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, S.; Awad, M.; Harrington, E.O.; Sellke, F.W.; Abid, M.R. Subcellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Cardiovascular Pathophysiology. Antioxidants 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, L.; Chen, L. Oxidative stress responses in different organs of carp (Cyprinus carpio) with exposure to ZnO nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Fang, T.; Yu, L.; Sima, X.; Zhu, W. Effects of nano-scale TiO2, ZnO and their bulk counterparts on zebrafish: Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and oxidative damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; You, H.; Lv, L. Acute ZnO nanoparticles exposure induces developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in embryo-larval zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136–137, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repossi, G.; Das, U.N.; Eynard, A.R. Molecular Basis of the Beneficial Actions of Resveratrol. Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Xia, T.; George, S.; Nel, A.E. A predictive toxicological paradigm for the safety assessment of nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, S.; Giorgi, C.; Suski, J.M.; Agnoletto, C.; Bononi, A.; Bonora, M.; De Marchi, E.; Missiroli, S.; Patergnani, S.; Poletti, F.; et al. Mitochondria-ros crosstalk in the control of cell death and aging. J. Signal. Transduct. 2012, 2012, 329635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Wu, L.Y.; Yang, W.X. Nanoparticles induce apoptosis via mediating diverse cellular pathways. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2939–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Anderson, D.; Dhawan, A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human liver cells (HepG2). Apoptosis 2012, 17, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-W.; Lee, C.-H.; Lin, M.-S.; Chi, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wang, G.-S.; Liao, K.-W.; Chiu, L.-P.; Wu, S.-H.; Huang, D.-M.; et al. ZnO Nanoparticles Induced Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Mitochondrial Dysfunction and p70S6K Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Sengupta, S.; Shukla, R.K.; Kumar, A. ZnO nanoparticles-associated mitochondrial stress-induced apoptosis and G2/M arrest in HaCaT cells: A mechanistic approach. Mutagenesis 2019, 34, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ren, X.; Zhu, R.; Luo, Z.; Ren, B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 180, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadino, A.M.; Cossu, A.; Giordo, R.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Vardeu, A.; Hoa, P.T.; Nguyen le, H.V.; Carru, C.; Pintus, G. Resveratrol alters human endothelial cells redox state and causes mitochondrial-dependent cell death. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadino, A.M.; Cossu, A.; Giordo, R.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Vardeu, A.; Hoa, P.T.; Deiana, L.; Carru, C.; Pintus, G. Coumaric acid induces mitochondrial damage and oxidative-mediated cell death of human endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2013, 13, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossu, A.; Posadino, A.M.; Giordo, R.; Emanueli, C.; Sanguinetti, A.M.; Piscopo, A.; Poiana, M.; Capobianco, G.; Piga, A.; Pintus, G. Apricot melanoidins prevent oxidative endothelial cell death by counteracting mitochondrial oxidation and membrane depolarization. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: Mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryter, S.W.; Kim, H.P.; Hoetzel, A.; Park, J.W.; Nakahira, K.; Wang, X.; Choi, A.M. Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 49–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hove, J.R.; Koster, R.W.; Forouhar, A.S.; Acevedo-Bolton, G.; Fraser, S.E.; Gharib, M. Intracardiac fluid forces are an essential epigenetic factor for embryonic cardiogenesis. Nature 2003, 421, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kteeba, S.M.; El-Ghobashy, A.E.; El-Adawi, H.I.; El-Rayis, O.A.; Sreevidya, V.S.; Guo, L.; Svoboda, K.R. Exposure to ZnO nanoparticles alters neuronal and vascular development in zebrafish: Acute and transgenerational effects mitigated with dissolved organic matter. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansode, R.R.; Ahmedna, M.; Svoboda, K.R.; Losso, J.N. Coupling in vitro and in vivo paradigm reveals a dose dependent inhibition of angiogenesis followed by initiation of autophagy by C6-ceramide. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, S.; Horiguchi, M.; Weinstein, B.M. The vascular anatomy of the developing zebrafish: An atlas of embryonic and early larval development. Dev. Biol. 2001, 230, 278–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tobia, C.; Gariano, G.; Guerra, J.; Presta, M. Zebrafish embryo intersegmental vessels: A tool for investigating sprouting angiogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1214, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, J.C.; Wiley, D.M.; Bautch, V.L. How blood vessel networks are made and measured. Cells Tissues Organs 2012, 195, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delov, V.; Muth-Köhne, E.; Schäfers, C.; Fenske, M. Transgenic fluorescent zebrafish Tg (fli1: EGFP) y1 for the identification of vasotoxicity within the zFET. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, N.; Salem, R.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Altamash, T.; Pintus, G.; Khraisheh, M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Toxicity evaluation of selected ionic liquid compounds on embryonic development of Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, G.K.; Salem, R.; Da’as, S.; Al-Jamal, O.L.A.; Scott, M.; Mustafa, I. Biocompatibility and toxicity of novel iron chelator Starch-Deferoxamine (S-DFO) compared to zinc oxide nanoparticles to zebrafish embryo: An oxidative stress based apoptosis, physicochemical and neurological study profile. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2019, 72, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranjali, P.; Meher, M.K.; Raj, R.; Prasad, N.; Poluri, K.M.; Kumar, D.; Guleria, A. Physicochemical and Antibacterial Properties of PEGylated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Dispersed in Peritoneal Dialysis Fluid. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 19255–19264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.T.; Yong, L.Q.; Hande, M.P.; Ong, C.N.; Yu, L.E.; Bay, B.H.; Baeg, G.H. Zinc oxide nanoparticles exhibit cytotoxicity and genotoxicity through oxidative stress responses in human lung fibroblasts and Drosophila melanogaster. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkheil, M.; Johari, S.A.; An, H.J.; Asghari, S.; Park, H.S.; Sohn, E.K.; Yu, I.J. Acute toxicity, uptake, and elimination of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using saltwater microcrustacean, Artemia franciscana. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 57, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenbrot, J.I.; Mehta, M.; Tserentsoodol, N.; Postlethwait, J.H.; Rebrik, T.I. EML1 (CNG-modulin) controls light sensitivity in darkness and under continuous illumination in zebrafish retinal cone photoreceptors. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 17763–17776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abou-Saleh, H.; Younes, N.; Rasool, K.; Younis, M.H.; Prieto, R.M.; Yassine, H.M.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Pintus, G.; Nasrallah, G.K. Impaired Liver Size and Compromised Neurobehavioral Activity are Elicited by Chitosan Nanoparticles in the Zebrafish Embryo Model. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younes, N.; Pintus, G.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Rasool, K.; Younes, S.; Calzolari, S.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Nasrallah, G.K. “Safe” chitosan/zinc oxide nanocomposite has minimal organ-specific toxicity in early stages of zebrafish development. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.A.; Zagho, M.M.; Rizeq, B.R.; Younes, N.N.; Pintus, G.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Elzatahry, A.A. Plasmonic MXene-based nanocomposites exhibiting photothermal therapeutic effects with lower acute toxicity than pure MXene. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Kandari, H.; Younes, N.; Al-Jamal, O.; Zakaria, Z.Z.; Najjar, H.; Alserr, F.; Pintus, G.; Al-Asmakh, M.A.; Abdullah, A.M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Ecotoxicological assessment of thermally-and hydrogen-reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 photocatalytic nanocomposites using the zebrafish embryo model. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posadino, A.M.; Giordo, R.; Cossu, A.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Shaito, A.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Eid, A.H.; Pintus, G. Flavin Oxidase-Induced ROS Generation Modulates PKC Biphasic Effect of Resveratrol on Endothelial Cell Survival. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fois, A.G.; Posadino, A.M.; Giordo, R.; Cossu, A.; Agouni, A.; Rizk, N.M.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A.; Pintus, G. Antioxidant activity mediates pirfenidone antifibrotic effects in human pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells exposed to sera of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2639081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasciu, V.; Posadino, A.M.; Cossu, A.; Sanna, B.; Tadolini, B.; Gaspa, L.; Marchisio, A.; Dessole, S.; Capobianco, G.; Pintus, G. Akt downregulation by flavin oxidase-induced ROS generation mediates dose-dependent endothelial cell damage elicited by natural antioxidants. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 114, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arbab, I.A.; Abdul, A.B.; Sukari, M.A.; Abdullah, R.; Syam, S.; Kamalidehghan, B.; Ibrahim, M.Y.; Taha, M.M.; Abdelwahab, S.I.; Ali, H.M.; et al. Dentatin isolated from Clausena excavata induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through the intrinsic pathway with involvement of NF-kappaB signalling and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest: A bioassay-guided approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackmann, C.; Santos, M.M.; Rainieri, S.; Barranco, A.; Hollert, H.; Spirhanzlova, P.; Velki, M.; Seiler, T.B. Novel procedures for whole organism detection and quantification of fluorescence as a measurement for oxidative stress in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasibhatla, S.; Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Finucane, D.; Brunner, T.; Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Green, D.R. Acridine Orange/Ethidium Bromide (AO/EB) staining to detect apoptosis. CSH Protoc. 2006, 2006, pdb.prot4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giordo, R.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Al-Jamal, O.; Paliogiannis, P.; Pintus, G. Resveratrol Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Prevents Mitochondrial Damage Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113838
Giordo R, Nasrallah GK, Al-Jamal O, Paliogiannis P, Pintus G. Resveratrol Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Prevents Mitochondrial Damage Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113838
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiordo, Roberta, Gheyath K. Nasrallah, Ola Al-Jamal, Panagiotis Paliogiannis, and Gianfranco Pintus. 2020. "Resveratrol Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Prevents Mitochondrial Damage Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113838
APA StyleGiordo, R., Nasrallah, G. K., Al-Jamal, O., Paliogiannis, P., & Pintus, G. (2020). Resveratrol Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Prevents Mitochondrial Damage Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113838