The Effect of Substituted Benzene-Sulfonamides and Clinically Licensed Drugs on the Catalytic Activity of CynT2, a Carbonic Anhydrase Crucial for Escherichia coli Life Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Production and Enzymatic Activity of the Target CynT2
2.2. CynT2 Sulfonamide Inhibition Profile
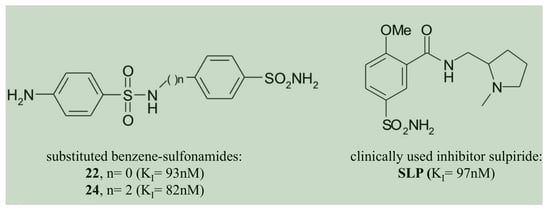
- The two homologous bacterial enzymes showed a sulfonamide inhibition pattern different from each other. In this context, it is relevant to note that the compounds 22, 24 and the clinically used inhibitor SLP were the best CynT2 inhibitors, showing a KI in the range of 82–97 nM. HTC is the only inhibitor in Table 2 that inhibited the bacterial VchCAβ with a KI = 87 nM. Exciting is the fact that the inhibitory behaviors of the two bacterial biocatalysts resulted in being highly distinct from those of the two human isoenzymes. The compound HTC inhibited the human isoforms, hCA I and h CAII, with a KI value of 290 and 328 nM, respectively. Even if it is challenging to identify selective inhibitors for the bacterial CAs, HTC represents a good example, resulting in medially 3.5 times more efficiently versus the VchCAβ than the human CAs. However, it is also true that HTC is a harmful inhibitor for the Escherichia coli enzyme (KI = 5.0 µM), being 57 times less effective. Other examples are the inhibitors 22, 24, and SLS, which are 8, 4, and 64 times less effective versus the Vibrio enzyme, respectively, or the inhibitors 13 and 14 with a KI = 68–82 nM are considered potent inhibitors of the Vibrio enzyme. All of these offer the possibility to investigate their molecular interaction with the three-dimensional structures of CynT2 and VchCAβ, identifying those structural factors responsible for the KI variations. This study allows the design of more efficient and selective inhibitors of the bacterial enzymes that worsen the KI when tested on the two human proteins.
- Among all the compounds investigated, 15 of them showed inhibition constants <1.0 μM for the CynT2. This is the case for compounds 1, 2, 3, 14, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 23, AAZ, MZA, EZA, DZA, BZA, and SLT. These compounds had the KI in the range of 0.2–0.79 μM. Interestingly, some of these CynT2 “strong inhibitors” were mild inhibitors of VchCAβ, such as 17, 19, 21, AAZ, MZA, EZA, and DZA with KI = 2.2–6.2 μM, and, vice versa, compounds 13 and 14 and the HTC compound mentioned above resulted in being more sensitive versus the Vibrio enzyme with a KI in the range of 68–87 nM.
- Several compounds of the series 1–24, such as 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, and 16, as well as inhibitors of the series AAZ–EPA, such as BRZ, TPM, IND, VLX, CLX, SAC, HTC, FAM, and EPA, had a moderate inhibitory effect on the CynT2 enzyme, showing a KI between 1.8 and 8.5 μM. Most of these inhibitors were efficient inhibitors of hCA II (KI = 3–917 nM) and weak inhibitors of the hCA I (KI = 5.8–78.5 μM), except for compound FAM (KI = 0.9 µM).
- Some CynT2 inhibitors showed a KI > 10 µM, such as compounds 7, 8, and DCP, which resulted in a weak inhibitory activity. The weakness inhibitors for the VchCAβ were 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10. As shown in Table 3, it is apparent that the human α-isoenzyme hCA II is efficiently inhibited by all these inhibitors (KI = 38–320 nM) and others with the KI in the range of 3–917 nM. The compound SAC represented the only exception having the KI = 5.9 µM. Remarkably, half of the compounds reported in Table 3 resulted in adverse inhibitors for the isoform hCA I. This confirms how important the amino acid surrounding the catalytic pocket is in the inhibition of the enzyme.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Instruments
3.2. Heterologous Expression and Purification of the Recombinant Enzyme
3.3. SDS–PAGE and Protonography
3.4. Kinetic Parameters and Inhibition Constants
4. Conclusions
- The compounds 22, 24, and the clinically used SLP were the best CynT2 inhibitors sowing a KI in the range of 82–97 nM;
- The inhibition profiles of the four proteins considered (CynT2, VchCAβ, hCA I, and hCA II) are rather different from each other.
- All the compounds showing a different behavior versus an enzyme belonging to the β- and α-class represent good candidates to identify, through the comparison of the three-dimensional structure of the protein with the inhibitor, the structural factors responsible for the KI variations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleischmann, R.D.; Adams, M.D.; White, O.; Clayton, R.A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Bult, C.J.; Tomb, J.F.; Dougherty, B.A.; Merrick, J.M.; et al. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science 1995, 269, 496–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraser, C.M.; Gocayne, J.D.; White, O.; Adams, M.D.; Clayton, R.A.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Bult, C.J.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Sutton, G.; Kelley, J.M.; et al. The minimal gene complement of Mycoplasma genitalium. Science 1995, 270, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostparast Torshizi, A.; Wang, K. Next-generation sequencing in drug development: Target identification and genetically stratified clinical trials. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M. A review of antimycobacterial drugs in development. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Selzer, P.M.; Brutsche, S.; Wiesner, P.; Schmid, P.; Mullner, H. Target-based drug discovery for the development of novel antiinfectives. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 290, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, E.J.; Burguener, G.; Lanzarotti, E.; Defelipe, L.; Radusky, L.; Pardo, A.M.; Marti, M.; Turjanski, A.G.; Fernandez Do Porto, D. Target-Pathogen: A structural bioinformatic approach to prioritize drug targets in pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D413–D418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchado, E.; Huang, C.H.; Tasdemir, N.; Tschaharganeh, D.F.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Lowe, S.W. A Pipeline for Drug Target Identification and Validation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2016, 81, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziato, G.; Angeli, A.; D’Alba, F.; Bruno, A.; Pieroni, M.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T.; Costantino, G. Discovery of New Potential Anti-Infective Compounds Based on Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors by Rational Target-Focused Repurposing Approaches. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1904–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozensoy Guler, O.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. A magnificent enzyme superfamily: Carbonic anhydrases, their purification and characterization. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Carginale, V.; Ferraroni, M.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Sulfonamide inhibition studies of the beta-carbonic anhydrase from the pathogenic bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, S.; De Luca, V.; De Simone, G.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Cloning, expression and purification of the complete domain of the eta-carbonic anhydrase from Plasmodium falciparum. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. An Overview of the Carbonic Anhydrases from Two Pathogens of the Oral Cavity: Streptococcus mutans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. An Overview of the Bacterial Carbonic Anhydrases. Metabolites 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. An overview of the alpha-, beta- and gamma-carbonic anhydrases from Bacteria: Can bacterial carbonic anhydrases shed new light on evolution of bacteria? J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Prete, S.; Nocentini, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Bacterial iota-carbonic anhydrase: A new active class of carbonic anhydrase identified in the genome of the Gram-negative bacterium Burkholderia territorii. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T. Advances in structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Inhibition of Bacterial Carbonic Anhydrases as a Novel Approach to Escape Drug Resistance. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T. How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist? J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, J.K.; Tikhomirova, A.; Gorrell, R.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Kotsanas, D.; Korman, T.M.; Garcia-Bustos, J.; Kwok, T.; Ferrero, R.L.; Supuran, C.T.; et al. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of ethoxzolamide. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronci, M.; Del Prete, S.; Puca, V.; Carradori, S.; Carginale, V.; Muraro, R.; Mincione, G.; Aceto, A.; Sisto, F.; Supuran, C.T.; et al. Identification and characterization of the alpha-CA in the outer membrane vesicles produced by Helicobacter pylori. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzas, G.M. Helicobacter pylori—2010. Orv. Hetil. 2010, 151, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuaita, B.H.; Withey, J.H. Bicarbonate Induces Vibrio cholerae virulence gene expression by enhancing ToxT activity. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4111–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohler, S.; Ouahrani-Bettache, S.; Winum, J.Y. Brucella suis carbonic anhydrases and their inhibitors: Towards alternative antibiotics? J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Supuran, C.T. 3D-QSAR CoMFA studies on sulfonamide inhibitors of the Rv3588c beta-carbonic anhydrase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and design of not yet synthesized new molecules. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceruso, M.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfonamides incorporating fluorine and 1,3,5-triazine moieties are effective inhibitors of three beta-class carbonic anhydrases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, F.; Maresca, A.; Covarrubias, A.S.; Mowbray, S.L.; Jones, T.A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Characterization and inhibition studies of the most active beta-carbonic anhydrase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Rv3588c. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6649–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollenhagen, C.; Bumann, D. Salmonella enterica highly expressed genes are disease specific. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lotlikar, S.R.; Kayastha, B.B.; Vullo, D.; Khanam, S.S.; Braga Reygan, E.; Murray, A.B.; McKenna, R.; Supuran, C.T.; Patrauchan, M.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa β-carbonic anhydrase, psCA1, is required for calcium deposition and contributes to virulence. Cell Calcium 2019, 84, 102080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfa and trimethoprim-like drugs—Antimetabolites acting as carbonic anhydrase, dihydropteroate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.L.; Clement, R.; Kosta, A.; Maberly, S.C.; Gontero, B. A new widespread subclass of carbonic anhydrase in marine phytoplankton. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2094–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikutani, S.; Nakajima, K.; Nagasato, C.; Tsuji, Y.; Miyatake, A.; Matsuda, Y. Thylakoid luminal theta-carbonic anhydrase critical for growth and photosynthesis in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9828–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Di Fiore, A.; D’Ambrosio, K.; Supuran, C.T.; De Simone, G. Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases: How to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4421–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Biomedical applications of prokaryotic carbonic anhydrases. Expert Opin. Pat. 2018, 28, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Carbonic Anhydrase from Porphyromonas Gingivalis as a Drug Target. Pathogens 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozensoy Guler, O.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Carbonic anhydrase IX as a novel candidate in liquid biopsy. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neri, D.; Supuran, C.T. Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. An Overview of the Selectivity and Efficiency of the Bacterial Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. New light on bacterial carbonic anhydrases phylogeny based on the analysis of signal peptide sequences. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Simone, G.; Monti, S.M.; Alterio, V.; Buonanno, M.; De Luca, V.; Rossi, M.; Carginale, V.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C.; Di Fiore, A. Crystal structure of the most catalytically effective carbonic anhydrase enzyme known, SazCA from the thermophilic bacterium Sulfurihydrogenibium azorense. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafeefy, A.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Vullo, D.; Al-Tamimi, A.M.; Al-Jaber, N.A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrases from the extremophilic bacteria Sulfurihydrogenibium yellostonense (SspCA) and S. azorense (SazCA) with a new series of sulfonamides incorporating aroylhydrazone-, [1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazinyl- or 2-(cyanophenylmethylene)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-3(2H)-yl moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Scozzafava, A.; Carginale, V.; Rossi, M.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. The extremo-alpha-carbonic anhydrase from the thermophilic bacterium Sulfurihydrogenibium azorense is highly inhibited by sulfonamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4521–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronk, J.D.; Endrizzi, J.A.; Cronk, M.R.; O’Neill, J.W.; Zhang, K.Y. Crystal structure of E. coli beta-carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme with an unusual pH-dependent activity. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, C.; Masters, M.; McAteer, S.; Coulson, A. Why is carbonic anhydrase essential to Escherichia coli? J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clermont, O.; Olier, M.; Hoede, C.; Diancourt, L.; Brisse, S.; Keroudean, M.; Glodt, J.; Picard, B.; Oswald, E.; Denamur, E. Animal and human pathogenic Escherichia coli strains share common genetic backgrounds. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, S.D.; Herbelin, C.J.; Bumbaugh, A.C.; Selander, R.K.; Whittam, T.S. Parallel evolution of virulence in pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nature 2000, 406, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szych, J.; Wolkowicz, T.; La Ragione, R.; Madajczak, G. Impact of antibiotics on the intestinal microbiota and on the treatment of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and Salmonella infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4535–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitout, J.D. Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A Combination of Virulence with Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriel, D.G.; Bertoldi, I.; Spagnuolo, A.; Marchi, S.; Rosini, R.; Nesta, B.; Pastorello, I.; Corea, V.A.; Torricelli, G.; Cartocci, E.; et al. Identification of protective and broadly conserved vaccine antigens from the genome of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9072–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agus, A.; Massier, S.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Billard, E.; Barnich, N. Understanding host-adherent-invasive Escherichia coli interaction in Crohn’s disease: Opening up new therapeutic strategies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 567929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozliak, E.I.; Guilloton, M.B.; Gerami-Nejad, M.; Fuchs, J.A.; Anderson, P.M. Expression of proteins encoded by the Escherichia coli cyn operon: Carbon dioxide-enhanced degradation of carbonic anhydrase. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 5711–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Luca, V.; Del Prete, S.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Protonography, a new technique for the analysis of carbonic anhydrase activity. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Carginale, V.; di Fonzo, P.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Anion inhibition profiles of alpha-, beta- and gamma-carbonic anhydrases from the pathogenic bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 3413–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.; Ahlawat, R. Famotidine. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534778/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Komiya, T.; Huang, C.H. Updates in the Clinical Development of Epacadostat and Other Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 Inhibitors (IDO1) for Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Carginale, V.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Comparison of the sulfonamide inhibition profiles of the alpha-, beta- and gamma-carbonic anhydrases from the pathogenic bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, A.; Ferraroni, M.; Supuran, C.T. Famotidine, an Antiulcer Agent, Strongly Inhibits Helicobacter pylori and Human Carbonic Anhydrases. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; Ghobril, C.; Hitce, J.; Clavaud, C.; Marat, X.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Cloning, Purification, and Characterization of a beta-Carbonic Anhydrase from Malassezia restricta, an Opportunistic Pathogen Involved in Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, C.; De Luca, V.; Carginale, V.; Cannio, R.; Rossi, M. Biochemical properties of a novel and highly thermostable bacterial alpha-carbonic anhydrase from Sulfurihydrogenibium yellowstonense YO3AOP1. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; De Luca, V.; Iandolo, E.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Protonography, a powerful tool for analyzing the activity and the oligomeric state of the gamma-carbonic anhydrase identified in the genome of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3747–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; De Luca, V.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Protonography, a technique applicable for the analysis of eta-carbonic anhydrase activity. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; Caminiti-Segonds, N.; Zoccola, D.; Tambutte, S.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Protonography and anion inhibition profile of the alpha-carbonic anhydrase (CruCA4) identified in the Mediterranean red coral Corallium rubrum. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifah, R.G. The carbon dioxide hydration activity of carbonic anhydrase. I. Stop-flow kinetic studies on the native human isoenzymes B and C. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Carginale, V.; di Fonzo, P.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Anion inhibition profiles of the complete domain of the eta-carbonic anhydrase from Plasmodium falciparum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4410–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, V.; Vullo, D.; Del Prete, S.; Carginale, V.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Cloning, characterization and anion inhibition studies of a gamma-carbonic anhydrase from the Antarctic bacterium Colwellia psychrerythraea. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Organism | Acronym | Class | 1 kcat (s−1) | 1 kcat/Km (M−1 × s−1) | 1 KI (Acetazolamide) (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiensa | hCA I | α | 2.0 × 105 | 5.0 × 107 | 250 |
| hCA II | α | 1.4 × 106 | 1.5 × 108 | 12 | |
| Vibrio choleraea | VchCAα | α | 8.2 × 105 | 7.0 × 107 | 6.8 |
| Escherichia coli | CynT2 | β | 5.3 × 105 | 4.1 × 107 | 227 |
| Vibrio choleraea | VchCAβ | β | 3.3 × 105 | 4.1 × 107 | 451 |
| Porphyromonas gingivalisb | PgiCAβ | β | 2.8 × 105 | 1.5 × 107 | 214 |
| Helicobacter pyloric | HpyCAβ | β | 7.1 × 105 | 4.8 × 107 | 40 |
| Porphyromonas gingivalisb | PgiCAγ | γ | 4.1 × 105 | 5.4 × 107 | 324 |
| Vibrio choleraea | VchCAγ | γ | 7.3 × 105 | 6.4 × 107 | 473 |
| Burkholderia territoriid | BteCAι | ι | 3.0 × 105 | 9.7 × 107 | 65 |
| Inhibitor Name | Trade Name | Acronym | Clinical Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetazolamide | Diamox | AAZ | glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, diuretic |
| Methazolamide | Neptazane | MZA | glaucoma |
| Ethoxzolamide | Cadrase | EZA | glaucoma, duodenal ulcers, diuretic |
| Dichlorophenamide | Keveyis | DCP | glaucoma, diuretic |
| Dorzolamide | Trusopt | DZA | glaucoma |
| Brinzolamide | Azopt | BRZ | glaucoma |
| Benzolamide | No generic name | BZA | glaucoma |
| Topiramate | Topamax | TMP | epilepsy, migraine |
| Zonisamide | Zonegran | ZNS | epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, migraine, bipolar depression |
| Sulpiride | Dogmatil | SLP | psychosis, schizophrenia, anxiety, mild depression |
| Indisulam | No generic name | IND | cancer |
| Valdecoxib | Bextra | VLX | osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, painful menstruation, menstrual symptoms |
| Celecoxib | Celebrex | CLX | osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, painful menstruation, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis |
| Sulthiame | Ospolot | SLT | epilepsy |
| Saccharin | No generic name | SAC | diet |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | CAPOZIDE | HCT | hypertension, congestive heart failure, symptomatic edema, diabetes insipidus, renal tubular acidosis |
| Famotidine | Pepcid | FAM | peptic ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux disease, |
| Epacadostat | No generic name | EPA | cancer |
| Inhibitor | KI *(nM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hCA I a | hCA II a | CynT2 | VchCAβ a | |
| 1 | 28,000 | 300 | 705 | 463 |
| 2 | 25,000 | 240 | 790 | 447 |
| 3 | 79 | 8 | 457 | 785 |
| 4 | 78,500 | 320 | 3015 | >10,000 |
| 5 | 25000 | 170 | 2840 | >10,000 |
| 6 | 21,000 | 160 | 3321 | >10,000 |
| 7 | 8300 | 60 | >10,000 | >10,000 |
| 8 | 9800 | 110 | >10,000 | 9120 |
| 9 | 6500 | 40 | 2712 | >10,000 |
| 10 | 7300 | 54 | 8561 | >10,000 |
| 11 | 5800 | 63 | 6246 | 879 |
| 12 | 8400 | 75 | 4385 | 4450 |
| 13 | 8600 | 60 | 4122 | 68,1 |
| 14 | 9300 | 19 | 440 | 82,3 |
| 15 | 5500 | 80 | 6445 | 349 |
| 16 | 9500 | 94 | 2340 | 304 |
| 17 | 21,000 | 125 | 502 | 3530 |
| 18 | 164 | 46 | 205 | 515 |
| 19 | 109 | 33 | 416 | 2218 |
| 20 | 6 | 2 | 726 | 859 |
| 21 | 69 | 11 | 473 | 4430 |
| 22 | 164 | 46 | 93 | 757 |
| 23 | 109 | 33 | 322 | 817 |
| 24 | 95 | 30 | 82 | 361 |
| AAZ | 250 | 12 | 227 | 4512 |
| MZA | 50 | 14 | 480 | 6260 |
| EZA | 25 | 8 | 557 | 6450 |
| DCP | 1200 | 38 | >10,000 | 2352 |
| DZA | 50,000 | 9 | 629 | 4728 |
| BRZ | 45,000 | 3 | 2048 | 845 |
| BZA | 15 | 9 | 276 | 846 |
| TPM | 250 | 10 | 3359 | 874 |
| ZNS | 56 | 35 | 3189 | 8570 |
| SLP | 1200 | 40 | 97 | 6245 |
| IND | 31 | 15 | 2392 | 7700 |
| VLX | 54,000 | 43 | 2752 | 8200 |
| CLX | 50,000 | 21 | 1894 | 4165 |
| SLT | 374 | 9 | 285 | 455 |
| SAC | 18,540 | 5959 | 6693 | 275 |
| HCT | 328 | 290 | 5010 | 87 |
| FAM | 922 | 58 | 2769 | - |
| EPA | 8262 | 917 | 2560 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Prete, S.; De Luca, V.; Bua, S.; Nocentini, A.; Carginale, V.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. The Effect of Substituted Benzene-Sulfonamides and Clinically Licensed Drugs on the Catalytic Activity of CynT2, a Carbonic Anhydrase Crucial for Escherichia coli Life Cycle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114175
Del Prete S, De Luca V, Bua S, Nocentini A, Carginale V, Supuran CT, Capasso C. The Effect of Substituted Benzene-Sulfonamides and Clinically Licensed Drugs on the Catalytic Activity of CynT2, a Carbonic Anhydrase Crucial for Escherichia coli Life Cycle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114175
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Prete, Sonia, Viviana De Luca, Silvia Bua, Alessio Nocentini, Vincenzo Carginale, Claudiu T. Supuran, and Clemente Capasso. 2020. "The Effect of Substituted Benzene-Sulfonamides and Clinically Licensed Drugs on the Catalytic Activity of CynT2, a Carbonic Anhydrase Crucial for Escherichia coli Life Cycle" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114175
APA StyleDel Prete, S., De Luca, V., Bua, S., Nocentini, A., Carginale, V., Supuran, C. T., & Capasso, C. (2020). The Effect of Substituted Benzene-Sulfonamides and Clinically Licensed Drugs on the Catalytic Activity of CynT2, a Carbonic Anhydrase Crucial for Escherichia coli Life Cycle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114175