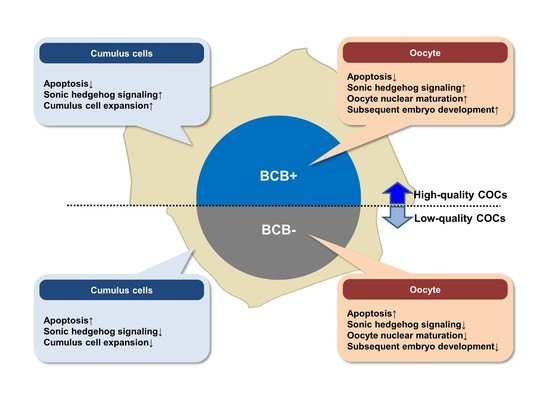
Effect of Oocyte Quality Assessed by Brilliant Cresyl Blue (BCB) Staining on Cumulus Cell Expansion and Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Porcine during In Vitro Maturation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation of the Cumulus Cell Expansion and Nuclear Maturation of Brilliant Cresyl Blue (BCB-) and BCB+ COCs
2.2. Evaluation of the Subsequent Development of Parthenogenetic Embryos Derived from BCB- and BCB+ Oocytes
2.3. Evaluation of the Subsequent Development of In Vitro Fertilized Embryos Derived from BCB- and BCB+ Oocytes
2.4. Evaluation of Apoptosis Levels in BCB- and BCB+ COCs
2.5. Evaluation of the Expression of SHH-Signaling Proteins in the BCB- and BCB+ COCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Isolation of COCs
4.3. Brilliant Cresyl Blue Staining
4.4. In Vitro Maturation of Oocytes
4.5. Assessment of Cumulus Cell Expansion
4.6. Assessment of the Nuclear Maturation of Oocytes
4.7. Parthenogenetic Activation of Oocytes
4.8. In Vitro Fertilization of Oocytes
4.9. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Mediated dUTP Digoxygenin Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.10. Immunocytochemical Staining
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IVM | In vitro maturation |
| ART | Assisted reproductive technology |
| BCB | Brilliant cresyl blue |
| G6PDH | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| SHH | Sonic hedgehog |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| PTCH1 | Patched 1 |
| SMO | Smoothened |
| GLI1 | Glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 |
| COCs | Cumulus-oocyte complexes |
| PA | Parthenogenetic activation |
| IVF | In vitro fertilization |
| TE | Trophectoderm |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| TCM | Tissue culture medium |
| PMSG | Pregnant mare serum gonadotropin |
| hCG | Human chorionic gonadotropin |
| MII | Metaphase II |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PZM-3 | Porcine zygote medium-3 |
| mTBM | Modified Tris-buffered medium |
| CASA | Computer-assisted sperm analysis |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP digoxygenin nick end labeling |
| CDX2 | Caudal type homeobox 2 |
References
- Hashimoto, S. Application of in vitro maturation to assisted reproductive technology. J. Reprod Dev. 2009, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Zhang, L.; He, C.; Ji, P.; Li, Y.; Tan, D.; Liu, G. Beneficial effect of resveratrol on bovine oocyte maturation and subsequent embryonic development after in vitro fertilization. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 101, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Song, B.S.; Lee, S.R.; Yoon, S.B.; Huh, J.W.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, E.; Kim, S.H.; Choo, Y.K.; Koo, D.B.; et al. Supplementation with estradiol-17beta improves porcine oocyte maturation and subsequent embryo development. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 95, 2582–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala, M.G.; Izquierdo, D.; Rodriguez-Prado, M.; Hammami, S.; Paramio, M.T. Effect of oocyte quality on blastocyst development after in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in a sheep model. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 97, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrecque, R.; Sirard, M.A. The study of mammalian oocyte competence by transcriptome analysis: Progress and challenges. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 20, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieci, C.; Lodde, V.; Labreque, R.; Dufort, I.; Tessaro, I.; Sirard, M.A.; Luciano, A.M. Differences in cumulus cell gene expression indicate the benefit of a pre-maturation step to improve in-vitro bovine embryo production. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 22, 882–897. [Google Scholar]
- Opiela, J.; Katska-Ksiazkiewicz, L. The utility of Brilliant Cresyl Blue (BCB) staining of mammalian oocytes used for in vitro embryo production (IVP). Reprod. Biol. 2013, 13, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, S.A.; Boice, M.L.; Funahashi, H.; Day, B.N. Assessment of porcine oocytes using brilliant cresyl blue. Theriogenology 1993, 39, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, H.; Torner, H.; Lohrke, B.; Viergutz, T.; Ghoneim, I.M.; Kanitz, W. Bovine blastocyst development rate in vitro is influenced by selection of oocytes by brillant cresyl blue staining before IVM as indicator for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Theriogenology 2005, 63, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, G.D.; Leibfried, M.L.; Lenz, R.W.; Ax, R.L.; Bavister, B.D.; First, N.L. Factors affecting successful in vitro fertilization of bovine follicular oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 1983, 28, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Jin, J.X.; Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Kim, G.A.; Ahn, C.; Lee, B.C. Melatonin influences the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in porcine cumulus oocyte complexes. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jin, J.X.; Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Kim, G.A.; Ahn, C.; Lee, B.C. Sonic hedgehog signaling mediates resveratrol to improve maturation of pig oocytes in vitro and subsequent preimplantation embryo development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5023–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevoral, J.; Orsák, M.; Klein, P.; Petr, J.; Dvořáková, M.; Weingartová, I.; Vyskočilová, A.; Zámostná, K.; Krejčová, T.; Jílek, F. Cumulus cell expansion, its role in oocyte biology and perspectives of measurement: A review. Sci. Agric. Bohem. 2015, 45, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.B.; Lan, G.C.; Wu, Y.G.; Han, D.; Feng, W.G.; Wang, J.Z.; Tan, J.H. Interactive effects of granulosa cell apoptosis, follicle size, cumulus-oocyte complex morphology, and cumulus expansion on the developmental competence of goat oocytes: A study using the well-in-drop culture system. Reproduction 2006, 132, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoo, M.; Kimura, N.; Sato, E. Induction of oocyte maturation by hyaluronan-CD44 interaction in pigs. J. Reprod. Dev. 2010, 56, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, Y.; Shi, W.Q.; Ding, J.T.; Sha, J.H.; Fan, B.Q. Predictive value of the area of expanded cumulus mass on development of porcine oocytes matured and fertilized in vitro. J. Reprod. Dev. 2003, 49, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoo, M.; Shimizu, T.; Kimura, N.; Tunjung, W.A.; Matsumoto, H.; Abe, H.; Sasada, H.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H.; Sato, E. Role of the hyaluronan receptor CD44 during porcine oocyte maturation. J. Reprod. Dev. 2007, 53, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walterhouse, D.O.; Lamm, M.L.; Villavicencio, E.; Iannaccone, P.M. Emerging roles for hedgehog-patched-Gli signal transduction in reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, M.C.; Cowan, R.G.; Harman, R.M.; Walker, A.L.; Quirk, S.M. The hedgehog signaling pathway in the mouse ovary. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, E.; Skinner, M.K. Cellular interactions that control primordial follicle development and folliculogenesis. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2001, 8, S17–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denef, N.; Neubuser, D.; Perez, L.; Cohen, S.M. Hedgehog induces opposite changes in turnover and subcellular localization of patched and smoothened. Cell 2000, 102, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Lin, D.P.; Yen, S.Y.; Tseng, J.K.; Chuang, J.F.; Chen, B.Y.; Lin, T.A.; Chang, H.H.; Ju, J.C. Sonic hedgehog promotes porcine oocyte maturation and early embryo development. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2009, 21, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Peng, H.; Hua, S.; Li, Q.; Quan, F.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Oocytes selected using BCB staining enhance nuclear reprogramming and the in vivo development of SCNT embryos in cattle. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wongsrikeao, P.; Otoi, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Agung, B.; Taniguchi, M.; Naoi, H.; Shimizu, R.; Nagai, T. Effects of single and double exposure to brilliant cresyl blue on the selection of porcine oocytes for in vitro production of embryos. Theriogenology 2006, 66, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala, M.G.; Izquierdo, D.; Uzbekova, S.; Morato, R.; Roura, M.; Romaguera, R.; Papillier, P.; Paramio, M.T. Brilliant Cresyl Blue stain selects largest oocytes with highest mitochondrial activity, maturation-promoting factor activity and embryo developmental competence in prepubertal sheep. Reproduction 2011, 142, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawlak, P.; Pers-Kamczyc, E.; Renska, N.; Kubickova, S.; Lechniak, D. Disturbances of nuclear maturation in BCB positive oocytes collected from peri-pubertal gilts. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, P.; Warzych, E.; Chabowska, A.; Lechniak, D. Differences in cytoplasmic maturation between the BCB+ and control porcine oocytes do not justify application of the BCB test for a standard IVM protocol. J Reprod Dev 2014, 60, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dekel, N. Spatial relationship of follicular cells in the control of meiosis. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1988, 267, 87–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tanghe, S.; Van Soom, A.; Nauwynck, H.; Coryn, M.; de Kruif, A. Minireview: Functions of the cumulus oophorus during oocyte maturation, ovulation, and fertilization. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2002, 61, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijgerde, M.; Ooms, M.; Hoogerbrugge, J.W.; Grootegoed, J.A. Hedgehog signaling in mouse ovary: Indian hedgehog and desert hedgehog from granulosa cells induce target gene expression in developing theca cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.C.; Huang, J.C.; Lo, N.W.; Chen, L.R.; Mermillod, P.; Ma, W.L.; Chiang, H.I.; Ju, J.C. Sonic Hedgehog promotes in vitro oocyte maturation and term development of embryos in Taiwan native goats. Theriogenology 2017, 103, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, L.J.; Sudo, S.; Aad, P.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Chun, S.Y.; Ben-Shlomo, I.; Klein, C.; Hsueh, A.J. The hedgehog-patched signaling pathway and function in the mammalian ovary: A novel role for hedgehog proteins in stimulating proliferation and steroidogenesis of theca cells. Reproduction 2009, 138, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alcedo, J.; Zou, Y.; Noll, M. Posttranscriptional regulation of smoothened is part of a self-correcting mechanism in the Hedgehog signaling system. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, L.V.; Johnson, R.L.; Milenkovic, L.; McMahon, J.A.; Scott, M.P. Conservation of the hedgehog/patched signaling pathway from flies to mice: Induction of a mouse patched gene by Hedgehog. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Platt, K.A.; Censullo, P.; Ruiz i Altaba, A. Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral neural tube development. Development 1997, 124, 2537–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, T.S.; Froiland, D.A.; Amato, F.; Thompson, J.G.; Gilchrist, R.B. Oocytes prevent cumulus cell apoptosis by maintaining a morphogenic paracrine gradient of bone morphogenetic proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 5257–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.Q.; Van Soom, A.; Leroy, J.L.; Dewulf, J.; Van Zeveren, A.; de Kruif, A.; Peelman, L.J. Apoptosis in cumulus cells, but not in oocytes, may influence bovine embryonic developmental competence. Theriogenology 2005, 63, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhyden, B.C.; Caron, P.J.; Buccione, R.; Eppig, J.J. Developmental pattern of the secretion of cumulus expansion-enabling factor by mouse oocytes and the role of oocytes in promoting granulosa cell differentiation. Dev. Biol. 1990, 140, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Kang, H.-G.; Jeong, P.-S.; Nanjidsuren, T.; Song, B.-S.; Jin, Y.B.; Lee, S.-R.; Kim, S.-U.; Sim, B.-W. Effect of Oocyte Quality Assessed by Brilliant Cresyl Blue (BCB) Staining on Cumulus Cell Expansion and Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Porcine during In Vitro Maturation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124423
Lee S, Kang H-G, Jeong P-S, Nanjidsuren T, Song B-S, Jin YB, Lee S-R, Kim S-U, Sim B-W. Effect of Oocyte Quality Assessed by Brilliant Cresyl Blue (BCB) Staining on Cumulus Cell Expansion and Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Porcine during In Vitro Maturation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124423
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sanghoon, Hyo-Gu Kang, Pil-Soo Jeong, Tsevelmaa Nanjidsuren, Bong-Seok Song, Yeung Bae Jin, Sang-Rae Lee, Sun-Uk Kim, and Bo-Woong Sim. 2020. "Effect of Oocyte Quality Assessed by Brilliant Cresyl Blue (BCB) Staining on Cumulus Cell Expansion and Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Porcine during In Vitro Maturation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124423
APA StyleLee, S., Kang, H. -G., Jeong, P. -S., Nanjidsuren, T., Song, B. -S., Jin, Y. B., Lee, S. -R., Kim, S. -U., & Sim, B. -W. (2020). Effect of Oocyte Quality Assessed by Brilliant Cresyl Blue (BCB) Staining on Cumulus Cell Expansion and Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Porcine during In Vitro Maturation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124423