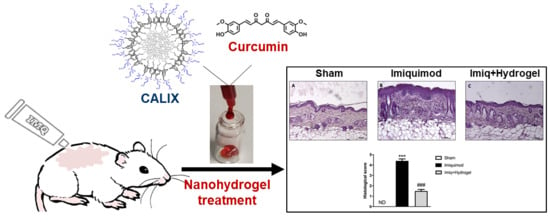
Topical Delivery of Curcumin by Choline-Calix[4]arene-Based Nanohydrogel Improves Its Therapeutic Effect on a Psoriasis Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CALIX/CUR Hydrogel
2.2. Effects of Hydrogel Treatment on Psoriasis-Like Histological Damage in IMQ-Treated BALB/c Mice
2.3. Effect of Hydrogel Treatment on TJs Proteins
2.4. Effect of Hydrogel Treatment on Mast Cell Quantification
2.5. Effect of Hydrogel Treatment on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
2.6. Effect of Hydrogel Treatment on iNOS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of the CALIX/CUR Hydrogel
4.2. Animals
4.3. Anti-Psoriatic Efficacy: IMQ Induced Psoriatic Plaque Model
4.4. Experimental Groups
4.5. Histological Analysis
4.6. Toluidine Blue Staining
4.7. Immunohistochemical Localization of ZO-1, Occludin, TNF-α, IL-1β and NOS2
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Materials
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CUR | curcumin |
| CALIX | micellar choline-calix[4]arene amphiphile |
| IMQ | imiquimod |
| TJs | tight junctions |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthetase |
References
- Michalek, I.M.; Loring, B.; John, S.M. A systematic review of worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; May, B.H.; Zhang, A.L.; Lu, C.; Xue, C.C. Plant extracts for the topical management of psoriasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; May, B.H.; Zhang, A.L.; Lu, C.; Xue, C.C. Topical herbal medicine combined with pharmacotherapy for psoriasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2013, 305, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbott, W.; Duffy, N. Complementary and alternative medicine for psoriasis: What the dermatologist needs to know. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, S.; Mukim, M.; Sharma, P.; Devi, S.; Nagar, J.C.; Khalid, M. Curcumin: A Review for health benefits. Int. J. Res. Rev. 2020, 7, 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Jiang, W.; Lu, Q.; Rong, M.; Lai, R. Curcumin shows excellent therapeutic effect on psoriasis in mouse model. Biochimie 2016, 123, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forni, C.; Facchiano, F.; Bartoli, M.; Pieretti, S.; Facchiano, A.; D’Arcangelo, D.; Norelli, S.; Valle, G.; Nisini, R.; Beninati, S.; et al. Beneficial role of phytochemicals on oxidative stress and age-related diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8748253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.Y.; Meng, X.; Li, S.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.B. Bioactivity, health benefits, and related molecular mechanisms of curcumin: Current progress, challenges, and perspectives. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, G. Topical nano drug delivery for treatment of psoriasis: Progressive and novel delivery. Asian J. Pharm. 2018, 12, S835–S848. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, S.A.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Namjoshi, S.; Grice, J.E.; Benson, H.A.E.; Sakran, W.; Roberts, M.S. Mechanistic evaluation of enhanced curcumin delivery through human skin in vitro from optimised nanoemulsion formulations fabricated with different penetration enhancers. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neri, P.; Sessler, J.L.; Wang, M.-X. Calixarenes and Beyond; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Cun, D.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Yan, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y. Enhanced topical penetration, system exposure and anti-psoriasis activity of two particle-sized, curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in hydrogel. J. Control. Release 2017, 254, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.-W.; Liu, Y.-C.; Guo, D.-S. Assembling features of calixarene-based amphiphiles and supra-amphiphiles. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 46–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Wu, Z.; Feng, N. CD44 assists the topical anti-psoriatic efficacy of curcumin-loaded hyaluronan-modified ethosomes: A new strategy for clustering drug in inflammatory skin. Theranostics 2019, 9, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.-C.; Hu, X.-Y.; Guo, D.-S. Biomedical applications of calixarenes: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, G.; Paterniti, I.; Geraci, C.; Cunsolo, F.; Esposito, E.; Cordaro, M.; Blanco, A.R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Consoli, G.M.L. Potential eye drop based on a calix[4]arene nanoassembly for curcumin delivery: Enhanced drug solubility, stability, and anti-inflammatory effect. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Petralia, S.; Forte, G.; Conoci, S.; Consoli, G.M.L. Injectable supramolecular nanohydrogel from a micellar self-assembling calix[4]arene derivative and curcumin for a sustained drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bari, I.; Picciotto, R.; Granata, G.; Blanco, A.R.; Consoli, G.M.; Sortino, S. A bactericidal calix[4]arene-based nanoconstruct with amplified NO photorelease. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 8047–8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Pan, M.H.; Cheng, A.L.; Lin, L.I.; Ho, Y.S.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, J.K. Stability of curcumin in buffer solutions and characterization of its degradation products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1997, 15, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, J.M.; Zorn-Kruppa, M.; Yoshida, T.; Moll, I.; Beck, L.A.; De Benedetto, A. Epidermal tight junctions in health and disease. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e974451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, M.; Crane, J.S. Histology, Mast Cells; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chima, M.; Lebwohl, M. TNF inhibitors for psoriasis. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2018, 37, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendros, P.; Papagoras, C.; Lefaki, I.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Kotsianidis, I.; Speletas, M.; Bocly, V.; Theodorou, I.; Dalla, V.; Ritis, K. Successful response in a case of severe pustular psoriasis after interleukin-1beta inhibition. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harbi, N.O.; Nadeem, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Al-Harbi, M.M.; Alotaibi, M.R.; AlSaad, A.M.; Ahmad, S.F. Psoriasis-like inflammation leads to renal dysfunction via upregulation of NADPH oxidases and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudjonsson, J.E.; Johnston, A.; Sigmundsdottir, H.; Valdimarsson, H. Immunopathogenic mechanisms in psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizzul, P.F.; Aphale, A.; Malaviya, R.; Sun, Y.; Masud, S.; Dombrovskiy, V.; Gottlieb, A.B. Differential expression of phosphorylated NF-kappaB/RelA in normal and psoriatic epidermis and downregulation of NF-kappaB in response to treatment with etanercept. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raja, M.A.; Zeenat, S.; Arif, M.; Liu, C. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on amphiphilic chitosan derivative and arginine for oral curcumin delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4397–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palamara, F.; Meindl, S.; Holcmann, M.; Luhrs, P.; Stingl, G.; Sibilia, M. Identification and characterization of pDC-like cells in normal mouse skin and melanomas treated with imiquimod. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3051–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.D.; Hulsebosch, H.J.; Krieg, S.R.; Bakker, P.M.; Cormane, R.H. Immunocompetent cells in psoriasis. In situ immunophenotyping by monoclonal antibodies. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1983, 275, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaba, L.C.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Eungdamrong, N.J.; Abello, M.V.; Novitskaya, I.; Pierson, K.C.; Gonzalez, J.; Krueger, J.G.; Lowes, M.A. Psoriasis is characterized by accumulation of immunostimulatory and Th1/Th17 cell-polarizing myeloid dendritic cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansen, C.; Usher, P.A.; Kjellerup, R.B.; Lundsgaard, D.; Iversen, L.; Kragballe, K. Characterization of the interleukin-17 isoforms and receptors in lesional psoriatic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Trepicchio, W.L.; Oestreicher, J.L.; Pittman, D.; Wang, F.; Chamian, F.; Dhodapkar, M.; Krueger, J.G. Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, T.; Kondo, S.; Pastore, S.; Shivji, G.M.; Tomai, M.A.; McKenzie, R.C.; Sauder, D.N. Effects of a novel topical immunomodulator, imiquimod, on keratinocyte cytokine gene expression. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1994, 13, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Al-Lamki, R.S.; Zhang, H.; Kirkiles-Smith, N.; Gaeta, M.L.; Thiru, S.; Pober, J.S.; Bradley, J.R. Histamine antagonizes tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling by stimulating TNF receptor shedding from the cell surface and Golgi storage pool. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21751–21760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ettehadi, P.; Greaves, M.W.; Wallach, D.; Aderka, D.; Camp, R.D. Elevated tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) biological activity in psoriatic skin lesions. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 96, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avramidis, G.; Kruger-Krasagakis, S.; Krasagakis, K.; Fragiadaki, I.; Kokolakis, G.; Tosca, A. The role of endothelial cell apoptosis in the effect of etanercept in psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Incio, J.; Soares, R. Angiogenesis and chronic inflammation: Cause or consequence? Angiogenesis 2007, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischon, H.; Radbruch, M.; Ostrowski, A.; Volz, P.; Gerecke, C.; Unbehauen, M.; Honzke, S.; Hedtrich, S.; Fluhr, J.W.; Haag, R.; et al. Stratum corneum targeting by dendritic core-multishell-nanocarriers in a mouse model of psoriasis. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Campolo, M.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Franco, D.; Filippone, A.; Peritore, A.F.; Cuzzocrea, S. Protective effects of xyloglucan in association with the polysaccharide gelose in an experimental model of gastroenteritis and urinary tract infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campolo, M.; Ahmad, A.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Morabito, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Combination therapy with melatonin and dexamethasone in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 217, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filippone, A.; Consoli, G.M.L.; Granata, G.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Ardizzone, A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. Topical Delivery of Curcumin by Choline-Calix[4]arene-Based Nanohydrogel Improves Its Therapeutic Effect on a Psoriasis Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145053
Filippone A, Consoli GML, Granata G, Casili G, Lanza M, Ardizzone A, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E, Paterniti I. Topical Delivery of Curcumin by Choline-Calix[4]arene-Based Nanohydrogel Improves Its Therapeutic Effect on a Psoriasis Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145053
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilippone, Alessia, Grazia M. L. Consoli, Giuseppe Granata, Giovanna Casili, Marika Lanza, Alessio Ardizzone, Salvatore Cuzzocrea, Emanuela Esposito, and Irene Paterniti. 2020. "Topical Delivery of Curcumin by Choline-Calix[4]arene-Based Nanohydrogel Improves Its Therapeutic Effect on a Psoriasis Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145053
APA StyleFilippone, A., Consoli, G. M. L., Granata, G., Casili, G., Lanza, M., Ardizzone, A., Cuzzocrea, S., Esposito, E., & Paterniti, I. (2020). Topical Delivery of Curcumin by Choline-Calix[4]arene-Based Nanohydrogel Improves Its Therapeutic Effect on a Psoriasis Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 5053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145053