A Rapid, Simple, Inexpensive, and Mobile Colorimetric Assay COVID-19-LAMP for Mass On-Site Screening of COVID-19
Abstract
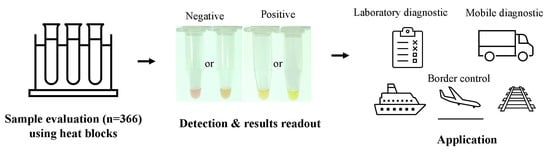
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. COVID-19-LAMP Assay Can Detect SARS-CoV-2 with a Low Detection Limit
2.2. COVID-19-LAMP Assay Is Highly Sensitive and Specific for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Samples
4.2. SARS-CoV-2 Culture
4.3. RNA Extraction from SARS-CoV-2 Culture Supernatant and Respiratory Samples
4.4. Development of COVID-19-LAMP Assay
4.5. Evaluation of COVID-19-LAMP Assay Using Clinical Samples
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verity, R.; Okell, L.C.; Dorigatti, I.; Winskill, P.; Whittaker, C.; Imai, N.; Cuomo-Dannenburg, G.; Thompson, H.; Walker, P.G.T.; Fu, H.; et al. Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: A model-based analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Tsoi, H.W.; Chan, K.H.; Wong, B.H.; Che, X.Y.; Tam, V.K.; Tam, S.C.; Cheng, V.C.; Hung, I.F.; et al. Relative rates of non-pneumonic SARS coronavirus infection and SARS coronavirus pneumonia. Lancet 2004, 363, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.W.; Wong, B.H.; Wong, S.S.; Leung, S.Y.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14040–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, S.K.; Feng, Y.; Chen, H.; Luk, H.K.; Yang, W.H.; Li, K.S.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, Y.; Song, Z.Z.; Chow, W.N.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Coronavirus ORF8 Protein Is Acquired from SARS-Related Coronavirus from Greater Horseshoe Bats through Recombination. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10532–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luk, H.K.H.; Li, X.; Fung, J.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Molecular epidemiology, evolution and phylogeny of SARS coronavirus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 71, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Wernery, U.; Wong, E.Y.; Tsang, A.K.; Johnson, B.; Yip, C.C.; Lau, C.C.; Sivakumar, S.; Cai, J.P.; et al. Novel betacoronavirus in dromedaries of the Middle East, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, K.G.; Rambaut, A.; Lipkin, W.I.; Holmes, E.C.; Garry, R.F. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheridan, C. Fast, portable tests come online to curb coronavirus pandemic. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, B.; Liang, H.; Fang, C.; Gong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhao, D.; Shen, J.; et al. Characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential evidence for persistent fecal viral shedding. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- To, K.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Leung, W.S.; Tam, A.R.; Wu, T.C.; Lung, D.C.; Yip, C.C.; Cai, J.P.; Chan, J.M.; Chik, T.S.; et al. Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: An observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Udugama, B.; Kadhiresan, P.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Malekjahani, A.; Osborne, M.; Li, V.Y.C.; Chen, H.; Mubareka, S.; Gubbay, J.B.; Chan, W.C.W. Diagnosing COVID-19: The Disease and Tools for Detection. ACS Nano 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Geng, M.; Peng, Y.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konrad, R.; Eberle, U.; Dangel, A.; Treis, B.; Berger, A.; Bengs, K.; Fingerle, V.; Liebl, B.; Ackermann, N.; Sing, A. Rapid establishment of laboratory diagnostics for the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in Bavaria, Germany, February 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhai, P.; Ding, Y.; Wu, X.; Long, J.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Y. The epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferle, S.; Reucher, S.; Norz, D.; Lutgehetmann, M. Evaluation of a quantitative RT-PCR assay for the detection of the emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 using a high throughput system. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Peng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhou, M.; Lin, W.; Wu, W.; Huang, S.; Jiang, L.; Luo, X.; et al. Recent progress in understanding 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) associated with human respiratory disease: Detection, mechanisms and treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 105950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Baek, Y.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, Y.K.; Song, M.S.; Ahn, J.Y. One-Pot Reverse Transcriptional Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) for Detecting MERS-CoV. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.F.; Li, M.; Zhong, L.L.; Lu, S.M.; Liu, Z.X.; Pu, J.Y.; Wen, J.S.; Huang, X. Development of reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection and differentiation of dengue virus serotypes 1-4. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajko-Nenow, P.; Flannery, J.; Arnold, H.; Howson, E.L.A.; Darpel, K.; Stedman, A.; Corla, A.; Batten, C. A rapid RT-LAMP assay for the detection of all four lineages of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 274, 113730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jimena, B.; Bekaert, M.; Bakheit, M.; Frischmann, S.; Patel, P.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Lambrechts, L.; Duong, V.; Dussart, P.; Harold, G.; et al. Development and validation of four one-step real-time RT-LAMP assays for specific detection of each dengue virus serotype. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, W.; Unger, H.; Haris, S.; Mobeen, A.; Farooq, M.; Asif, M.; Khan, Q.M. Genetic detection of peste des petits ruminants virus under field conditions: A step forward towards disease eradication. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirato, K.; Semba, S.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Tolah, A.M.; Takayama, I.; Kageyama, T.; Notomi, T.; Kamitani, W.; Matsuyama, S.; et al. Development of fluorescent reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) using quenching probes for the detection of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 258, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, K.; Bi, Z.; Gu, J.; Song, D.; Lei, D.; Luo, S.; Huang, D.; Wu, Q.; Ding, Z.; et al. Development of a reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay for the detection of porcine pegivirus. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 270, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| qRT-PCR | Portable qRT-PCR | Automated Platform | Point-of-Care Diagnostic Machine | COVID-19-LAMP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timing | 75–90 min | 75–90 min | 60–120 min | 15–20 min | 30–90 min |
| User requirement | Experienced lab technologist | Junior lab technologist or healthcare worker with short training | |||
| Reagent cost/test (USD) | $20–60 | $20–60 | >$110 | >$100 | $2–4 |
| Equipment cost | >$45,000 | >$4500 | >$32,000 | >$10,000 | $100–1000 |
| Apparatus | qRT-PCR machine | Portable qRT-PCR machine | GeneXpert/Filmarray | Abbott ID NOW | Heat block |
| RNA Extraction | Required | Not required | Required | ||
| Capacity | 96 samples per run | 16 samples per run | Up to 16 samples per run | 1 sample per run | Unrestricted (48–96 samples per block) |
| Point-of-care testing | Not feasible | Not feasible | Feasible | Feasible | Feasible |
| Mass on-site screening | Partially feasible | Not feasible | Not feasible | Not feasible | Feasible |
| Result readout | Not easy | Not easy | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| (Ct value may require interpretation | (report by machine) | (naked eye) | |||
| Reaction Time | Number of Positives | Number of Negatives | Sensitivity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Respiratory Samples Positive for SARS-CoV-2 by qRT-PCR (n = 223) | |||
| 60 min | 212 | 11 | 95.07% (0.92–0.98) |
| 90 min | 219 | 4 | 98.21% (0.96–1.00) |
| Nasopharyngeal Swabs Positive for SARS-CoV-2 by qRT-PCR (n = 96) | |||
| 60 min | 93 | 3 | 96.88% (0.93–1.00) |
| 90 min | 95 | 1 | 98.96% (0.97–1.00) |
| Sputum/Deep Throat Saliva Positive for SARS-CoV-2 by qRT-PCR (n = 67) | |||
| 60 min | 63 | 4 | 94.03% (0.88–1.00) |
| 90 min | 65 | 2 | 97.02% (0.93–1.00) |
| Throat Swabs Positive for SARS-CoV-2 by qRT-PCR (n = 60) | |||
| 60 min | 56 | 4 | 93.33% (0.87–1.00) |
| 90 min | 59 | 1 | 98.33% (0.95–1.00) |
| Respiratory Samples with Other Respiratory Viruses | Number Tested | COVID-19-LAMP |
|---|---|---|
| Parainfluenza virus 1 | 10 | Negative |
| Parainfluenza virus 2 | 10 | Negative |
| Parainfluenza virus 3 | 10 | Negative |
| Influenza A virus | 20 | Negative |
| Influenza B virus | 6 | Negative |
| Adenovirus | 18 | Negative |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | 20 | Negative |
| Human metapneumovirus | 2 | Negative |
| Human rhinovirus A | 3 | Negative |
| Human rhinovirus B | 3 | Negative |
| Human rhinovirus C | 3 | Negative |
| Human enterovirus A71 | 7 | Negative |
| Human enterovirus D68 | 10 | Negative |
| Coxsackievirus A6 | 10 | Negative |
| Human coronavirus HKU1 | 5 | Negative |
| Human coronavirus NL63 | 1 | Negative |
| Human coronavirus 229E | 1 | Negative |
| Human coronavirus OC43 | 5 | Negative |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chow, F.W.-N.; Chan, T.T.-Y.; Tam, A.R.; Zhao, S.; Yao, W.; Fung, J.; Cheng, F.K.-K.; Lo, G.C.-S.; Chu, S.; Aw-Yong, K.L.; et al. A Rapid, Simple, Inexpensive, and Mobile Colorimetric Assay COVID-19-LAMP for Mass On-Site Screening of COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155380
Chow FW-N, Chan TT-Y, Tam AR, Zhao S, Yao W, Fung J, Cheng FK-K, Lo GC-S, Chu S, Aw-Yong KL, et al. A Rapid, Simple, Inexpensive, and Mobile Colorimetric Assay COVID-19-LAMP for Mass On-Site Screening of COVID-19. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(15):5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155380
Chicago/Turabian StyleChow, Franklin Wang-Ngai, Tony Tat-Yin Chan, Anthony Raymond Tam, Suhui Zhao, Weiming Yao, Joshua Fung, Flora Ka-Kei Cheng, George Chi-Shing Lo, Stella Chu, Kam Leng Aw-Yong, and et al. 2020. "A Rapid, Simple, Inexpensive, and Mobile Colorimetric Assay COVID-19-LAMP for Mass On-Site Screening of COVID-19" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 15: 5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155380
APA StyleChow, F. W. -N., Chan, T. T. -Y., Tam, A. R., Zhao, S., Yao, W., Fung, J., Cheng, F. K. -K., Lo, G. C. -S., Chu, S., Aw-Yong, K. L., Tang, J. Y. -M., Tsang, C. -C., Luk, H. K. -H., Wong, A. C. -P., Li, K. S. -M., Zhu, L., He, Z., Tam, E. W. T., Chung, T. W. -H., ... Lau, S. K. -P. (2020). A Rapid, Simple, Inexpensive, and Mobile Colorimetric Assay COVID-19-LAMP for Mass On-Site Screening of COVID-19. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155380