Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to CNS Function and Pathophysiology
Abstract
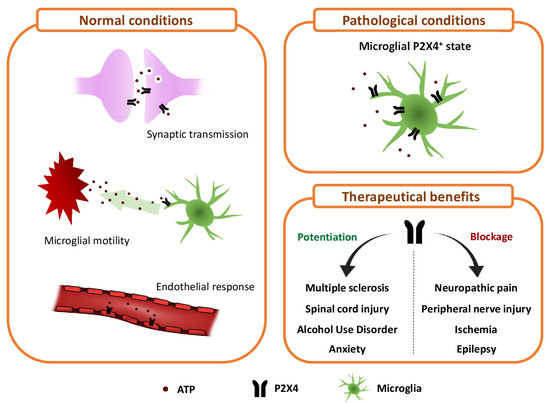
:1. Introduction
2. P2X4R Location in the CNS
3. Role of P2X4 Receptor in CNS Physiology
3.1. Role of P2X4 Receptor in Synaptic Transmission
3.2. Role of P2X4 Receptors in Glial Cells
3.3. Intracellular Role of P2X4 Receptor
4. Role of P2X4 Receptor in CNS Pathologies
4.1. Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nerve Injury: Neuropathic Pain
4.2. Epilepsy
4.3. Ischemia
4.4. Multiple Sclerosis
4.5. Neurodegenerative Diseases
4.6. P2X4 and Psychiatric Diseases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol. Rev. 1972, 24, 509–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnstock, G. The therapeutic potential of purinergic signalling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, F. Purinergic signalling in the immune system. A brief update. Purinergic Signal. 2007, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domercq, M.; Vazquez-Villoldo, N.; Matute, C. Neurotransmitter signaling in the pathophysiology of microglia. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stokes, L.; Layhadi, J.A.; Bibic, L.; Dhuna, K.; Fountain, S.J. P2X4 receptor function in the nervous system and current breakthroughs in pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- North, R.A. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 1013–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddou, C.; Yan, Z.; Obsil, T.; Pablo Huidobro-Toro, J.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Activation and regulation of purinergic P2X receptor channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collo, G.; North, R.A.; Kawashima, E.; Merlo-Pich, E.; Neidhart, S.; Surprenant, A.; Buell, G. Cloning of P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2495–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadio, S.; Montilli, C.; Picconi, B.; Calabresi, P.; Volonté, C. Mapping P2X and P2Y receptor proteins in striatum and substantia nigra: An immunohistological study. Purinergic Signal. 2007, 3, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler-Schilling, T.H.; Marquordt, K.; Kohler, K.; Guenther, E.; Jabs, R. Identification of purinergic receptors in retinal ganglion cells. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 92, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, I.; Tanaka, K.; Hattori, Y.; Uezono, Y.; Harayama, N.; Noguchi, J.; Ueta, Y.; Izumi, F.; Yamashita, H. Evidence that multiple P2X purinoceptors are functionally expressed in rat supraoptic neurones. J. Physiol. 1999, 514, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cham, J.L.; Owens, N.C.; Barden, J.A.; Lawrence, A.J.; Badoer, E. P2X purinoceptor subtypes on paraventricular nucleus neurones projecting to the rostral ventrolateral medulla in the rat. Exp. Physiol. 2006, 91, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bardoni, R.; Goldstein, P.A.; Lee, C.J.; Gu, J.G.; MacDermott, A.B. ATP P(2X) receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5297–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buell, G.; Lewis, C.; Collo, G.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. An antagonist-insensitive P2X receptor expressed in epithelia and brain. Embo J. 1996, 15, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yin, G.F.; Gu, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.; Dai, J.P.; Li, C.; Li, Z.W. Characterization of three types of ATP-activated current in relation to P2X subunits in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. Brain Res. 2006, 1115, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bernstein, A.M.; Wong, A.; Lu, X.H.; Khoja, S.; Yang, X.W.; Davies, D.L.; Micevych, P.; Sofroniew, M.V.; Khakh, B.S. P2X4 receptor reporter mice: Sparse brain expression and feeding-related presynaptic facilitation in the arcuate nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8902–8920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Shigemoto-Mogami, Y.; Koizumi, S.; Mizokoshi, A.; Kohsaka, S.; Salter, M.W.; Inoue, K. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 2003, 424, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, H.; Grosche, J.; Schädlich, H.; Krügel, U.; Allgaier, C.; Illes, P. P2X receptor expression on astrocytes in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Neuroscience 2001, 108, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukley, M.; Barden, J.A.; Steinhäuser, C.; Jabs, R. Distribution of P2X receptors on astrocytes in juvenile rat hippocampus. Glia 2001, 36, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, F.; Deuchars, J. Electron microscopic localisation of P2X 4 receptor subunit immunoreactivity to pre- and post-synaptic neuronal elements and glial processes in the dorsal vagal complex of the rat. Brain Res. 2004, 1026, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabs, R.; Matthias, K.; Grote, A.; Grauer, M.; Seifert, G.; Steinhäuser, C. Lack of P2X Receptor Mediated Currents in Astrocytes and GluR Type Glial Cells of the Hippocampal CA1 Region. Glia 2007, 55, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalo, U.; Verkhratsky, A.; Pankratov, Y. Ivermectin potentiates ATP-induced ion currents in cortical neurones: Evidence for functional expression of P2X4 receptors? Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 421, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agresti, C.; Meomartini, M.E.; Amadio, S.; Ambrosini, E.; Serafini, B.; Franchini, L.; Volonté, C.; Aloisi, F.; Visentin, S. Metabotropic P2 receptor activation regulates oligodendrocyte progenitor migration and development. Glia 2005, 50, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabala, A.; Vazquez-Villoldo, N.; Rissiek, B.; Gejo, J.; Martin, A.; Palomino, A.; Perez-Samartín, A.; Pulagam, K.R.; Lukowiak, M.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; et al. P2X4 receptor controls microglia activation and favors remyelination in autoimmune encephalitis. Embo Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.D. Release of Atp from a Synaptosomal Preparation By Elevated Extracellular K+ and By Veratridine. J. Neurochem. 1978, 30, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic cotransmission. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.H.; Schlichter, R. Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, G.R.J.; Baimoukhametova, D.V.; Hewitt, S.A.; Rajapaksha, W.R.A.K.J.S.; Fisher, T.E.; Bains, J.S. Norepinephrine triggers release of glial ATP to increase postsynaptic efficacy. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1078–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.G.; Macdermott, A.B. Activation of ATP P2X receptors elicits glutamate release from sensory neuron synapses. Nature 1997, 389, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigetomi, E.; Kato, F. Action Potential-Independent Release of Glutamate by Ca2+ Entry through Presynaptic P2X Receptors Elicits Postsynaptic Firing in the Brainstem Autonomic Network. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3125–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lê, K.T.; Villeneuve, P.; Ramjaun, A.R.; McPherson, P.S.; Beaudet, A.; Séguéla, P. Sensory presynaptic and widespread somatodendritic immunolocalization of central ionotropic P2X ATP receptors. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugel, S.; Schlichter, R. Presynaptic P2X receptors facilitate inhibitory GABAergic transmission between cultured rat spinal cord dorsal horn neurons. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2121–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vavra, V.; Bhattacharya, A.; Zemkova, H. Facilitation of glutamate and GABA release by P2X receptor activation in supraoptic neurons from freshly isolated rat brain slices. Neuroscience 2011, 188, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Cunha, R.A.; Mulle, C.; Amédée, T. Microglia-derived purines modulate mossy fibre synaptic transmission and plasticity through P2X4 and A1 receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 43, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.E.; Soto, F. Distinct localization of P2X receptors at excitatory postsynaptic specializations. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baxter, A.W.; Choi, S.J.; Sim, J.A.; North, R.A. Role of P2X4 receptors in synaptic strengthening in mouse CA1 hippocampal neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, J.A.; Chaumont, S.; Jo, J.; Ulmann, L.; Young, M.T.; Cho, K.; Buell, G.; North, R.A.; Rassendren, F. Altered hippocampal synaptic potentiation in P2X4 knock-out mice. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 9006–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Zhou, X.; Sydes, J.; Galligan, J.J.; Lester, H.A. State-dependent cross-inhibition between transmitter-gated cation channels. Nature 2000, 406, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, Y.H.; Donier, E.; Martinez, A.; Garret, M.; Toulmé, E.; Boué-Grabot, E. Cross-talk between P2X4 and γ-aminobutyric acid, type A receptors determines synaptic efficacy at a central synapse. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 19993–20004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulmann, L.; Hatcher, J.P.; Hughes, J.P.; Chaumont, S.; Green, P.J.; Conquet, F.; Buell, G.N.; Reeve, A.J.; Chessell, I.P.; Rassendren, F. Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11263–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Iwamoto, S.; Yoshinaga, R.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Nishiyama, A.; Mak, T.W.; Tamura, T.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K. Transcription factor IRF5 drives P2X4R+-reactive microglia gating neuropathic pain. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krausgruber, T.; Blazek, K.; Smallie, T.; Alzabin, S.; Lockstone, H.; Sahgal, N.; Hussell, T.; Feldmann, M.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and T H1-TH17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Villoldo, N.; Domercq, M.; Martín, A.; Llop, J.; Gómez-Vallejo, V.; Matute, C. P2X4 receptors control the fate and survival of activated microglia. Glia 2014, 62, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.F.; Davies, C.L.; Holloway, R.K.; Labrak, Y.; Ireland, G.; Carradori, D.; Dillenburg, A.; Borger, E.; Soong, D.; Richardson, J.C.; et al. Central nervous system regeneration is driven by microglia necroptosis and repopulation. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Bastien, D.; Yurcisin, G.; Pineau, I.; Dalton Dietrich, W.; De Koninck, Y.; Keane, R.W.; Lacroix, S. P2X4 receptors influence inflammasome activation after spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 3058–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, K.; Irino, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Akazawa, C.; Inoue, K.; Kohsaka, S. Involvement of P2X4 and P2Y12 receptors in ATP-induced microglial chemotaxis. Glia 2007, 55, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayakawa, K.; Ohkawa, Y.; Yoshizaki, S.; Tamaru, T.; Saito, T.; Kijima, K.; Yokota, K.; Hara, M.; Kubota, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; et al. Macrophage centripetal migration drives spontaneous healing process after spinal cord injury. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.W.; Xiao, J.; Kemper, D.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Murray, S.S. Oligodendroglial expression of TrkB independently regulates myelination and progenitor cell proliferation. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4947–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolwani, R.J.; Cosgaya, J.M.; Varma, S.; Jacob, R.; Kuo, L.E.; Shooter, E.M. BDNF overexpression produces a long-term increase in myelin formation in the peripheral nervous system. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 77, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.F.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.H.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Fei, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Xing, L.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; et al. Overexpression of P2X4 receptor in Schwann cells promotes motor and sensory functional recovery and remyelination via BDNF secretion after nerve injury. Glia 2019, 67, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmann, L.; Hirbec, H.; Rassendren, F. P2X4 receptors mediate PGE2 release by tissue-resident macrophages and initiate inflammatory pain. Embo. J. 2010, 29, 2290–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csóka, B.; Németh, Z.H.; Szabó, I.; Davies, D.L.; Varga, Z.V.; Pálóczi, J.; Falzoni, S.; Di Virgilio, F.; Muramatsu, R.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Macrophage P2X4 receptors augment bacterial killing and protect against sepsis. Jci Insight 2018, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royle, S.J.; Qureshi, O.S.; Bobanović, L.K.; Evans, P.R.; Owen, D.J.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.D. Non-canonical YXXGΦ endocytic motifs: Recognition by AP2 and preferential utilization in P2X4 receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3073–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, O.S.; Paramasivam, A.; Yu, J.C.H.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.D. Regulation of P2X4 receptors by lysosomal targeting, glycan protection and exocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3838–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Q.; Zhong, X.Z.; Zou, Y.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.; Zhu, M.X.; Dong, X.P. Calcium release through P2X4 activates calmodulin to promote endolysosomal membrane fusion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, L.E.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.D. The trafficking and targeting of P2X receptors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Chai, H.; Ehinger, K.; Egan, T.M.; Srinivasan, R.; Frick, M.; Khakh, B.S. Imaging P2X4 receptor subcellular distribution, trafficking, and regulation using P2X4-pHluorin. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 144, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, G.; Föhr, K.J.; Kling, C.; Fauler, M.; Wittekindt, O.H.; Dietl, P.; Frick, M. P2X4 receptor re-sensitization depends on a protonation/deprotonation cycle mediated by receptor internalization and recycling. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 4893–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, E.; Deluc, T.; Pilch, K.S.; Martinez, A.; Pougnet, J.T.; Doudnikoff, E.; Allain, A.E.; Bergmann, P.; Russeau, M.; Toulmé, E.; et al. Increased surface P2X4 receptor regulates anxiety and memory in P2X4 internalization-defective knock-in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell-Lagnado, R.D.; Frick, M. P2X4 and lysosome fusion. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, X.Z.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, M.X.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.; Dong, X.P. P2X4 forms functional ATP-activated cation channels on lysosomal membranes regulated by luminal pH. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17658–17667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, K.E.; Korbmacher, J.P.; Hecht, E.; Hobi, N.; Wittekindt, O.H.; Dietl, P.; Kranz, C.; Frick, M. Fusion-activated cation entry (FACE) via P2X4 couples surfactant secretion and alveolar fluid transport. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, S.; Trang, T.; Salter, M.W. P2X4R + microglia drive neuropathic pain. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Zhang, J.; Kometani, M.; Tomiyama, D.; Kohno, K.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Inoue, K.; Tsuda, M. Duloxetine inhibits microglial P2X4 receptor function and alleviates neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumura, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Sasaki, A.; Nakata, E.; Kohno, K.; Masuda, T.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Imai, T.; Kuraishi, Y.; Tsuda, M.; et al. A novel P2X4 receptor-selective antagonist produces anti-allodynic effect in a mouse model of herpetic pain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulmann, L.; Levavasseur, F.; Avignone, E.; Peyroutou, R.; Hirbec, H.; Audinat, E.; Rassendren, F. Involvement of P2X4 receptors in hippocampal microglial activation after status epilepticus. Glia 2013, 61, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Cronin, C.G.; Hudobenko, J.; Venna, V.R.; McCullough, L.D.; Liang, B.T. Deletion of the P2X4 receptor is neuroprotective acutely, but induces a depressive phenotype during recovery from ischemic stroke. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.; Muramatsu, R.; Sasai, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kubota, Y.; Fujinaka, T.; Yoshimine, T.; Yamashita, T. The P2X4 receptor is required for neuroprotection via ischemic preconditioning. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Yang, T.; Huang, L.; Yang, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Li, F. TNP-ATP is Beneficial for Treatment of Neonatal Hypoxia-Induced Hypomyelination and Cognitive Decline. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoja, S.; Shah, V.; Garcia, D.; Asatryan, L.; Jakowec, M.W.; Davies, D.L. Role of purinergic P2X4 receptors in regulating striatal dopamine homeostasis and dependent behaviors. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varma, R.; Chai, Y.; Troncoso, J.; Gu, J.; Xing, H.; Stojilkovic, S.S.; Mattson, M.P.; Haughey, N.J. Amyloid-β induces a caspase-mediated cleavage of P2X4 to promote purinotoxicity. Neuromolecular Med. 2009, 11, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, L.R.; Godar, S.C.; Khoja, S.; Jakowec, M.W.; Alkana, R.L.; Bortolato, M.; Davies, D.L. Sociocommunicative and sensorimotor impairments in male P2X4-deficient mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoja, S.; Asatryan, L.; Jakowec, M.W.; Davies, D.L. Dopamine Receptor Blockade Attenuates Purinergic P2X4 Receptor-Mediated Prepulse Inhibition Deficits and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, K.M.; Asatryan, L.; Jakowec, M.W.; Trudell, J.R.; Bell, R.L.; Davies, D.L. P2X4 receptors (P2X4Rs) represent a novel target for the development of drugs to prevent and/or treat alcohol use disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoja, S.; Huynh, N.; Asatryan, L.; Jakowec, M.W.; Davies, D.L.; California, S.; Angeles, L.; Angeles, L. Reduced Expression of Purinergic P2X4 Receptors Increases Voluntary Ethanol Intake in C57BL/6J Mice. Alcohol 2018, 68, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Artelt, M.; Burnet, M.; Trautmann, K.; Schluesener, H.J. Lesional accumulation of P2X4 receptor+ monocytes following experimental traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 197, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Toyomitsu, E.; Komatsu, T.; Masuda, T.; Kunifusa, E.; Nasu-Tada, K.; Koizumi, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Ando, J.; Inoue, K. Fibronectin/integrin system is involved in P2X4 receptor upregulation in the spinal cord and neuropathic pain after nerve injury. Glia 2008, 56, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Toyomitsu, E.; Kometani, M.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Inoue, K. Mechanisms underlying fibronectin-induced up-regulation of P2X 4R expression in microglia: Distinct roles of PI3K-Akt and MEK-ERK signalling pathways. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 3251–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coull, J.A.M.; Beggs, S.; Boudreau, D.; Boivin, D.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K.; Gravel, C.; Salter, M.W.; De Koninck, Y. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 2005, 438, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalisse, S.; Hua, J.; Lenoir, M.; Linck, N.; Rassendren, F.; Ulmann, L. Sensory neuronal P2RX4 receptors controls BDNF signaling in inflammatory pain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dale, N.; Frenguelli, B. Release of Adenosine and ATP During Ischemia and Epilepsy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 7, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiega, O.; Beccari, S.; Diaz-Aparicio, I.; Nadjar, A.; Layé, S.; Leyrolle, Q.; Gómez-Nicola, D.; Domercq, M.; Pérez-Samartín, A.; Sánchez-Zafra, V.; et al. Neuronal Hyperactivity Disturbs ATP Microgradients, Impairs Microglial Motility, and Reduces Phagocytic Receptor Expression Triggering Apoptosis/Microglial Phagocytosis Uncoupling. Plos Biol. 2016, 14, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avignone, E.; Ulmann, L.; Levavasseur, F.; Rassendren, F.; Audinat, E. Status epilepticus induces a particular microglial activation state characterized by enhanced purinergic signaling. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9133–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doná, F.; Ulrich, H.; Persike, D.S.; Conceição, I.M.; Blini, J.P.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Fernandes, M.J.S. Alteration of purinergic P2X4 and P2X7 receptor expression in rats with temporal-lobe epilepsy induced by pilocarpine. Epilepsy Res. 2009, 83, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, T.; Jimenez-Pacheco, A.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Henshall, D.C. P2X7 receptor in epilepsy; role in pathophysiology and potential targeting for seizure control. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 4, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fordyce, C.B.; Jagasia, R.; Zhu, X.; Schlichter, L.C. Microglia Kv1.3 channels contribute to their ability to kill neurons. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7139–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Wang, L.; Li, J.W.; Gong, M.; He, L.; Feng, R.; Dai, Z.; Li, S.Q. Hypoxia induced amoeboid microglial cell activation in postnatal rat brain is mediated by ATP receptor P2X4. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, R.D.; Ren, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ye, X.M. P2X4 receptors expressed on microglial cells in post-ischemic inflammation of brain ischemic injury. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 67, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wixey, J.A.; Reinebrant, H.E.; Carty, M.L.; Buller, K.M. Delayed P2X4R expression after hypoxia-ischemia is associated with microglia in the immature rat brain. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 212, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, F.; Florenzano, F.; Amadio, S.; Fusco, F.R.; Viscomi, M.T.; D’Ambrosi, N.; Vacca, F.; Sancesario, G.; Bernardi, G.; Molinari, M.; et al. Up-regulation of P2X2, P2X4 receptor and ischemic cell death: Prevention by P2 antagonists. Neuroscience 2003, 120, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domercq, M.; Perez-Samartin, A.; Aparicio, D.; Alberdi, E.; Pampliega, O.; Matute, C. P2X7 receptors mediate ischemic damage to oligodendrocytes. Glia 2010, 58, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, R.; Burnstock, G. Immunohistochemical identification of cells expressing ATP-gated cation channels (P2X receptors) in the adult rat thyroid. J. Anat. 2001, 198, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Sokabe, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Shibata, M.; Ohura, N.; Fukuda, T.; Sato, T.; Sekine, K.; Kato, S.; et al. Impaired flow-dependent control of vascular tone and remodeling in P2X4-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domercq, M.; Matute, C. Targeting P2X4 and P2X7 receptors in multiple sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.H.; Schluesener, H.J. Lesional accumulation of P2X4 receptor+ macrophages in rat CNS during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, C.; Liu, K.; Kondo, Y.; Slubowski, C.J.; Dertnig, T.; Denicoló, S.; Arbab, M.; Hubner, J.; Konrad, K.; Fakhari, M.; et al. Purinergic P2X4 receptors and mitochondrial ATP production regulate T cell migration. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3583–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotter, M.R.; Setzu, A.; Sim, F.J.; Van Rooijen, N.; Franklin, R.J.M. Macrophage depletion impairs oligodendrocyte remyelination following lysolecithin-induced demyelination. Glia 2001, 35, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, L.R.; Finn, D.A.; Khoja, S.; Yardley, M.M.; Asatryan, L.; Alkana, R.L.; Davies, D.L. Contribution of P2X4 receptors to ethanol intake in male C57BL/6 mice. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casanovas, A.; Hernández, S.; Tarabal, O.; Rosselló, J.; Esquerda, J.E. Strong P2X4 purinergic receptor-like immunoreactivity is selectively associated with degenerating neurons in transgenic rodent models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 506, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, S.; Heekeren, K.; Klosterkötter, J.; Kuhn, J. Prepulse inhibition in psychiatric disorders—Apart from schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Li, C.; Weight, F.F. Inhibition by ethanol of rat P2X4 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostrovskaya, O.; Asatryan, L.; Wyatt, L.; Popova, M.; Li, K.; Peoples, R.W.; Alkana, R.L.; Davies, D.L. Ethanol is a fast channel inhibitor of P2X4 receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Pathology | Model | Therapeutic Benefit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuropathic and inflammatory pain | Peripheral nerve or spinal cord injury in mice | Antisense oligonucleotide to P2X4 alleviates neuropathic pain | [17] |
| P2X4−/− mice lack mechanical hyperalgesia and have reduced inflammatory pain | [40,51] | ||
| Neuropathic pain was alleviated in the present of P2X4 antagonists such as paroxetine, duloxetine, NP-1815-PX | [64,65] | ||
| Spinal cord and peripheral nerve injury | Spinal cord injury in mice | P2X4R−/− mice showed impaired inflammasome signaling and improved functional outcome | [45] |
| Sciatic nerve crush in mice | Overexpression of P2X4R promoted motor and sensory functional recovery | [50] | |
| Epilepsy | Kainate induced status epilepticus in mice | P2X4−/− mice showed ameliorated microglia response and reduced neuronal death | [66] |
| Ischemia | Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) (60 min) in mice | P2X4−/− mice showed reduced infarct volume | [67] |
| MCAO in mice | P2X4R antagonists did not affect MCAO-mediated infarct formation | [68] | |
| Neonatal hypoxia in mice | TNP-ATP antagonist reduced hypomyelination and cognitive decline | [69] | |
| Multiple sclerosis | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Ivermectin ameliorate clinical signs | [24] |
| Lysolecithin (LPC) model in organotypic slices | Ivermectin potentiates remyelination after in LPC-induced demyelination | [24] | |
| Parkinson’s disease | 6-hydroxydopamine model of DA depletion | P2X4R KO mice exhibited an attenuated levodopa (L-DOPA)-induced motor behavior, whereas ivermectin enhanced this behavior | [70] |
| Alzheimer’s disease | Amyloid β (Aβ) exposure in vitro | Overexpression of P2X4Rs in neurons enhanced Aβ toxicity while silencing of P2X4Rs decreased neuronal death | [71] |
| Conditional knock-in mice (P2X4mCherryIN) mimicking the pathological increase of surface P2X4R | Impairment of memory processing and altered synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus | [59] | |
| Psychiatric disorders | P2X4R KO mice | P2X4 KO mice showed altered prepulse inhibition and reductions in social interactions | [70,72,73] |
| Alcohol use disorders models in mice | Ivermectin and other avermectins reduces EtOH intake and preference | [74,75] | |
| Anxiety | Increases surface expression of P2X4 at excitatory synapses alleviates anxiety | [59] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montilla, A.; Mata, G.P.; Matute, C.; Domercq, M. Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to CNS Function and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155562
Montilla A, Mata GP, Matute C, Domercq M. Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to CNS Function and Pathophysiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(15):5562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155562
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontilla, Alejandro, Gilda Paloma Mata, Carlos Matute, and Maria Domercq. 2020. "Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to CNS Function and Pathophysiology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 15: 5562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155562
APA StyleMontilla, A., Mata, G. P., Matute, C., & Domercq, M. (2020). Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to CNS Function and Pathophysiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155562