Role of the Transcription Factor Yin Yang 1 and Its Selectively Identified Target Survivin in High-Grade B-Cells Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. JASPAR Screening Allows the Identification of YY1 Putative Binding Sites on the Transcriptional Regulatory Regions of Several Apoptotic Genes: Identification of BIRC5/Survivin
2.2. YY1-ChIP-Sequencing Data Confirm That YY1 Strongly Binds the BIRC5 Promoter
2.3. Bioinformatics Data Confirm That YY1 and BIRC5 Are Positively Correlated within the B-NHL GEO Datasets and They Are Both Associated with B-NHL Clinical-Pathological Features
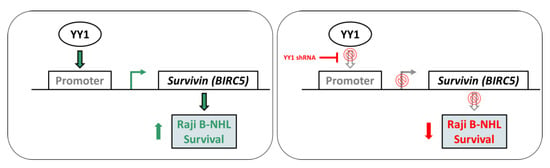
2.4. YY1 Silencing Does Not Affect Raji BL Cellular Growth and It Is Associated with Selective BIRC5 (Survivin) Downregulation
2.5. YY1 Silencing Sensitizes Raji BL Cells to Chemotherapy-Induced Cytotoxicity and Enhances Their Apoptotic Response UponTreatments
2.6. YY1 and Survivin Association Is Reverted upon Doxorubicin and Vincristine Treatment Only in BL Raji Cells Which are Efficiently Silenced for YY1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Determination of YY1 Binding Sites Localized within the Promoters of Apoptosis Regulator Genes by Ensembl Search and JASPAR Analysis
4.2. Bioinformatics Analyses
4.3. Cell Lines and Culture
4.4. Generation of Raji Cells Constitutively Silenced for YY1
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Trypan Blue Cell Count
4.7. Total RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and Semiquantitative and Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4.8. Protein Lysates Preparation, Quantification and Immunoblotting Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| B-NHLs | B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas |
| YY1 | Yin Yang 1 |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| BLs | Burkitt’s lymphomas |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| FL | Follicular lymphoma |
| MCL | Mantle Cells lymphoma |
| MZL | Marginal Zone lymphoma |
| PcG | Polycomb Group |
| TSS | Transcription Starting Site |
References
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Marcos-Gragera, R.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in the incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Causes Control 2019, 30, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, J.W. Aggressive B-cell lymphomas: How many categories do we need? Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, S42–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapozzi, V.; Zorzet, S.; Comelli, M.; Mavelli, I.; Perissin, L.; Giraldi, T. Melatonin decreases bone marrow and lymphatic toxicity of adriamycin in mice bearing TLX5 lymphoma. Life Sci. 1998, 63, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juskevicius, D.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A. Genetic background and evolution of relapses in aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Akopyan, G.; Garban, H.; Bonavida, B. Transcription factor YY1: Structure, function, and therapeutic implications in cancer biology. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliala, I.T.S.; Hosea, R.; Kasim, V.; Wu, S. The biological implications of Yin Yang 1 in the hallmarks of cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4183–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nigris, F.; Botti, C.; Rossiello, R.; Crimi, E.; Sica, V.; Napoli, C. Cooperation between Myc and YY1 provides novel silencing transcriptional targets of α3β1-integrin in tumour cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nigris, F.; Crudele, V.; Giovane, A.; Casamassimi, A.; Giordano, A.; Garban, H.J.; Cacciatore, F.; Pentimalli, F.; Marquez-Garban, D.C.; Petrillo, A.; et al. CXCR4/YY1 inhibition impairs VEGF network and angiogenesis during malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14484–14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvagalla, S.; Kolapalli, S.P.; Vallabhapurapu, S. The Two Sides of YY1 in Cancer: A Friend and a Foe. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, E.; Jia, H.; Loguercio, S.; Su, A.I.; Feeney, A.J. YY1 plays an essential role at all stages of B-cell differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3911–E3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, G.; Torrisi, E.; Ligresti, G.; Malaponte, G.; Militello, L.; Russo, A.E.; McCubrey, J.A.; Canevari, S.; Libra, M. The involvement of the transcription factor Yin Yang 1 in cancer development and progression. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, G.; Torrisi, E.; Ligresti, G.; Nicoletti, F.; Malaponte, G.; Traval, S.; McCubrey, J.A.; Canevari, S.; Libra, M. Yin Yang 1 overexpression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is associated with B-cell transformation and tumor progression. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.M.; Kanda, K.; Zhang, L.; Boxer, L.M. Activation of the c-myc p1 promoter in Burkitt’s lymphoma by the hs3 immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene enhancer. Leukemia 2007, 21, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.I.; Jazirehi, A.R.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Bonavida, B. Rituximab-Induced Inhibition of YY1 and Bcl-x L Expression in Ramos Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Cell Line via Inhibition of NF-κB Activity: Role of YY1 and Bcl-x L in Fas Resistance and Chemoresistance, Respectively. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2174–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccaluga, P.P.; De Falco, G.; Kustagi, M.; Gazzola, A.; Agostinelli, C.; Tripodo, C.; Leucci, E.; Onnis, A.; Astolfi, A.; Sapienza, M.R.; et al. Gene expression analysis uncovers similarity and differences among Burkitt lymphoma subtypes. Blood 2011, 117, 3596–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardesa-Salzmann, T.M.; Colomo, L.; Gutierrez, G.; Chan, W.C.; Weisenburger, D.; Climent, F.; Gonzalez-Barca, E.; Mercadal, S.; Arenillas, L.; Serrano, S.; et al. High microvessel density determines a poor outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus chemotherapy. Haematologica 2011, 96, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybkær, K.; Bøgsted, M.; Falgreen, S.; Bødker, J.S.; Kjeldsen, M.K.; Schmitz, A.; Bilgrau, A.E.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Li, L.; Bergkvist, K.S.; et al. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Classification System That Associates Normal B-Cell Subset Phenotypes With Prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, S.; Viailly, P.-J.; Bohers, E.; Bertrand, P.; Ruminy, P.; Marchand, V.; Maingonnat, C.; Mareschal, S.; Picquenot, J.-M.; Penther, D.; et al. Biological and Clinical Relevance of Associated Genomic Alterations in MYD88 L265P and non-L265P–Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Analysis of 361 Cases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouska, A.; McKeithan, T.W.; Deffenbacher, K.E.; Lachel, C.; Wright, G.W.; Iqbal, J.; Smith, L.M.; Zhang, W.; Kucuk, C.; Rinaldi, A.; et al. Genome-wide copy-number analyses reveal genomic abnormalities involved in transformation of follicular lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, S.; Tesson, B.; Jais, J.-P.; Feldman, A.L.; Magnano, L.; Thomas, E.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Albaud, B.; Carrère, M.; Xerri, L.; et al. A gene-expression profiling score for prediction of outcome in patients with follicular lymphoma: A retrospective training and validation analysis in three international cohorts. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Abrisqueta, P.; Wright, G.W.; Slack, G.W.; Mottok, A.; Villa, D.; Jares, P.; Rauert-Wunderlich, H.; Royo, C.; Clot, G.; et al. New Molecular Assay for the Proliferation Signature in Mantle Cell Lymphoma Applicable to Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Biopsies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, R.B.; Hevezi, P.; Lee, J.; Willhite, D.; Lechner, S.M.; Foster, A.C.; Zlotnik, A. Gene expression analyses reveal molecular relationships among 20 regions of the human CNS. Neurogenetics 2006, 7, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, Y.J.; Pennell, C.E.; Chua, H.N.; Perkins, J.E.; Lye, S.J. Whole Blood Gene Expression Profile Associated with Spontaneous Preterm Birth in Women with Threatened Preterm Labor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, M.; Bentink, S.; Berger, H.; Klapper, W.; Wessendorf, S.; Barth, T.F.E.; Bernd, H.-W.; Cogliatti, S.B.; Dierlamm, J.; Feller, A.C.; et al. A Biologic Definition of Burkitt’s Lymphoma from Transcriptional and Genomic Profiling. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recurrent mutation of the ID3 gene in Burkitt lymphoma identified by integrated genome, exome and transcriptome sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1316–1320. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholtysik, R.; Kreuz, M.; Hummel, M.; Rosolowski, M.; Szczepanowski, M.; Klapper, W.; Loeffler, M.; Trümper, L.; Siebert, R.; Küppers, R. Characterization of genomic imbalances in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by detailed SNP-chip analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.I.; Wiltshire, T.; Batalov, S.; Lapp, H.; Ching, K.A.; Block, D.; Zhang, J.; Soden, R.; Hayakawa, M.; Kreiman, G.; et al. A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6062–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baty, F.; Facompré, M.; Wiegand, J.; Schwager, J.; Brutsche, M.H. Analysis with respect to instrumental variables for the exploration of microarray data structures. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Affar, B.; Gay, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, H.; Huarte, M.; Wu, S.; Collins, T.; Li, E. Essential dosage-dependent functions of the transcription factor yin yang 1 in late embryonic development and cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 3565–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabais Sá, M.J.; Gabriele, M.; Testa, G.; de Vries, B.B. Gabriele-de Vries Syndrome; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Sindhava, V.; Vuyyuru, R.; Jha, V.; Hodewadekar, S.; Manser, T.; Atchison, M.L. YY1 Is Required for Germinal Center B Cell Development. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, M.; Kodela, R.; Santiago, G.; Le, T.T.C.; Nath, N.; Kashfi, K. NOSH-aspirin (NBS-1120) inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth in a xenograft mouse model: Modulation of FoxM1, p53, NF-κB, iNOS, caspase-3 and ROS. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 176, 113857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.S.; Chan, H.Y.E. Transcriptional dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: Who tipped the balance of Yin Yang 1 in the brain. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arribas Arranz, J.; Winter, D.N.; Drexler, H.G.; Eberth, S. Suitability of Yin Yang 1 transcript and protein levels for biomarker studies in B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colnaghi, R.; Connell, C.M.; Barrett, R.M.; Wheatley, S.P. Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33450–33456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, N.R.; Ball, K.F.; Stiff, T.; Wall, N.R. Yin Yang 1 (YY1): Regulation of Survivin and Its Role In Invasion and Metastasis. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2017, 22, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.I.; Baritaki, S.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Martinez-Paniagua, M.A.; Bonavida, B. A potential mechanism of rituximab-induced inhibition of tumor growth through its sensitization to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-expressing host cytotoxic cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.I.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Jazirehi, A.R.; Garban, H.; Bonavida, B. Rituximab (chimeric anti-CD20) sensitizes B-NHL cell lines to Fas-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 8114–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potluri, V.; Noothi, S.K.; Vallabhapurapu, S.D.; Yoon, S.O.; Driscoll, J.J.; Lawrie, C.H.; Vallabhapurapu, S. Transcriptional repression of Bim by a novel YY1-RelA complex is essential for the survival and growth of Multiple Myeloma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jacamo, R.; Konopleva, M.; Garzon, R.; Croce, C.; Andreeff, M. CXCR4 downregulation of let-7a drives chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Andrés, G.; Rangel-Santiago, J.; Tirado-Rodríguez, B.; Martinez-Ruiz, G.U.; Klunder-Klunder, M.; Vega, M.I.; Lopez-Martinez, B.; Jiménez-Hernández, E.; Torres Nava, J.; Medina-Sanson, A.; et al. Role of Yin Yang-1 (YY1) in the transcription regulation of the multi-drug resistance. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Martinez, M.; Valencia-Hipolito, A.; Vega, G.G.; Neri, N.; Nambo, M.J.; Alvarado, I.; Cuadra, I.; Duran-Padilla, M.A.; Martinez-Maza, O.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; et al. Regulation of Krüppel-Like Factor 4 (KLF4) expression through the transcription factor Yin-Yang 1 (YY1) in non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2173–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C. Sp1 Upregulates Survivin Expression in Adenocarcinoma of Lung Cell Line A549. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2011, 294, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Galvin, K.M.; Shi, Y. Evidence for physical interaction between the zinc-finger transcription factors YY1 and Sp1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6145–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, S.; Zheng, K.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, H.; et al. Sp1 and c-Myc modulate drug resistance of leukemia stem cells by regulating survivin expression through the ERK-MSK MAPK signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletic, A.V.; Jellusova, J.; Cato, M.H.; Lee, C.R.; Baracho, G.V.; Conway, E.M.; Rickert, R.C. Essential Role for Survivin in the Proliferative Expansion of Progenitor and Mature B Cells. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Ji, J.; Zhu, H. Prognostic value of survivin in patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 5847–5854. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosini, G.; Adida, C.; Altieri, D.C. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, S.M.; Arendt, B.K.; Grote, D.M.; Jelinek, D.F.; Novak, A.J.; Wellik, L.E.; Remstein, E.D.; Bennett, C.F.; Fielding, A. Inhibition of survivin expression suppresses the growth of aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leukemia 2004, 18, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, S.; Keerthivasan, G.; Huang, Z.; Gurbuxani, S.; Crispino, J.D. Overexpression of survivin initiates hematologic malignancies in vivo. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1920–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Duan, N.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Survivin and Tumorigenesis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Aljahdali, I.; Ling, X. Cancer therapeutics using survivin BIRC5 as a target: What can we do after over two decades of study? J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.M.; Zhu, Y.K.; Ma, Y.H.; Zhang, M.E.N.G.; Liao, B.; Wu, H.Y.; Lin, H.L. Knockdown of Survivin Gene by Vector-Based Short Hairpin RNA Technique Induces Apoptosis and Growth Inhibition in Burkitt’s Lymphoma Raji Cell Line. Neoplasma 2006, 53, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galloway, N.R.; Diaz Osterman, C.J.; Reiber, K.; Jutzy, J.M.; Li, F.; Sui, G.; Soto, U.; Wall, N.R. Yin Yang 1 regulates the transcriptional repression of Survivin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Wu, C.W.; Dong, Y.; Cai, M.; Mok, M.T.S.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ng, S.S.M.; Chen, M.; et al. microRNA-7 is a novel inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5078–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Stovall, D.B.; Inoue, K.; Sui, G. The oncogenic role of Yin Yang 1. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2011, 16, 163–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.-S.; Wong, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-F.; Li, H.-Y. Survivin withdrawal by nuclear export failure as a physiological switch to commit cells to apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, C.M.; Colnaghi, R.; Wheatley, S.P. Nuclear Survivin Has Reduced Stability and Is Not Cytoprotective. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3289–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Boddu, S.; et al. Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D745–D751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornes, O.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Khan, A.; van der Lee, R.; Zhang, X.; Richmond, P.A.; Modi, B.P.; Correard, S.; Gheorghe, M.; Baranašić, D.; et al. JASPAR 2020: Update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D87–D92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.H.; Tokheim, C.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Sengupta, S.; Bertrand, D.; Weerasinghe, A.; Colaprico, A.; Wendl, M.C.; Kim, J.; Reardon, B.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Cancer Driver Genes and Mutations. Cell 2018, 173, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A.; Hitz, B.C.; Sloan, C.A.; Chan, E.T.; Davidson, J.M.; Gabdank, I.; Hilton, J.A.; Jain, K.; Baymuradov, U.K.; Narayanan, A.K.; et al. The Encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE): Data portal update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D794–D801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, A.D. The Human Genome Browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, J. R2: Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform. Available online: http://r2.amc.nl (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Onder, T.T.; Kara, N.; Cherry, A.; Sinha, A.U.; Zhu, N.; Bernt, K.M.; Cahan, P.; Marcarci, B.O.; Unternaehrer, J.; Gupta, P.B.; et al. Chromatin-modifying enzymes as modulators of reprogramming. Nature 2012, 483, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestro, R.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Hamamori, Y.; Krasnokutsky, S.; Sartorelli, V.; Kedes, L.; Doglioni, C.; Beach, D.H.; Hannon, G.J. Twist is a potential oncogene that inhibits apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seger, Y.R.; García-Cao, M.; Piccinin, S.; Cunsolo, C.L.; Doglioni, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Hannon, G.J.; Maestro, R. Transformation of normal human cells in the absence of telomerase activation. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, G.J.; Sun, P.; Carnero, A.; Xie, L.Y.; Maestro, R.; Conklin, D.S.; Beach, D. MaRX: An approach to genetics in mammalian cells. Science 1999, 283, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Relative Score | Start | End | Strand | Predicted Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.845 | 770 | 781 | + | AAACATGGTGAA |
| 0.845 | 155 | 166 | − | CACCATGGCCTC |
| 0.807 | 2491 | 2502 | + | GCAGATGGCCGA |
| 0.804 | 2819 | 2830 | + | TAAGATGCCTGA |
| 0.804 | 1002 | 1013 | + | AAGAATGGGGGC |
| GEO ID | Method | Samples Type | Samples | Contributor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE26673 | u133p2 | T-BL | 16 | Piccaluga PP | [15] |
| GSE132929 | u133p2 | T-B-NHL (BL-59; DLBCL-95; FL-65; HGBCL-4; MCL-43; MZL-23) | 290 | Green MR | na |
| GSE10846 | u133p2 | T-DLBCL | 420 | Xiao W | [16] |
| GSE56315 | u133p2 | T-DLBCL | 122 | Boedker JS | [17] |
| GSE87371 | u133p2 | T-DLBCL | 223 | Jardin F | [18] |
| GSE81183 | u133p2 | T-FL | 42 | McKeithan TW | [19] |
| GSE93261 | u133p2 | T-FL | 149 | Salles G | [20] |
| GSE16024 | u133p2 | T-B-NHL (7-MCL; 7-FL) | 14 | Du MQ | na |
| GSE93291 | u133p2 | T-MCL | 122 | Staudt LM | [21] |
| GSE7307 | u133p2 | N-Various tissues | 504 | Roth RB | na |
| GSE3526 | u133p2 | N-Various tissues | 353 | Roth RB | [22] |
| GSE46510 | u133p2 | N-PBC | 154 | Lye SJ | [23] |
| GSE4475 | u133a | T-BL | 215 | Hummel M | [24] |
| GSE10172 | u133a | T-Pediatric ma-B-NHL (8-BL; 5- BL like; 14-DLBCL; 2-FL; 7-AU B-NHL) | 36 | Siebert R | [25] |
| GSE57611 | u133a | T-DLBCL | 148 | Kreuz M | [26] |
| GSE1133 | u133a | N-Various tissues | 158 | Su AI | [27] |
| GSE3846 | u133a | N-PBC | 108 | Baty F | [28] |
| GEO ID | Analyzed Samples | YY1 Normality Test | BIRC5 Normality Test | Pearson R | Pearson P | Spearman R | Spearman P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE93261 | 149 | 0.3874 (Y) | 0.0013 (N) | 0.2658 | 0.0011 (**) | 0.2523 | 0.0019 (**) |
| GSE81183 | 42 | 0.0001 (N) | 0.4082 (Y) | 0.4293 | 0.0046 (**) | 0.3948 | 0.0097 (**) |
| GSE16024 | 14 | 0.0049 (N) | 0.0042 (N) | 0.7882 | 0.0008 (***) | 0.5413 | 0.0481 (*) |
| GSE93291 | 122 | 0.0843 (Y) | 0.0001 (N) | 0.3638 | <0.0001 (****) | 0.3926 | <0.0001 (****) |
| GSE87371 | 223 | 0.3301 (Y) | 0.2087 (Y) | 0.572 | <0.0001 (****) | 0.5937 | <0.0001 (****) |
| GSE57611 | 116 | 0.2843 (Y) | 0.8101 (Y) | 0.2379 | 0.0101 (*) | 0.226 | 0.0147 (*) |
| GSE56315 | 89 | 0.2221 (Y) | 0.3798 (Y) | 0.4523 | <0.0001 (****) | 0.4365 | <0.0001 (****) |
| GSE10846 | 414 | 0.7196 (Y) | 0.0414 (N) | 0.5321 | <0.0001 (****) | 0.5524 | <0.0001 (****) |
| GSE26673 | 16 | 0.4792 (Y) | 0.4778 (Y) | 0.7747 | 0.0004 (***) | 0.7491 | 0.0012 (**) |
| GSE4475 | 215 | 0.0001 (N) | 0.3127 (Y) | 0.2204 | 0.0011 (**) | 0.2781 | <0.0001 (****) |
| GSE10172 | 36 | 0.3155 (Y) | 0.9022 (Y) | 0.498 | 0.002 (**) | 0.6044 | <0.0001 (****) |
| GSE132929 | 290 | 0.0001 (N) | 0.0001 (N) | 0.6306 | <0.0001 (****) | 0.5355 | <0.0001 (****) |
| GENE ID | Primer F | Primer R | bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCL2 | TGAACTGGGGGAGGATTGTG | CGTACAGTTCCACAAAGGCA | 183 |
| BCL2L1 02 | AGCTTTGAACAGGATACTTTTGTGG | GGTGGGAGGGTAGAGTGGAT | 183 |
| BCL2L1 01 | CTGTGCGTGGAAAGCGTAGA | GCTGCTGCATTGTTCCCATAG | 155 |
| BCL2L2 | CACCCAGGTCTCCGATGAAC | GCTGTGAACTCCGCCCAG | 210 |
| BCL2L3 | TTTTCAGCGACGGCGTAACA | CAAACCCATCCCAGCCTCTTT | 189 |
| BCL2L4 | CCCCGAGAGGTCTTTTTCCG | TGGTTCTGATCAGTTCCGGC | 145 |
| BCL2L7 | GATCCCGGCAGGCTGATCC | GTAGCTGCGGAAAACCTCCT | 156 |
| BCL2L8 | CTTTAAGAAGGGACTTCCTCGC | GTGGAGTTTCGGGATGTGGA | 163 |
| BCL2L15 | ACCTGGTGTGCTCAGGATTC | TCCAGATTTTCCCAACCTCCC | 194 |
| BIRC1 | TCAAGCCGTCCCATTTGTTG | TGCTGACACTGCTGGATGAT | 204 |
| BIRC2 | AAGTGGTTTCCAAGGTGTGAGT | AAGCCCATTTCCAAGGCAGATT | 230 |
| BIRC3 | TCTGGGCAGCAGGTTTACAA | GCATTCTTTGGATAGTAAAACACCA | 191 |
| BIRC4 | TGTCCTGGCGCGAAAAGGT | CGTGCCAGTGTTGATGCTGA | 190 |
| BIRC5 | CAAGGACCACCGCATCTCTA | TGTTCCTCTATGGGGTCGTCA | 189 |
| BIRC7 | GGCTCTGAGGAGTTGCGTCT | CTGATGGCCTGTGTGGAAGAAG | 105 |
| BIK | CCGCCAGAGGAGAAATGTCTGA | TCCTCCATAGGGTCCAGGTC | 145 |
| TP53 | CCCCTCCTCAGCATCTTATCC | GTACAGTCAGAGCCAACCTCAG | 124 |
| YY1 | GAGAGAACTCACCTCCTGAT | GGCTTCTCTCCAGTATGAAC | 325 |
| GAPDH | AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTTG | AGGGGCCATCCACAGTCTTC | 258 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vivarelli, S.; Falzone, L.; Ligresti, G.; Candido, S.; Garozzo, A.; Magro, G.G.; Bonavida, B.; Libra, M. Role of the Transcription Factor Yin Yang 1 and Its Selectively Identified Target Survivin in High-Grade B-Cells Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176446
Vivarelli S, Falzone L, Ligresti G, Candido S, Garozzo A, Magro GG, Bonavida B, Libra M. Role of the Transcription Factor Yin Yang 1 and Its Selectively Identified Target Survivin in High-Grade B-Cells Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176446
Chicago/Turabian StyleVivarelli, Silvia, Luca Falzone, Giovanni Ligresti, Saverio Candido, Adriana Garozzo, Gaetano Giuseppe Magro, Benjamin Bonavida, and Massimo Libra. 2020. "Role of the Transcription Factor Yin Yang 1 and Its Selectively Identified Target Survivin in High-Grade B-Cells Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176446
APA StyleVivarelli, S., Falzone, L., Ligresti, G., Candido, S., Garozzo, A., Magro, G. G., Bonavida, B., & Libra, M. (2020). Role of the Transcription Factor Yin Yang 1 and Its Selectively Identified Target Survivin in High-Grade B-Cells Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176446