White Adipose Tissue Expansion in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Is Associated with Upregulation of CK2, AKT and ERK1/2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
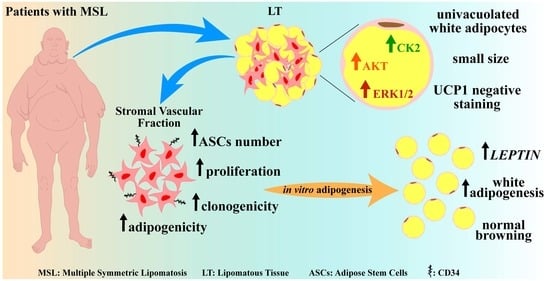
2.1. Morphological and Gene Expression Analyses Reveal White Features of LT
2.2. Protein Kinases CK2, AKT and ERK1/2 Are Hyperactivated in LT
2.3. Adipose Stem Cells Are More Abundant in LT Than in SAT
2.4. LT-Derived ASCs Display a Great In Vitro White Adipogenic Potential
2.5. The Clonogenic and Adipogenic Potential of LT Are Higher Compared to Healthy SAT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Patient Characterization and Tissue Collection
4.2. Histological and IHC Analysis
4.3. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.4. Protein Extraction
4.5. CK2 Kinase Activity Assay
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) Isolation, Morphological Analysis and Adipogenic Differentiation
4.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.9. Proliferation Assays
4.10. Limiting Dilution Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| ALAT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ASC | Adipose Stem Cell |
| AT | Adipose Tissue |
| BAT | Brown Adipose Tissue |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| CAPSL | Calcyphosin-like |
| CIDEA | Cell death inducing DFFA like effector A |
| CK2 | Casein kinase 2 |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ELOVL3 | Elongation of very long chain fatty acid-like 3 |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| EVA1 | Epithelial V-like antigen 1 |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta |
| h-AdM | Human Adipogenic Medium |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| h-SdM | Human Standard Medium |
| IBMX | 3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LT | Lipomatous Tissue |
| MFNT2 | Mitofusin 2 |
| MSL | Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain reaction |
| PPARG2 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| PRAS40 | Proline-rich AKT substrate |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| RhoA | Ras Homolog Family Member A |
| ROCK | Rho-associated protein kinase |
| SAT | Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue |
| SVF | Stromal Vascular Fraction |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling Protein 1 |
| WAT | White Adipose Tissue |
References
- Enzi, G.; Busetto, L.; Ceschin, E.; Coin, A.; Digito, M.; Pigozzo, S. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: Clinical aspects and outcome in a long-term longitudinal study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busetto, L.; Sträter, D.; Enzi, G.; Coin, A.; Sergi, G.; Inelmen, E.M.; Pigozzo, S. Differential clinical expression of multiple symmetric lipomatosis in men and women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enzi, G.; Busetto, L.; Sergi, G.; Coin, A.; Inelmen, E.M.; Vindigni, V.; Bassetto, F.; Cinti, S. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: A rare disease and its possible links to brown adipose tissue. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, M.; Bianchi, M.C.; Santorelli, F.M.; Tessa, A.; Casali, C.; Murri, L.; Siciliano, G. Encephalomyopathy with multiple mitochondrial DNA deletions and multiple symmetric lipomatosis: Further evidence of a possible association. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 1197–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Blanco, R.; Rojo-Sebastián, A.; Torregrosa-Martínez, M.H.; Blazquez, A. Beyond cervical lipomas: Myoclonus, gait disorder and multisystem involvement leading to mitochondrial disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, O.; Barca, E.; Lamperti, C.; Servidei, S.; Comi, G.P.; Moggio, M.; Mongini, T.; Siciliano, G.; Filosto, M.; Pegoraro, E.; et al. Lipomatosis Incidence and Characteristics in an Italian Cohort of Mitochondrial Patients. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gallardo, E.; Cammarata-Scalisi, F.; Emperador, S.; Hernández-Ainsa, C.; Habbane, M.; Vela-Sebastián, A.; Bayona-Bafaluy, M.P.; Montoya, J.; Ruiz-Pesini, E. Mitochondrial DNA pathogenic mutations in multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Clin. Genet. 2020, 97, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, S.L.; Cheuk-Him, N.A.; Innes, A.M.; Wagner, J.D.; Dyment, D.A.; Tetreault, M.; Care4Rare Canada Consortium; Majewski, J.; Boycott, K.M.; Screaton, R.A.; et al. Homozygous mutations in MFN2 cause multiple symmetric lipomatosis associated with neuropathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5109–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plummer, C.; Spring, P.J.; Marotta, R.; Chin, J.; Taylor, G.; Sharpe, D.; Athanasou, N.A.; Thyagarajan, D.; Berkovic, S.F. Multiple Symmetrical Lipomatosis-a mitochondrial disorder of brown fat. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiltz, D.; Tschernitz, S.; Ortner, C.; Anker, A.; Klein, S.; Felthaus, O.; Biermann, N.; Schreml, J.; Prantl, L.; Schreml, S. Adipose Tissue in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Shows Features of Brown/Beige Fat. Aesthetic. Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coin, A.; Enzi, G.; Bussolotto, M.; Ceschin, E.; Difito, M.; Angelini, C. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: Evidence for mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2000, 1, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.R.; Gámez, J.; Solano, A.; Playán, A.; Schwartz, S.; Santorelli, F.M.; Cervera, C.; Casali, C.; Montoya, J.; Villarroya, F. Uncoupling protein-1 mRNA expression in lipomas from patients bearing pathogenic mitochondrial DNA mutations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 278, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisoli, E.; Regianini, L.; Briscini, L.; Bulbarelli, A.; Busetto, L.; Coin, A.; Enzi, G.; Carruba, M.O. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis may be the consequence of defective noradrenergic modulation of proliferation and differentiation of brown fat cells. J. Pathol. 2002, 198, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Gurmaches, J.; Hung, C.M.; Sparks, C.A.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Guertin, D.A. PTEN loss in the Myf5 lineage redistributes body fat and reveals subsets of white adipocytes that arise from Myf5 precursors. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppler-Noreuil, K.M.; Parker, V.E.; Darling, T.N.; Martinez-Agosto, J.A. Somatic overgrowth disorders of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway & therapeutic strategies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2016, 172, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; He, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, S.; Wan, X.; Yang, W.; Mo, Z. miR-125a-3p and miR-483-5p promote adipogenesis via suppressing the RhoA/ROCK1/ERK1/2 pathway in multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, A.; Marbach, F.; Tschernitz, S.; Ortner, C.; Berneburg, M.; Felthaus, O.; Prantl, L.; Kye, M.J.; Rappl, G.; Altmüller, J.; et al. Calcyphosine-like (CAPSL) is regulated in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis and is involved in Adipogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frontini, A.; Vitali, A.; Perugini, J.; Murano, I.; Romiti, C.; Ricquier, D.; Guerrieri, M.; Cinti, S. White-to-brown transdifferentiation of omental adipocytes in patients affected by pheochromocytoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Franco, A.; Guasti, D.; Mazzanti, B.; Ercolino, T.; Francalanci, M.; Nesi, G.; Bani, D.; Forti, G.; Mannelli, M.; Valeri, A.; et al. Dissecting the origin of inducible brown fat in adult humans through a novel adipose stem cell model from adipose tissue surrounding pheochromocytoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1903–E1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Seale, P. Control of brown and beige fat development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Emanuelli, B.; Kahn, C.R. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. AKT/PKB signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell 2007, 129, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiza, C.; Nascimento, E.B.; Ouwens, D.M. Role of PRAS40 in Akt and mTOR signaling in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E1453–E1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Yu, S.X.; Lu, Y.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Woodgett, J.R.; Mills, G.B. Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11960–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotnikov, A.; Zehorai, E.; Procaccia, S.; Seger, R. The MAPK cascades: Signaling components, nuclear roles and mechanisms of nuclear translocation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Boström, P.; Sparks, L.M.; Ye, L.; Choi, J.H.; Giang, A.H.; Khandekar, M.; Virtanen, K.A.; Nuutila, P.; Schaart, G.; et al. Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell 2012, 150, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cinti, S.; Enzi, G.; Cigolini, M.; Bosello, O. Ultrastructural features of cultured mature adipocyte precursors from adipose tissue in multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 1983, 5, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xie, Y.; Hu, P.; Zhao, S.; Mo, Z. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: Substantial subcutaneous adipose tissue accumulation did not induce glucose and lipid metabolism dysfunction. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 57, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zancanaro, C.; Sbarbati, A.; Morroni, M.; Carraro, R.; Cigolini, M.; Enzi, G.; Cinti, S. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Ultrastructural investigation of the tissue and preadipocytes in primary culture. Lab. Investig. 1990, 63, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Kazumi, T.; Ricquier, D.; Maeda, T.; Masuda, T.; Hozumi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Yoshida, M. Failure to detect brown adipose tissue uncoupling protein mRNA in benign symmetric lipomatosis (Madelung’s disease). Endocr. J. 1994, 41, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Hu, G.; Mo, Z. Profiling of differentially expressed genes in adipose tissues of multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6570–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Molina, A.; Efeyan, A.; Lopez-Guadamillas, E.; Muñoz-Martin, M.; Gómez-López, G.; Cañamero, M.; Mulero, F.; Pastor, J.; Martinez, S.; Romanos, E.; et al. Pten positively regulates brown adipose function, energy expenditure, and longevity. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgo, C.; Milan, G.; Favaretto, F.; Stasi, F.; Fabris, R.; Salizzato, V.; Cesaro, L.; Belligoli, A.; Sanna, M.; Foletto, M.; et al. CK2 modulates adipocyte insulin-signaling and is up-regulated in human obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinoda, K.; Ohyama, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Ogura, M.; Sato, A.; Hong, H.; Hosono, T.; Sharp, L.Z.; Scheel, D.W.; et al. Phosphoproteomics Identifies CK2 as a Negative Regulator of Beige Adipocyte Thermogenesis and Energy Expenditure. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Hino, Y.; Ando, M.; Kotani, K.; Konishi, H.; Matsuzaki, H.; Kikkawa, U.; Ogawa, W.; et al. Insulin-induced phosphorylation and activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3B by the serine-threonine kinase Akt. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 6286–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sancak, Y.; Thoreen, C.C.; Peterson, T.R.; Lindquist, R.A.; Kang, S.A.; Spooner, E.; Carr, S.A.; Sabatini, D.M. PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein kinase. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felthaus, O.; Schön, T.; Schiltz, D.; Aung, T.; Kühlmann, B.; Jung, F.; Anker, A.; Klein, S.; Prantl, L. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells from affected and unaffected areas in patients with multiple symmetric lipomatosis show differential regulation of mTOR pathway genes. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2018, 69, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Song, M.J.; Yoo, E.J.; Choe, S.S.; Park, S.D.; Kim, J.B. Regulatory role of glycogen synthase kinase 3 for transcriptional activity of ADD1/SREBP1c. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51999–512006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartelt, A.; Heeren, J. Adipose tissue browning and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, K.; Luijten, I.H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hong, H.; Sonne, S.B.; Kim, M.; Xue, R.; Chondronikola, M.; Cypess, A.M.; Tseng, Y.H.; et al. Genetic and functional characterization of clonally derived adult human brown adipocytes. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bettini, S.; Favaretto, F.; Compagnin, C.; Belligoli, A.; Sanna, M.; Fabris, R.; Serra, R.; Dal Prà, C.; Prevedello, L.; Foletto, M.; et al. Resting Energy Expenditure, Insulin Resistance and UCP1 Expression in Human Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue of Patients with Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prantl, L.; Schreml, J.; Gehmert, S.; Klein, S.; Bai, X.; Zeitler, K.; Schreml, S.; Alt, E.; Gehmert, S.; Felthaus, O. Transcription Profile in Sporadic Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Reveals Differential Expression at the Level of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salizzato, V.; Borgo, C.; Cesaro, L.; Pinna, L.A.; Donella-Deana, A. Inhibition of protein kinase CK2 by CX-5011 counteracts imatinib-resistance preventing rpS6 phosphorylation in chronic myeloid leukaemia cells: New combined therapeutic strategies. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18204–18218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, M.; Franzin, C.; Pozzobon, M.; Favaretto, F.; Rossi, C.A.; Calcagno, A.; Scarda, A.; Dal Prà, C.; Pilon, C.; Milan, G.; et al. Adipogenic potential of skeletal muscle satellite cells. Clin. Lipidol. 2009, 4, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belligoli, A.; Compagnin, C.; Sanna, M.; Favaretto, F.; Fabris, R.; Busetto, L.; Foletto, M.; Dal Prà, C.; Serra, R.; Prevedello, L.; et al. Characterization of subcutaneous and omental adipose tissue in patients with obesity and with different degrees of glucose impairment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerlin, L.; Donnenberg, V.S.; Rubin, J.P.; Donnenberg, A.D. Mesenchymal markers on human adipose stem/progenitor cells. Cytom. A 2013, 83, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guimarães-Camboa, N.; Evans, S.M. Are Perivascular Adipocyte Progenitors Mural Cells or Adventitial Fibroblasts? Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Smyth, G.K. ELDA: Extreme limiting dilution analysis for comparing depleted and enriched populations in stem cell and other assays. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 347, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| (A) | |||||||
| ID | Gender | Age | MSL Type | LT Site | SAT | T2D | BMI |
| 2884 | M | 58 | I | Neck | Abdominal | no | 22.5 |
| 2891 I | M | 62 | I | Neck | Abdominal | no | 26.6 |
| 2891 II | M | 63 | I | Neck | Abdominal | no | 26.5 |
| 3002 I | M | 64 | I | Neck and upper arm | Lumbar region | no | 29.7 |
| 3002 II | M | 67 | I | Upper arm | Lower limb | no | 33 |
| 3030 | M | 49 | I | Upper arm | Abdominal | yes | 29.4 |
| 5091 | M | 70 | I | Neck and upper arm | Abdominal | no | 28.3 |
| 5937 | F | 63 | I | Upper arm | Abdominal | yes | 33.8 |
| (B) | |||||||
| ID | Alcohol | Alcohol Amount (L/Day) | Smoking Status | Smoking Frequency (Cigarettes/Day) | |||
| 2884 | yes | - | never | - | |||
| 2891 | yes | 2 (red wine) | current | 15 | |||
| 3002 | yes | - | never | - | |||
| 3030 | no | - | current | 20 | |||
| 5091 | yes | 1 (red wine) | previous | - | |||
| 5937 | yes | - | never | - | |||
| (C) | |||||||
| ID | FPG (mmol/L) | Total Chol (mg/dL) | LDL-Chol (mg/dL) | HDL-Chol (mg/dL) | Triglycerides (mg/dL) | ALAT (UI/L) | GGT (UI/L) |
| 2884 | 4.9 | 200 | 139 | 41 | 150 | 18 | - |
| 2891 | 4.2 | 148 | 61 | 52 | 170 | - | 47 |
| 3002 | 5.9 | 152 | 109 | 24 | 95 | 23 | 45 |
| 3030 | 8.5 | 191 | 129 | 46 | 80 | 26 | 22 |
| 5091 | 5.4 | 151 | 39 | 92 | 105 | 23 | 79 |
| 5937 | 6.3 | 183 | 109 | 36 | 189 | 26 | 32 |
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) Reverse (5′-3′) | Annealing (°C) | Primers (F/R nM) | Amplicon (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPARG2 | ACCCAGAAAGCGATTCCTTCA AGTGGTCTTCCATTACGGAGAGATC | 60 | 900/900 | 87 |
| LEPTIN | GTGCGGATTCTTGTGGCTTT GGAATGAAGTCCAAACCGGTG | 63 | 100/100 | 174 |
| UCP1 | CTACGACACGGTCCAGGAGT AGTGGCAGTATTCATTGGGC | 60 | 300/300 | 110 |
| CIDEA | ACGTGAAGGCCACCATGTATGA TGCCCAGATAGATGAGAAACTGTCC | 62 | 300/300 | 141 |
| ELOVL3 | CCTTGCAATCTTCAGTATCCTGG GATGAAGTTGATGAAGCACACG | 60 | 300/300 | 146 |
| EVA1 | CAGTTCGACGACAATGGGACAT AGAGAAGCGTACAGTGTGCACGA | 60 | 300/300 | 108 |
| CD137 | CGACCCTGGACAAACTGTTCTTT AAGGAGATGATCTGCGGAGAGTGT | 63 | 300/300 | 170 |
| 18S | CGGCTACCACATCCAAGGAA GCTGGAATTACCGCGGCT | 60 | 100/100 | 186 |
| Samples | FITC | PE | perCP-Cy5.5 | APC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstained | - | - | - | - |
| Negative | IgG1 | IgG1 | IgG1 | IgG1 |
| Sample 1 | CD45 | CD31 | CD34 | - |
| Sample 2 | CD45 CD31 | CD90 | CD34 | CD73 |
| Sample 3 | CD45 CD31 | CD146 | CD34 | CD271 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanna, M.; Borgo, C.; Compagnin, C.; Favaretto, F.; Vindigni, V.; Trento, M.; Bettini, S.; Comin, A.; Belligoli, A.; Rugge, M.; et al. White Adipose Tissue Expansion in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Is Associated with Upregulation of CK2, AKT and ERK1/2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217933
Sanna M, Borgo C, Compagnin C, Favaretto F, Vindigni V, Trento M, Bettini S, Comin A, Belligoli A, Rugge M, et al. White Adipose Tissue Expansion in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Is Associated with Upregulation of CK2, AKT and ERK1/2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):7933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217933
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanna, Marta, Christian Borgo, Chiara Compagnin, Francesca Favaretto, Vincenzo Vindigni, Mariangela Trento, Silvia Bettini, Alessandra Comin, Anna Belligoli, Massimo Rugge, and et al. 2020. "White Adipose Tissue Expansion in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Is Associated with Upregulation of CK2, AKT and ERK1/2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 7933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217933
APA StyleSanna, M., Borgo, C., Compagnin, C., Favaretto, F., Vindigni, V., Trento, M., Bettini, S., Comin, A., Belligoli, A., Rugge, M., Bassetto, F., Donella-Deana, A., Vettor, R., Busetto, L., & Milan, G. (2020). White Adipose Tissue Expansion in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Is Associated with Upregulation of CK2, AKT and ERK1/2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 7933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217933