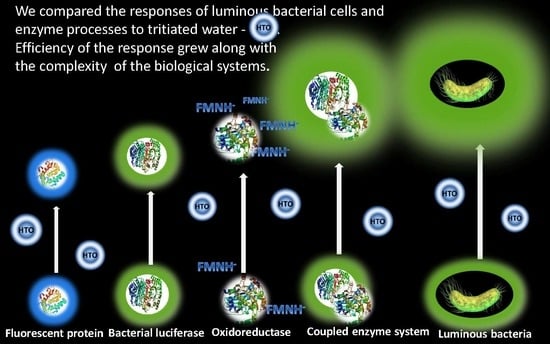
Enzymatic Responses to Low-Intensity Radiation of Tritium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Marine bacteria [18,19,20,21] and their enzymes [22] have been used as bioassays for several decades; this is why the effects of exogenous compounds on these assay systems have been intensively studied. The effects of a series of radionuclides [23,24,25,26] and gamma radiation [27,28] on the bacteria and their enzymatic reactions were studied and compared. Thus, the predictive premise for the bioassays was formed based on the molecular mechanisms of the radiation-induced effects.
- (2)
- Bioluminescence intensity is a tested physiological parameter under monitoring. The registration of luminescence is a convenient bioassay procedure; its advantages are a high sensitivity, high rates (duration down to 1–3 min), simplicity, as well as the availability of reagents and instruments. The high rates adapt the tests for a large number of measurements under comparable conditions and hence for a proper statistical processing, which is extremely important for low-dose exposures usually described in terms of “stochastic effects” [29]. Furthermore, the quick luminescence response assumes a nongenetic mechanism of low-intensity effects [30,31].
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reaction of Bacterial Luciferase. Reagents, Procedure, and Data Analysis
2.2. Effect of Tritium on the Reaction of NAD(P)H:FMN-Oxidoreductase. Reagents, Procedure, and Data Analysis
2.3. Coupled System of Two Enzymatic Reactions: Bacterial Luciferase–NAD(P)H:FMN-Oxidoreductase. Procedure and Data Analysis
2.4. Effect of Tritium on Photoluminescence of CLM-FP Reagents, Procedure, and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Tritium on the Bioluminescence System of Coupled Enzymatic Reactions: Bacterial Luciferase–NAD(P)H:FMN-Oxidoreductase
3.2. Effect of Tritium on the Enzymatic Activity of Bacterial Luciferase
3.3. Effect of Tritium on the Enzymatic Activity of NAD(P)H:FMN-Oxidoreductase
3.4. Effects of Tritium on Coelinteramide-Containing Fluorescent Protein
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLM | Coelenteramide |
| FP | Fluorescent Protein |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| FMN | Flavin mononucleotide |
| NADH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| HTO | Tritiated water |
References
- Vaiserman, A.; Koliada, A.; Zabuga, O.; Socol, Y. Health impacts of low-dose ionizing radiation: Current scientific debates and regulatory issues. Dose-Response 2018, 16, 1559325818796331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kojima, S.; Thukimoto, M.; Cuttler, J.M.; Inoguchi, K.; Otaki, T.; Shimura, N.; Koga, H.; Murata, A. Recovery from rheumatoid arthritis following 15 months of therapy with low doses of ionizing radiation: A Case Report. Dose-Response 2018, 16, 1559325818784719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehrer, S.; Green, S.; Rosenzweig, K.E. Reduced ovarian cancer incidence in women exposed to low dose ionizing background radiation or radiation to the ovaries after treatment for breast cancer or rectosigmoid cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 2979–2982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, G.; Kapoor, R.; Dhamija, A.; Singh, R.; Monga, B.; Calabrese, E.J. Necrotizing fasciitis: Low-dose radiotherapy as a potential adjunct treatment. Dose-Response 2019, 17, 1559325819871757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azzam, E.I.; Colangelo, N.W.; Domogauer, J.D.; Sharma, N.; de Toledo, S.M. Is ionizing radiation harmful at any exposure? An echo that continues to vibrate. Health Phys. 2016, 110, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, J. Sipping from a poisoned chalice. Science 2003, 302, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis: A revolution in toxicology, risk assessment and medicine. Re-Fram. Dose–Response Relatsh. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5 (Suppl. 1), S37–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis: Path and progression to significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormetic mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 580–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis: A fundamental concept in biology. Microb. Cell 2014, 1, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agathokleous, E.; Calabrese, E.J. A global environmental health perspective and optimisation of stress. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2020, 704, 135263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckey, T.D. Hormesis with Ionizing Radiation; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1980; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Jargin, S.V. Hormesis and radiation safety norms: Comments for an update. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Nakamura, H. Overview of biological, epidemiological, and clinical evidence of radiation hormesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iavicoli, I.; Leso, V.; Fontana, L.; Calabrese, E.J. Nanoparticle exposure and hormetic dose–responses: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kudryasheva, N.S.; Kovel, E.S. Monitoring of low-intensity exposures via luminescent bioassays of different complexity: Cells, enzyme reactions, and fluorescent proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, H.; Zhou, M.; Lv, D.; Wang, M.; Xie, D.; Yang, X.; Dong, C.; Li, S.; Lin, P. Novel segmented concentration addition method to predict mixture hormesis of chlortetracycline hydrochloride and oxytetracycline hydrochloride to Aliivibrio fischeri. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulich, A.A.; Isenberg, D.L. Use of the luminescent bacterial system for rapid assessment of aquatic toxicity. ISA Trans. 1981, 20, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girotti, S.; Ferri, E.N.; Fumo, M.G.; Maiolini, E. Monitoring of environmental pollutants by bioluminescent bacteria. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008, 608, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Pasini, P.; Mirasoni, M.; Michchelini, E.; Guardigli, M. Biotechnological application of bioluminescence and chemiluminescence. Trends Biotech. 2004, 22, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Adil, M.; Ehtisham-Ul-Haque, S.; Munir, B.; Yameen, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Shar, G.A.; Tahir, M.A.; Iqbal, M. Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratasyuk, V.A.; Esimbekova, E.N. Applications of luminous bacteria enzymes in toxicology. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen 2015, 18, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozhko, T.V.; Kudryasheva, N.S.; Kuznetsov, A.M.; Vydryakova, G.A.; Bondareva, L.G.; Bolsunovsky, A.Y. Effect of low-level α-radiation on bioluminescent assay systems of various complexity. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selivanova, M.A.; Mogilnaya, O.A.; Badun, G.A.; Vydryakova, G.A.; Kuznetsov, A.M.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Effect of tritium on luminous marine bacteria and enzyme reactions. J. Environ. Radioact. 2013, 120, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryasheva, N.S.; Rozhko, T.V. Effect of low-dose ionizing radiation on luminous marine bacteria: Radiation hormesis and toxicity. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 142, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selivanova, M.A.; Rozhko, T.V.; Devyatlovskaya, A.N.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Comparison of chronic low-dose effects of alpha-and beta-emitting radionuclides on marine bacteria. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2014, 9, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryasheva, N.S.; Petrova, A.S.; Dementyev, D.V.; Bondar, A.A. Exposure of luminous marine bacteria to low-dose gamma-radiation. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 169, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, V.J.; Lee, C.W.; Gu, M.B. Gamma-radiation dose-rate effects on DNA damage and toxicity in bacterial cells. Radiat. Environ. Bioph. 2003, 42, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilenko, I.Y.; Vasilenko, O.I. Radiation risk when exposed to small doses is negligible. Atomic Energy Bull. 2001, 12, 34–37. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rozhko, T.V.; Guseynov, O.A.; Guseynova, V.E.; Bondar, A.A.; Devyatlovskaya, A.N.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Is bacterial luminescence response to low-dose radiation associated with mutagenicity? J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 177, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandrova, M.; Rozhko, T.; Vydryakova, G.; Kudryasheva, N. Effect of americium-241 on luminous bacteria. Role of peroxides. J. Environ. Radioact. 2011, 102, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhko, T.V.; Nogovitsyna, E.I.; Badun, G.A.; Lukyanchuk, A.N.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Reactive Oxygen Species and low-dose effects of tritium on bacterial cells. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 208, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozhko, T.V.; Badun, G.A.; Razzhivina, I.A.; Guseynov, O.A.; Guseynova, V.E.; Kudryasheva, N.S. On mechanism of biological activation by tritium. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 157, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burlakova, E.B.; Konradov, A.A.; Maltseva, E.X. Effect of extremely weak chemical and physical stimuli on biological systems. Biophysics 2004, 49, 522–534. [Google Scholar]
- Kurvet, I.; Ivask, A.; Bondarenko, O.; Sihtmäe, M.; Kahru, A. LuxCDABE—transformed constitutively bioluminescent Escherichia coli for toxicity screening: Comparison with naturally luminous Vibrio fischeri. Sensors 2011, 11, 7865–7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, L.A. Ca2+-regulated photoproteins: Effective immunoassay reporters. Sensors 2010, 10, 11287–11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasitskaya, V.V.; Burakova, L.P.; Pyshnaya, I.A.; Frank, L.A. Bioluminescent reporters for identification of gene allelic variants. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2012, 38, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasitskaya, V.V.; Goncharova, N.S.; Biriukov, V.V.; Bashmakova, E.E.; Kabilov, M.R.; Sokolov, A.E.; Frank, L.A. The Ca2+-regulated photoprotein obelin as a tool for SELEX monitoring and DNA aptamer affinity evaluation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alieva, R.R.; Tomilin, F.N.; Kuzubov, A.A.; Ovchinnikov, S.G.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Ultraviolet fluorescence of coelenteramide and coelenteramide-containing fluorescent proteins. Experimental and theoretical study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 162, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.F.; Ferre, N.; Liu, Y.J. QM/MM Study on the light emitters of aequorin chemiluminescence, bioluminescence, and fluorescence: A general understanding of the bioluminescence of several marine organisms. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 8466–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.G.; Li, Z.S.; Ren, A.M.; Zou, L.Y.; Guo, J.F.; Goddard, J.D. The fluorescent properties of coelenteramide, a substrate of aequorin and obelin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2013, 251, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oort, B.; Eremeeva, E.V.; Koehorst, R.B.M.; Laptenok, S.P.; van Amerongen, H.; van Berkel, W.J.H.; Malikova, N.P.; Markova, S.V.; Vysotski, E.S.; Visser, A.J.W.G.; et al. Picosecond fluorescence relaxation spectroscopy of the calcium-discharged photoproteins aequorin and obelin. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 10486–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belogurova, N.V.; Kudryasheva, N.S.; Alieva, R.R.; Sizykh, A.G. Spectral components of bioluminescence of aequorin and obelin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2008, 92, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belogurova, N.V.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Discharged photoprotein obelin: Fluorescence peculiarities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 101, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alieva, R.R.; Belogurova, N.V.; Petrova, A.S.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Fluorescence properties of Ca2+-independent discharged obelin and its application prospects. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Liu, Y.J. Photoluminescence rainbow from coelenteramide—A theoretical study. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 95, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alieva, R.R.; Belogurova, N.V.; Petrova, A.S.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Effects of alcohols on fluorescence intensity and color of a discharged-obelin-based biomarker. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, A.S.; Alieva, R.R.; Belogurova, N.V.; Tirranen, L.S.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Variation of spectral characteristics of coelenteramide-containing fluorescent protein from Obelia longissima exposed to Dimethyl sulfoxide. Russ. Phys. J. 2016, 59, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrova, A.S.; Lukonina, A.A.; Badun, G.A.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Fluorescent coelenteramide-containing protein as a color bioindicator for low-dose radiation effects. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4377–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, A.S.; Lukonina, A.A.; Dementyev, D.V.; Bolsunovsky, A.Y.; Popov, A.V.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Protein-based fluorescent bioassay for low-dose gamma radiation exposures. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6837–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alieva, R.R.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Variability of fluorescence spectra of coelenteramide-containing proteins as a basis for toxicity monitoring. Talanta 2017, 170, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, J.W.; Baldwin, T.O.; Nicoli, M.Z. Bacterial luciferase: Assay, purification, and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 57, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illarionov, B.A.; Frank, L.A.; Illarionova, V.A.; Bondar, V.S.; Vysotski, E.S.; Blinks, J.R. Recombinant obelin: Cloning and expression of cDNA, purification, and characterization as a calcium indicator. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 305, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.; Hastings, J.W. Bioluminescence. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 14, 197–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyn, G.; Czyz, A. How do marine bacteria produce light, why are they luminescent, and can we employ bacterial bioluminescence in biotechnology. Oceanologia 2002, 44, 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- The International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 99. Low-dose Extrapolation of Radiation-related Cancer Risk. In Annals of the ICPR; Valentin, J., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Morgan, D.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhko, T.V.; Kolesnik, O.V.; Badun, G.A.; Stom, D.I.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Humic substances mitigate the impact of tritium on luminous marine bacteria. Involvement of reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamnev, A.A.; Dykman, R.L.; Kovács, K.; Pankratov, A.N.; Tugarova, A.V.; Homonnay, Z.; Kuzmann, E. Redox interactions between structurally different alkylresorcinols and iron(III) in aqueous media: Frozen-solution 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopic studies, redox kinetics and quantum chemical evaluation of the alkylresorcinol reactivities. Struct. Chem. 2014, 25, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rozhko, T.V.; Nemtseva, E.V.; Gardt, M.V.; Raikov, A.V.; Lisitsa, A.E.; Badun, G.A.; Kudryasheva, N.S. Enzymatic Responses to Low-Intensity Radiation of Tritium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228464
Rozhko TV, Nemtseva EV, Gardt MV, Raikov AV, Lisitsa AE, Badun GA, Kudryasheva NS. Enzymatic Responses to Low-Intensity Radiation of Tritium. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(22):8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228464
Chicago/Turabian StyleRozhko, Tatiana V., Elena V. Nemtseva, Maria V. Gardt, Alexander V. Raikov, Albert E. Lisitsa, Gennadii A. Badun, and Nadezhda S. Kudryasheva. 2020. "Enzymatic Responses to Low-Intensity Radiation of Tritium" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 22: 8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228464
APA StyleRozhko, T. V., Nemtseva, E. V., Gardt, M. V., Raikov, A. V., Lisitsa, A. E., Badun, G. A., & Kudryasheva, N. S. (2020). Enzymatic Responses to Low-Intensity Radiation of Tritium. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), 8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228464