Enhancement in Phospholipase D Activity as a New Proposed Molecular Mechanism of Haloperidol-Induced Neurotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- chlorpromazine (CPZ) in doses of 10 mmol/kg (3.2 mg/kg) and 20 mmol/kg (6.4 mg/kg),
- fluphenazine (FLU) at 10 mmol/kg (4.35 mg) and 20 mmol/kg (8.7 mg/kg),
- haloperidol (HAL) in doses of 10 mmol/kg (3.75 mg/kg) and 20 mmol/kg (7.5 mg/kg).
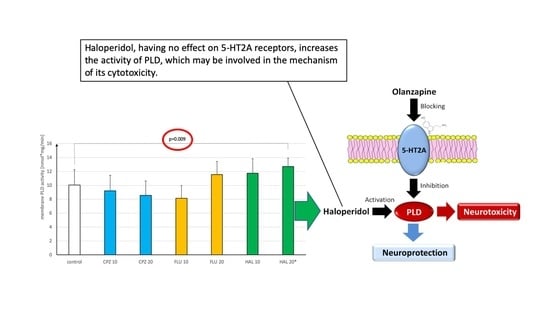
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PLD | phospholipase D |
| PC | phosphatidylcholine |
| PA | phosphatidic acid |
| CPZ | chlorpromazine |
| FLU | fluphenazine |
| HAL | haloperidol |
References
- Shukla, S.D.; Halenda, S.P. Phospholipase D in cell signaling and its relationship to phospholipase C. Life Sci. 1991, 48, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, T.; Kanfer, J.N. Partial purification and properties of a rat brain phospholipase D. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 9761–9765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frohman, M.A.; Sung, T.; Morris, A.J. Mammalian phospholipase D structure and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1439, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscovitch, M.; Czarny, M.; Fiucci, G.; Lavie, Y.; Tang, X. Localization and possible functions of phospholipase D isozymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 439, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, R.A.; Smith, J.L.; Ross, A.H.; Quo, R.G.; Symons, M.; Exton, J.H. Regulation of phospholipase D in HL60 cells. Evidence for a cytosolic phospholipase D. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 8466–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hattori, H.; Kanfer, J.N. Synaptosomal phospholipase D potential role in providing choline for acetylcholine synthesis. J. Neurochem. 1985, 45, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, D.; Cui, Y.; Siddiqui, R.A. Messenger functions of phosphatidic acid. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1996, 80, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, K.; Kodaki, T.; Nagamachi, Y.; Yamashita, S. Cloning, differential regulation and tissue distribution of alternatively spliced isoforms of ADP-ribosylation-factor-dependent phospholipase D from rat liver. Biochem. J. 1998, 329, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burkhardt, U.; Stegner, D.; Hattingen, E.; Beyer, S.; Nieswandt, B.; Klein, J. Impaired brain development and reduced cognitive function in phospholipase D-deficient mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 572, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzystanek, M.; Trzeciak, H.I.; Krzystanek, E.; Małecki, A. Effects of olanzapine and paroxetine on phospholipase D activity in the rat brain. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, K.; Miyanaga, K.; Machiyama, Y. Profiles of the affinity of antipsychotic drugs for neurotransmitter receptors and their clinical implication. Kitakanto Med. J. 1998, 48, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujimura, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamagami, K. Effects of antipsychotic drugs on neurotoxicity, expression of fos-like protein and c-fos mRNA in the retrosplenial cortex after administration of dizocilpine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 398, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Sato, K.; Horikoshi, R.; Yaginuma, M.; Yaginuma, N.; Shiragata, M.; Kumashiro, H. Effect of haloperidol on cyclic AMP and inositol trisphosphate in rat striatum in vivo. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 1992, 46, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, I.; Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kameda, K.; Koyama, T. Differential effects of subchronic treatments with atypical antipsychotic drugs on dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in the rat brain. J. Neural. Transm. (Vienna) 2000, 107, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trzeciak, H.I.; Kalaciński, W.; Małecki, A.; Kokot, D. Effect of neuroleptics on phospholipase A2 activity in the brain of rats. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1995, 245, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelsema, C.L. Light activation of phospholipase A2 in rod outer segments of bovine retina and its modulation by GTP-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strosznajder, J.; Strosznajder, R.P. Guanine nucleotides and fluoride enhance carbachol-mediated arachidonic acid release from phosphatidylinositol. Evidence for infolvement of GTP-binding protein on phospholipase A2 activation. J. Lipid Mediat. 1989, 1, 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Diwu, Z.; Panchuk-Voloshina, N.; Haugland, R.P. A stable nonfluorescent derivative of resorufin for the fluorometric determination of trace hydrogen peroxide: Applications in detecting the activity of phagocyte NADPH oxidase and other oxidases. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 253, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzystanek, M.; Trzeciak, H.I.; Krzystanek, E.; Małecki, A. Fluorometric assay of oleate-activated phospholipase D isoenzyme in membranes of rat nervous tissue and human platelets. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2010, 57, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakatabe, H.; Tsukahara, T.; Ishigooka, J.; Miura, S. Effects of chlorpromazine on phosphatidylinositol turnover following thrombin stimulation of human platelets. Biol. Psychiatry 1991, 29, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daasvatn, K.O.; Holmsen, H. Chlorpromazine and human platelet glycerolipid metabolism: Precursor specificity and significance of drug-platelet interaction time. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 57, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, M.; Da Prada, M.; Valerio, A.; Memo, M.; Spano, P.F.; Haefely, W.E. Dopamine D2 receptor stimulation inhibits inositol phosphate generating system in rat striatal slices. Brain Res. 1988, 456, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, H.A.; Chen, A.T. Multiple neurotoxic effects of haloperidol resulting in neuronal death. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 29, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishida, A.; Emoto, K.; Shimizu, M.; Uozumi, T.; Yamawaki, S. Brain ischaemia decreases phosphatidylcholine-phospholipase D but not phosphatidylinositol-phospholipase C in rats. Stroke 1994, 25, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A. Phospholipase D as a therapeutic target in brain disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Selvy, P.E.; Buck, J.; Cho, H.P.; Criswell, T.L.; Thomas, A.L.; Armstrong, M.D.; Arteaga, C.L.; Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A. Design of isoform-selective phospholipase D inhibitors that modulate cancer cell invasiveness. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavieri, R.; Scott, S.A.; Selvy, P.E.; Brown, H.A.; Lindsley, C.W. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of halogenated N-(2-(4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triazasprio[4.5]decan-8-yl)ethylbenzamides: Discovery of an isoform selective small-molecule phospholipase D2 (PLD2) inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6706–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.T.; Nasrallah, H.A. Neuroprotective effects of the second generation antipsychotics. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 208, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krzystanek, M.; Krzystanek, E.; Skałacka, K.; Pałasz, A. Enhancement in Phospholipase D Activity as a New Proposed Molecular Mechanism of Haloperidol-Induced Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239265
Krzystanek M, Krzystanek E, Skałacka K, Pałasz A. Enhancement in Phospholipase D Activity as a New Proposed Molecular Mechanism of Haloperidol-Induced Neurotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(23):9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239265
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrzystanek, Marek, Ewa Krzystanek, Katarzyna Skałacka, and Artur Pałasz. 2020. "Enhancement in Phospholipase D Activity as a New Proposed Molecular Mechanism of Haloperidol-Induced Neurotoxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 23: 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239265
APA StyleKrzystanek, M., Krzystanek, E., Skałacka, K., & Pałasz, A. (2020). Enhancement in Phospholipase D Activity as a New Proposed Molecular Mechanism of Haloperidol-Induced Neurotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(23), 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239265