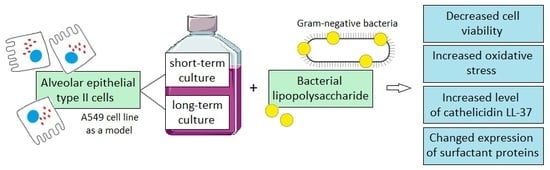
Short-Term versus Long-Term Culture of A549 Cells for Evaluating the Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on Oxidative Stress, Surfactant Proteins and Cathelicidin LL-37
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effect of LPS on Cell Viability
2.2. Generation of ROS by Epithelial Cells after LPS Exposure
2.3. Levels of Cathelicidin LL-37
2.4. Gene Expression of Surfactant Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Drug Treatment
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Detection of Intracellular ROS Production
4.5. Measurement of Cathelicidin LL-37
4.6. Real-Time PCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALI | acute lung injury |
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ATII cells | alveolar epithelial type II cells |
| DCF | 2′, 7′ –dichlorofluorescein |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| GSH | glutathione |
| H2DCF | 2′7′-dichlorofluorescin |
| H2DCFDA | 2′7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate |
| IL | interleukin |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MFI | mean fluorescence intensity |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-kappa B |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| SP-A | surfactant protein A |
| SP-B | surfactant protein B |
| SP-C | surfactant protein C |
| SP-D | surfactant protein D |
| SPs | surfactant proteins |
| RNS | reactive nitrogen species |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
References
- Kolomaznik, M.; Nova, Z.; Calkovska, A. Pulmonary Surfactant and Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide: The Interaction and its Functional Consequences. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, S147–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nova, Z.; Skovierova, H.; Calkovska, A. Alveolar-Capillary Membrane-Related Pulmonary Cells as a Target in Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bucki, R.; Leszczyńska, K.; Namiot, A.; Sokołowski, W. Cathelicidin LL-37: A multitask antimicrobial peptide. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2010, 58, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, P.S.; Amatngalim, G.D.; van der Does, A.M.; Taube, C. Antimicrobial Peptides and Innate Lung Defenses: Role in Infectious and Noninfectious Lung Diseases and Therapeutic Applications. Chest 2016, 149, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.J. Biology of Alveolar Type II Cells. Respirology 2006, 11, S12–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.; Medford, A.R.; Uppington, K.M.; Robertson, J.; Witherden, I.R.; Tetley, T.D.; Millar, A.B. Expression of functional toll-like receptor-2 and -4 on alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.Y.; Chen, T.L.; Chen, R.M. Molecular mechanisms of lipopolysaccharide-caused induction of surfactant protein-A gene expression in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Schéele, I.; Larsson, K.; Palmberg, L. Interactions between alveolar epithelial cells and neutrophils under pro-inflammatory conditions. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatia, M.; Moochhala, S. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Pathol. 2004, 202, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, S. Pathophysiology and biomarkers of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Intensive Care 2014, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Mizuta, N.; Kobayashi, A.; Kooguchi, K.; Fujiwara, I.; Nakajima, H. Fas/FasL-dependent apoptosis of alveolar cells after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuang, C.Y.; Chen, T.L.; Cherng, Y.G.; Tai, Y.T.; Chen, T.G.; Chen, R.M. Lipopolysaccharide induces apoptotic insults to human alveolar epithelial A549 cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of an intrinsic mitochondrion-dependent pathway. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, W. Apoptosis and surfactant protein-C expression inhibition induced by lipopolysaccharide in AEC II cell may associate with NF-κB pathway. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 42, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shao, K.; Sun, T. SIRT1 Regulates the Human Alveolar Epithelial A549 Cell Apoptosis Induced by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Lipopolysaccharide. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 31, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingenito, E.P.; Mora, R.; Cullivan, M.; Marzan, Y.; Haley, K.; Mark, L.; Sonna, L.A. Decreased surfactant protein-B expression and surfactant dysfunction in a murine model of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 25, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, C.L.; White, M.L.; O’Neill, M.E.; Thorne, P.S.; Schwartz, D.A.; Snyder, J.M. Altered surfactant protein A gene expression and protein metabolism associated with repeat exposure to inhaled endotoxin. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.N.; Zhou, J.H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.J. The localization of SP-B and influences of lipopolysaccharide on it. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 2338–2345. [Google Scholar]
- Rushworth, G.F.; Megson, I.L. Existing and potential therapeutic uses for N-acetylcysteine: The need for conversion to intracellular glutathione for antioxidant benefits. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruoma, O.I.; Halliwell, B.; Hoey, B.M.; Butler, J. The antioxidant action of N-acetylcysteine: Its reaction with hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, superoxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic Biol. Med. 1989, 6, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, J.J. A redox microenvironment is essential for MAPK-dependent secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines: Modulation by glutathione (GSH/GSSG) biosynthesis and equilibrium in the alveolar epithelium. Cell Immunol. 2011, 270, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopincova, J.; Mokra, D.; Mikolka, P.; Kolomaznik, M.; Calkovska, A. N-acetylcysteine advancement of surfactant therapy in experimental meconium aspiration syndrome: Possible mechanisms. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63 (Suppl. 4), 629–642. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, J.R.; Abdullatif, M.B.; Burnett, E.C.; Kempsell, K.E.; Conforti, F.; Tolley, H.; Collins, J.E.; Davies, D.E. Long Term Culture of the A549 Cancer Cell Line Promotes Multilamellar Body Formation and Differentiation towards an Alveolar Type II Pneumocyte Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beers, M.F.; Moodley, Y. When Is an Alveolar Type 2 Cell an Alveolar Type 2 Cell? A Conundrum for Lung Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, R.J.; Kemp, S.J.; Goldstraw, P.; Tetley, T.D.; Stevens, M.M. Assessment of Cell Line Models of Primary Human Cells by Raman Spectral Phenotyping. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corbière, V.; Dirix, V.; Norrenberg, S.; Cappello, M.; Remmelink, M.; Mascart, F. Phenotypic characteristics of human type II alveolar epithelial cells suitable for antigen presentation to T lymphocytes. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Zou, M.; He, J.; Han, Y.; Wu, D.; Yang, H.; Wu, J. miR-135a inhibition protects A549 cells from LPS-induced apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Li, P.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. Mechanisms mediating propofol protection of pulmonary epithelial cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced cell death. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physio. 2012, 39, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, P.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Jin, Y.; Hehir, M.; Xu, C. Different mechanism of LPS-induced calcium increase in human lung epithelial cell and microvascular endothelial cell: A cell culture study in a model for ARDS. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4253–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zheng, H.; He, W.; Lu, G.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, M. Ghrelin ameliorates the human alveolar epithelial A549 cell apoptosis induced by lipopolysaccharide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, G.; Halici, Z.; Albayrak, A.; Karakus, E.; Cadirci, E. Evaluation of 5-HT7 Receptor Trafficking on In Vivo and In Vitro Model of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammatory Cell Injury in Rats and LPS-Treated A549 Cells. Biochem. Genet. 2017, 55, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, L.; Qian, P.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, A.; Ji, F.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Qian, G. Lipopolysaccharide Induces Autophagic Cell Death through the PERK-Dependent Branch of the Unfolded Protein Response in Human Alveolar Epithelial A549 Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 2403–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, H.; Xu, S.; Sun, X. Downregulation of p300 alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injuries through regulation of RhoA/ROCK/NF-κB pathways in A549 cells. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 97, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Duan, S.; Zhao, S.; Cai, Y.; Chen, P.; Fang, X. Atorvastatin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human pulmonary epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, R.; Wang, Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, X. Picfeltarraenin IA inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine production by the nuclear factor-κB pathway in human pulmonary epithelial A549 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thorley, A.J.; Grandolfo, D.; Lim, E.; Goldstraw, P.; Young, A.; Tetley, T.D. Innate immune responses to bacterial ligands in the peripheral human lung-role of alveolar epithelial TLR expression and signalling. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, P.S.; Tsang, M.E.; Lodyga, M.; Bai, X.H.; Miller, A.; Han, B.; Liu, M. Lipopolysaccharide Accelerates Caspase-Independent but Cathepsin B-Dependent Death of Human Lung Epithelial Cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2006, 209, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Farkas, L.; Wolf, K.; Kratzel, K.; Eissner, G.; Pfeifer, M. Differences in LPS-induced activation of bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) and type II-like pneumocytes (A-549). Scand. J. Immunol. 2002, 56, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Normark, S.; Schweda, E.K.; Oscarson, S.; Richter-Dahlfors, A. Structural requirements for TLR4-mediated LPS signalling: A biological role for LPS modifications. Microbes Infect 2003, 5, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migale, R.; Herbert, B.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Sykes, L.; Waddington, S.N.; Peebles, D.; Hagberg, H.; Johnson, M.R.; Bennett, P.R.; MacIntyre, D.A. Specific Lipopolysaccharide Serotypes Induce Differential Maternal and Neonatal Inflammatory Responses in a Murine Model of Preterm Labor. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morona, R.; Daniels, C.; Van Den Bosch, L. Genetic modulation of Shigella flexneri 2a lipopolysaccharide O antigen modal chain length reveals that it has been optimized for virulence. Microbiology 2003, 149, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eder, K.; Vizler, C.; Kusz, E.; Karcagi, I.; Glavinas, H.; Balogh, G.E.; Vigh, L.; Duda, E.; Gyorfy, Z. The role of lipopolysaccharide moieties in macrophage response to Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 389, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRedmond, R.; Greene, C.; Taggart, C.C.; McElvaney, N.; O’Neill, S. Respiratory epithelial cells require Toll-like receptor 4 for induction of human beta-defensin 2 by lipopolysaccharide. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kellner, M.; Noonepalle, S.; Lu, Q.; Srivastava, A.; Zemskov, E.; Black, S.M. ROS Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 967, 105–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukgul, A.; Eedogan, S. Low concentration of oleic acid exacerbates LPS-induced cell death and inflammation in human alveolar epithelial cells. Exp. Lung Res. 2017, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Dodia, C.; Chatterjee, S.; Feinstein, S.I.; Fisher, A.B. Protection against LPS-induced acute lung injury by a mechanism-based inhibitor of NADPH oxidase (type 2). Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L635–L644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, A.B.; Dodia, C.; Chatterjee, S.; Feinstein, S.I. A Peptide Inhibitor of NADPH Oxidase (NOX2) Activation Markedly Decreases Mouse Lung Injury and Mortality Following Administration of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopincova, J.; Puzserova, A.; Bernatova, I. Biochemical aspects of nitric oxide synthase feedback regulation by nitric oxide. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2011, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, P.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Min, S.S.; Seol, G.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of anethole in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, H.; Shimoda, L.A.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Semenza, G.L. Analysis of hypoxia-induced metabolic reprogramming. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 542, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wei, W.; Wang, N. Tremella polysaccharides inhibit cellular apoptosis and autophagy induced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide in A549 cells through sirtuin 1 activation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9609–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, M.; Mojtahedzadeh, M.; Mandegari, A.; Soltan-Sharifi, M.S.; Najafi, A.; Khajavi, M.R.; Hajibabayee, M.; Ghahremani, M.H. The role of glutathione-S-transferase polymorphisms on clinical outcome of ALI/ARDS patient treated with N-acetylcysteine. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zafarullah, M.; Li, W.Q.; Sylvester, J.; Ahmad, M. Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matera, M.G.; Calzetta, L.; Cazzola, M. Oxidation pathway and exacerbations in COPD: The role of NAC. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; MacNee, W. Regulation of redox glutathione levels and gene transcription in lung inflammation: Therapeutic approaches. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofidou-Solomidou, M.; Muzykantov, V.R. Antioxidant strategies in respiratory medicine. Treat. Respir. Med. 2006, 5, 47–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Seo, J.Y.; Roh, K.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, K.H. Suppression of NF-kappa B activation and cytokine production by N-acetylcysteine in pancreatic acinar cells. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.A.; Smith, M.F., Jr.; Sanders, M.K.; Ernst, P.B. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species differentially regulate Toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of NF-kappa B and interleukin-8 expression. Infect Immun. 2004, 72, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paterson, R.L.; Galley, H.F.; Webster, N.R. The effect of N-acetylcysteine on nuclear factor-KB activation, interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in patients with sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 2574–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Fang, F.; Lu, Z.; Kuang, F.; Xu, F. N-acetylcysteine protects alveolar epithelial cells from hydrogen peroxide–induced apoptosis through scavenging reactive oxygen species and suppressing c-Jun N-terminalkinase. Exp. Lung Res. 2010, 36, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhafs, R.K.; Jarstrand, C. Effects of antioxidants on surfactant peroxidation by stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Free Radic Res. 2002, 36, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, L.; Paton, J. Oxygen toxicity. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2014, 15, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carballal, S.; Bartesaghi, S.; Radi, R. Kinetic and mechanistic considerations to assess the biological fate of peroxynitrite. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filewod, N.C.; Pistolic, J.; Hancock, R.E. Low concentrations of LL-37 alter IL-8 production by keratinocytes and bronchial epithelial cells in response to proinflammatory stimuli. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, M.X.; Yang, Z.H.; Pan, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.C.; Xing, Y. The effect of human antibacterial peptide LL-37 in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, G.; Minton, J.E.; Ross, C.R.; Blecha, F. Regulation of cathelicidin gene expression: Induction by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin-6, retinoic acid, and Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium infection. Infect Immun. 2000, 68, 5552–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivas-Santiago, B.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Carranza, C.; Juarez, E.; Contreras, J.L.; Aguilar-Leon, D.; Torres, M.; Sada, E. Expression of cathelicidin LL-37 during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in human alveolar macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, and epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 2008, 76, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Méndez-Samperio, P.; Miranda, E.; Trejo, A. Expression and secretion of cathelicidin LL-37 in human epithelial cells after infection by Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaoka, I.; Hirota, S.; Niyonsaba, F.; Hirata, M.; Adachi, Y.; Tamura, H.; Heumann, D. Cathelicidin family of antibacterial peptides CAP18 and CAP11 inhibit the expression of TNF-alpha by blocking the binding of LPS to CD14(+) cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, K.; Murakami, T.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Tamura, H.; Hiramatsu, K.; Nagaoka, I. Human anti-microbial cathelicidin peptide LL-37 suppresses the LPS-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.T.; Chen, T.L.; Loon, W.S.; Tai, Y.T.; Cherng, Y.G.; Chen, R.M. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates syntheses of toll-like receptor 2 and surfactant protein-A in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells through upregulating phosphorylation of MEK1 and ERK1/2 and sequential activation of NF-κB. Cytokine 2011, 55, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolomaznik, M.; Nova, Z.; Mokra, D.; Zila, I.; Kopincova, J.; Vidomanova, E.; Skovierova, H.; Halasova, E.; Calkovska, A. Modified porcine surfactant restores lung homeostasis in LPS-challenged and artificially ventilated adult rats. Neonatology 2018, 13, 419. [Google Scholar]
- Nardone, L.L.; Andrews, S.B. Cell line A549 as a model of the type II pneumocyte. Phospholipid biosynthesis from native and organometallic precursors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 573, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, T. Stimulant-dependent modulation of cytokines and chemokines by airway epithelial cells: Cross talk between pulmonary epithelial and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Clin. Diagn. Lab Immunol. 2002, 9, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsutsumi-Ishii, Y.; Nagaoka, I. Modulation of human beta-defensin-2 transcription in pulmonary epithelial cells by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mononuclear phagocytes via proinflammatory cytokine production. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4226–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bein, K.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Mischler, S.E.; Ortiz, L.A.; Leikauf, G.D. LPS-treated macrophage cytokines repress surfactant protein-B in lung epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janga, H.; Cassidy, L.; Wang, F.; Spengler, D.; Oestern-Fitschen, S.; Krause, M.F.; Seekamp, A.; Tholey, A.; Fuchs, S. Site-Specific and Endothelial-Mediated Dysfunction of the Alveolar-Capillary Barrier in Response to Lipopolysaccharides. J Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nova, Z.; Skovierova, H.; Strnadel, J.; Halasova, E.; Calkovska, A. Short-Term versus Long-Term Culture of A549 Cells for Evaluating the Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on Oxidative Stress, Surfactant Proteins and Cathelicidin LL-37. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031148
Nova Z, Skovierova H, Strnadel J, Halasova E, Calkovska A. Short-Term versus Long-Term Culture of A549 Cells for Evaluating the Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on Oxidative Stress, Surfactant Proteins and Cathelicidin LL-37. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031148
Chicago/Turabian StyleNova, Zuzana, Henrieta Skovierova, Jan Strnadel, Erika Halasova, and Andrea Calkovska. 2020. "Short-Term versus Long-Term Culture of A549 Cells for Evaluating the Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on Oxidative Stress, Surfactant Proteins and Cathelicidin LL-37" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031148
APA StyleNova, Z., Skovierova, H., Strnadel, J., Halasova, E., & Calkovska, A. (2020). Short-Term versus Long-Term Culture of A549 Cells for Evaluating the Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on Oxidative Stress, Surfactant Proteins and Cathelicidin LL-37. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031148