Is Sleep Disruption a Cause or Consequence of Alzheimer’s Disease? Reviewing Its Possible Role as a Biomarker
Abstract
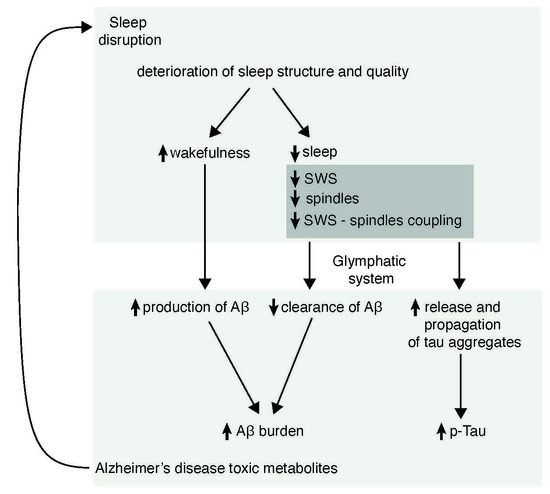
:1. Introduction
2. Role of Sleep in Declarative Memory Consolidation
3. Sleep and Memory in Sleep Disorders
3.1. Insomnia
3.2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome
4. Changes in Sleep and Memory in Normal Aging
5. Sleep Disorders in Alzheimer’s Disease
6. Possible Mechanisms by Which Sleep May Participate in the Pathogenesis of AD
6.1. Mechanisms Linking Sleep Respiratory Disorders with AD
6.2. Sleep and Amyloid Burden
6.3. Sleep and Tau Pathology
6.4. Sleep and Glymphatic System
7. Sleep-Related Proposed Biomarkers in AD
7.1. General EEG Features
7.2. SWA in NREM
7.3. Other Possible Biomarkers
8. Could Sleep Oscillatory Activities be Good Biomarkers for AD?
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bature, F.; Guinn, B.A.; Pang, D.; Pappas, Y. Signs and symptoms preceding the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic scoping review of literature from 1937 to 2016. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.F.; Tan, L.; Wang, H.F.; Jiang, T.; Tan, M.S.; Tan, L.; Xu, W.; Li, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Lai, T.J.; et al. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 190, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, B.; Adorni, F.; Musicco, M.; Appollonio, I.; Bonanni, E.; Caffarra, P.; Caltagirone, C.; Cerroni, G.; Concari, L.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; et al. Prevalence of Sleep Disturbances in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementing Disorders: A Multicenter Italian Clinical Cross-Sectional Study on 431 Patients. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2012, 33, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gehrman, P.; Gooneratne, N.S.; Brewster, G.S.; Richards, K.C.; Karlawish, J. Impact of Alzheimer disease patients’ sleep disturbances on their caregivers. Geriatr. Nurs. (Minneap). 2018, 39, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillon, S.; Gasper, A.; Wilson-Morkeh, F.; Pritchard, M.; Jesu, A.; Velayudhan, L. Prevalence and Severity of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Early- Versus Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dementias® 2019, 34, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhong, R.; Li, S.; Fu, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, T.; Huang, Z.; Le, W. Alteration in sleep architecture and electroencephalogram as an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease preceding the disease pathology and cognitive decline. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, O.; Lorrain, D.; Forget, H.; Dubé, M.; Grenier, S.; Préville, M.; Hudon, C. Sleep quality and 1-year incident cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older adults. Sleep 2012, 35, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, A.S.; Kowgier, M.; Yu, L.; Buchman, A.S.; Bennett, D.A. Sleep Fragmentation and the Risk of Incident Alzheimer’s Disease and Cognitive Decline in Older Persons. Sleep 2013, 36, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedict, C.; Byberg, L.; Cedernaes, J.; Hogenkamp, P.S.; Giedratis, V.; Kilander, L.; Lind, L.; Lannfelt, L.; Schiöth, H.B. Self-reported sleep disturbance is associated with Alzheimer’s disease risk in men. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubu, O.M.; Brannick, M.; Mortimer, J.; Umasabor-Bubu, O.; Sebastião, Y.V.; Wen, Y.; Schwartz, S.; Borenstein, A.R.; Wu, Y.; Morgan, D.; et al. Sleep, Cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep 2017, 40, zsw032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shireen, S.; Ingemar, K.; Lena, J.; Johan, S.; Linnea, S.; Hui-Xin, W.; Boo, J.; Laura, F.; Hilkka, S.; Alina, S.; et al. Sleep disturbances and dementia risk: A multicenter study. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Tian, J.; Bauer, A.; Huang, R.; Wen, H.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Xia, L.; Jiang, G. Reduced integrity of right lateralized white matter in patients with primary insomnia: A diffusion-tensor imaging study. Radiology 2016, 280, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, D.L.; Shin, J.H.; Lim, J.S.; Seong, J.K.; Joo, E.Y. Changes in subcortical shape and cognitive function in patients with chronic insomnia. Sleep Med. 2017, 35, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alperin, N.; Wiltshire, J.; Lee, S.H.; Ramos, A.R.; Hernandez-Cardenache, R.; Rundek, T.; Curiel Cid, R.; Loewenstein, D. Effect of sleep quality on amnestic mild cognitive impairment vulnerable brain regions in cognitively normal elderly individuals. Sleep 2018, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altena, E.; Vrenken, H.; Van Der Werf, Y.D.; van den Heuvel, O.A.; Van Someren, E.J.W. Reduced orbitofrontal and parietal gray matter in chronic insomnia: A voxel-based morphometric study. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Jianhao, Y.; Shumei, L.; Tianyue, W.; Hua, W.; Yi, Y.; Shishun, F.; Luxian, Z.; Junzhang, T.; Guihua, J. Altered gray matter volume in primary insomnia patients: A DARTEL-VBM study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, J.W.; Plante, D.T.; Schoerning, L.; Benson, K.; Buxton, O.M.; O’Connor, S.P.; Jensen, J.E.; Renshaw, P.F.; Gonenc, A. Increased rostral anterior cingulate cortex volume in chronic primary insomnia. Sleep 2013, 36, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riemann, D.; Voderholzer, U.; Spiegelhalder, K.; Hornyak, M.; Buysse, D.J.; Nissen, C.; Hennig, J.; Perlis, M.L.; van Elst, L.T.; Feige, B. Chronic insomnia and MRI-measured hippocampal volumes: A pilot study. Sleep 2007, 30, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeon, J.E.; Hosung, K.; Sooyeon, S.; Bong, H.S. Hippocampal Substructural Vulnerability to Sleep Disturbance and Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Chronic Primary Insomnia: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Morphometry. Sleep 2014, 37, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, C.E.; Storsve, A.B.; Walhovd, K.B.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Fjell, A.M. Poor sleep quality is associated with increased cortical atrophy in community-dwelling adults. Neurology 2014, 83, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grau-Rivera, O.; Operto, G.; Falcón, C.; Sánchez-Benavides, G.; Cacciaglia, R.; Brugulat-Serrat, A.; Gramunt, N.; Salvadó, G.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Minguillon, C.; et al. Association between insomnia and cognitive performance, gray matter volume, and white matter microstructure in cognitively unimpaired adults. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wennberg, A.M.V.; Wu, M.N.; Rosenberg, P.B.; Spira, A.P. Sleep Disturbance, Cognitive Decline, and Dementia: A Review. Semin. Neurol. 2017, 37, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McDade, E.; Bateman, R.J. Stop Alzheimer’s before it starts. Nature 2017, 547, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, M.G. Erasing synapses in sleep: Is it time to be SHY? Neural Plast. 2012, 2012, 264378–264393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peigneux, P.; Smith, C. Memory Processing in Relation to Sleep. In Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine, 5th ed.; Kryger, M., Roth, T., Dement, W., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: St Louis, MO, USA, 2010; Chapter 29; p. 335347. ISBN 9781416066453. [Google Scholar]
- Godbolt, A.K.; Cipolotti, L.; Watt, H.; Fox, N.C.; Janssen, J.C.; Rossor, M.N. The natural history of Alzheimer disease: A longitudinal presymptomatic and symptomatic study of a familial cohort. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molinuevo, J.L.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Rami, L. From mild cognitive impairment to prodromal Alzheimer disease: A nosological evolution. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2010, 73, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howieson, D.B. Cognitive decline in presymptomatic Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasch, B.; Born, J. About Sleep’s Role in Memory. Physiol Rev. 2013, 93, 681–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.M. The role of sleep in cognitive processing: Focusing on memory consolidation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2017, 8, e1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Wolf, E.; Maier, J.G.; Mainberger, F.; Feige, B.; Schmid, H.; Bürklin, J.; Maywald, S.; Mall, V.; Jung, N.H.; et al. Sleep recalibrates homeostatic and associative synaptic plasticity in the human cortex. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12455–12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staresina, B.P.; Bergmann, T.O.; Bonnefond, M.; Van Der Meij, R.; Jensen, O.; Deuker, L.; Elger, C.E.; Axmacher, N.; Fell, J. Hierarchical nesting of slow oscillations, spindles and ripples in the human hippocampus during sleep. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirota, A.; Buzsáki, G. Interaction between neocortical and hippocampal networks via slow oscillations. Thalamus Relat. Syst. 2005, 3, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buzsáki, G.; Horváth, Z.; Urioste, R.; Hetke, J.; Wise, K. High-frequency network oscillation in the hippocampus. Science 1992, 256, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylinen, A.; Bragin, A.; Nadasdy, Z.; Jando, G.; Szabo, I.; Sik, A.; Buzsaki, G. Sharp wave-associated high-frequency oscillation (200 hz) in the intact hippocampus: Network and intracellular mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, N.; Nimmrich, V.; Draguhn, A. Cellular and network mechanisms underlying spontaneous sharp wave-ripple complexes in mouse hippocampal slices. J. Physiol. 2003, 550, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.J.; Kloosterman, F.; Wilson, M.A. Hippocampal Replay of Extended Experience. Neuron 2009, 63, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, R.; Schapiro, A.C.; Manoach, D.S.; Stickgold, R. Individual Differences in Frequency and Topography of Slow and Fast Sleep Spindles. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klinzing, J.G.; Niethard, N.; Born, J. Mechanisms of systems memory consolidation during sleep. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Bandarabadi, M.; Boyce, R.; Herrera, C.G.; Bassetti, C.; Williams, S.; Schindler, K.; Adamantidis, A. Dynamical modulation of theta-gamma coupling during REM sleep. Sleep 2019, 42, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, I.C.; Rathore, S. The role of REM sleep theta activity in emotional memory. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Born, J.; Wilhelm, I. System consolidation of memory during sleep. Psychol Res. 2012, 76, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cellini, N. Memory consolidation in sleep disorders. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 35, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemann, D.; Baglioni, C.; Bassetti, C.; Bjorvatn, B.; Dolenc Groselj, L.; Ellis, J.G.; Espie, C.A.; Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Gjerstad, M.; Gonçalves, M.; et al. European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. J. Sleep Res. 2017, 26, 675–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Liao, D.; Shaffer, M.L.; Vela-Bueno, A.; Basta, M.; Bixler, E.O. Insomnia with objective short sleep duration and incident hypertension: The Penn State Cohort. Hypertension 2012, 60, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baglioni, C.; Battagliese, G.; Feige, B.; Spiegelhalder, K.; Nissen, C.; Voderholzer, U.; Lombardo, C.; Riemann, D. Insomnia as a predictor of depression: A meta-analytic evaluation of longitudinal epidemiological studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 135, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaffe, K.; Falvey, C.M.; Hoang, T. Connections between sleep and cognition in older adults. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 10, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemann, D.; Nissen, C.; Palagini, L.; Otte, A.; Perlis, M.L.; Spiegelhalder, K. The neurobiology investigation and treatment of chronic insomnia. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofzinger, E.A.; Buysse, D.J.; Germain, A.; Price, J.C.; Miewald, J.M.; Kupfer, D.J. Functional neuroimaging evidence for hyperarousal in insomnia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhaus, J.; Junghanns, K.; Born, J.; Hohaus, K.; Faasch, K.; Hohagen, F. Impaired Declarative Memory Consolidation during Sleep in Patients with Primary Insomnia: Influence of Sleep Architecture and Nocturnal Cortisol Release. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaratna, C.V.; Perret, J.L.; Lodge, C.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Campbell, B.E.; Matheson, M.C.; Hamilton, G.S.; Dharmage, S.C. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in the general population: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 34, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, I.; Glasser, M.; Polsek, D.; Leschziner, G.D.; Williams, S.C.; Morrell, M.J. Sleep apnoea and the brain: A complex relationship. Lancet Respir Med. 2015, 3, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olaithe, M.; Bucks, R.S.; Hillma, D.R.; Eastwood, P.R. Cognitive deficits in obstructive sleep apnea: Insights from a meta-review and comparison with deficits observed in COPD; insomnia; and sleep deprivation. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 38, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macey, P.M.; Haris, N.; Kumar, R.; Thomas, M.A.; Woo, M.A.; Harper, R.M. Obstructive sleep apnea and cortical thickness in females and males. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.G.; Riedner, B.A.; Smith, R.F.; Ferrarelli, F.; Tononi, G.; Davidson, R.J.; Benca, R.M. Regional reductions in sleep electroencephalography power in obstructive sleep apnea: A high-density EEG study. Sleep 2014, 37, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ondze, B.; Espa, F.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Billiard, M.; Besset, A. Sleep architecture; slow wave activity and sleep spindles in mild sleep disordered breathing. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, S.L.; Virkkala, J.; Huupponen, E.; Hasan, J. Spindle frequency remains slow in sleep apnea patients throughout the night. Sleep Med. 2003, 4, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, N.A.; Roose, S.P. Obstructive Sleep Apnea is Linked to Depression and Cognitive Impairment: Evidence and Potential Mechanisms. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2016, 24, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorffner, G.; Vitr, M.; Anderer, P. The Effects of Aging on Sleep Architecture in Healthy Subjects. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 821, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Vitiello, M.V.; Gooneratne, N.S. Sleep in Normal Aging. Sleep Med. Clin. 2018, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, J.A.; Medler, S.M.; Ager, J.W.; Janisse, J.J. Age-related changes in initiation and maintenance of sleep: A meta-analysis. Res. Nurs. Health 2000, 32, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.M.; Carskadon, M.A.; Guilleminault, C.; Vitiello, M.V. Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: Developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep 2004, 27, 1255–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.S.; Murphy, P.J. The nature of spontaneous sleep across adulthood. J. Sleep Res. 2007, 16, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, F.; Arzilli, C.; Errico, B.M.; Giganti, F.; Iovino, D.; Ficca, G.; Giganti, F.; Iovino, D.; Ficca, G. Sleep Measures Expressing “Functional Uncertainty” in Elderlies’ Sleep. Gerontology 2014, 60, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, H.-P.; Dijk, D.-J.; Achermann, P.; Borbély, A.A. Effect of age on the sleep EEG: Slow-wave activity and spindle frequency activity in young and middle-aged men. Brain Res. 1996, 738, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klerman, E.B.; Dijk, D.-J. Age-Related Reduction in the Maximal Capacity for Sleep—Implications for Insomnia. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dijk, D.; Beersma, D.; Vandenhoofdakker, R. All night spectral analysis of EEG sleep in young adult and middle-aged male subjects. Neurobiol. Aging 1989, 10, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubé, J.; LaFortune, M.; Bedetti, C.; Bouchard, M.; Gagnon, J.F.; Doyon, J.; Evans, A.C.; Lina, J.-M.; Carrier, J. Cortical Thinning Explains Changes in Sleep Slow Waves during Adulthood. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7795–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, N.; LaFortune, M.; Godbout, J.; Barakat, M.; Robillard, R.; Poirier, G.; Bastien, C.; Carrier, J. Topography of age-related changes in sleep spindles. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.C.; Sim, S.K.Y.; Chee, M.W.L. Sleep Reduces False Memory in Healthy Older Adults. Sleep 2014, 37, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mander, B.A.; Rao, V.; Lu, B.; Saletin, J.M.; Lindquist, J.R.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Jagust, W.; Walker, M.P. Prefrontal atrophy, disrupted NREM slow waves and impaired hippocampal-dependent memory in aging. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, A.W.; Ducca, E.L.; Kishi, A.; Fischer, E.; Parekh, A.; Koushyk, V.; Yau, P.L.; Gumb, T.; Leibert, D.P.; Wohlleber, M.E.; et al. Effects of aging on slow-wave sleep dynamics and human spatial navigational memory consolidation. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 42, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foley, D.J.; Monjan, A.A.; Brown, S.L.; Simonsick, E.M.; Wallace, R.B.; Blazer, D.G. Sleep complaints among elderly persons—An epidemiological study of 3 communities. SleIep 1995, 18, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.B.; Enright, P.L.; Manolio, T.A.; Haponik, E.F.; Wahl, P.W.; On behalf of the Cardiovascular Health Study Research Group; Mhs, T.A.M. Sleep Disturbance, Psychosocial Correlates, and Cardiovascular Disease in 5201 Older Adults: The Cardiovascular Health Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1997, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.; E Peppard, P.; Gottlieb, D.J. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: A population health perspective. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altena, E.; Van Der Werf, Y.D.; Strijers, R.L.M.; Van Someren, E.J.W. Sleep loss affects vigilance: Effects of chronic insomnia and sleep therapy. J. Sleep Res. 2008, 17, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimov, I.; Hanuka, E.; Horowitz, Y. Chronic Insomnia and Cognitive Functioning Among Older Adults. Behav. Sleep Med. 2008, 6, 32–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, A.; Lim, M.L.; Gwee, X.; Ho, R.C.; Collinson, S.L.; Ng, T.-P. Insomnia and daytime neuropsychological test performance in older adults. Sleep Med. 2016, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, P.N.; Vitaliano, P.P.; Vitiello, M.V.; Bokan, J.; Raskind, M.; Peskind, E.; Gerber, C. Sleep; EEG and mental function changes in senile dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Neurobiol. Aging 1982, 3, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeshita, Y.; Adachi, H.; Matsushita, M.; Kanemoto, H.; Sato, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshiyama, K.; Shimomura, T.; Yoshida, T.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Sleep disturbances are key symptoms of very early stage Alzheimer disease with behavioral and psychological symptoms: A Japan multi-center cross-sectional study (J-BIRD). Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 32, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancoli-Israel, S.; Klauber, M.R.; Butters, N.; Parker, L.; Kripke, D.F. Dementia in institutionalized elderly: Relation to sleep apnea. J. Am. Geriatr Soc. 1991, 39, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzecka, A.; Leszek, J.; Ashraf, G.M.; Ejma, M.; Ávila-Rodriguez, M.F.; Yarla, N.S.; Tarasov, V.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Samsonova, A.N.; Barreto, G.E.; et al. Sleep Disorders Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease: A Perspective. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, J.-F.; Petit, D.; Latreille, V.; Montplaisir, J. Neurobiology of sleep disturbances in neurodegenerative disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3430–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rongve, A.; Boeve, B.F.; Aarsland, D. Frequency and Correlates of Caregiver-Reported Sleep Disturbances in a Sample of Persons with Early Dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, N.; Terpening, Z.; Rogers, N.L.; Duffy, S.L.; Hickie, I.B.; Lewis, S.J.; Naismith, S.L. Napping in older people ‘at risk’ of dementia: Relationships with depression, cognition, medical burden and sleep quality. J. Sleep Res. 2015, 24, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurry, S.M.; Ancoli-Israel, S. Sleep dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2003, 5, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Most, E.I.; Aboudan, S.; Scheltens, P.; Van Someren, E.J. Discrepancy Between Subjective and Objective Sleep Disturbances in Early- and Moderate-Stage Alzheimer Disease. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2012, 20, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, P.N.; Peskind, E.R.; Vitaliano, P.P.; Raskind, M.A.; Eisdorfer, C.; Zemcuznikov, H.N.; Gerber, C.J. Changes in the Sleep and Waking EEGs of Nondemented and Demented Elderly Subjects. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1982, 30, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, M.V.; Prinz, P.N.; Williams, D.E.; Frommlet, M.S.; Ries, R.K. Sleep Disturbances in Patients With Mild-Stage Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Gerontol. 1990, 45, M131–M138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer, A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg Zeitschr f Psychiatr. u Psych.-Gerichtl Med. 1907, 64, 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Duyckaerts, C.; Delatour, B.; Potier, M.-C. Classification and basic pathology of Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Tung, Y.C.; Quinlan, M.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Binder, L.I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4913–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ju, Y.-E.S.; Zangrilli, M.A.; Finn, M.B.; Fagan, A.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Obstructive sleep apnea treatment, slow wave activity, and amyloid-β. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emamian, F.; Khazaie, H.; Tahmasian, M.; Leschziner, G.D.; Morrell, M.J.; Hsiung, G.-Y.R.; Rosenzweig, I.; Sepehry, A.A. The Association Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis Perspective. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, R.J. Obstructive sleep apnea, apolipoprotein E e4, and mild cognitive impairment. Sleep Med. 2008, 9, 816–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osorio, R.S.; Gumb, T.; Pirraglia, E.; Varga, A.W.; Lu, S.-E.; Lim, J.; Wohlleber, M.E.; Ducca, E.L.; Koushyk, V.; Glodzik, L.; et al. Sleep-disordered breathing advances cognitive decline in the elderly. Neurology 2015, 84, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y. Sleep-disordered breathing and the risk of cognitive decline: A meta-analysis of 19;940 participants. Sleep Breath. 2018, 22, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, R.S.; Ayappa, I.; Mantua, J.; Gumb, T.; Varga, A.; Mooney, A.M.; Burschtin, O.E.; Taxin, Z.; During, E.; Spector, N.; et al. The interaction between sleep-disordered breathing and apolipoprotein E genotype on cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in cognitively normal elderly individuals. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, Y.-E.S.; Finn, M.B.; Sutphen, C.L.; Herries, E.M.; Jerome, G.M.; Ladenson, J.H.; Crimmins, D.L.; Fagan, A.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Obstructive sleep apnea decreases central nervous system-derived proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Erum, J.; Van Dam, D.; Sheorajpanday, R.; De Deyn, P.P. Sleep architecture changes in the APP23 mouse model manifest at onset of cognitive deficits. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 373, 112089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, R.M.; Farber, S.A.; Growdon, J.H.; Wurtman, R.J. Release of amyloid beta-protein precursor derivatives by electrical depolarization of rat hippocampal slices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5191–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bero, A.W.; Yan, P.; Roh, J.H.; Cirrito, J.R.; Stewart, F.R.; Raichle, M.E.; Lee, J.-M.; Holtzman, D.M. Neuronal activity regulates the regional vulnerability to amyloid-β deposition. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bateman, R.J.; Wen, G.; Morris, J.C.; Holtzman, D.M. Fluctuations of CSF amyloid-β levels: Implications for a diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker. Neurology 2007, 68, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, B.P.; Hicks, T.J.; McLeland, J.S.; Toedebusch, C.D.; Boyd, J.; Elbert, N.L.; Patterson, B.W.; Baty, J.; Morris, J.C.; Ovod, V.; et al. Effect of sleep on overnight cerebrospinal fluid amyloid β kinetics. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-E.; Lim, M.M.; Bateman, R.J.; Lee, J.J.; Smyth, L.P.; Cirrito, J.R.; Fujiki, N.; Nishino, S.; Holtzman, D.M. Amyloid- Dynamics Are Regulated by Orexin and the Sleep-Wake Cycle. Science 2009, 326, 1005–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musiek, E.S.; Holtzman, D.M. Mechanisms linking circadian clocks, sleep, and neurodegeneration. Science 2016, 354, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ooms, S.; Overeem, S.; Besse, K.; Rikkert, M.O.; Verbeek, M.; Claassen, J.A.H.R. Effect of 1 Night of Total Sleep Deprivation on Cerebrospinal Fluid β-Amyloid 42 in Healthy Middle-Aged Men. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri-Kojori, E.; Wang, G.-J.; Wiers, C.E.; Demiral Şükrü, B.; Guo, M.; Kim, S.W.; Lindgren, E.; Ramirez, V.; Zehra, A.; Freeman, C.; et al. β-Amyloid accumulation in the human brain after one night of sleep deprivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4483–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, Y.-E.S.; McLeland, J.S.; Toedebusch, C.D.; Xiong, C.; Fagan, A.M.; Duntley, S.P.; Morris, J.C.; Holtzman, D.M. Sleep quality and preclinical Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, A.W.; Wohlleber, M.E.; Giménez, S.; Romero, S.; Alonso, J.F.; Ducca, E.L.; Kam, K.; Lewis, C.; Tanzi, E.B.; Tweardy, S.; et al. Reduced Slow-Wave Sleep Is Associated with High Cerebrospinal Fluid Aβ42 Levels in Cognitively Normal Elderly. Sleep 2016, 39, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander, B.A.; Marks, S.M.; Vogel, J.W.; Rao, V.; Lu, B.; Saletin, J.M.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Jagust, W.J.; Walker, M.P. β-amyloid disrupts human NREM slow waves and related hippocampus-dependent memory consolidation. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, M.; Riedner, B.A.; Huber, R.; Massimini, M.; Ferrarelli, F.; Tononi, G. Source modeling sleep slow waves. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buckner, R.L.; Snyder, A.Z.; Shannon, B.J.; LaRossa, G.; Sachs, R.; Fotenos, A.F.; Sheline, Y.I.; Klunk, W.E.; Mathis, C.A.; Morris, J.C.; et al. Molecular; structural; and functional characterization of Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence for a relationship between default activity; amyloid; and memory. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7709–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jack, C.R.; Knopman, D.S.; Jagust, W.J.; Shaw, L.M.; Aisen, P.S.; Weiner, M.W.; Petersen, R.C.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer’s pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elman, J.A.; Oh, H.; Madison, C.M.; Baker, S.L.; Vogel, J.W.; Marks, S.M.; Crowley, S.; O’Neil, J.P.; Jagust, W.J. Neural compensation in older people with brain amyloid-beta deposition. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1316–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, N.; Insel, P.S.; Aisen, P.S.; Jagust, W.; Mackin, S.; Weiner, M.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Brain structure and function as mediators of the effects of amyloid on memory. Neurology 2015, 84, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leow, A.D.; Yanovsky, I.; Parikshak, N.; Hua, X.; Lee, S.; Toga, A.W.; Jack, C.R.; Bernstein, M.A.; Britson, P.J.; Gunter, J.L.; et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: A one-year follow up study using tensor-based morphometry correlating degenerative rates, biomarkers and cognition. NeuroImage 2009, 45, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Holtzman, D.M. Bidirectional relationship between sleep and Alzheimer’s disease: Role of amyloid, tau, and other factors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 45, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, B.P.; McCullough, A.; Landsness, E.C.; Toedebusch, C.D.; McLeland, J.S.; Zaza, A.M.; Fagan, A.M.; McCue, L.; Xiong, C.; Morris, J.C.; et al. Reduced non-rapid eye movement sleep is associated with tau pathology in early Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, K.; Parekh, A.; Sharma, R.A.; Andrade, A.; Lewin, M.; Castillo, B.; Bubu, O.M.; Chua, N.J.; Miller, M.D.; Mullins, A.E.; et al. Sleep oscillation-specific associations with Alzheimer’s disease CSF biomarkers: Novel roles for sleep spindles and tau. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holth, J.K.; Fritschi, S.K.; Wang, C.; Pedersen, N.P.; Cirrito, J.R.; Mahan, T.E.; Finn, M.B.; Manis, M.; Geerling, J.C.; Fuller, P.M.; et al. The sleep-wake cycle regulates brain interstitial fluid tau in mice and CSF tau in humans. Science 2019, 363, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K. The pathological process underlying Alzheimer’s disease in individuals under thirty. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhan, G.; Fenik, P.; Brandes, M.; Bell, P.; Francois, N.; Shulman, K.; Veasey, S. Chronic Sleep Disruption Advances the Temporal Progression of Tauopathy in P301S Mutant Mice. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10255–10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Meco, A.; Joshi, Y.B.; Praticò, D. Sleep deprivation impairs memory; tau metabolism; and synaptic integrity of a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, S.M.; Herdener, N.; Frankola, K.A.; Mughal, M.R.; Mattson, M.P. Chronic mild sleep restriction accentuates contextual memory impairments; and accumulations of cortical Ab and pTau in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2013, 1529, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winer, J.R.; Mander, B.A.; Helfrich, R.F.; Maass, A.; Harrison, T.M.; Baker, S.L.; Knight, R.T.; Jagust, W.J.; Walker, M.P. Sleep as a Potential Biomarker of Tau and β-Amyloid Burden in the Human Brain. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 6315–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendelsohn, A.R.; Larrick, J.W. Sleep Facilitates Clearance of Metabolites from the Brain: Glymphatic Function in Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow Through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boespflug, E.L.; Iliff, J.J. The Emerging Relationship Between Interstitial Fluid–Cerebrospinal Fluid Exchange, Amyloid-β, and Sleep. Boil. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Christensen, D.J.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J.J.; et al. Sleep Drives Metabolite Clearance from the Adult Brain. Science 2013, 342, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kress, B.T.; Iliff, J.J.; Xia, M.; Wang, M.; Wei, H.S.; Zeppenfeld, U.; Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Liew, J.A.; et al. Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasoff-Conway, J.M.; Carare, R.O.; Osorio, R.S.; Glodzik, L.; Butler, T.; Fieremans, E.; Axel, L.; Rusinek, H.; Nicholson, C.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Clearance systems in the brain—Implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallina, P.; Scollato, A.; Conti, R.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Porfirio, B. Aβ Clearance, “hub” of Multiple Deficiencies Leading to Alzheimer Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, M.K.; Mestre, H.; Nedergaard, M. The glymphatic pathway in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.J.; Verkman, A.S. The “glymphatic” mechanism for solute clearance in Alzheimer’s disease: Game changer or unproven speculation? FASEB J. 2018, 32, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, Y.-E.S.; Ooms, S.J.; Sutphen, C.; Macauley, S.L.; Zangrilli, M.A.; Jerome, G.; Fagan, A.M.; Mignot, E.; Zempel, J.M.; Claassen, J.A.; et al. Slow wave sleep disruption increases cerebrospinal fluid amyloid-β levels. Brain 2017, 140, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekelmann, S.; Born, J. The memory function of sleep. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, W.; Brankačk, J.; Weyer, S.W.; Müller, U.C.; Tort, A.B.L.; Draguhn, A. Impaired theta-gamma coupling in APP-deficient mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakazono, T.; Lam, T.N.; Patel, A.Y.; Kitazawa, M.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.C.; Igarashi, K.M. Impaired In Vivo Gamma Oscillations in the Medial Entorhinal Cortex of Knock-in Alzheimer Model. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.M.; Sirota, A.; Buzsáki, G. Theta and gamma coordination of hippocampal networks during waking and rapid eye movement sleep. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6731–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerberg, C.E.; Mander, B.A.; Florczak, S.M.; Weintraub, S.; Mesulam, M.-M.; Zee, P.C.; Paller, K.A. Concurrent Impairments in Sleep and Memory in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2012, 18, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liguori, C.; Romigi, A.; Nuccetelli, M.; Zannino, S.; Sancesario, G.; Martorana, A.; Albanese, M.; Mercuri, N.B.; Izzi, F.; Bernardini, S.; et al. Orexinergic System Dysregulation, Sleep Impairment, and Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Blackwell, T.; Yaffe, K.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Redline, S.; Stone, K.L. Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study Group. Relationships Between Sleep Stages and Changes in Cognitive Function in Older Men: The MrOS Sleep Study. Sleep 2015, 38, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humpel, C. Identifying and validating biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Oscillatory Parameter | Aβ Burden | Tau Pathology | AD-Related Localization |
|---|---|---|---|
| NREM SWA (< 1 Hz) | ✓ | Prefrontal Cortex Posterior cingulate Precuneus CSF | |
| NREM SWA (1–4 Hz) | ✓ | Entorhinal Parahippocampal Orbital frontal Precuneus Inferior parietal Inferior temporal | |
| Spindles | ✓ | ✓ | CSF |
| SO-Spindle coupling | ✓ | Medial temporal lobe |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lloret, M.-A.; Cervera-Ferri, A.; Nepomuceno, M.; Monllor, P.; Esteve, D.; Lloret, A. Is Sleep Disruption a Cause or Consequence of Alzheimer’s Disease? Reviewing Its Possible Role as a Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031168
Lloret M-A, Cervera-Ferri A, Nepomuceno M, Monllor P, Esteve D, Lloret A. Is Sleep Disruption a Cause or Consequence of Alzheimer’s Disease? Reviewing Its Possible Role as a Biomarker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031168
Chicago/Turabian StyleLloret, Maria-Angeles, Ana Cervera-Ferri, Mariana Nepomuceno, Paloma Monllor, Daniel Esteve, and Ana Lloret. 2020. "Is Sleep Disruption a Cause or Consequence of Alzheimer’s Disease? Reviewing Its Possible Role as a Biomarker" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031168
APA StyleLloret, M.-A., Cervera-Ferri, A., Nepomuceno, M., Monllor, P., Esteve, D., & Lloret, A. (2020). Is Sleep Disruption a Cause or Consequence of Alzheimer’s Disease? Reviewing Its Possible Role as a Biomarker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031168