Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation and Structure-Activity Analysis of Novel (E)- 5-(2-Arylvinyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
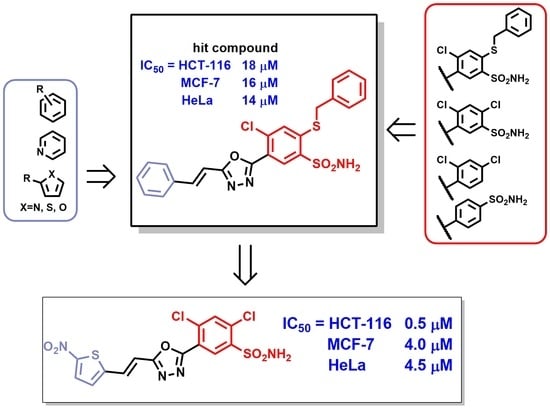
2.2. Anticancer Activity
2.3. Structure-Activity Relationship
2.4. Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. Procedure for the Preparation of 2,4-Dichloro-5-(5-(Chloromethyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl])Benzenesulfonamide (4)
3.1.2. Procedure for the Preparation of ((5-(2,4-Dichloro-5-Sulfamoylphenyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)Methyl)Triphenylphosphonium chloride (5)
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of (E)-5-(5-(2-Arylvinyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl) -4-Chloro-2-R1-Benzenesulfonamides (7–36)
3.1.4. Procedure for the Preparation of 4-(5-(Chloromethyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)Benzenesulfonamide (43)
3.1.5. Procedure for the Preparation of ((5-(4-Sulfamoylphenyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)Methyl)Triphenylphosphonium Chloride (45)
3.1.6. Procedure for the Preparation of ((5-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)Methyl)Triphenylphosphonium Chloride (46)
3.1.7. General Procedure for the Preparation of (E)-4-(5-(2-arylvinyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-yl)Benzenesulfonamides (47–50)
3.1.8. General Procedure for the Preparation of (E)-2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-5-(2-Arylvinyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazols 51–54
3.2. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
3.3. QSAR Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, B.W.; Wild, C.P. World Cancer Report 2014—IARC WHO; IARC Nonserial Publ: Lyon, France, 2014; Volume 630. [Google Scholar]
- Arruebo, M.; Vilaboa, N.; Sáez-Gutierrez, B.; Lambea, J.; Tres, A.; Valladares, M.; González-Fernández, Á. Assessment of the evolution of cancer treatment therapies. Cancers 2011, 3, 3279–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rakesh, K.P.; Wang, S.-M.; Leng, J.; Ravindar, L.; Asiri, A.M.; Marwani, H.M.; Qin, H.-L. Recent Development of Sulfonyl or Sulfonamide Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents: A Key Review. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L.; Gong, X.; Wang, P. Anticancer sulfonamide hybrids that inhibit bladder cancer cells growth and migration as tubulin polymerisation inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Zhen, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, G. Design, synthesis and antiproliferative evaluation of novel sulfanilamide-1,2,3-triazole derivatives as tubulin polymerization inhibitors. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Maksoud, M.S.; Ammar, U.M.; Oh, C.H. Anticancer profile of newly synthesized BRAF inhibitors possess 5-(pyrimidin-4-yl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Duan, W.; Zhang, H.; Mao, S.; Sun, H.; Xin, M. Alkylsulfonamide-containing quinazoline derivatives as potent and orally bioavailable PI3Ks inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 114930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besbes, S.; Mirshahi, M.; Pocard, M.; Billard, C. New dimension in therapeutic targeting of BCL-2 family proteins. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12862–12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassadonia, A.; Cioffi, P.; Simiele, F.; Iezzi, L.; Zilli, M.; Natoli, C. Role of hydroxamate-based histone deacetylase inhibitors (Hb-HDACIs) in the treatment of solid malignancies. Cancers 2013, 5, 919–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Nassan, H.B. Recent progress in the identification of BRAF inhibitors as anti-cancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 72, 170–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Goralski, M.; Gaskill, N.; Capota, E.; Kim, J.; Ting, T.C.; Xie, Y.; Williams, N.S.; Nijhawan, D. Anticancer sulfonamides target splicing by inducing RBM39 degradation via recruitment to DCAF15. Science 2017, 356, eaal3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żołnowska, B.; Sławiński, J.; Szafrański, K.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Kawiak, A.; Wieczór, M.; Zielińska, J.; Bączek, T.; Bartoszewska, S. Novel 2-(2-arylmethylthio-4-chloro-5-methylbenzenesulfonyl)-1-(1,3,5-triazin-2-ylamino)guanidine derivatives: Inhibition of human carbonic anhydrase cytosolic isozymes I and II and the transmembrane tumor-associated isozymes IX and XII, anticancer activit. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelska, A.; Żołnowska, B.; Sławiński, J.; Kawiak, A.; Szafrański, K.; Belka, M.; Bączek, T. Synthesis of 2-alkylthio-N-(quinazolin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide derivatives: Anticancer activity, QSAR studies, and metabolic stability. Mon. Chem. Chem. Mon. 2018, 149, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pogorzelska, A.; Sławiński, J.; Żołnowska, B.; Szafrański, K.; Kawiak, A.; Chojnacki, J.; Ulenberg, S.; Zielińska, J.; Bączek, T. Novel 2-(2-alkylthiobenzenesulfonyl)-3-(phenylprop-2-ynylideneamino)guanidine derivatives as potent anticancer agents—Synthesis, molecular structure, QSAR studies and metabolic stability. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołnowska, B.; Sławiński, J.; Pogorzelska, A.; Szafrański, K.; Kawiak, A.; Stasiłojć, G.; Belka, M.; Zielińska, J.; Bączek, T. Synthesis, QSAR studies, and metabolic stability of novel 2-alkylthio-4-chloro-N-(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)benzenesulfonamide derivatives as potential anticancer and apoptosis-inducing agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 90, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławiński, J.; Szafrański, K.; Pogorzelska, A.; Żołnowska, B.; Kawiak, A.; Macur, K.; Belka, M.; Bączek, T. Novel 2-benzylthio-5-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamides with anticancer activity: Synthesis, QSAR study, and metabolic stability. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhadi, S.; Shiri, F.; Ghasemi, J.B. Multivariate statistical analysis methods in QSAR. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 104635–104665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Shi, L.M.; Kohn, K.W.; Pommier, Y.; Weinstein, J.N. Quantitative structure-antitumor activity relationships of camptothecin analogues: Cluster analysis and genetic algorithm-based studies. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.B.; Braga, F.S.; Lobato, C.C.; Santos, C.F.; Costa, J.S.; Bittencourt, J.A.H.M.; Brasil, D.S.B.; Silva, J.O.; Hage-Melim, L.I.S.; Macêdo, W.J.C.; et al. A QSAR, pharmacokinetic and toxicological study of new artemisinin compounds with anticancer activity. Molecules 2014, 19, 10670–10697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veerasamy, R.; Rajak, H.; Jain, A.; Sivadasan, S.; Varghese, C.P.; Agrawal, R.K. Validation of QSAR Models—Strategies and Importance. Int. J. Drug Des. Discov. 2011, 2, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Tropsha, A.; Gramatica, P.; Gombar, V.K. The importance of being earnest: Validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSPR models. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2003, 22, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławiński, J.; Pogorzelska, A.; Zołnowska, B.; Brozewicz, K.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Synthesis of a novel series of 5-substituted 2,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonamides and their inhibition of human cytosolic isozymes i and II and the transmembrane tumor-associated isozymes IX and XII. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 82, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, C.; Kumari, S.; Angeli, A.; Bua, S.; Buonanno, M.; Maria, S.; Tiwari, M.; Supuran, C.T. Discovery of potent anti-convulsant carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Design, synthesis, in vitro and in vivo appraisal. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 430–443. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Zhang, R. Syntheses and Insecticidal Activities of Novel 2,5-Disubstituted- 1,3,4-0xadiazoles. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1996, 67, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Baldridge, K.K.; Boatz, J.A.; Elbert, S.T.; Gordon, M.S.; Jensen, J.H.; Koseki, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Nguyen, K.A.; Su, S.; et al. General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J. Comput. Chem. 1993, 14, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIBCO Software Inc. Statistica (Data Analysis Software System), Version 13. 2017. Available online: http://statistica.io (accessed on 28 February 2020).









| Compd | Ar | R1 | IC50 [µM] a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT-116 | MCF-7 | HeLa | HaCaT | |||
| 7 | Ph | Cl | 86 ± 3 | 165 ± 5 | 455 ±14 | n.t. |
| 8[18] | SCH2Ph | 18.1 ± 0.2 | 16.3 ± 0.2 | 13.8 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 1 | |
| 9 | 3-Cl-Ph | Cl | 24 ± 1 | 150 ± 10 | 19 ± 1 | 98 ± 2 |
| 10[18] | SCH2Ph | 12.0 ± 0.2 | 11.3 ± 0.4 | 16.1 ± 0.1 | 16 ± 0.5 | |
| 11 | 4-Cl-Ph | Cl | 22 ± 1 | 28 ± 1 | 42 ±1 | 51 ± 3 |
| 12[18] | SCH2Ph | 11.7 ± 0.4 | 10.7 ± 0.3 | 40 ± 1 | n.t. | |
| 13 | 2,6-diCl-Ph | Cl | 16 ± 1 | 92 ± 5 | 25 ± 1 | 95 ± 2 |
| 14[18] | SCH2Ph | 31.8 ± 0.3 | 29.4 ± 0.3 | 12.5 ± 0.1 | 160 ± 2 | |
| 15 | 4-Br-Ph | Cl | 34 ± 1 | 41 ± 1 | 34 ± 2 | 55 ± 2 |
| 16[18] | SCH2Ph | 15.0 ± 0.3 | 12.9 ± 0.4 | 29.2 ± 0.8 | 31 ± 1 | |
| 17 | 4-OH-Ph | Cl | 49 ± 1 | 73 ± 3 | 99 ± 1 | 100 ± 5 |
| 18 | SCH2Ph | 18 ± 1 | 59 ± 3 | 18.2 ± 0.5 | 25.6 ± 0.5 | |
| 19 | 4-CN-Ph | Cl | 13.7 ± 0.5 | 10.0 ± 0.3 | 117 ± 6 | 102 ± 3 |
| 20 | SCH2Ph | 10.3 ± 0.2 | 8.9 ± 0.5 | 12.2 ± 0.5 | 20 ± 1 | |
| 21 | 4-CF3-Ph | Cl | 18 ± 1 | 75 ± 2 | 90 ± 2 | 95 ± 4 |
| 22 | SCH2Ph | 15.2 ± 0.1 | 30 ± 1 | 33.4 ± 0.5 | 33 ± 1 | |
| 23 | Pyridin-4-yl | Cl | 255 ± 13 | 640 ± 13 | 740 ± 37 | n.t. |
| 24 | SCH2Ph | 31±1 | 225 ± 11 | 135 ± 8 | 150 ± 8 | |
| 25 | Pyridin-3-yl | Cl | 220 ± 11 | 760 ± 24 | 570 ±17 | n.t. |
| 26 | SCH2Ph | 85 ± 5 | 350 ± 17 | 135 ± 4 | n.t. | |
| 27 | Pyridin-2-yl | Cl | 117 ± 4 | 110 ± 2 | 170 ± 5 | n.t. |
| 28 | SCH2Ph | 25 ± 1 | 115 ± 3 | 130 ± 6 | 140 ± 10 | |
| 29 | Thiophen-2-yl | Cl | 108 ± 4 | 175 ± 12 | 245 ±12 | n.t. |
| 30 | SCH2Ph | 32 ± 2 | 66 ± 2 | 87 ± 3 | 85 ± 4 | |
| 31 | 5-Nitrothiophen-2-yl | Cl | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 4.5 ±0.3 | 8.1 ± 0.5 |
| 32 | SCH2Ph | 17 ± 1 | 55 ± 3 | 58 ± 2 | 57 ± 1 | |
| 33 | Furan-2-yl | Cl | 33 ± 1 | 170 ± 9 | 210 ± 8 | 200 ± 12 |
| 34 | SCH2Ph | 27.8 ± 0.3 | 62 ± 1 | 85 ± 3 | 91 ± 3 | |
| 35 | 5-Nitrofuran-2-yl | SCH2Ph | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 150 ± 8 | 69 ± 3 | 87 ± 4 |
| 36 | Pyrrol-2-yl | Cl | 39 ± 1 | 40 ± 1 | 73 ± 3 | 98 ± 4 |
| Cisplatin | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ±0.1 | n.t. | ||

| Compd | R2 | R3 | R4 | IC50 [µM] a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT-116 | MCF-7 | HeLa | HaCaT | ||||
| 47 | SO2NH2 | H | H | 185 ± 11 | 168 ± 8 | 130 ± 7 | n.t. |
| 48 | SO2NH2 | H | 4-Cl | 105 ± 5 | 76 ± 4 | 25 ± 3 | 95 ± 4 |
| 49 | SO2NH2 | H | 4-CN | 32 ± 2 | 75 ± 4 | 99 ± 3 | 98 ± 4 |
| 50 | SO2NH2 | H | 4-CF3 | 155 ± 7 | 280 ± 15 | 520 ± 25 | n.t. |
| 51 | Cl | Cl | H | 92 ± 2 | 125 ± 6 | 190 ± 10 | n.t. |
| 52 | Cl | Cl | 4-Cl | 64 ± 3 | 110 ± 6 | 215 ± 6 | n.t. |
| 53 | Cl | Cl | 4-CN | 106 ± 3 | 142 ± 6 | 225 ± 11 | n.t. |
| 54 | Cl | Cl | 4-CF3 | 98 ± 1 | 102 ± 5 | 104 ± 3 | n.t. |
| IC50 [µM] R1 = Cl | IC50 [µM] R1 = SBn | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Line | Min | Max | Average | Standard Deviation | Min | Max | Average | Standard Deviation |
| HCT-116 | 0.5 | 255 | 69 | 76.8 | 4 | 85 | 24 | 19.0 |
| MCF-7 | 4 | 760 | 169 | 224.3 | 9 | 350 | 80 | 96.3 |
| HeLa | 4.5 | 740 | 193 | 222.9 | 12 | 135 | 58 | 46.3 |
| Cell Line | R1 = Cl | R1 = SBn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation | Statistics | Equation | Statistics | |
| HCT-116 | “E1” pIC50= 4.4571 + 0.5082(SMR_VSA2) − 0.2849(logS) + 0.1829(SMR_VSA3) ± 0.1579 | F = 75.21 p < 10−6 R2 = 0.94 Q2 = 0.92 | “E2” pIC50 = 4.7247 + 0.2994(FCASA−) + 0.2222(vsurf_DD23) − 0.1596(SMR_VSA1) ± 0.1415 | F = 17.19 p = 2 × 10−4 R2 = 0.78 Q2 = 0.72 |
| MCF-7 | “E3” pIC50 = 4.0959 + 0.5488(vsurf_Wp2) + 0.2418(vsa_other) − 0.2190(vsurf_HB1) ± 0.2263 | F = 29.43 p = 2 × 10−5 R2 = 0.86 Q2 = 0.83 | “E4” pIC50 = 4.3633 + 0.5904(PEOE_VSA_FNEG) + 0.2738(vsurf_ID8) − 0.2166(vsurf_IW2) ± 0.1365 | F = 60.43 p < 10−6 R2 = 0.93 Q2 = 0.80 |
| HeLa | “E5” pIC50 = 4.0280 + 0.4800(FASA−) + 0.3253(SMR_VSA2) − 0.2252(E_ele) ± 0.2094 | F = 35.47 p = 6 × 10−6 R2 = 0.88 Q2 = 0.81 | “E6” pIC50 = 4.3872 + 0.4976(chi1v_C) + 0.2609(BCUT_SMR_2) − 0.1388(pmi) ± 0.1258 | F = 42.30 p = 3 × 10−6 R2 = 0.90 Q2 = 0.85 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szafrański, K.; Sławiński, J.; Tomorowicz, Ł.; Kawiak, A. Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation and Structure-Activity Analysis of Novel (E)- 5-(2-Arylvinyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062235
Szafrański K, Sławiński J, Tomorowicz Ł, Kawiak A. Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation and Structure-Activity Analysis of Novel (E)- 5-(2-Arylvinyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(6):2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062235
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzafrański, Krzysztof, Jarosław Sławiński, Łukasz Tomorowicz, and Anna Kawiak. 2020. "Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation and Structure-Activity Analysis of Novel (E)- 5-(2-Arylvinyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamides" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 6: 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062235
APA StyleSzafrański, K., Sławiński, J., Tomorowicz, Ł., & Kawiak, A. (2020). Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation and Structure-Activity Analysis of Novel (E)- 5-(2-Arylvinyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(6), 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062235