Abnormal Upregulation of GPR17 Receptor Contributes to Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in SOD1 G93A Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
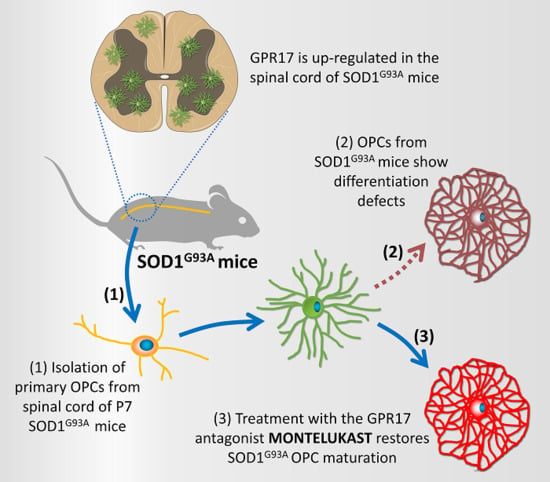
2.1. Time-Dependent Upregulation of GPR17 Expression in the Spinal Cord of SOD1G93A Mice
2.2. Impaired Oligodendrogenesis in the Developing Spinal Cord of SOD1G93A Mice
2.3. Impaired Differentiation Capabilities of OPCs Isolated from P7 SOD1G93A Mice
2.4. Restoration of the Differentiation Capabilities of OPCs from P7 SOD1G93A Mice by Montelukast
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Genotyping
4.2. Western Blot
4.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Analysis
4.4. OPC Cell Culture
4.5. Immunocytochemistry
4.6. Proliferation Assay
4.7. Total RNA Extraction, Retrotranscription, and Real-Time PCR
4.8. Pharmacological Treatment
4.9. Statistical Analisys
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GPR17 | G Protein-coupled Receptor 17 |
| SOD1 | Superoxide Dismutase 1 |
| ALS | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
| MN | Motor Neurons |
| OPCs | Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells |
| GM | Grey Matter |
| WM | White Matter |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| WT | Wild Type |
| OLIG2 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 |
| NG2 | Neural Glial antigen 2 |
| MACS | Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting |
| PDGFRα | Platelet Derived Growth Factor α |
| T3 | Triiodothyronine |
| MBP | Myelin Basic Protein |
| DIV | Days In Vitro |
| EdU | 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine |
| MTK | Montelukast |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
Appendix A

References
- Eisen, A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-evolutionary and other perspectives. Muscle Nerve 2009, 40, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Homma, K.; Ichijo, H. SOD1 in neurotoxicity and its controversial roles in SOD1 mutation-negative ALS. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2016, 60, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafałowska, J.; Dziewulska, D. White matter injury in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Folia Neuropathol. 1996, 34, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mollink, J.; Hiemstra, M.; Miller, K.L.; Huszar, I.N.; Jenkinson, M.; Raaphorst, J.; Wiesmann, M.; Ansorge, O.; Pallebage-Gamarallage, M.; van Cappellen van Walsum, A.M. White matter changes in the perforant path area in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2019, 45, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serio, A.; Patani, R. Concise Review: The Cellular Conspiracy of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boillée, S.; Yamanaka, K.; Lobsiger, C.S.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Kassiotis, G.; Kollias, G.; Cleveland, D.W. Onset and progression in inherited ALS determined by motor neurons and microglia. Science 2006, 312, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Giorgio, F.P.; Boulting, G.L.; Bobrowicz, S.; Eggan, K.C. Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Motor Neurons Are Sensitive to the Toxic Effect of Glial Cells Carrying an ALS-Causing Mutation. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, K.; Chun, S.J.; Boillee, S.; Fujimori-Tonou, N.; Yamashita, H.; Gutmann, D.H.; Takahashi, R.; Misawa, H.; Cleveland, D.W. Astrocytes as determinants of disease progression in inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frakes, A.E.; Ferraiuolo, L.; Haidet-Phillips, A.M.; Schmelzer, L.; Braun, L.; Miranda, C.J.; Ladner, K.J.; Bevan, A.K.; Foust, K.D.; Godbout, J.P.; et al. Microglia induce motor neuron death via the classical NF-κB pathway in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron 2014, 81, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nave, K.A. Myelination and support of axonal integrity by glia. Nature 2010, 468, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Morrison, B.M.; Li, Y.; Lengacher, S.; Farah, M.H.; Hoffman, P.N.; Liu, Y.; Tsingalia, A.; Jin, L.; Zhang, P.W.; et al. Oligodendroglia metabolically support axons and contribute to neurodegeneration. Nature 2012, 487, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Li, Y.; Fukaya, M.; Lorenzini, I.; Cleveland, D.W.; Ostrow, L.W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E. Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philips, T.; Bento-Abreu, A.; Nonneman, A.; Haeck, W.; Staats, K.; Geelen, V.; Hersmus, N.; Küsters, B.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Van Damme, P.; et al. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 2013, 136, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferraiuolo, L.; Meyer, K.; Sherwood, T.W.; Vick, J.; Likhite, S.; Frakes, A.; Miranda, C.J.; Braun, L.; Heath, P.R.; Pineda, R.; et al. Oligodendrocytes contribute to motor neuron death in ALS via SOD1-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6496–E6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chung, A.Y.; Na, J.E.; Lee, S.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, E.; Sun, W.; Rhyu, I.J.; Park, H.C. Myelin degeneration induced by mutant superoxide dismutase 1 accumulation promotes amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Glia 2019, 67, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Lecca, D.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Gelosa, P.; Sironi, L.; Ciana, P.; Fumagalli, M.; Villa, G.; Verderio, C.; Grumelli, C.; Guerrini, U.; et al. The recently identified P2Y-like receptor GPR17 is a sensor of brain damage and a new target for brain repair. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boda, E.; Viganò, F.; Rosa, P.; Fumagalli, M.; Labat-Gest, V.; Tempia, F.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Dimou, L.; Buffo, A. The GPR17 receptor in NG2 expressing cells: Focus on in vivocell maturation and participation in acute trauma and chronic damage. Glia 2011, 59, 1958–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Daniele, S.; Lecca, D.; Lee, P.R.; Parravicini, C.; Douglas Fields, R.; Rosa, P.; Antonucci, F.; Verderio, C.; Letizia Trincavelli, M.; et al. Phenotypic changes, signaling pathway, and functional correlates of GPR17-expressing neural precursor cells during oligodendrocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10593–10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fratangeli, A.; Parmigiani, E.; Fumagalli, M.; Lecca, D.; Benfante, R.; Passafaro, M.; Buffo, A.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Rosa, P. The regulated expression, intracellular trafficking, and membrane recycling of the P2Y-like receptor GPR17 in Oli-neu oligodendroglial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 5241–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceruti, S.; Villa, G.; Genovese, T.; Mazzon, E.; Longhi, R.; Rosa, P.; Bramanti, P.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Abbracchio, M.P. The P2Y-like receptor GPR17 as a sensor of damage and a new potential target in spinal cord injury. Brain 2009, 132, 2206–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franke, H.; Parravicini, C.; Lecca, D.; Zanier, E.R.; Heine, C.; Bremicker, K.; Fumagalli, M.; Rosa, P.; Longhi, L.; Stocchetti, N.; et al. Changes of the GPR17 receptor, a new target for neurorepair, in neurons and glial cells in patients with traumatic brain injury. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, C.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, X.Q.; Shi, W.Z.; Fang, S.H.; Lu, Y.B.; Zhang, W.P.; Xia, Q.; Wei, E.Q. The new P2Y-like receptor G protein-coupled receptor 17 mediates acute neuronal injury and late microgliosis after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viganò, F.; Schneider, S.; Cimino, M.; Bonfanti, E.; Gelosa, P.; Sironi, L.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Dimou, L. GPR17 expressing NG2-Glia: Oligodendrocyte progenitors serving as a reserve pool after injury. Glia 2016, 64, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfanti, E.; Gelosa, P.; Fumagalli, M.; Dimou, L.; Viganò, F.; Tremoli, E.; Cimino, M.; Sironi, L.; Abbracchio, M.P. The role of oligodendrocyte precursor cells expressing the GPR17 receptor in brain remodeling after stroke. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppolino, G.T.; Marangon, D.; Negri, C.; Menichetti, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Gelosa, P.; Dimou, L.; Furlan, R.; Lecca, D.; Abbracchio, M.P. Differential local tissue permissiveness influences the final fate of GPR17-expressing oligodendrocyte precursors in two distinct models of demyelination. Glia 2018, 66, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Bonfanti, E.; Daniele, S.; Zappelli, E.; Lecca, D.; Martini, C.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Abbracchio, M.P. The ubiquitin ligase Mdm2 controls oligodendrocyte maturation by intertwining mTOR with G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in the regulation of GPR17 receptor desensitization. Glia 2015, 63, 2327–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Koito, H.; Li, J.; Ye, F.; Hoang, J.; Escobar, S.S.; Gow, A.; Arnett, H.A.; et al. The oligodendrocyte-specific G protein-coupled receptor GPR17 is a cell-intrinsic timer of myelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fumagalli, M.; Lecca, D.; Coppolino, G.T.; Parravicini, C.; Abbracchio, M.P. Pharmacological properties and biological functions of the GPR17 receptor, a potential target for neuro-regenerative medicine. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1051, pp. 169–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ciana, P.; Fumagalli, M.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Verderio, C.; Rosa, P.; Lecca, D.; Ferrario, S.; Parravicini, C.; Capra, V.; Gelosa, P.; et al. The orphan receptor GPR17 identified as a new dual uracil nucleotides/cysteinyl-leukotrienes receptor. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4615–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelosa, P.; Bonfanti, E.; Castiglioni, L.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Gruart, A.; Fontana, L.; Gotti, M.; Tremoli, E.; Lecca, D.; Fumagalli, M.; et al. Improvement of fiber connectivity and functional recovery after stroke by montelukast, an available and safe anti-asthmatic drug. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L.; You, N.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Cao, L.; Han, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Olig2-targeted G-protein-coupled receptor Gpr17 regulates oligodendrocyte survival in response to lysolecithin-induced demyelination. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 10560–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fumagalli, M.; Lecca, D.; Abbracchio, M.P. CNS remyelination as a novel reparative approach to neurodegenerative diseases: The roles of purinergic signaling and the P2Y-like receptor GPR17. Neuropharmacology 2016, 104, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stifanese, R.; Averna, M.; De Tullio, R.; Pedrazzi, M.; Beccaria, F.; Salamino, F.; Milanese, M.; Bonanno, G.; Pontremoli, S.; Melloni, E. Adaptive modifications in the calpain/calpastatin system in brain cells after persistent alteration in Ca2+ homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milanese, M.; Zappettini, S.; Onofri, F.; Musazzi, L.; Tardito, D.; Bonifacino, T.; Messa, M.; Racagni, G.; Usai, C.; Benfenati, F.; et al. Abnormal exocytotic release of glutamate in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stifanese, R.; Averna, M.; De Tullio, R.; Pedrazzi, M.; Milanese, M.; Bonifacino, T.; Bonanno, G.; Salamino, F.; Pontremoli, S.; Melloni, E. Role of calpain-1 in the early phase of experimental ALS. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 562, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, A.H.; Tripathi, R.B.; Richardson, W.D.; Franklin, R.J.M. Developmental Origin of Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells Determines Response to Demyelination and Susceptibility to Age-Associated Functional Decline. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergles, D.E.; Richardson, W.D. Oligodendrocyte development and plasticity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a020453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieran, D.; Hafezparast, M.; Bohnert, S.; Dick, J.R.T.; Martin, J.; Schiavo, G.; Fisher, E.M.C.; Greensmith, L. A mutation in dynein rescues axonal transport defects and extends the life span of ALS mice. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pugliese, A.M.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Lecca, D.; Coppi, E.; Fumagalli, M.; Ferrario, S.; Failli, P.; Daniele, S.; Martini, C.; Pedata, F.; et al. Functional characterization of two isoforms of the P2Y-like receptor GPR17: [35S]GTPγS binding and electrophysiological studies in 1321N1 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C1028–C1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, M.; Ritter, K.; Thiemke, K.; Gillard, M.; Kostenis, E.; Müller, C.E. Development of [3H]2-carboxy-4,6-dichloro-1 H -indole-3-propionic acid ([3H]PSB-12150): A useful tool for studying GPR17. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.I.; Haddon, J.E.; Ahmed Syed, Y.; Trent, S.; Lin, T.C.E.; Patel, Y.; Carter, J.; Haan, N.; Honey, R.C.; Humby, T.; et al. Cyfip1 haploinsufficient rats show white matter changes, myelin thinning, abnormal oligodendrocytes and behavioural inflexibility. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volonté, C.; Apolloni, S.; Parisi, C.; Amadio, S. Purinergic contribution to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropharmacology 2016, 104, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieślak, M.; Roszek, K.; Wujak, M. Purinergic implication in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—From pathological mechanisms to therapeutic perspectives. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lecca, D.; Raffaele, S.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Fumagalli, M. Regulation and signaling of the GPR17 receptor in oligodendroglial cells. Glia 2020, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, E.G.; Kang, S.H.; Fukaya, M.; Bergles, D.E. Oligodendrocyte progenitors balance growth with self-repulsion to achieve homeostasis in the adult brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonifacino, T.; Cattaneo, L.; Gallia, E.; Puliti, A.; Melone, M.; Provenzano, F.; Bossi, S.; Musante, I.; Usai, C.; Conti, F.; et al. In-vivo effects of knocking-down metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the SOD1G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropharmacology 2017, 123, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, R.; Oliván, S.; Osta, R.; Navarro, X. Evolution of gait abnormalities in SOD1 G93A transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2011, 1406, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinsant, S.; Mansfield, C.; Jimenez-Moreno, R.; Moore, V.D.G.; Yoshikawa, M.; Hampton, T.G.; Prevette, D.; Caress, J.; Oppenheim, R.W.; Milligan, C. Characterization of early pathogenesis in the SOD1G93A mouse model of ALS: Part I, background and methods. Brain Behav. 2013, 3, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.J.; Schonewille, M.; Siddique, T.; Schults, A.N.A.; Fu, R.; Bär, P.R.; Anelli, R.; Heckman, C.J.; Kroese, A.B.A. Hyperexcitability of Cultured Spinal Motoneurons from Presymptomatic ALS Mice. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 91, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williamson, T.L.; Cleveland, D.W. Slowing of axonal transport is a very early event in the toxicity of ALS-linked SOD1 mutants to motor neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, J.; Verrier, B.; Roubertoux, P.; Durand, J. Altered sensorimotor development in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2822–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zundert, B.; Peuscher, M.H.; Hynynen, M.; Chen, A.; Neve, R.L.; Brown, R.H.; Constantine-Paton, M.; Bellingham, M.C. Neonatal neuronal circuitry shows hyperexcitable disturbance in a mouse model of the adult-onset neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10864–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinsant, S.; Mansfield, C.; Jimenez-Moreno, R.; Moore, V.D.G.; Yoshikawa, M.; Hampton, T.G.; Prevette, D.; Caress, J.; Oppenheim, R.W.; Milligan, C. Characterization of early pathogenesis in the SOD1G93A mouse model of ALS: Part II, results and discussion. Brain Behav. 2013, 3, 431–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, R.G.; Mustafi, S.M.; Amin, M.Y.; Mareci, T.H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Magin, R.L. Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging Can Detect Presymptomatic Axonal Degeneration in The Spinal Cord of ALS Mice. Funct. Neurol. 2018, 33, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bechler, M.E.; Byrne, L.; Ffrench-Constant, C. CNS Myelin Sheath Lengths Are an Intrinsic Property of Oligodendrocytes. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 2411–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benned-Jensen, T.; Rosenkilde, M. Distinct expression and ligand-binding profiles of two constitutively active GPR17 splice variants. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buccioni, M.; Marucci, G.; Ben, D.D.; Giacobbe, D.; Lambertucci, C.; Soverchia, L.; Thomas, A.; Volpini, R.; Cristalli, G. Innovative functional cAMP assay for studying G protein-coupled receptors: Application to the pharmacological characterization of GPR17. Purinergic Signal. 2011, 7, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppi, E.; Maraula, G.; Fumagalli, M.; Failli, P.; Cellai, L.; Bonfanti, E.; Mazzoni, L.; Coppini, R.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Pedata, F.; et al. UDP-glucose enhances outward K + currents necessary for cell differentiation and stimulates cell migration by activating the GPR17 receptor in oligodendrocyte precursors. Glia 2013, 61, 1155–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, S.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Gabelloni, P.; Lecca, D.; Rosa, P.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Martini, C. Agonist-induced desensitization/resensitization of human G protein-coupled receptor 17: A functional cross-talk between purinergic and cysteinyl-leukotriene ligands. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennen, S.; Wang, H.; Peters, L.; Merten, N.; Simon, K.; Spinrath, A.; Blättermann, S.; Akkari, R.; Schrage, R.; Schröder, R.; et al. Decoding signaling and function of the orphan g protein-coupled receptor GPR17 with a small-molecule agonist. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maekawa, A.; Balestrieri, B.; Austen, K.F.; Kanaoka, Y. GPR17 is a negative regulator of the cysteinyl leukotriene 1 receptor response to leukotriene D4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11685–11690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merten, N.; Fischer, J.; Simon, K.; Zhang, L.; Schröder, R.; Peters, L.; Letombe, A.G.; Hennen, S.; Schrage, R.; Bödefeld, T.; et al. Repurposing HAMI3379 to Block GPR17 and Promote Rodent and Human Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parravicini, C.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Fantucci, P.; Ranghino, G. Forced unbinding of GPR17 ligands from wild type and R255I mutant receptor models through a computational approach. BMC Struct. Biol. 2010, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, A.D.; Kendall Harden, T.; Nicholas, R.A. Is GPR17 a P2Y/leukotriene receptor? examination of uracil nucleotides, nucleotide sugars, and cysteinyl leukotrienes as agonists of GPR17. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 347, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marschallinger, J.; Schäffner, I.; Klein, B.; Gelfert, R.; Rivera, F.J.; Illes, S.; Grassner, L.; Janssen, M.; Rotheneichner, P.; Schmuckermair, C.; et al. Structural and functional rejuvenation of the aged brain by an approved anti-asthmatic drug. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurney, M.E.; Pu, H.; Chiu, A.Y.; Dal Canto, M.C.; Polchow, C.Y.; Alexander, D.D.; Caliendo, J.; Hentati, A.; Kwon, Y.W.; Deng, H.X.; et al. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 1994, 264, 1772–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonfanti, E.; Bonifacino, T.; Raffaele, S.; Milanese, M.; Morgante, E.; Bonanno, G.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Fumagalli, M. Abnormal Upregulation of GPR17 Receptor Contributes to Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in SOD1 G93A Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072395
Bonfanti E, Bonifacino T, Raffaele S, Milanese M, Morgante E, Bonanno G, Abbracchio MP, Fumagalli M. Abnormal Upregulation of GPR17 Receptor Contributes to Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in SOD1 G93A Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(7):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072395
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonfanti, Elisabetta, Tiziana Bonifacino, Stefano Raffaele, Marco Milanese, Erica Morgante, Giambattista Bonanno, Maria P. Abbracchio, and Marta Fumagalli. 2020. "Abnormal Upregulation of GPR17 Receptor Contributes to Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in SOD1 G93A Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 7: 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072395
APA StyleBonfanti, E., Bonifacino, T., Raffaele, S., Milanese, M., Morgante, E., Bonanno, G., Abbracchio, M. P., & Fumagalli, M. (2020). Abnormal Upregulation of GPR17 Receptor Contributes to Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in SOD1 G93A Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(7), 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072395