Antimigraine Drug Avitriptan Is a Ligand and Agonist of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor that Induces CYP1A1 in Hepatic and Intestinal Cells
Abstract
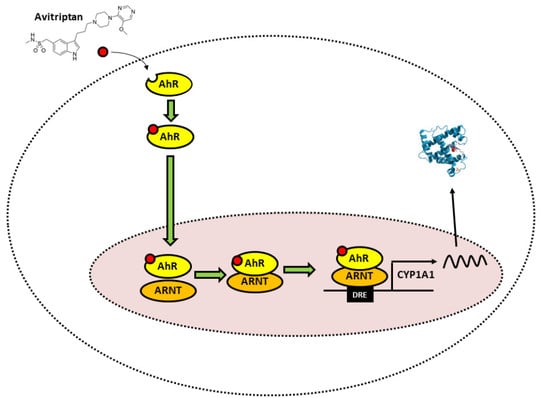
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Triptans Are Activators of Human AhR
2.2. Avitriptan and Donitriptan induce CYP1A1 in Hepatic and Intestinal Cells via AhR
2.3. Avitriptan Is a Low-Affinity Ligand of AhR
2.4. Avitriptan and Donitriptan Trigger Nuclear Translocation of AhR
2.5. Formation of AhR-ARNT Heterodimer by Avitriptan and Donitriptan
2.6. Avitriptan and Donitriptan Enhance the Recruitment of AhR into CYP1A1 Promotor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. Reporter Gene Assay
4.5. Isolation of RNA and qRT-PCR
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Nuclear Translocation of AhR–Immune Histochemistry
4.8. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.9. Radio-Ligand Binding Assay
4.10. Protein Immune-Precipitation
4.11. Molecular Docking Studies
4.12. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CYP1A1 | Cytochrome P450 1A1 |
| AhR | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| ARNT | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator |
| TCDD | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin |
| TCDF | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran |
| BaP | Benzo[a]pyrene |
| FICZ | 6-Formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| LBD | Ligand-binding domain |
| DMSO | dimethylsulfoxide |
References
- Denison, M.S.; Nagy, S.R. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelos, M.G.; Kaufman, D.S. Advances in the role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor to regulate early hematopoietic development. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2018, 25, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, K.W. From TCDD-mediated toxicity to searches of physiologic AHR functions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, K.W. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): From selected human target genes and crosstalk with transcription factors to multiple AHR functions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 168, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Quintana, F.J. Regulation of the Immune Response by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Immunity 2018, 48, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Z.Z.; Krausz, K.W.; Nagaoka, K.; Tanaka, N.; Gowda, K.; Amin, S.G.; Perdew, G.H.; Gonzalez, F.J. In vivo effects of the pure aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonist GNF-351 after oral administration are limited to the gastrointestinal tract. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safe, S.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, U.H. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) as a Drug Target for Cancer Chemotherapy. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi-Smiraglia, A.; Bagati, A.; Fink, E.E.; Affronti, H.C.; Lipchick, B.C.; Moparthy, S.; Long, M.D.; Rosario, S.R.; Lightman, S.M.; Moparthy, K.; et al. Inhibition of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/polyamine biosynthesis axis suppresses multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4682–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre, S.; Tardif, N.; Mouchet, N.; Leclair, H.M.; Boussemart, L.; Gautron, A.; Bachelot, L.; Perrot, A.; Soshilov, A.; Rogiers, A.; et al. Sustained activation of the Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor transcription factor promotes resistance to BRAF-inhibitors in melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghotbaddini, M.; Moultrie, V.; Powell, J.B. Constitutive Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer Progression. J. Cancer Treatment Diagn. 2018, 2, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Darakhshan, S.; Pour, A.B. Tranilast: A review of its therapeutic applications. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 91, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Rjater, R.G.; Kale-Pradhan, P.B. Perils and pitfalls of long-term effects of proton pump inhibitors. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 6, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepankova, M.; Bartonkova, I.; Jiskrova, E.; Vrzal, R.; Mani, S.; Kortagere, S.; Dvorak, Z. Methylindoles and Methoxyindoles are Agonists and Antagonists of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.; Safe, S.; Bjeldanes, L. Indole-3-carbinol and diindolylmethane as aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor agonists and antagonists in T47D human breast cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.K.; Balaguer, P.; Ekstrand, B.; Daujat-Chavanieu, M.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S. Skatole (3-Methylindole) Is a Partial Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist and Induces CYP1A1/2 and CYP1B1 Expression in Primary Human Hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, U.H.; Lee, S.O.; Sridharan, G.; Lee, K.; Davidson, L.A.; Jayaraman, A.; Chapkin, R.S.; Alaniz, R.; Safe, S. Microbiome-derived tryptophan metabolites and their aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent agonist and antagonist activities. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubbard, T.D.; Murray, I.A.; Bisson, W.H.; Lahoti, T.S.; Gowda, K.; Amin, S.G.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Adaptation of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor to sense microbiota-derived indoles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tfelt-Hansen, P.; De Vries, P.; Saxena, P.R. Triptans in migraine: A comparative review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Drugs 2000, 60, 1259–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, N.R.; Salazar, D.E.; Jhee, S.S.; Fulmor, I.E.; Ford, N.; Smith, R.A.; Sramek, J.J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of avitriptan in patients with migraine after oral dosing. Headache 1998, 38, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.W.; Perez, M.; Pauwels, P.J.; Le Grand, B.; Verscheure, Y.; Colpaert, F.C. Donitriptan, a unique high-efficacy 5-HT1B/1D agonist: Key features and acute antimigraine potential. CNS Drug Rev. 2000, 6, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilt, L.A.; Nguyen, D.; Roberts, A.G. Insights into the Molecular Mechanism of Triptan Transport by P-glycoprotein. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, P.H.; Greene, D.S.; Barbhaiya, R.H. Disposition of [14C]avitriptan in rats and humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marathe, P.H.; Greene, D.S.; Kollia, G.D.; Barbhaiya, R.H. A pharmacokinetic interaction study of avitriptan and propranolol. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 63, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, B.; Richard, M.L.; Leducq, V.; Pham, H.P.; Michel, M.L.; Da Costa, G.; Bridonneau, C.; Jegou, S.; Hoffmann, T.W.; Natividad, J.M.; et al. CARD9 impacts colitis by altering gut microbiota metabolism of tryptophan into aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelante, T.; Iannitti, R.G.; Cunha, C.; De Luca, A.; Giovannini, G.; Pieraccini, G.; Zecchi, R.; D’Angelo, C.; Massi-Benedetti, C.; Fallarino, F.; et al. Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity 2013, 39, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denison, M.S.; Faber, S.C. And Now for Something Completely Different: Diversity in Ligand-Dependent Activation of Ah Receptor Responses. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tagliabue, S.G.; Faber, S.C.; Motta, S.; Denison, M.S.; Bonati, L. Modeling the binding of diverse ligands within the Ah receptor ligand binding domain. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seok, S.H.; Lee, W.; Jiang, L.; Molugu, K.; Zheng, A.; Li, Y.; Park, S.; Bradfield, C.A.; Xing, Y. Structural hierarchy controlling dimerization and target DNA recognition in the AHR transcriptional complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5431–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goettel, J.A.; Gandhi, R.; Kenison, J.E.; Yeste, A.; Murugaiyan, G.; Sambanthamoorthy, S.; Griffith, A.E.; Patel, B.; Shouval, D.S.; Weiner, H.L.; et al. AHR Activation Is Protective against Colitis Driven by T Cells in Humanized Mice. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, P.R.; De Vries, P.; Wang, W.; Heiligers, J.P.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Bax, W.A.; Yocca, F.D. Effects of avitriptan, a new 5-HT 1B/1D receptor agonist, in experimental models predictive of antimigraine activity and coronary side-effect potential. Naunyn. Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 355, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, C.Q. Migraine: Current drug discovery trend. Curr. Med. Chem. 1997, 4, 385–404. [Google Scholar]
- Marathe, P.H.; Sandefer, E.P.; Kollia, G.E.; Greene, D.S.; Barbhaiya, R.H.; Lipper, R.A.; Page, R.C.; Doll, W.J.; Ryo, U.Y.; Digenis, G.A. In vivo evaluation of the absorption and gastrointestinal transit of avitriptan in fed and fasted subjects using gamma scintigraphy. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1998, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Jusko, W.J.; Fulmor, I.E.; Norton, J.; Uderman, H.D.; Salazar, D.E. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of avitriptan during intravenous administration in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 39, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, P.H.; Greene, D.S.; Lee, J.S.; Barbhaiya, R.H. Assessment of effect of food, gender, and intra-subject variability in the pharmacokinetics of avitriptan. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1998, 19, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotna, A.; Pavek, P.; Dvorak, Z. Novel stably transfected gene reporter human hepatoma cell line for assessment of aryl hydrocarbon receptor transcriptional activity: Construction and characterization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10133–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzal, R.; Knoppová, B.; Bachleda, P.; Dvořák, Z. Effects of oral anorexiant sibutramine on the expression of cytochromes P450s in human hepatocytes and cancer cell lines. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2013, 27, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soshilov, A.A.; Denison, M.S. Ligand promiscuity of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists and antagonists revealed by site-directed mutagenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 1707–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motto, I.; Bordogna, A.; Soshilov, A.A.; Denison, M.S.; Bonati, L. New aryl hydrocarbon receptor homology model targeted to improve docking reliability. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2868–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vyhlídalová, B.; Krasulová, K.; Pečinková, P.; Poulíková, K.; Vrzal, R.; Andrysík, Z.; Chandran, A.; Mani, S.; Dvorak, Z. Antimigraine Drug Avitriptan Is a Ligand and Agonist of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor that Induces CYP1A1 in Hepatic and Intestinal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082799
Vyhlídalová B, Krasulová K, Pečinková P, Poulíková K, Vrzal R, Andrysík Z, Chandran A, Mani S, Dvorak Z. Antimigraine Drug Avitriptan Is a Ligand and Agonist of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor that Induces CYP1A1 in Hepatic and Intestinal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082799
Chicago/Turabian StyleVyhlídalová, Barbora, Kristýna Krasulová, Petra Pečinková, Karolína Poulíková, Radim Vrzal, Zdeněk Andrysík, Aneesh Chandran, Sridhar Mani, and Zdenek Dvorak. 2020. "Antimigraine Drug Avitriptan Is a Ligand and Agonist of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor that Induces CYP1A1 in Hepatic and Intestinal Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082799
APA StyleVyhlídalová, B., Krasulová, K., Pečinková, P., Poulíková, K., Vrzal, R., Andrysík, Z., Chandran, A., Mani, S., & Dvorak, Z. (2020). Antimigraine Drug Avitriptan Is a Ligand and Agonist of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor that Induces CYP1A1 in Hepatic and Intestinal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082799