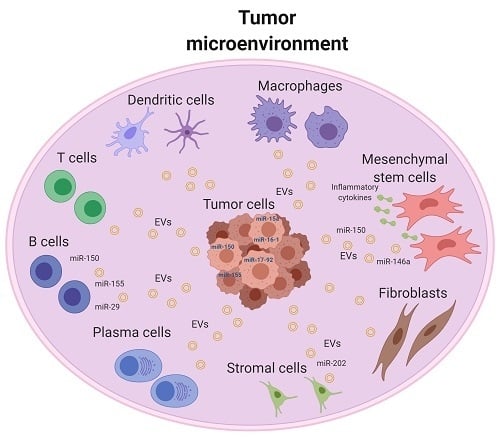
The Interplay between MicroRNAs and the Components of the Tumor Microenvironment in B-Cell Malignancies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tumor Microenvironment of B-Cell Malignancy
3. MiRNAs and Their Contribution to Tumor Microenvironment
4. Involvement of TME-Associated miRNAs in Diagnosis and/or Prognosis
5. Involvement of TME-Associated miRNAs in Proliferation and Survival of Tumor Cells
6. Involvement of TME-Associated miRNAs in Cancer Therapy Resistance
7. Crosstalk of Exosomal MiRNAs and TME in B-Cell Malignancy
8. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCL6 | B-cell lymphoma 6 |
| BL | Burkitt lymphoma |
| BMSC | Bone marrow stromal cells |
| CAFs | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| CHL | Classical Hodgkin lymphoma |
| CLL | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| C-MYC | MYC Proto-Oncogene |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| EMT | Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition |
| FDCs | Follicular dendritic cells |
| FL | Follicular lymphoma |
| FOXP3 | Forkhead box protein P3 |
| GC | Germinal centers |
| HRS | Hodgkin Reed–Sternberg |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| LL | Lymphoblastic lymphoma |
| MALT | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue |
| MCL | Mantle cell lymphoma |
| MiRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| MiRNome | MiRNAs expression profile |
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| moMDSCs | Monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| MVs | Microvesicles |
| MZLs | Marginal zone B-cell lymphomas |
| ncRNA | Non-coding RNA |
| NHLs | Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas |
| PRDM1 | PR domain containing 1 |
| PS | Proliferation gene signature |
| SLL | Small-cell lymphocytic lymphoma |
| SOCS3 | Suppressor of Cytokine Signalling-3 |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| TH | T helper |
| TILs | Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| Treg | Regulatory T-cells |
References
- Bullrich, F.; Fujii, H.; Calin, G.; Mabuchi, H.; Negrini, M.; Pekarsky, Y. Characterization of the 13q14 tumor suppressor locus in CLL: Identification of ALT1, an alternative splice variant of the LEU2 gene. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6640–6648. [Google Scholar]
- Calin, G.A.; Trapasso, F.; Shimizu, M.; Dumitru, C.D.; Yendamuri, S.; Godwin, A.K. Familial cancer associated with a polymorphism in ARLTS1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, M.; Garzon, R.; Andreeff, M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs and noncoding RNAs in hematological malignancies: Molecular, clinical and therapeutic implications. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shain, K.H.; Dalton, W.S.; Tao, J. The tumor microenvironment shapes hallmarks of mature B-cell malignancies. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4673–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marusyk, A.; Almendro, V.; Polyak, K. Intra-tumour heterogeneity: A looking glass for cancer? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, P.; Sage, E.H. Matricellular proteins: Extracellular modulators of cell function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2002, 14, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Nilendu, P.; Jahagirdar, D.; Pal, J.K.; Sharma, N.K. Modulating secreted components of tumor microenvironment: A masterstroke in tumor therapeutics. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuninty, P.R.; Schnittert, J.; Storm, G.; Prakash, J. MicroRNA Targeting to Modulate Tumor Microenvironment. Front Oncol. 2016, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.P.; Tonino, S.H.; Egle, A.; Ramsay, A.G. How does lenalidomide target the chronic lymphocytic leukemia microenvironment? Blood 2014, 124, 2184–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Q.; Xu, Q.; Duan, W.; Lei, J.; Wu, E. Targeting the cancer-stroma interaction: A potential approach for pancreatic cancer treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashidi, A.; DiPersio, J.F. Targeting the leukemia-stroma interaction in acute myeloid leukemia: Rationale and latest evidence. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2016, 7, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F.R.; Capasso, M.; Hagemann, T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rui, L.; Goodnow, C.C. Lymphoma and the control of B cell growth and differentiation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2006, 6, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yu, T.T.; Young, K.H. Cross-talk between Myc and p53 in B-cell lymphomas. Chronic. Dis. Transl. Med. 2019, 5, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruga, F.; Vaisitti, T.; Deaglio, S. The NOTCH Pathway and Its Mutations in Mature B Cell Malignancies. Front Oncol. 2018, 8, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.O. Development of BTK inhibitors for the treatment of B-cell malignancies. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.P.; O’Brien, S. Small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Are they the same disease? Cancer J. 2012, 18, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarin, A.T.; Dorfman, D.M. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: Current classification and management. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1997, 47, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, D.W.; Gascoyne, R.D. The tumour microenvironment in B cell lymphomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2014, 14, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, N.H.; Cheah, C.Y.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Gribben, J.; Neelapu, S.S.; Ghia, P. Role of the tumor microenvironment in mature B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Haematologica 2016, 101, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldinucci, D.; Gloghini, A.; Pinto, A.; De Filippi, R.; Carbone, A. The classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma microenvironment and its role in promoting tumour growth and immune escape. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E. Understanding MYC-driven aggressive B-cell lymphomas: Pathogenesis and classification. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ Program 2013, 2013, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Melnick, A. The epigenetic basis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaknovich, R.; Melnick, A. Epigenetics and B-cell lymphoma. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2011, 18, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. Epigenetics and miRNAs in human cancer. Adv. Genet. 2010, 70, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Pichler, M.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in cancer: From developmental genes in worms to their clinical application in patients. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayraktar, R.; Ivan, C.; Bayraktar, E.; Kanlikilicer, P.; Kabil, N.N.; Kahraman, N. Dual Suppressive Effect of miR-34a on the FOXM1/eEF2-Kinase Axis Regulates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth and Invasion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4225–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayraktar, R.; Pichler, M.; Kanlikilicer, P.; Ivan, C.; Bayraktar, E.; Kahraman, N. MicroRNA 603 acts as a tumor suppressor and inhibits triple-negative breast cancer tumorigenesis by targeting elongation factor 2 kinase. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11641–11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Mangala, L.S.; Mooberry, L.; Bayraktar, E.; Dasari, S.K.; Ma, S. Identifying and targeting angiogenesis-related microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6095–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Mattei, E.; Bayraktar, R.; Manshouri, T.; Silva, A.M.; Ivan, C.; Gulei, D. miR-543 regulates the epigenetic landscape of myelofibrosis by targeting TET1 and TET2. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangala, L.S.; Wang, H.; Jiang, D.; Wu, S.Y.; Somasunderam, A.; Volk, D.E. Improving vascular maturation using noncoding RNAs increases antitumor effect of chemotherapy. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e87754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Daly, S.M.; Abba, M.L.; Patil, N.; Allgayer, H. miRs-134 and -370 function as tumor suppressors in colorectal cancer by independently suppressing EGFR and PI3K signalling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Daly, S.M.; Omara, E.A.; Hussein, J.; Youness, E.R.; El-Khayat, Z. Differential expression of miRNAs regulating NF-kappaB and STAT3 crosstalk during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell Probes. 2019, 47, 101442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M.; Bottoni, A.; Shimizu, M.; Spizzo, R.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Rossi, S. Association of a microRNA/TP53 feedback circuitry with pathogenesis and outcome of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. JAMA 2011, 305, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrajoli, A.; Ivan, C.; Ciccone, M.; Shimizu, M.; Kita, Y.; Ohtsuka, M. Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNAs are Expressed in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Correlate with Overall Survival. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaheer, U.; Faheem, M.; Qadri, I.; Begum, N.; Yassine, H.M.; Al Thani, A.A. Expression profile of MicroRNA: An Emerging Hallmark of Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, A.; Vafaizadeh, V.; Jarry, H.; Fiedler, J.; Klemmt, P.A.; Thum, T. miR-212 and miR-132 are required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soon, P.; Kiaris, H. MicroRNAs in the tumour microenvironment: Big role for small players. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R257–R267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. Genomics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia microRNAs as new players with clinical significance. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klein, U.; Lia, M.; Crespo, M.; Siegel, R.; Shen, Q.; Mo, T. The DLEU2/miR-15a/16-1 cluster controls B cell proliferation and its deletion leads to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrajoli, A.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Ivan, C.; Shimizu, M.; Rabe, K.G.; Nouraee, N. Prognostic value of miR-155 in individuals with monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis and patients with B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psathas, J.N.; Doonan, P.J.; Raman, P.; Freedman, B.D.; Minn, A.J.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A. The Myc-miR-17-92 axis amplifies B-cell receptor signaling via inhibition of ITIM proteins: A novel lymphomagenic feed-forward loop. Blood 2013, 122, 4220–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigorito, E.; Perks, K.L.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Bunting, S.; Xiang, Z.; Kohlhaas, S. microRNA-155 regulates the generation of immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells. Immunity 2007, 27, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, C.; Calado, D.P.; Galler, G.; Thai, T.H.; Patterson, H.C.; Wang, J. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 2007, 131, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, S.; Mayr, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Lodish, H.F. miR-150, a microRNA expressed in mature B and T cells, blocks early B cell development when expressed prematurely. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7080–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Wang, B.; Borde, M.; Nardone, J.; Maika, S.; Allred, L. Foxp1 is an essential transcriptional regulator of B cell development. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willimott, S.; Wagner, S.D. Stromal cells and CD40 ligand (CD154) alter the miRNome and induce miRNA clusters including, miR-125b/miR-99a/let-7c and miR-17-92 in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fu, K.; Jaffe, E.S.; Liu, C. Genome-wide miRNA profiling of mantle cell lymphoma reveals a distinct subgroup with poor prognosis. Blood 2012, 119, 4939–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wake, L.; Liu, C. Global microRNA expression profiling uncovers molecular markers for classification and prognosis in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpeli, G.; Barbi, S.; Greco, C.; Zupo, S.; Bertolaso, A.; Scupoli, M.T. MicroRNA signatures and Foxp3(+) cell count correlate with relapse occurrence in follicular lymphoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19961–19979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merkerova, M.; Belickova, M.; Bruchova, H. Differential expression of microRNAs in hematopoietic cell lineages. Eur. J. Haematol. 2008, 81, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F. MicroRNA expression and activity in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5445–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Nourse, J.P.; Keane, C.; Bhatnagar, A.; Gandhi, M.K. Plasma microRNA are disease response biomarkers in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Q.; Vari, F.; Cristino, A.S.; Salomon, C.; Rice, G.E.; Sabdia, M.B. Circulating cell-free miR-494 and miR-21 are disease response biomarkers associated with interim-positron emission tomography response in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34644–34657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, J.; Ye, C.; Dominguez, D.; Zhang, Y. Host miR155 promotes tumor growth through a myeloid-derived suppressor cell-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kuzel, T.M.; Zhang, B. Regulating Tumor Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells by MicroRNAs. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Shimizu, M.; Barbarotto, E.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Dimitri, F.; Sampath, D. microRNA fingerprinting of CLL patients with chromosome 17p deletion identify a miR-21 score that stratifies early survival. Blood 2010, 116, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Ji, J.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Shi, G.; Liu, F. MiR-30a increases MDSC differentiation and immunosuppressive function by targeting SOCS3 in mice with B-cell lymphoma. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 2410–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dave, S.S.; Wright, G.; Tan, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Chan, W.C. Prediction of survival in follicular lymphoma based on molecular features of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glas, A.M.; Kersten, M.J.; Delahaye, L.J.; Witteveen, A.T.; Kibbelaar, R.E.; Velds, A. Gene expression profiling in follicular lymphoma to assess clinical aggressiveness and to guide the choice of treatment. Blood 2005, 105, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burger, J.A.; Quiroga, M.P.; Hartmann, E.; Burkle, A.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J. High-level expression of the T-cell chemokines CCL3 and CCL4 by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells in nurselike cell cocultures and after BCR stimulation. Blood 2009, 113, 3050–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Tsukada, N.; Burger, M.; Zvaifler, N.J.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Kipps, T.J. Blood-derived nurse-like cells protect chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from spontaneous apoptosis through stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 2000, 96, 2655–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herishanu, Y.; Perez-Galan, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-kappaB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtova, A.V.; Balakrishnan, K.; Chen, R.; Ding, W.; Schnabl, S.; Quiroga, M.P. Diverse marrow stromal cells protect CLL cells from spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis: Development of a reliable and reproducible system to assess stromal cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance. Blood 2009, 114, 4441–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivina, M.; Hartmann, E.; Vasyutina, E.; Boucas, J.M.; Breuer, A.; Keating, M.J. Stromal cells modulate TCL1 expression, interacting AP-1 components and TCL1-targeting micro-RNAs in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Nierop, K.; de Groot, C. Human follicular dendritic cells: Function, origin and development. Semin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lwin, T.; Zhao, J.J.; Tam, W.; Choi, Y.S.; Moscinski, L.C. Follicular dendritic cell-induced microRNA-mediated upregulation of PRDM1 and downregulation of BCL-6 in non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2011, 25, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ci, W.; Polo, J.M.; Melnick, A. B-cell lymphoma 6 and the molecular pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2008, 15, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): From understanding the basics towards therapeutic targeting. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecteau, J.F.; Kipps, T.J. Structure and function of the hematopoietic cancer niche: Focus on chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Front Biosci. 2012, 4, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granziero, L.; Ghia, P.; Circosta, P.; Gottardi, D.; Strola, G.; Geuna, M. Survivin is expressed on CD40 stimulation and interfaces proliferation and apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 2777–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Mraz, M.; Fecteau, J.F.; Yu, J. MicroRNA-155 influences B-cell receptor signaling and associates with aggressive disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauls, S.D.; Marshall, A.J. Regulation of immune cell signaling by SHIP1: A phosphatase, scaffold protein, and potential therapeutic target. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, R.; Van Roosbroeck, K. miR-155 in cancer drug resistance and as target for miRNA-based therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceppi, M.; Pereira, P.M.; Dunand-Sauthier, I.; Barras, E.; Reith, W.; Santos, M.A. MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Cheng, G.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Cecco, L.; Capaia, M.; Zupo, S.; Cutrona, G.; Matis, S.; Brizzolara, A. Interleukin 21 Controls mRNA and MicroRNA Expression in CD40-Activated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, R.; Zhang, W.; Naseem, M.; Puccini, A.; Berger, M.D.; Soni, S. CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11/CXCR3 axis for immune activation—A target for novel cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018, 63, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croker, B.A.; Kiu, H.; Nicholson, S.E. SOCS regulation of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navari, M.; Etebari, M.; Ibrahimi, M.; Leoncini, L.; Piccaluga, P.P. Pathobiologic Roles of Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded MicroRNAs in Human Lymphomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Roosbroeck, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Calin, S.; Bloehdorn, J.; Dragomir, M.P.; Okubo, K. The involvement of microRNA in the pathogenesis of Richter syndrome. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fachko, D.; Ivanov, N.S.; Skinner, C.M.; Skalsky, R.L. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs regulate B cell receptor signal transduction and lytic reactivation. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Ding, H.; Qian, L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs as regulators in host immune responses. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, T.; O’Hara, A.; Araujo, I.; Barreto, J.; Carvalho, E.; Sapucaia, J.B. EBV microRNAs in primary lymphomas and targeting of CXCL-11 by ebv-mir-BHRF1-3. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, Y.; Osuga, Y.; Koga, K.; Yoshino, O.; Hirata, T.; Morimoto, C. The expression and possible roles of chemokine CXCL11 and its receptor CXCR3 in the human endometrium. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8813–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, L.A.; Hemann, M.T. DNA damage-mediated induction of a chemoresistant niche. Cell 2010, 143, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ame-Thomas, P.; Maby-El Hajjami, H.; Monvoisin, C.; Jean, R.; Monnier, D.; Caulet-Maugendre, S. Human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from bone marrow and lymphoid organs support tumor B-cell growth: Role of stromal cells in follicular lymphoma pathogenesis. Blood 2007, 109, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagneaux, L.; Delforge, A.; Bron, D.; De Bruyn, C.; Stryckmans, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells but not normal B cells are rescued from apoptosis by contact with normal bone marrow stromal cells. Blood 1998, 91, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudry, R.E.; Fortney, J.E.; York, T.; Hall, B.M.; Gibson, L.F. Stromal cells regulate survival of B-lineage leukemic cells during chemotherapy. Blood 2000, 96, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meads, M.B.; Gatenby, R.A.; Dalton, W.S. Environment-mediated drug resistance: A major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwin, T.; Hazlehurst, L.A.; Li, Z.; Dessureault, S.; Sotomayor, E.; Moscinski, L.C. Bone marrow stromal cells prevent apoptosis of lymphoma cells by upregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins associated with activation of NF-kappaB (RelB/p52) in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lwin, T.; Lin, J.; Choi, Y.S.; Zhang, X.; Moscinski, L.C.; Wright, K.L. Follicular dendritic cell-dependent drug resistance of non-Hodgkin lymphoma involves cell adhesion-mediated Bim down-regulation through induction of microRNA-181a. Blood 2010, 116, 5228–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwin, T.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, X.; Huang, A.; Shah, B. A microenvironment-mediated c-Myc/miR-548m/HDAC6 amplification loop in non-Hodgkin B cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4612–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moses, B.S.; Evans, R.; Slone, W.L.; Piktel, D.; Martinez, I.; Craig, M.D. Bone Marrow Microenvironment Niche Regulates miR-221/222 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Roosbroeck, K.; Fanini, F.; Setoyama, T.; Ivan, C.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Fuentes-Mattei, E. Combining Anti-Mir-155 with Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Due, H.; Schonherz, A.A.; Ryo, L.; Primo, M.N.; Jespersen, D.S.; Thomsen, E.A. MicroRNA-155 controls vincristine sensitivity and predicts superior clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhao, H.J.; Fu, D.; Zhong, H.J.; Weng, X.Q. MiR155 sensitized B-lymphoma cells to anti-PD-L1 antibody via PD-1/PD-L1-mediated lymphoma cell interaction with CD8+T cells. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktar, R.; Bertilaccio, M.T.S.; Calin, G.A. The Interaction Between Two Worlds: MicroRNAs and Toll-Like Receptors. Front Immunol. 2019, 10, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayraktar, R.; Van Roosbroeck, K.; Calin, G.A. Cell-to-cell communication: MicroRNAs as hormones. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bullock, M.D.; Silva, A.M.; Kanlikilicer-Unaldi, P.; Filant, J.; Rashed, M.H.; Sood, A.K. Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Applications in Cancer. Noncoding RNA 2015, 1, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, M.H.; Kanlikilicer, P.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Pichler, M.; Bayraktar, R.; Bayraktar, E. Exosomal miR-940 maintains SRC-mediated oncogenic activity in cancer cells: A possible role for exosomal disposal of tumor suppressor miRNAs. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20145–20164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redis, R.S.; Calin, S.; Yang, Y.; You, M.J.; Calin, G.A. Cell-to-cell miRNA transfer: From body homeostasis to therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Villasana, V.; Rashed, M.H.; Gonzalez-Cantu, Y.; Bayraktar, R.; Menchaca-Arredondo, J.L.; Vazquez-Guillen, J.M. Presence of Circulating miR-145, miR-155, and miR-382 in Exosomes Isolated from Serum of Breast Cancer Patients and Healthy Donors. Dis. Markers. 2019, 2019, 6852917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlikilicer, P.; Bayraktar, R.; Denizli, M.; Rashed, M.H.; Ivan, C.; Aslan, B. Exosomal miRNA confers chemo resistance via targeting Cav1/p-gp/M2-type macrophage axis in ovarian cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 38, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanlikilicer, P.; Rashed, M.H.; Bayraktar, R.; Mitra, R.; Ivan, C.; Aslan, B. Ubiquitous Release of Exosomal Tumor Suppressor miR-6126 from Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7194–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farahani, M.; Rubbi, C.; Liu, L.; Slupsky, J.R.; Kalakonda, N. CLL Exosomes Modulate the Transcriptome and Behaviour of Recipient Stromal Cells and Are Selectively Enriched in miR-202-3p. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paggetti, J.; Haderk, F.; Seiffert, M.; Janji, B.; Distler, U.; Ammerlaan, W. Exosomes released by chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce the transition of stromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Blood 2015, 126, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, Y.Y.; Ozer, H.G.; Lehman, A.M.; Maddocks, K.; Yu, L.; Johnson, A.J. Characterization of CLL exosomes reveals a distinct microRNA signature and enhanced secretion by activation of BCR signaling. Blood 2015, 125, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, G.V.; Peterson, K.J.; Emanuel, K.; Mittal, A.K.; Joshi, A.D.; Dickinson, J.D. Hedgehog-induced survival of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in a stromal cell microenvironment: A potential new therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rimkus, T.K.; Carpenter, R.L.; Qasem, S.; Chan, M.; Lo, H.W. Targeting the Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway: Review of Smoothened and GLI Inhibitors. Cancers 2016, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Veirman, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Leleu, X.; Himpe, E.; Maes, K. Induction of miR-146a by multiple myeloma cells in mesenchymal stromal cells stimulates their pro-tumoral activity. Cancer Lett. 2016, 377, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloudizargari, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Asghari, M.H.; Zimta, A.A.; Neagoe, I.B.; Nabavi, S.M. The emerging role of exosomes in multiple myeloma. Blood Rev. 2019, 38, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Y.; Tan, S. Multiple Myeloma-Derived Exosomes Regulate the Functions of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Partially via Modulating miR-21 and miR-146a. Stem. Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9012152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinska, Z.; Luczkowska, K.; Machalinski, B. Extracellular vesicles in hematological malignancies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Maiso, P.; Azab, A.K.; Tai, Y.T.; Reagan, M. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1542–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type of B-Cell Malignancy | TME/Stoma Associated MiRNAs | Function | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic and prognostic function | Mantle cell lymphoma | miR-23a, miR-23b, let-7c, let-7-b, miR-125b, miR-636, miR-539, miR-485-3p | Stroma-associated miRNAs is correlated with proliferation gene signature for MCL subtyping. | [52] |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | miR-542-3p | Stromal miR-542-3p was set for the robust classification of DLBCL subgroups. | [53] | |
| Follicular lymphoma | miR-342 and miR-370 | These miRNAs act as signature marker for FL enriched with CD4+ T-cells in the microenvironment. | [54] | |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | miR-494 and miR-21 | The MDSCs associated miRNAs were set as disease response biomarkers in patients with DLBCL. | [58] | |
| Controlling diseases proliferation and survival | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | miR-29b, miR-181b, miR-34b | The decrease expression of these TCL1-regulatory miRNA’s following co-culturing of CLL cells with stromal cells is partially responsible for enhancing pro-survival signaling molecules. | [69] |
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | miR-155 | Upregulation of miR-155 by accessory cells of lymphoid tissue microenvironment is associated with activated BCR signaling and a more aggressive disease. | [76] | |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | miR-9, let-7, miR-30a, b, c and d | The elevated expression of these miRNAs following the adhesion of B-lymphocytes and FDCs regulates B-cell survival and differentiation by targeting the regulators of terminal B-cell differentiation PRDM1 and BCL6. | [71] | |
| B-cell lymphoma mouse model | miR-30a | Regulate the differentiation of MDSCs and modulate their immunosuppressive function and eventually control B-cell lymphoma progression | [62] | |
| Mediating drug resistance | EBV-associated non–Hodgkin’s lymphomas (Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma) | EBV-miRNA BHRF1-3 | The targeting suppression of ebv-miR-BHRF1-3 to its putative target gene, T-cell attracting chemokine CXCL-11/I-TAC, functions as an immunomodulatory mechanism in EBV-related lymphomas. | [88] |
| Mantle cell lymphoma and Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | miR-181a | The elevation in miR-181a following adhesion of lymphoma cells to FDCs enhanced the drug resistance mechanism toward mitoxantrone through reducing the pro-apoptotic protein BIM11. | [96] | |
| Mantle cell lymphoma and Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | miR-548m | The downregulation of miR-548m contributes to the stroma-mediated cell survival and mitoxantrone resistance through HDAC6 upregulation and a c-Myc/miR-548m feed-forward loop. | [97] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Daly, S.M.; Bayraktar, R.; Anfossi, S.; Calin, G.A. The Interplay between MicroRNAs and the Components of the Tumor Microenvironment in B-Cell Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093387
El-Daly SM, Bayraktar R, Anfossi S, Calin GA. The Interplay between MicroRNAs and the Components of the Tumor Microenvironment in B-Cell Malignancies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093387
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Daly, Sherien M., Recep Bayraktar, Simone Anfossi, and George A. Calin. 2020. "The Interplay between MicroRNAs and the Components of the Tumor Microenvironment in B-Cell Malignancies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093387
APA StyleEl-Daly, S. M., Bayraktar, R., Anfossi, S., & Calin, G. A. (2020). The Interplay between MicroRNAs and the Components of the Tumor Microenvironment in B-Cell Malignancies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093387