Structure-Based Design, Docking and Binding Free Energy Calculations of A366 Derivatives as Spindlin1 Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
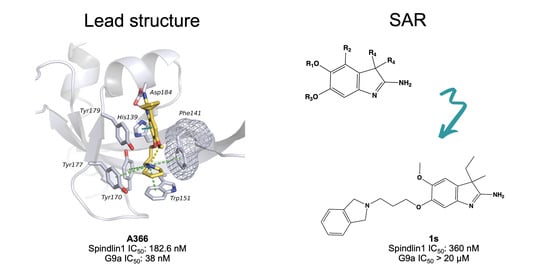
2.1. Analysis of Spindlin1-A366 Complex
2.2. Docking Studies
2.3. Molecular Dynamic Simulations
2.4. Re-Scoring Using Prime MM-GBSA
2.5. Structure–Activity Relationships
2.6. Synthesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. General Methods and Materials
3.1.2. Synthesis and Analytical Data
3.2. Biological Assays
3.2.1. Fluorescence Polarization Assay
3.2.2. Reagents for Histone Methyltransferase Assays
3.2.3. Expression and Purification of G9a and GLP and SAHH
3.2.4. Coupled Enzyme Fluorescent Histone Methyltransferase Assay
3.3. Computational Studies
3.3.1. Docking Studies
3.3.2. Molecular Dynamic Simulations
3.3.3. Prime MM-GBSA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ding, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhu, B. Nucleolar protein spindlin1 recognizes H3K4 methylation and stimulates the expression of rRNA genes. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, N.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Rao, Z.; Zhu, B.; Xu, R.-M. Distinct mode of methylated lysine-4 of histone H3 recognition by tandem tudor-like domains of spindlin1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17954–17959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Zhu, G.; Ding, X.; Lee, S.Y.; Dou, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wu, W.; Li, H. Molecular basis underlying histone H3 lysine-arginine methylation pattern readout by Spin/Ssty repeats of spindlin1. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanle, E.K.; Shinsky, S.A.; Bridgers, J.; Bae, N.; Sagum, C.; Krajewski, K.; Rothbart, S.B.; Bedford, M.T.; Strahl, B.D. Histone peptide microarray screen of chromo and Tudor domains defines new histone lysine methylation interactions. Epigenetics Chromatin 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Zhan, L.; Wu, M.; Ma, R.; Yao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Pan, Y.; Guan, S.; Zhang, X.; Zang, J. Spindlin-1 recognizes methylations of K20 and R23 of histone H4 tail. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 4098–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Lee, J.-E.; Song, Y.; Wang, D.; Ge, K.; Gao, J.; Zhang, M.Q.; Li, H. Molecular basis for histone H3 “K4me3-K9me3/2” methylation pattern readout by spindlin1. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 16877–16887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zang, C.; Rosenfeld, A.J.; Schones, E.D.; Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.Q.; et al. Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, L.; Pang, H.; Pei, X.; Rao, Z. Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-Ray analysis of human spindlin1, an ovarian cancer-related protein. Protein Pept. Lett. 2006, 13, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.-W.; Xing, A.-Y.; Xiang, S.; Shi, D.-B.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.-X.; Gao, P. Suppression of SPIN1-mediated PI3K-Akt pathway by miR-489 increases chemosensitivity in breast cancer. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago-Ferrante, R.; Pentimalli, F.; Carlisi, D.; De Blasio, A.; Saliba, C.; Baldacchino, S.; Degaetano, J.; Debono, J.; Caruana-Dingli, G.; Grech, G.; et al. Suppressive role exerted by microRNA-29b-1-5p in triple negative breast cancer through SPIN1 regulation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28939–28958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Q.; Ji, Q.; Xiao, J.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiao, S. miR-409 inhibits human non-small-cell lung cancer progression by directly targeting SPIN1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franz, H.; Greschik, H.; Willmann, D.; Ozretić, L.; Jilg, C.A.; Wardelmann, E.; Jung, M.; Buettner, R.; Schule, R. The histone code reader SPIN1 controls RET signaling in liposarcoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4773–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Bu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. SPIN1 triggers abnormal lipid metabolism and enhances tumor growth in liver cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 470, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.-W.; Gao, P. SPIN1, negatively regulated by miR-148/152, enhances Adriamycin resistance via upregulating drug metabolizing enzymes and transporter in breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yue, W.; Zhang, P.; Li, L.; Xie, X.; Yuan, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Yan, F.; Pei, X. spindlin1, a novel nuclear protein with a role in the transformation of NIH3T3 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Cong, B.; Yuan, H.; Chen, L.; Lv, Y.; Bai, C.; Nan, X.; Shi, S.; Yue, W.; Pei, X. Overexpression of spindlin1 induces metaphase arrest and chromosomal instability. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 217, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, P.; Qin, L.; Chen, L.; Shi, S.; Lu, Y.; Yan, F.; Bai, C.; Nan, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Overexpression of SPINDLIN1 induces cellular senescence, multinucleation and apoptosis. Gene 2008, 410, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Cao, B.; Liao, J.-M.; Deng, J.; Plummer, K.D.; Liao, P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; et al. SPIN1 promotes tumorigenesis by blocking the uL18 (universal large ribosomal subunit protein 18)-MDM2-p53 pathway in human cancer. eLife 2018, 7, e31275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecki, D.M.; Sajek, M.; Smialek, M.J.; Kotecki, M.; Ginter-Matuszewska, B.; Kuczynska, B.; Spik, A.; Kolanowski, T.J.; Kitazawa, R.; Kurpisz, M.; et al. SPIN1 is a proto-oncogene and SPIN3 is a tumor suppressor in human seminoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 32466–32477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-X.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, L.; Du, J.-C.; Yan, X.-L.; Yuan, H.-F.; Zhai, C.; Zhou, J.-N.; Jia, Y.-L.; Yue, W.; et al. SPINDLIN1 Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation through Activation of WNT/TCF-4 Signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greschik, H.; Duteil, D.; Messaddeq, N.; Willmann, D.; Arrigoni, L.; Sum, M.; Jung, M.; Metzger, D.; Manke, T.; Günther, T.; et al. The histone code reader Spin1 controls skeletal muscle development. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.-W.; Zhou, W.; Nie, Z.-W.; Niu, Y.-J.; Shin, K.-T.; Cui, X.-S. Spindlin1 alters the metaphase to anaphase transition in meiosis I through regulation of BUB3 expression in porcine oocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8963–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Qin, L.; Jiang, F.; Wu, B.; Yue, W.; Xu, F.; Rong, Z.; Yuan, H.; Xie, X.; Gao, Y.; et al. Structure of human spindlin1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, N.; Viviano, M.; Su, X.; Lv, J.; Cheng, D.; Sagum, C.; Castellano, S.; Bai, X.; Johnson, C.; Khalil, M.I.; et al. Developing spindlin1 small-molecule inhibitors by using protein microarrays. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fagan, V.; Johansson, C.; Gileadi, C.; Monteiro, O.; Dunford, J.E.; Nibhani, R.; Philpott, M.; Malzahn, J.; Wells, G.; Farham, R.; et al. A chemical probe for tudor domain protein spindlin1 to investigate chromatin function. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 9008–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Greschik, H.; Johansson, C.; Seifert, L.; Bacher, J.; Park, K.-S.; Babault, N.; Martini, M.; Fagan, V.; Li, F.; et al. Discovery of a potent and selective fragment-like inhibitor of methyllysine reader protein spindlin 1 (SPIN1). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8996–9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaa, D.; Wagner, T.; Luise, C.; Carlino, L.; McMillan, J.; Flaig, R.; Schüle, R.; Jung, M.; Sippl, W. Identification and structure-activity relationship studies of small-molecule inhibitors of the methyllysine reader protein spindlin1. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweis, R.F.; Pliushchev, M.; Brown, P.J.; Guo, J.; Li, F.; Maag, D.; Petros, A.M.; Soni, N.B.; Tse, C.; Vedadi, M.; et al. Discovery and development of potent and selective inhibitors of histone methyltransferase G9a. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, T.; Greschik, H.; Burgahn, T.; Schmidtkunz, K.; Schott, A.-K.; McMillan, J.; Baranauskiene, L.; Xiong, Y.; Fedorov, O.; Jin, J.; et al. Identification of a small-molecule ligand of the epigenetic reader protein spindlin1 via a versatile screening platform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2017-1: Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Case, D.A.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Ghoreishi, D.; Gilson, M.K.; et al. AMBER 2018; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, F.; Babault, N.; Wu, H.; Dong, A.; Zeng, H.; Chen, X.; Arrowsmith, C.; Brown, P.J.; Liu, J.; et al. Structure-activity relationship studies of G9a-like protein (GLP) inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collazo, E.; Couture, J.-F.; Bulfer, S.; Trievel, R.C. A coupled fluorescent assay for histone methyltransferases. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 342, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2018-1: Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA; Impact, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA; Prime, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Schrödinger Release 2018-1: Maestro; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Schrödinger Release 2018-1: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Schrödinger Release 2018-1: ConfGen; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Watts, K.S.; Dalal, P.; Murphy, R.B.; Sherman, W.; Friesner, R.A.; Shelley, J.C. ConfGen: A conformational search method for efficient generation of bioactive conformers. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakalian, A.; Bush, B.L.; Jack, D.B.; Bayly, C.I. Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: I. Method. J. Comput. Chem. 2000, 21, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakalian, A.; Jack, D.B.; Bayly, C.I. Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J. Comput. Chem. 2002, 23, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, I.T.E. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2018-1: Prime; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.R.; Wu, C.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Spin1 IC50 ± SD (nM) [a] | G9a IC50 (nM) [b] | GLP IC50 (nM) [b] |
| A366 | Me | H |  |  | 182.6 ± 9.1 [31] | 38 [c] | 51 |
| 1a | Et | OEt |  |  | 70% @ 25 μM [d] | ||
| 1b | Me | H |  |  | 81% @ 100 μM [d] | ||
| 1c | Me | H |  |  | 42% @ 50 μM [d] | >20,000 | >20,000 |
| 1d | Me | H |  |  | Inactive | ||
| 1e | Me | H |  |  | Inactive | ||
| 1f | Me | H |  |  | 169 ± 13 | 431 | 334 |
| 1g | Et | H |  |  | 316 ± 26 | 243 | 2969 |
| 1h | Me | CN |  |  | 3900 ± 700 | ||
| 1i | Me | Cl |  |  | 1600 ± 200 | >20,000 | >20,000 |
| 1j | Me | OMe |  |  | 2500 ± 200 | ||
| 1k | Me | Ac |  |  | 11,800 ± 210 | ||
| 1l | Et | H |  |  | 567 ± 35 | ||
| 1m | 2-Pr | H |  |  | 3300 ± 470 | ||
| 1n | Me | H |  |  | 255 ± 35 | 779 | 527 |
| 1o | Me | H |  |  | 1210 ± 90 | >20,000 | >20,000 |
| 1p | Me | H |  |  | 157 ± 12 | 759 | 470 |
| 1q | Me | H |  |  | (R): 470 ± 27 (S): 478 ± 34 (rac): 584 ± 31 | (rac): 2321 | (rac): 4432 |
| 1r | Me | H |  |  | 408 ± 35 | 3191 | 3185 |
| 1s | Me | H |  |  | 360 ± 20 | >20,000 | >20,000 |
| 1t | Me | H |  |  | 467 ± 15 | >20,000 | >20,000 |
| 1u | Me | H |  |  | 1250 ± 50 | >20,000 | >20,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luise, C.; Robaa, D.; Regenass, P.; Maurer, D.; Ostrovskyi, D.; Seifert, L.; Bacher, J.; Burgahn, T.; Wagner, T.; Seitz, J.; et al. Structure-Based Design, Docking and Binding Free Energy Calculations of A366 Derivatives as Spindlin1 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115910
Luise C, Robaa D, Regenass P, Maurer D, Ostrovskyi D, Seifert L, Bacher J, Burgahn T, Wagner T, Seitz J, et al. Structure-Based Design, Docking and Binding Free Energy Calculations of A366 Derivatives as Spindlin1 Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115910
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuise, Chiara, Dina Robaa, Pierre Regenass, David Maurer, Dmytro Ostrovskyi, Ludwig Seifert, Johannes Bacher, Teresa Burgahn, Tobias Wagner, Johannes Seitz, and et al. 2021. "Structure-Based Design, Docking and Binding Free Energy Calculations of A366 Derivatives as Spindlin1 Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115910
APA StyleLuise, C., Robaa, D., Regenass, P., Maurer, D., Ostrovskyi, D., Seifert, L., Bacher, J., Burgahn, T., Wagner, T., Seitz, J., Greschik, H., Park, K. -S., Xiong, Y., Jin, J., Schüle, R., Breit, B., Jung, M., & Sippl, W. (2021). Structure-Based Design, Docking and Binding Free Energy Calculations of A366 Derivatives as Spindlin1 Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115910