Synergistic Effect of PVDF-Coated PCL-TCP Scaffolds and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Osteogenesis
Abstract
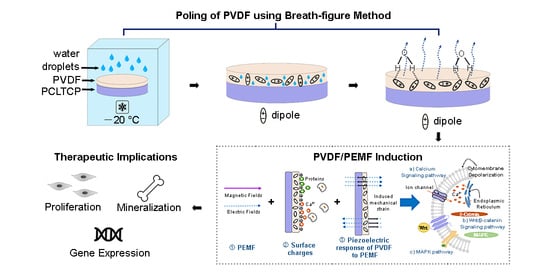
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of β-PVDF by Polar Solvent
2.2. Surface Properties
2.3. Ferroelectric and Piezoelectric Behavior
2.4. Cell Morphology
2.5. Cell Metabolic Activity
2.6. Cell Proliferation
2.7. Cell Differentiation and Mineralization
2.8. Osteogenic Gene Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Scaffold Fabrication
4.2. Piezoelectric Characterization
4.3. Ferroelectric Characterization
4.4. Surface and Bulk Film Characterization
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. PEMF Instrumentation
4.7. Cell Metabolic Activity
4.8. Cell Proliferation
4.9. ALP Activity
4.10. OsteoImage
4.11. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bone Grafts and Substitutes Market—Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, and Forecast 2020–2030; Transparency Market Research: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–318.
- Hutmacher, D.W.; Schantz, T.; Zein, I.; Ng, K.W.; Teoh, S.H.; Tan, K.C. Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 55, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The return of a forgotten polymer—Polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teoh, S.H.; Goh, B.T.; Lim, J. Three-Dimensional Printed Polycaprolactone Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration Success and Future Perspective. Tissue Eng. Part A 2019, 25, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lim, J.; Teoh, S.-H. Review: Development of clinically relevant scaffolds for vascularised bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 688–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Teoh, S.H.; Chong, W.-S.; Foo, T.-T.; Chng, Y.-C.; Choolani, M.; Chan, J. A biaxial rotating bioreactor for the culture of fetal mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2694–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, A.; Lim, J.; Chong, M.S.K.; Wen, F.; Liu, Y.; Pillay, Y.T.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Teoh, S.-H. In vitro cyclic compressive loads potentiate early osteogenic events in engineered bone tissue. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 105, 2366–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseti, L.; Parisi, V.; Petretta, M.; Cavallo, C.; Desando, G.; Bartolotti, I.; Grigolo, B. Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1246–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remes, A.; Williams, D. Relationship between chemotaxis and complement activation by ceramic biomaterials. Biomaterials 1991, 12, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakielski, P.; Pawłowska, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Ziai, Y.; De Sio, L.; Urbanek, O.; Zembrzycki, K.; Pruchniewski, M.; Lanzi, M.; Salatelli, E.; et al. Multifunctional Platform Based on Electrospun Nanofibers and Plasmonic Hydrogel: A Smart Nanostructured Pillow for Near-Infrared Light-Driven Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 54328–54342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dai, H.; Lin, Y. Design and application of proximity hybridization-based multiple stimuli-responsive immunosensing platform for ovarian cancer biomarker detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Municoy, S.; Echazú Álvarez, M.I.; Antezana, P.E.; Galdopórpora, J.M.; Olivetti, C.; Mebert, A.M.; Foglia, M.L.; Tuttolomondo, M.V.; Alvarez, G.S.; Hardy, J.G.; et al. Stimuli-Responsive Materials for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, E.; Yasuda, I. On the Piezoelectric Effect of Bone. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1957, 12, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, B.; Blaker, J.J.; Cartmell, S.H. Piezoelectric materials as stimulatory biomedical materials and scaffolds for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2018, 73, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Low, Y.K.A.; Zou, X.; Fang, Y.M.; Wang, J.L.; Lin, W.S.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Ng, K.W. beta-Phase poly(vinylidene fluoride) films encouraged more homogeneous cell distribution and more significant deposition of fibronectin towards the cell-material interface compared to alpha-phase poly(vinylidene fluoride) films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 34, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.M.O.; Pärssinen, J.; Sencadas, V.; Correia, V.M.G.; Miettinen, S.; Hytönen, V.P.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Dynamic piezoelectric stimulation enhances osteogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 2172–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Low, Y.K.A.; Meenubharathi, N.; Niphadkar, N.D.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Ng, K.W. α- and β-Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Evoke Different Cellular Behaviours. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2011, 22, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Gradys, A.; Kim, S.K.; Persano, L.; Marzec, M.; Kryshtal, A.; Busolo, T.; Toncelli, A.; Pisignano, D.; Bernasik, A.; et al. Enhanced Piezoelectricity of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Fibers for Energy Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13575–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Correia, V.; Martins, P.; Gama, F.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Proving the suitability of magnetoelectric stimuli for tissue engineering applications. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markov, M. Electromagnetic Fields in Biology and Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.-Y.; Hsieh, D.-K.; Yu, T.-C.; Chiu, H.-T.; Lu, S.-F.; Luo, G.-H.; Kuo, T.K.; Lee, O.K.; Chiou, T.-W. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on the proliferation and differentiation potential of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2009, 30, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryani, L.; Too, J.H.; Hassanbhai, A.M.; Wen, F.; Lin, D.J.; Yu, N.; Teoh, S.H. Effects of Electromagnetic Field on Proliferation, Differentiation, and Mineralization of MC3T3 Cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2019, 25, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, C.; Pedrazzi, G.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M.; Guizzardi, S. The Use of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields to Promote Bone Responses to Biomaterials In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Biomater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, D.; Basu, B.; Dubey, A.K. Electrical stimulation and piezoelectric biomaterials for bone tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2020, 258, 120280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Martins, P.; Lopes, A.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Yao, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qin, G.; Zhang, X. Properties and Applications of the beta Phase Poly(vinylidene fluoride). Polymers 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, E.; Yuan, R.; Gao, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y. A robust superhydrophobic PVDF composite coating with wear/corrosion-resistance properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Ribeiro, S.; Sencadas, V.; Gomes, A.C.; Gama, F.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Effect of poling state and morphology of piezoelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes for skeletal muscle tissue engineering. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17938–17944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Yao, K. Crystallization mechanism and piezoelectric properties of solution-derived ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yao, K.; Tay, F.E.H.; Chew, L.L.S. Comparative investigation of the structure and properties of ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) and poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) thin films crystallized on substrates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 3331–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Park, Y.J.; Sung, J.; Jo, P.S.; Park, C.; Kim, K.J.; Cho, B.O. Spin cast ferroelectric beta poly(vinylidene fluoride) thin films via rapid thermal annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 012921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín, J.; Zhao, D.; Lenz, T.; de Leeuw, D.M.; Stingelin, N. Solid-state-processing of δ-PVDF. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parida, K.; Bhavanasi, V.; Kumar, V.; Bendi, R.; Lee, P.S. Self-powered pressure sensor for ultra-wide range pressure detection. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3557–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hwang, H.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, H.; Kim, G. Physical and bioactive properties of multi-layered PCL/silica composite scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 250, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-J.; Kim, S.-N.; Cho, S.-A. Comparison of alkaline phosphatase activity of MC3T3-E1 cells cultured on different Ti surfaces: Modified sandblasted with large grit and acid-etched (MSLA), laser-treated, and laser and acid-treated Ti surfaces. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2016, 8, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heremans, P.; Gelinck, G.H.; Müller, R.; Baeg, K.-J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Noh, Y.-Y. Polymer and Organic Nonvolatile Memory Devices†. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, M.; Euler, W.B.; Gregory, O.J. The Influence of Preparation Conditions on the Surface Morphology of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Films. Langmuir 2001, 17, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Y.K.A.; Tan, L.Y.; Tan, L.P.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Ng, K.W. Increasing solvent polarity and addition of salts promote β-phase poly(vinylidene fluoride) formation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Yao, K.; Tay, F.E.H.; Kumar, A.; Zeng, K. Self-polarized ferroelectric PVDF homopolymer ultra-thin films derived from Langmuir–Blodgett deposition. Polymers 2012, 53, 1404–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garain, S.; Sinha, T.K.; Adhikary, P.; Henkel, K.; Sen, S.; Ram, S.; Sinha, C.; Schmeißer, D.; Mandal, D. Self-Poled Transparent and Flexible UV Light-Emitting Cerium Complex–PVDF Composite: A High-Performance Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karan, S.K.; Bera, R.; Paria, S.; Das, A.K.; Maiti, S.; Maitra, A.; Khatua, B.B. An Approach to Design Highly Durable Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Based on Self-Poled PVDF/AlO-rGO Flexible Nanocomposite with High Power Density and Energy Conversion Efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1601016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, N.; Lee, Y.-S.; Shanmugasundaram, S.; Jaffe, M.; Arinzeh, T. Characterization and in vitro cytocompatibility of piezoelectric electrospun scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3550–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Zhengnan, Z.; Qian, L.; Tan, G.; Ning, C. Polarization of an electroactive functional film on titanium for inducing osteogenic differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.B.; Lakes, R.S. Biomaterials: An Introduction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1979; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Uzieliene, I.; Bernotas, P.; Mobasheri, A.; Bernotiene, E. The Role of Physical Stimuli on Calcium Channels in Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pärssinen, J.; Hammarén, H.; Rahikainen, R.; Sencadas, V.J.G.S.; Ribeiro, C.; Vanhatupa, S.; Miettinen, S.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Hytönen, V.P. Enhancement of adhesion and promotion of osteogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells by poled electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, J.H.; van der Jagt, O.P.; Punt, B.J.; Verhaar, J.A.; van Leeuwen, J.P.; Weinans, H.; Jahr, H. Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation in human osteoprogenitor cells by pulsed electromagnetic fields: An in vitro study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferroni, L.; Gardin, C.; Dolkart, O.; Salai, M.; Barak, S.; Piattelli, A.; Amir-Barak, H.; Zavan, B. Pulsed electromagnetic fields increase osteogenetic commitment of MSCs via the mTOR pathway in TNF-α mediated inflammatory conditions: An in-vitro study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.L.; Lau, C.P.; Lai, K.; Cheung, K.F.; Lau, G.K.; Li, G.R. Cell cycle-dependent expression of potassium channels and cell proliferation in rat mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. Cell Prolif. 2007, 40, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruderer, M.; Richards, R.G.; Alini, M.; Stoddart, M.J. Role and regulation of RUNX2 in osteogenesis. Eur Cell Mater 2014, 28, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, G.J.; Findlay, D.M.; Anderson, P.H.; Morris, H.A. Target Genes: Bone Proteins. In Vitamin D, 3rd ed.; Feldman, D., Pike, J.W., Adams, J.S., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; Chapter 23; pp. 411–424. [Google Scholar]
- Komori, T. Regulation of Osteoblast Differentiation by Runx2. In Osteoimmunology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kaivosoja, E.; Sariola, V.; Chen, Y.; Konttinen, Y.T. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields and dehydroepiandrosterone on viability and osteo-induction of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2012, 9, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Saburi, E.; Enderami, S.E.; Barati Bagherabad, M.; Enderami, S.E.; Chokami, M.; Shapouri Moghadam, A.; Salarinia, R.; Ardeshirylajimi, A.; Mansouri, V. Synergistic effects of polyaniline and pulsed electromagnetic field to stem cells osteogenic differentiation on polyvinylidene fluoride scaffold. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3058–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Xin, F.; Jiang, W. Underlying Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Applications of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields in Bone Repair. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titushkin, I.; Rao, V.; Cho, M. Mode- and Cell-Type Dependent Calcium Responses Induced by Electrical Stimulus. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2004, 32, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy-Hulbert, A.; Metcalfe, J.C.; Hesketh, R. Biological responses to electromagnetic fields 1. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daish, C.; Blanchard, R.; Fox, K.; Pivonka, P.; Pirogova, E. The Application of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMFs) for Bone Fracture Repair: Past and Perspective Findings. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundelacruz, S.; Moody, A.T.; Levin, M.; Kaplan, D.L. Membrane Potential Depolarization Alters Calcium Flux and Phosphate Signaling During Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Bioelectricity 2019, 1, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, R.H.W.; Monsees Tand Özkucur, N. Electromagnetic effects—From cell biology to medicine. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 43, 177–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorio, J.R.; Cestari, M. Effect of crystallization temperature on the crystalline phase content and morphology of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1994, 32, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Mano, J.F.; Costa, A.M.; Schmidt, V.H. FTIR AND DSC STUDIES OF MECHANICALLY DEFORMED β-PVDF FILMS. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2001, 40, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.-Z.; Yang, W.; Yang, F.; Kersten-Niessen, M.; Jansen, J.A.; Both, S.K. Effects of Continuous Passaging on Mineralization of MC3T3-E1 Cells with Improved Osteogenic Culture Protocol. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2014, 20, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Huo, Q.; Shao, Y.; Bao, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Strontium promotes osteogenic differentiation by activating autophagy via the the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| PCLTCP + PEMF | PCLTCP + PVDF | PCLTCP + PEMF + PVDF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Metabolic Activity | + | 0 | + | |
| Cell Proliferation | ++ | 0 | ++ | |
| Alkaline Phosphatase Activity | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cell Mineralization | 0 | + | + | |
| Osteogenic Gene expression | RUNX2 | + | 0 | + |
| BSP | + | + | + | |
| OC | ++ | ++ | +++ | |
| OP | + | 0 | ++ | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Suryani, L.; Zhou, X.; Muthukumaran, P.; Rakshit, M.; Yang, F.; Wen, F.; Hassanbhai, A.M.; Parida, K.; Simon, D.T.; et al. Synergistic Effect of PVDF-Coated PCL-TCP Scaffolds and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Osteogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126438
Dong Y, Suryani L, Zhou X, Muthukumaran P, Rakshit M, Yang F, Wen F, Hassanbhai AM, Parida K, Simon DT, et al. Synergistic Effect of PVDF-Coated PCL-TCP Scaffolds and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Osteogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126438
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yibing, Luvita Suryani, Xinran Zhou, Padmalosini Muthukumaran, Moumita Rakshit, Fengrui Yang, Feng Wen, Ammar Mansoor Hassanbhai, Kaushik Parida, Daniel T. Simon, and et al. 2021. "Synergistic Effect of PVDF-Coated PCL-TCP Scaffolds and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Osteogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126438
APA StyleDong, Y., Suryani, L., Zhou, X., Muthukumaran, P., Rakshit, M., Yang, F., Wen, F., Hassanbhai, A. M., Parida, K., Simon, D. T., Iandolo, D., Lee, P. S., Ng, K. W., & Teoh, S. H. (2021). Synergistic Effect of PVDF-Coated PCL-TCP Scaffolds and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Osteogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126438