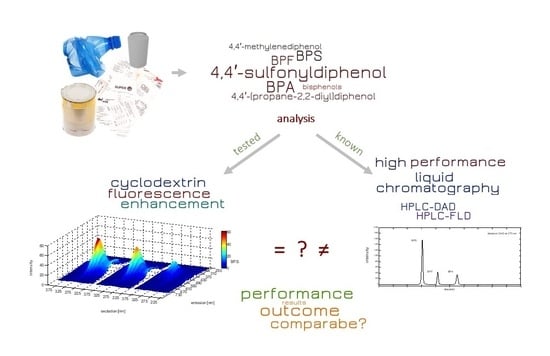
Comparison of Quantitative Detection Methods Based on Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Chromatographic Techniques Used for the Determination of Bisphenol Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Exploration of Fluorescence Properties
2.2. Chromatographic Analysis
2.3. Analytical Methods
- (1)
- selected BP in phosphate buffer,
- (2)
- selected BP and β-CD (1:1 molar ratio) in phosphate buffer (pH = 7.00),
- (3)
- selected BP and m-β-CD (1:1 molar ratio) in phosphate buffer (pH = 7.00).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.3. Chromatographic Method
3.4. Samples Preparation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications with Special Reference to Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate). Polymers 2013, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, R.C.; Pahl, S. Plastics, the Environment and Society: Current Consensus and Future Directions. In Plastics and the Environment; RSC: London, UK, 2018; pp. 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Jatkowska, N.; Kudłak, B.; Lewandowska, P.; Liu, W.; Williams, M.J.; Schiöth, H.B. Identification of Synergistic and Antagonistic Actions of Environmental Pollutants: Bisphenols A, S and F in the Presence of DEP, DBP, BADGE and BADGE·2HCl in Three Component Mixtures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.V.L.; Kim, K.-H.; Kavitha, B.; Kumar, V.; Raza, N.; Kalagara, S. Photocatalytic Degradation of Bisphenol A in Aqueous Media: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehse, S.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C. Microplastics Reduce Short-Term Effects of Environmental Contaminants. Part I: Effects of Bisphenol A on Freshwater Zooplankton Are Lower in Presence of Polyamide Particles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiege, H.; Voges, H.-W.; Hamamoto, T.; Umemura, S.; Iwata, T.; Miki, H.; Fujita, Y.; Buysch, H.-J.; Garbe, D.; Paulus, W. Phenol Derivatives. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH &Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2000; ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Roark, A.M. Endocrine Disruptors and Marine Systems. In Encyclopedia of the World’s Biomes; Goldstein, M.I., DellaSala, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 188–194. ISBN 978-0-12-816097-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, P.E.; Feng, L.G.H. 17—Mercury, BPA, and Pesticides in Food. In Risks of Hazardous Wastes; Rosenfeld, P.E., Feng, L.G.H., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 223–235. ISBN 978-1-4377-7842-7. [Google Scholar]
- Frankowski, R.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T.; Sójka, K. The Presence of Bisphenol A in the Thermal Paper in the Face of Changing European Regulations—A Comparative Global Research. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and Human Health: A Review of the Literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andújar, N.; Gálvez-Ontiveros, Y.; Zafra-Gómez, A.; Rodrigo, L.; Álvarez-Cubero, M.J.; Aguilera, M.; Monteagudo, C.; Rivas, A. Bisphenol A Analogues in Food and Their Hormonal and Obesogenic Effects: A Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelch, K.; Wignall, J.A.; Goldstone, A.E.; Ross, P.K.; Blain, R.B.; Shapiro, A.J.; Holmgren, S.D.; Hsieh, J.-H.; Svoboda, D.; Auerbach, S.S.; et al. A Scoping Review of the Health and Toxicological Activity of Bisphenol A (BPA) Structural Analogues and Functional Alternatives. Toxicology 2019, 424, 152235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Ike, M.; Fujita, M. Acute Toxicity, Mutagenicity, and Estrogenicity of Bisphenol-A and Other Bisphenols. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.S. Bisphenol A: An Endocrine Disruptor with Widespread Exposure and Multiple Effects. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, Z.A.; Mirlohi, M.; Pourzamani, H.; Malekpour, A. Bisphenol A in “BPA Free” Baby Feeding Bottles. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2012, 17, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Björnsdotter, M.K.; de Boer, J.; Ballesteros-Gómez, A. Bisphenol A and Replacements in Thermal Paper: A Review. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.b.; Harrison, S.M.; Monahan, F.J.; Cummins, E.; Brunton, N.P. Bisphenol A and Metabolites in Meat and Meat Products: Occurrence, Toxicity, and Recent Development in Analytical Methods. Foods 2021, 10, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, J.R.; Bolden, A.L. Bisphenol S and F: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the Hormonal Activity of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eladak, S.; Grisin, T.; Moison, D.; Guerquin, M.-J.; N’Tumba-Byn, T.; Pozzi-Gaudin, S.; Benachi, A.; Livera, G.; Rouiller-Fabre, V.; Habert, R. A New Chapter in the Bisphenol A Story: Bisphenol S and Bisphenol F Are Not Safe Alternatives to This Compound. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.-L. A Review Recent Development on Analytical Methods for Determination of Bisphenol a in Food and Biological Samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 2795–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajiki, J.; Takahashi, K.; Yonekubo, J. Sensitive Method for the Determination of Bisphenol-A in Serum Using Two Systems of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 736, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, A.; del Olmo, M.; Suárez, B.; Hontoria, E.; Navalón, A.; Vílchez, J.L. Gas Chromatographic-Mass Spectrometric Method for the Determination of Bisphenol A and Its Chlorinated Derivatives in Urban Wastewater. Water Res. 2003, 37, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, A.; Biesaga, M. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Bisphenols Extraction from Food Samples—A Review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, L.; Wang, P.; Ali, Z.; Li, J. Electrochemical Detection of Bisphenols in Food: A Review. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugoasa, L.A.D. Review—Electrochemical Sensors for Determination of the Endocrine Disruptor, Bisphenol A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, M.L.; Marini, F.; Sarabia, L.A.; Ortiz, M.C. Migration Test of Bisphenol A from Polycarbonate Cups Using Excitation-Emission Fluorescence Data with Parallel Factor Analysis. Talanta 2017, 167, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallimberti, M.; Rocha, B.A.; Souza, V.C.O.; Campiglia, A.D.; Barbosa, F. Determination of Bisphenol A in Paper Products by Synchronous Fluorescence Spectoscopy and Estimation of Daily Exposure. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2020, 31, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.B.P.; Ibañez, G.A.; Escandar, G.M. Spectrofluorimetric Study of Phenolic Endocrine Disruptors in Cyclodextrin Media. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20914–20923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgar, R.; Olea-Serrano, M.F.; Novillo-Fertrell, A.; Rivas, A.; Pazos, P.; Pedraza, V.; Navajas, J.M.; Olea, N. Determination of Bisphenol A and Related Aromatic Compounds Released from Bis-GMA-Based Composites and Sealants by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Squares | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | 3.643 | 1 | 3.640 | 6.356 | 0.065 |
| x2 | 5.625 | 1 | 5.620 | 9.814 | 0.035 |
| x12 | 45.0 | 1 | 45.0 | 78.580 | 0.001 |
| x22 | 5.0 | 1 | 5.0 | 8.731 | 0.042 |
| x1 x2 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.969 |
| Model | 152.0 | 4 | 38.0 | 66.356 | 0.001 |
| Residuals | 8.586 | 15 | 0.573 |
| System | Analytical Technique | Spectral Information * | Slope | Intercept | r | LOD ** [μg∙mL−1] | RSD *** | Linear Range [μg∙mL−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | MSF | Ex = 235 nm Em = 300 nm | 26.35 | 22.64 | 0.998 | 0.14 | 3.8% | 0–2.4 |
| BPA + β-CD | MSF | Ex = 235 nm Em = 300 nm | 132.41 | 45.68 | 0.999 | 0.13 | 3.1% | 0–2.8 |
| BPA + m-β-CD | MSF | Ex = 235 nm Em = 300 nm | 308.84 | 124.72 | 0.998 | 0.38 | 2.3% | 0–2.8 |
| BPA | HPLC-DAD | 275 nm | 6.3 × 103 | 10.16 | 0.999 | 0.04 | - | 0–1125 |
| BPA | HPLC-FLD | Ex = 230 nm Em = 300 nm | 1.56 × 105 | 1.88∙× 104 | 0.999 | 0.07 | - | 0–3.5 |
| BPF | MSF | Ex = 235 nm Em = 304 nm | 55.91 | 22.93 | 0.999 | 0.60 | 4.8% | 0–2.8 |
| BPF + β-CD | MSF | Ex = 235 nm Em = 304 nm | 106.28 | 61.26 | 0.991 | 0.35 | 2.8% | 0–2.8 |
| BPF + m-β-CD | MSF | Ex = 235 nm Em = 304 nm | 259.3 | 70.76 | 0.999 | 0.11 | 2.6% | 0–2.8 |
| BPF | HPLC-DAD | 275 nm | 6.26 × 103 | 18.98 | 0.999 | 0.04 | - | 0–1125 |
| BPF | HPLC-FLD | Ex = 230 nm Em = 300 nm | 1.49 × 105 | 1.45 × 104 | 0.999 | 0.10 | - | 0–3.5 |
| BPS | MSF | Ex = 335 nm Em = 400 nm | 0.61 | 19.31 | 0.986 | 1.82 | 4.3% | 0–15 |
| BPS + β-CD | MSF | Ex = 335 nm Em = 400 nm | 14.76 | 29.17 | 0.997 | 0.84 | 4.3% | 0–15 |
| BPS + m-β-CD | MSF | Ex = 335 nm Em = 400 nm | 14.77 | 32.33 | 0.997 | 0.83 | 3.0% | 0–15 |
| BPS | MSF | Ex = 295 nm Em = 471 nm | 0.31 | 18.52 | 0.986 | 8.30 | 5.7% | 0–180 |
| BPS + β-CD | MSF | Ex = 295 nm Em = 471 nm | 0.36 | 24.81 | 0.997 | 15.44 | 4.9% | 0–300 |
| BPS + m-β-CD | MSF | Ex = 295 nm Em = 471 nm | 0.45 | 17.96 | 0.997 | 7.35 | 2.8% | 0–300 |
| BPS | HPLC-DAD | 225 nm | 1.38 × 104 | 167.95 | 0.999 | 0.04 | - | 0–1125 |
| HPLC-DAD | HPLC-FLD | MFS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | BP | Concentration * [μg∙g−1] or [μg∙mL−1] | ||
| TP no. 1 | BPS | 2. 8 ± 0.05 | - | 3.84 ± 0.30 |
| TP no. 1 | BPF | not detected | 6.49 ± 1.00 | 6.28 ± 0.35 |
| TP no. 2 | BPS | 2.28 ± 0.05 | - | 3.13 ± 0.15 |
| TP no. 3 | BPF | 10.04 ± 0.03 | 10.78 ± 0.03 | 12.05 ± 0.38 |
| Peas | BPA | 12.35 ± 0.07 | 13.05 ± 0.06 | 13.61 ± 0.12 |
| Corn | BPA | 18.21 ± 0.02 | 17.91 ± 0.02 | 20.61 ± 0.35 |
| Jack fruit | BPA | 28.26 ± 0.04 | 26.41 ± 0.05 | 27.64 ± 0.25 |
| Oryginal | Coded | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 (%ACN) | x2 (Flow [mL∙min−1]) | x0 | x1 | x2 | x12 | x22 | x1x2 |
| 85 | 0.85 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 |
| 85 | 0.85 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 |
| 15 | 0.85 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 15 | 0.85 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 85 | 1.35 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 85 | 1.35 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 15 | 1.35 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 |
| 15 | 1.35 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 |
| 100 | 1 | 1 | 1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 100 | 1 | 1 | 1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 | −1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 50 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 | −1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 50 | 1.5 | 1 | 0 | 1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 50 | 1.5 | 1 | 0 | 1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | −1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | −1.414 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orzel, J.; Swit, P. Comparison of Quantitative Detection Methods Based on Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Chromatographic Techniques Used for the Determination of Bisphenol Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910569
Orzel J, Swit P. Comparison of Quantitative Detection Methods Based on Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Chromatographic Techniques Used for the Determination of Bisphenol Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910569
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrzel, Joanna, and Pawel Swit. 2021. "Comparison of Quantitative Detection Methods Based on Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Chromatographic Techniques Used for the Determination of Bisphenol Compounds" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910569
APA StyleOrzel, J., & Swit, P. (2021). Comparison of Quantitative Detection Methods Based on Molecular Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Chromatographic Techniques Used for the Determination of Bisphenol Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10569. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910569