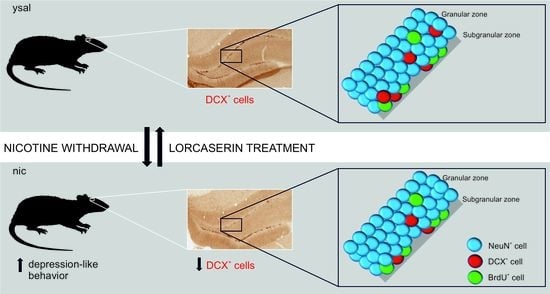
Chronic Lorcaserin Treatment Reverses the Nicotine Withdrawal-Induced Disruptions to Behavior and Maturation in Developing Neurons in the Hippocampus of Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rats Acquired Intravenous Nicotine Self-Administration
2.2. Nicotine Exerts Anxiolytic-Like Properties, While its Withdrawal Does Not Induce Anxiety-Like State
2.3. Lorcaserin Reverses the Enhanced Immobility Time during Nicotine Withdrawal
2.4. Lorcaserin Reduces Locomotor Hyperactivity during Nicotine Withdrawal
2.5. Lorcaserin Nonspecifically Attenuates ‘Drug-Seeking’ Behavior during Abstinence
2.6. Lorcaserin Partially Attenuates the Cognition-Like Deficits during Nicotine Withdrawal
2.7. Lorcaserin Does Not Affect the Proliferation of Newborn Neurons during Nicotine Withdrawal
2.8. Lorcaserin Does Not Alter the Disrupted Survival of Newborn Cells during Nicotine Withdrawal
2.9. Lorcaserin Increases the Number of Immature Neurons in Rats
2.10. Lorcaserin Does Not Alter the Disrupted Maturation of New Neurons during Nicotine Withdrawal
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. Behavioral Signs of Nicotine Withdrawal
4.3.1. Training and Self-Administration
4.3.2. Withdrawal
- Effects of Nicotine Withdrawal on Anxiety Behavior in the LDB
- Effects of Nicotine Withdrawal on the Behavior in the FST
- Effects of Nicotine Withdrawal on Locomotor Activity
- Induction of ‘Nicotine-Seeking’ under Extinction Conditions
- Effects of Protracted Nicotine Withdrawal on the Behavior in the NORT
4.4. Hippocampal Neurogenesis during Nicotine Withdrawal
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| 5-HT2C receptor | Serotonin 2C receptor |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BrdU | 5-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine |
| DA | Dopamine |
| DCX | Doublecortin |
| DG | Dentate gyrus |
| DI | Discrimination index |
| FR | Fixed ratio |
| FST | Forced swim test |
| LDB | Light/dark box test |
| NORT | Novel object recognition task |
References
- Crocq, M.A. Alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, and mental disorders. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2003, 5, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tulloch, H.; Pipe, A.L.; Clyde, M.J.; Reid, R.D.; Els, C. The quit experience and concerns of smokers with psychiatric illness. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 50, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watkins, S.S.; Koob, G.F.; Markou, A. Neural mechanisms underlying nicotine addiction: Acute positive reinforcement and withdrawal. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2000, 2, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meneses, A.; Liy-Salmeron, G. Serotonin and emotion, learning and memory. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 23, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.T.; Gerak, L.R.; France, C.P. The behavioral pharmacology and therapeutic potential of lorcaserin for substance use dis-orders. Neuropharmacology 2018, 142, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, W.J.; Grottick, A.J.; Al-Shamma, H.; Smith, B.; Chalmers, D.; Behan, D.; Menzaghi, F.; Reyes-Saldana, H.; Espitia, S.; Yuskin, D.; et al. Lorcaserin, a novel selective human 5-hydroxytryptamine2c agonist: In vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurt, R.T.; Croghan, I.T.; Schroeder, D.R.; Hays, J.T.; Choi, D.-S.; Ebbert, J.O. Combination varenicline and lorcaserin for tobacco dependence treatment and weight gain prevention in overweight and obese smokers: A pilot study. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2017, 19, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, W.R.; Rose, J.E.; Glicklich, A.; Stubbe, S.; Sanchez-Kam, M. Lorcaserin for smoking cessation and associated weight gain: A randomized 12-week clinical trial. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2017, 19, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharretts, J.; Galescu, O.; Gomatam, S.; Andraca-Carrera, E.; Hampp, C.; Yanoff, L. Cancer risk associated with Lorcaserin-The FDA’s review of the CAMELLIA-TIMI 61 trial. N. Eng. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.; Mancini, M.C. Should the same safety scrutiny of antiobesity medications be applied to other chronic usage drugs? Obesity 2020, 28, 1171–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, S.A.; Hall, B.J.; Wells, C.; Slade, S.; Jaskowski, P.; Morrison, M.; Rezvani, A.H.; Rose, J.E.; Levin, E.D. Dextromethorphan interactions with histaminergic and serotonergic treatments to reduce nicotine self-administration in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2016, 142, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cousins, V.; Rose, J.E.; Levin, E.D. IV nicotine self-administration in rats using a consummatory operant licking response: Sensitivity to serotonergic, glutaminergic and histaminergic drugs. Prog. Neuro. Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 54, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levin, E.D.; Johnson, J.E.; Slade, S.; Wells, C.; Cauley, M.; Petro, A.; Rose, J.E. Lorcaserin, a 5-HT2C agonist, decreases nicotine self-administration in female rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quarta, D.; Naylor, C.G.; Stolerman, I.P. The serotonin2C receptor agonist Ro-60-0175 attenuates effects of nicotine in the five-choice serial reaction time task and in drug discrimination. Psychopharmacology 2007, 193, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaniewska, M.; McCreary, A.C.; Przegaliński, E.; Filip, M. Effects of the serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor ligands on the discriminative stimulus effects of nicotine in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 571, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaniewska, M.; McCreary, A.C.; Filip, M. Interactions of serotonin (5-HT)2receptor-targeting ligands and nicotine: Locomotor activity studies in rats. Synapse 2009, 63, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaniewska, M.; McCreary, A.C.; Wydra, K.; Filip, M. Differential effects of serotonin (5-HT)2 receptor-targeting ligands on loco-motor responses to nicotine-repeated treatment. Synapse 2010, 64, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeb, F.D.; Higgins, G.A.; Fletcher, P.J. The serotonin 2C receptor agonist lorcaserin attenuates intracranial self-stimulation and blocks the reward-enhancing effects of nicotine. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, P.J.; Rizos, Z.; Noble, K.; Soko, A.D.; Silenieks, L.B.; Lê, A.D.; Higgins, G.A. Effects of the 5-HT2C receptor agonist Ro60-0175 and the 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100907 on nicotine self-administration and reinstatement. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2288–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, P.J.; Li, Z.; Silenieks, L.B.; Macmillan, C.; Delannoy, I.; Higgins, G.A. Preclinical evidence for combining the 5- HT 2C receptor agonist lorcaserin and varenicline as a treatment for nicotine dependence. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grottick, A.; Corrigall, W.; Higgins, G. Activation of 5-HT2C receptors reduces the locomotor and rewarding effects of nicotine. Psychopharmacology 2001, 157, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, E.G.; Fisher, D.C.; Higgins, G.A.; Fletcher, P.J. Examination of the effects of varenicline, bupropion, lorcaserin, or naltrexone on responding for conditioned reinforcement in nicotine-exposed rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2014, 25, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.J.; Mosher, T.M.; Greenshaw, A.J. Differential effects of 5-HT2C receptor activation by WAY 161503 on nicotine-induced place conditioning and locomotor activity in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 197, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, G.A.; Silenieks, L.B.; Rossmann, A.; Rizos, Z.; Noble, K.; Soko, A.D.; Fletcher, P.J. The 5-ht2c receptor agonist lorcaserin reduces nicotine self-administration, discrimination, and reinstatement: Relationship to feeding behavior and impulse control. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, G.A.; Silenieks, L.B.; Lau, W.; De Lannoy, I.A.M.; Lee, D.K.H.; Izhakova, J.; Coen, K.; Le, A.D.; Fletcher, P.J. Evaluation of chemically diverse 5-HT2C receptor agonists on behaviours motivated by food and nicotine and on side effect profiles. Psychopharmacology 2013, 226, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.-P.; Zhang, Y.; Van Cleemput, J.; Jiang, W.; Liao, M.; Li, L.; Wan, Q.; Backstrom, J.R.; Zhang, X. Disruption of PTEN coupling with 5-HT2C receptors suppresses behavioral responses induced by drugs of abuse. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaniewska, M.; McCreary, A.C.; Wydra, K.; Filip, M. Effects of serotonin (5-HT)2 receptor ligands on depression-like behavior during nicotine withdrawal. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaniewska, M.; Alenina, N.; Wydra, K.; Fröhler, S.; Kuśmider, M.; McCreary, A.C.; Chen, W.; Bader, M.; Filip, M. Discovering the mechanisms underlying serotonin (5-HT)2A and 5-HT2C receptor regulation following nicotine withdrawal in rats. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrous, D.N.; Adriani, W.; Montaron, M.-F.; Aurousseau, C.; Rougon, G.; Le Moal, M.; Piazza, P.V. Nicotine Self-Administration Impairs Hippocampal Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 3656–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, A.; Soleiman, M.T.; Talia, R.; Koob, G.F.; George, O.; Mandyam, C.D. Extended access nicotine self-administration with periodic deprivation increases immature neurons in the hippocampus. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Belal, C.; Tu, W.; Chigurupati, S.; Ameli, N.J.; Lu, Y.; Chan, S.L. Chronic nicotine administration impairs activation of cyclic amp-response element binding protein and survival of newborn cells in the dentate gyrus. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.M.G.; Jessberger, S. Review: Adult neurogenesis and its role in neuropsychiatric disease, brain repair and normal brain function. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2014, 40, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandyam, C.D.; Koob, G.F. The addicted brain craves new neurons: Putative role for adult-born progenitors in promoting re-covery. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klempin, F.; Babu, H.; Tonelli, D.D.P.; Alarcon, E.; Fabel, K.; Kempermann, G. Oppositional effects of serotonin receptors 5-HT1a, 2, and 2c in the regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2010, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banasr, M.; Hery, M.; Printemps, R.; Daszuta, A. Serotonin-induced increases in adult cell proliferation and neurogenesis are me-diated through different and common 5-HT receptor subtypes in the dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irvine, E.; Bagnalasta, M.; Marcon, C.; Motta, C.; Tessari, M.; File, S.; Chiamulera, C. Nicotine self-administration and withdrawal: Modulation of anxiety in the social interaction test in rats. Psychopharmacology 2001, 153, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Treweek, J.; Edwards, S.; Leão, R.M.; Schulteis, G.; Koob, G.F.; George, O. Extended access to nicotine leads to a CRF1receptor dependent increase in anxiety-like behavior and hyperalgesia in rats. Addict. Biol. 2015, 20, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilmouth, C.E.; Spear, L.P. Withdrawal from chronic nicotine in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzás, A.; Bokor, P.; Balangó, B.; Pintér, D.; Palotai, M.; Simon, B.; Csabafi, K.; Telegdy, G.; Szabó, G.; Bagosi, Z. Changes in striatal dopamine release and locomotor activity following acute withdrawal from chronic nicotine are mediated by CRF1, but not CRF2, receptors. Brain Res. 2019, 1706, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, Y.K.; Schmid, M.J.; Anderson, T.M.; Lau, Y.-S. Effects of nicotine withdrawal on central dopaminergic systems. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1996, 53, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, M.M.; Mendelsohn, D.; Stamp, J.A. The HR/LR model: Further evidence as an animal model of sensation seeking. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahler, C.W.; Spillane, N.S.; Metrik, J.; Leventhal, A.M.; Monti, P.M. Sensation seeking as a predictor of treatment compliance and smoking cessation treatment outcomes in heavy social drinkers. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 93, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aydin, C.; Oztan, O.; Isgor, C. Hippocampal Y2 receptor-mediated mossy fiber plasticity is implicated in nicotine absti-nence-related social anxiety-like behavior in an outbred rat model of the novelty-seeking phenotype. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 125, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motaghinejad, M.; Fatima, S.; Karimian, M.; Ganji, S. Protective effects of forced exercise against nicotine-induced anxiety, depression and cognition impairment in rat. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, C.; Tedesco, M.; Bellomo, M.; Caputi, A.P.; Calapai, G. Long-term effects of nicotine on the forced swimming test in mice: An experimental model for the study of depression caused by smoke. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 49, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.; Allan, S. The role of defeat and entrapment (arrested flight) in depression: An exploration of an evolutionary view. Psychol. Med. 1998, 28, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Hoyer, D.; Markou, A. Withdrawal from chronic amphetamine induces Depressive-Like behavioral effects in rodents. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolotkin, R.L.; Crosby, R.D.; Wang, Z. Health-related quality of life in randomized controlled trials of lorcaserin for obesity man-agement: What mediates improvement? Clin. Obes. 2017, 7, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakofsky, J.J.; Tang, Y.; Dunlop, B.W. Depression worsening associated with lorcaserin a case report. J. Clin. Psycho. Pharmacol. 2015, 35, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymel, K.A.; Eans, S.O.; Sitchenko, K.L.; Gomes, S.M.; Lukowsky, A.L.; Medina, J.M.; Sypek, E.I.; Carey, A.N.; McLaughlin, J.P. Stress-induced increases in depression-like and cocaine place-conditioned behaviors are reversed by disruption of memories during reconsolidation. Behav. Pharmacol. 2014, 25, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, M.; Frankowska, M.; Zaniewska, M.; Gołda, A.; Przegaliński, E.; Vetulani, J. Diverse effects of GABA-mimetic drugs on co-caine-evoked self-administration and discriminative stimulus effects in rats. Psychopharmacology 2007, 192, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solecki, W.; Wilczkowski, M.; Pradel, K.; Karwowska, K.; Kielbinski, M.; Drwięga, G.; Zajda, K.; Blasiak, T.; Soltys, Z.; Rajfur, Z.; et al. Effects of brief inhibition of the ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons on the cocaine seeking during abstinence. Addict. Biol. 2020, 25, e12826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, G.A.; Silenieks, L.B.; Altherr, E.B.; Macmillan, C.; Fletcher, P.J.; Pratt, W.E. Lorcaserin and CP-809101 reduce motor impulsivity and reinstatement of food seeking behavior in male rats: Implications for understanding the anti-obesity property of 5-HT2C receptor agonists. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2841–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, G.A.; Brown, M.; John, J.S.; Macmillan, C.; Silenieks, L.B.; Thevarkunnel, S. Effects of 5-HT2C receptor modulation and the NA reuptake inhibitor atomoxetine in tests of compulsive and impulsive behaviour. Neuropharmacology 2020, 170, 108064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del’Guidice, T.; Lemay, F.; Lemasson, M.; Levasseur-Moreau, J.; Manta, S.; Etievant, A.; Escoffier, G.; Dore, F.Y.; Roman, F.R.; Beaulieu, J.-M. Stimulation of 5-HT 2C receptors im-proves cognitive deficits induced by human tryptophan hydroxylase 2 loss of function mutation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siuciak, J.A.; Chapin, D.S.; Iredale, P.A.; McCarthy, S.A.; Guanowsky, V.; Brown, J.; Chiang, P.; Marala, R.; Patterson, T.; Seymour, P.A.; et al. CP-809,101, a selective 5-HT2C agonist, shows activity in animal models of antipsychotic activity. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashare, R.L.; Schmidt, H.D. Optimizing treatments for nicotine dependence by increasing cognitive performance during with-drawal. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pranzatelli, M.R.; Murthy, J.N.; Tailor, P.T. Novel regulation of 5-HT1C receptors: Down-regulation induced both by 5-HT1C/2 receptor agonists and antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 244, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovanni, G.; De Deurwaerdère, P. New therapeutic opportunities for 5-HT2C receptor ligands in neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 157, 125–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beninger, R.J. The role of dopamine in locomotor activity and learning. Brain Res. Rev. 1983, 6, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alex, K.; Pehek, E. Pharmacologic mechanisms of serotonergic regulation of dopamine neurotransmission. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 296–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bubar, M.; Cunningham, K.A. Distribution of serotonin 5-HT2C receptors in the ventral tegmental area. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Deurwaerdère, P.; Ramos, M.; Bharatiya, R.; Puginier, E.; Chagraoui, A.; Manem, J.; Cuboni, E.; Pierucci, M.; Deidda, G.; Casarrubea, M.; et al. Lorcaserin bidirectionally regulates dopaminergic function site-dependently and disrupts dopamine brain area correlations in rats. Neuropharmacology 2020, 166, 107915. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, D.-M.; Tu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, P. Electroacupuncture restores 5-ht system deficit in chronic mild stress-induced depressed rats. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benwell, M.E.M.; Balfour, D.J.K. Effects of nicotine administration and its withdrawal on plasma corticosterone and brain 5-hydroxyindoles. Psychopharmacology 1979, 63, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenina, N.; Klempin, F. The role of serotonin in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA Briefing Document: NDA 22529, Lorqess (Lorcaserin Hydrochloride) Tablets. Available online: http://www.diabetesincontrol.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/www.fda.gov_downloads_AdvisoryCommittees_CommitteesMeetingMaterials_Drugs_EndocrinologicandMetabolicDrugsAdvisoryCommittee_UCM303198.pdf. (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Le Foll, B.; Chakraborty-Chatterjee, M.; Lev-Ran, S.; Barnes, C.; Pushparaj, A.; Gamaleddin, I.; Yan, Y.; Khaled, M.; Goldberg, S.R. Varenicline decreases nicotine self-administration and cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behaviour in rats when a long pretreatment time is used. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocyk, A.; Bobula, B.; Dudys, D.; Przyborowska, A.; Majcher-Maślanka, I.; Hess, G.; Wędzony, K. Early-life stress affects the structural and functional plasticity of the medial prefrontal cortex in adolescent rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 38, 2089–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potasiewicz, A.; Hołuj, M.; Kos, T.; Popik, P.; Arias, H.R.; Nikiforuk, A. 3-Furan-2-yl-N-p-tolyl-acrylamide, a positive allosteric modulator of the α7 nicotinic receptor, reverses schizophrenia-like cognitive and social deficits in rats. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocyk, A.; Majcher-Maślanka, I.; Przyborowska, A.; Maćkowiak, M.; Wędzony, K. Early-life stress increases the survival of midbrain neurons during postnatal development and enhances reward-related and anxiolytic-like behaviors in a sex-dependent fashion. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2015, 44, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćkowiak, M.; Kolasiewicz, W.; Markowicz-Kula, K.; Wedzony, K. Purvalanol A, inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases attenuates proliferation of cells in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat hippocampus. Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 845–849. [Google Scholar]
- Mackowiak, M.; Chocyk, A.; Dudys, D.; Wedzony, K. Activation of CB1 cannabinoid receptors impairs memory consolidation and hippocampal polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule expression in contextual fear conditioning. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaniewska, M.; Nikiforuk, A.; Głowacka, U.; Brygider, S.; Wesołowska, J.; Litwa, E.; Maćkowiak, M. Chronic Lorcaserin Treatment Reverses the Nicotine Withdrawal-Induced Disruptions to Behavior and Maturation in Developing Neurons in the Hippocampus of Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020868
Zaniewska M, Nikiforuk A, Głowacka U, Brygider S, Wesołowska J, Litwa E, Maćkowiak M. Chronic Lorcaserin Treatment Reverses the Nicotine Withdrawal-Induced Disruptions to Behavior and Maturation in Developing Neurons in the Hippocampus of Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020868
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaniewska, Magdalena, Agnieszka Nikiforuk, Urszula Głowacka, Sabina Brygider, Julita Wesołowska, Ewa Litwa, and Marzena Maćkowiak. 2021. "Chronic Lorcaserin Treatment Reverses the Nicotine Withdrawal-Induced Disruptions to Behavior and Maturation in Developing Neurons in the Hippocampus of Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020868
APA StyleZaniewska, M., Nikiforuk, A., Głowacka, U., Brygider, S., Wesołowska, J., Litwa, E., & Maćkowiak, M. (2021). Chronic Lorcaserin Treatment Reverses the Nicotine Withdrawal-Induced Disruptions to Behavior and Maturation in Developing Neurons in the Hippocampus of Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020868