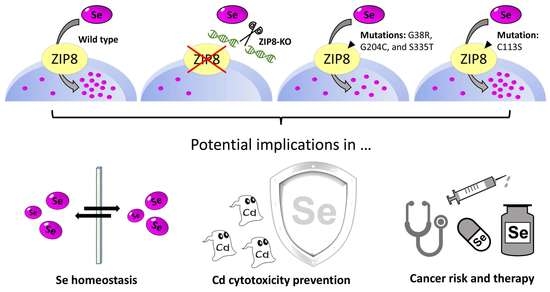
The Impact of ZIP8 Disease-Associated Variants G38R, C113S, G204C, and S335T on Selenium and Cadmium Accumulations: The First Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation and Verification of a ZIP8 Gene Knockout Human Cell Model
2.2. Involvement of Human ZIP8 in Intracellular Mn, Zn, Cd, and Se Uptakes
2.3. The Effects of Disease-Associated ZIP8 Single-Point Mutations on Cellular Se Uptake Ability
2.4. The Role of ZIP8 and Se in Cd Cytotoxicity
2.5. Investigating the Potential Anticancer Effects of Se and Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Se and Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy
2.6. Clinical Database Analysis: Gene Expressions of ZIP8 and Selenoproteins in Cancers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. Generation of ZIP8-KO HeLa Cell Model Using CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Technology
4.3. Plasmids and Cell Transfection
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.5. Immunoblot Analysis
4.6. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
4.7. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.8. Clinical-Based Bioinformatics Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, A.T.Y.; Tan, H.W.; Xu, Y.M. Epigenetic effects of dietary trace elements. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 3, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forootanfar, H.; Adeli-Sardou, M.; Nikkhoo, M.; Mehrabani, M.; Amir-Heidari, B.; Shahverdi, A.R.; Shakibaie, M. Antioxidant and cytotoxic effect of biologically synthesized selenium nanoparticles in comparison to selenium dioxide. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaghi, A.; Poorebrahim, M.; Sarhan, D.; Bjornstedt, M. Selenium stimulates the antitumour immunity: Insights to future research. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 155, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alehagen, U.; Aaseth, J.; Lindahl, T.L.; Larsson, A.; Alexander, J. Dietary supplementation with selenium and coenzyme Q10 prevents increase in plasma d-dimer while lowering cardiovascular mortality in an elderly swedish population. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Franke, S.I.; Bordin, D.L.; Pra, D.; Henriques, J.A. Biological functions of selenium and its potential influence on Parkinson’s disease. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2016, 88, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Bao, Y.; Broadley, M.R.; Collings, R.; Ford, D.; Hesketh, J.E.; Hurst, R. Selenium in human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1337–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, H.D.; Pipkin, F.B.; Redman, C.W.; Poston, L. Selenium in reproductive health. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 206, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raisbeck, M.F. Selenosis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2000, 16, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.W.; Mo, H.Y.; Lau, A.T.Y.; Xu, Y.M. Selenium species: Current status and potentials in cancer prevention and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Fan, W.; Wang, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Selenium exposure and cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis and meta-regression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kieliszek, M.; Lipinski, B.; Blazejak, S. Application of sodium selenite in the prevention and treatment of cancers. Cells 2017, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramoutar, R.R.; Brumaghim, J.L. Antioxidant and anticancer properties and mechanisms of inorganic selenium, oxo-sulfur, and oxo-selenium compounds. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 58, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, H.L.; Dunn, B.K. Selenium and prostate cancer prevention: Insights from the selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial (SELECT). Nutrients 2013, 5, 1122–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippman, S.M.; Klein, E.A.; Goodman, P.J.; Lucia, M.S.; Thompson, I.M.; Ford, L.G.; Parnes, H.L.; Minasian, L.M.; Gaziano, J.M.; Hartline, J.A.; et al. Effect of selenium and vitamin E on risk of prostate cancer and other cancers: The Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT). JAMA 2009, 301, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakalli Cetin, E.; Naziroglu, M.; Cig, B.; Ovey, I.S.; Aslan Kosar, P. Selenium potentiates the anticancer effect of cisplatin against oxidative stress and calcium ion signaling-induced intracellular toxicity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: Involvement of the TRPV1 channel. J. Recept. Sig. Transd. 2017, 37, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y. Selenium transport mechanism via selenoprotein P—Its physiological role and related diseases. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 685517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.R.; Geng, X.; Jiang, L.; Gálvez-Peralta, M.; Chen, F.; Nebert, D.W.; Liu, Z. Zinc- and bicarbonate-dependent ZIP8 transporter mediates selenite uptake. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35327–35340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, E.; Barone, R.; Sturiale, L.; Pasquariello, R.; Alessandri, M.G.; Pinto, A.M.; Renieri, A.; Panteghini, C.; Garavaglia, B.; Cioni, G.; et al. Clinical, molecular and glycophenotype insights in SLC39A8-CDG. Orphanet. J. Rare. Dis. 2021, 16, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Gao, Y.M.; Wu, D.D.; Yu, F.Y.; Zang, Z.S.; Yang, L.; Yao, Y.; Cai, N.L.; Zhou, Y.; Chiu, J.F.; et al. Aberrant cytokine secretion and zinc uptake in chronic cadmium-exposed lung epithelial cells. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2017, 11, 1600059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Kosman, D.J. Molecular mechanisms of non-transferrin-bound and transferring-bound iron uptake in primary hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 2015, 133, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boycott, K.M.; Beaulieu, C.L.; Kernohan, K.D.; Gebril, O.H.; Mhanni, A.; Chudley, A.E.; Redl, D.; Qin, W.; Hampson, S.; Küry, S.; et al. Autosomal-recessive intellectual disability with cerebellar atrophy syndrome caused by mutation of the manganese and zinc transporter gene SLC39A8. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Hogrebe, M.; Gruneberg, M.; DuChesne, I.; von der Heiden, A.L.; Reunert, J.; Schlingmann, K.P.; Boycott, K.M.; Beaulieu, C.L.; Mhanni, A.A.; et al. SLC39A8 deficiency: A disorder of manganese transport and glycosylation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, E.-K.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Gupta, N.; Iwase, S.; Seo, Y.A. Functional analysis of SLC39A8 mutations and their implications for manganese deficiency and mitochondrial disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Tan, H.W.; Liang, Z.L.; Wu, G.Q.; Xu, Y.M.; Lau, A.T.Y. The impact of coilin nonsynonymous SNP Variants E121K and V145I on cell growth and cajal body Formation: The first characterization. Genes 2020, 11, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Song, Z.; Liu, A.; Dahmen, U.; Yang, X.; Fang, H. Effects of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in infections, inflammatory diseases, metabolic disorders and cancers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 681810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liang, C.; Xi, H.; Yang, S.; Hu, J.; Pang, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Tang, C.; Xie, W.; et al. Case report: Novel NIPBL variants cause cornelia de lange syndrome in Chinese patients. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 699894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Hogrebe, M.; Fobker, M.; Brackmann, R.; Fiedler, B.; Reunert, J.; Rust, S.; Tsiakas, K.; Santer, R.; Grüneberg, M.; et al. SLC39A8 deficiency: Biochemical correction and major clinical improvement by manganese therapy. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerkeb, L.; Mukherjee, I.; Chatterjee, I.; Lahner, B.; Salt, D.E.; Connolly, E.L. Iron-induced turnover of the Arabidopsis IRON-REGULATED TRANSPORTER1 metal transporter requires lysine residues. Plant. Physiol. 2008, 146, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zang, Z.S.; Xu, Y.M.; Lau, A.T.Y. Molecular and pathophysiological aspects of metal ion uptake by the zinc transporter ZIP8 (SLC39A8). Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Ge, J.; Lv, M.; Zhang, Q.; Talukder, M.; Li, J.L. Selenium prevent cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity through modulation of endoplasmic reticulum-resident selenoproteins and attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, T.; Yang, T.; Lu, Y.; Lee, R.J.; Ma, X.; et al. Selenium-doped calcium carbonate nanoparticles loaded with cisplatin enhance efficiency and reduce side effects. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.A.; Hoffmann, P.R. The human selenoproteome: Recent insights into functions and regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2457–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, D.J.; Kunicka, T.; Schomburg, L.; Liska, V.; Swan, N.; Soucek, P. Expression of selenoprotein genes and association with selenium status in colorectal adenoma and colorectal cancer. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.K.; Chen, Q.H.; Pan, D.; Chang, B.; Sang, L.X. A novel therapeutic strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Immunomodulatory mechanisms of selenium and/or selenoproteins on a shift towards anti-cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, L.G.; Cowley, M.J.; Gayevskiy, V.; Roscioli, T.; Thorburn, D.R.; Prelog, K.; Bahlo, M.; Sue, C.M.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Christodoulou, J. A SLC39A8 variant causes manganese deficiency, and glycosylation and mitochondrial disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2017, 40, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Achkar, J.P.; Haritunians, T.; Jacobs, J.P.; Hui, K.Y.; D’Amato, M.; Brand, S.; Radford-Smith, G.; Halfvarson, J.; Niess, J.H.; et al. A pleiotropic missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with crohn’s disease and human gut microbiome composition. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Witkowska, K.; Afonso Guerra-Assunção, J.; Ren, M.; Ng, F.L.; Mauro, C.; Tucker, A.T.; Caulfield, M.J.; Ye, S. A blood pressure-associated variant of the SLC39A8 gene influences cellular cadmium accumulation and toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 4117–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haller, G.; McCall, K.; Jenkitkasemwong, S.; Sadler, B.; Antunes, L.; Nikolov, M.; Whittle, J.; Upshaw, Z.; Shin, J.; Baschal, E.; et al. A missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with severe idiopathic scoliosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCoy, T.H., Jr.; Pellegrini, A.M.; Perlis, R.H. Using phenome-wide association to investigate the function of a schizophrenia risk locus at SLC39A8. Transl. Psychiat. 2019, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaugg, J.; Melhem, H.; Huang, X.; Wegner, M.; Baumann, M.; Surbek, D.; Körner, M.; Albrecht, C. Gestational diabetes mellitus affects placental iron homeostasis: Mechanism and clinical implications. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7311–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Hamid, Y.; Liu, D.; Shohag, M.J.I.; Zehra, A.; He, Z.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X. Foliar application of zinc and selenium alleviates cadmium and lead toxicity of water spinach—Bioavailability/cytotoxicity study with human cell lines. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.W.; Liang, Z.L.; Yao, Y.; Wu, D.D.; Mo, H.Y.; Gu, J.; Chiu, J.F.; Xu, Y.M.; Lau, A.T.Y. Lasting DNA damage and aberrant DNA repair gene expression profile are associated with post-chronic cadmium exposure in human bronchial epithelial cells. Cells 2019, 8, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misra, S.; Boylan, M.; Selvam, A.; Spallholz, J.E.; Bjornstedt, M. Redox-active selenium compounds—From toxicity and cell death to cancer treatment. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3536–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahmanto, A.S.; Davies, M.J. Selenium-containing amino acids as direct and indirect antioxidants. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jeong, D. Bimodal actions of selenium essential for antioxidant and toxic pro-oxidant activities: The selenium paradox (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.S.; Zhang, J. Selenium nanoparticles are more efficient than sodium selenite in producing reactive oxygen species and hyper-accumulation of selenium nanoparticles in cancer cells generates potent therapeutic effects. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2018, 126, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevinakoppamath, S.; Saleh Ahmed, A.M.; Ramachandra, S.C.; Vishwanath, P.; Prashant, A. Chemopreventive and anticancer property of selenoproteins in obese breast cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 618172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.L.; Wu, D.D.; Yao, Y.; Yu, F.Y.; Yang, L.; Tan, H.W.; Hylkema, M.N.; Rots, M.G.; Xu, Y.M.; Lau, A.T.Y. Epiproteome profiling of cadmium-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells by quantitative histone post-translational modification-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lau, A.T.Y. Preparation of highly specific polyclonal antibody for human zinc transporter ZIP8. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2015, 47, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riisom, M.; Gammelgaard, B.; Lambert, I.H.; Sturup, S. Development and validation of an ICP-MS method for quantification of total carbon and platinum in cell samples and comparison of open-vessel and microwave-assisted acid digestion methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 158, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Site(aa) | Type | Variant | Disease | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 38 | Homozygous variant | c.112G>C (p. Gly38Arg) | Type II congenital disorder of glycosylation | [21,23,28] |
| 113 | Homozygous variant | c.338G>C (p. Cys113Ser) | Leigh syndrome | [23] |
| 204 | Heterozygous variant | c.610G>T (p. Gly204Cys) | Type II congenital disorder of glycosylation | [22,23] |
| 335 | Heterozygous variant | c.1004G>C (p. Ser335Thr) | Type II congenital disorder of glycosylation | [22,23] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Z.-L.; Tan, H.W.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Xu, Y.-M.; Lau, A.T.Y. The Impact of ZIP8 Disease-Associated Variants G38R, C113S, G204C, and S335T on Selenium and Cadmium Accumulations: The First Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111399
Liang Z-L, Tan HW, Wu J-Y, Chen X-L, Wang X-Y, Xu Y-M, Lau ATY. The Impact of ZIP8 Disease-Associated Variants G38R, C113S, G204C, and S335T on Selenium and Cadmium Accumulations: The First Characterization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111399
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Zhan-Ling, Heng Wee Tan, Jia-Yi Wu, Xu-Li Chen, Xiu-Yun Wang, Yan-Ming Xu, and Andy T. Y. Lau. 2021. "The Impact of ZIP8 Disease-Associated Variants G38R, C113S, G204C, and S335T on Selenium and Cadmium Accumulations: The First Characterization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111399
APA StyleLiang, Z. -L., Tan, H. W., Wu, J. -Y., Chen, X. -L., Wang, X. -Y., Xu, Y. -M., & Lau, A. T. Y. (2021). The Impact of ZIP8 Disease-Associated Variants G38R, C113S, G204C, and S335T on Selenium and Cadmium Accumulations: The First Characterization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(21), 11399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111399