Deciphering the Genomic Landscape and Pharmacological Profile of Uncommon Entities of Adult Rhabdomyosarcomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Clinicopathological Characteristics
2.2. Diagnosis of RMS Case Series
2.3. Tumor Tissue Gene Expression Analyses
2.4. Chemotherapy Assessment in 2D and 3D Patient-Derived Primary Culture RMS Model
2.5. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Profiling and Microsatellite Instability (MSI) Status of Sclerosing RMS
2.6. In Silico Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
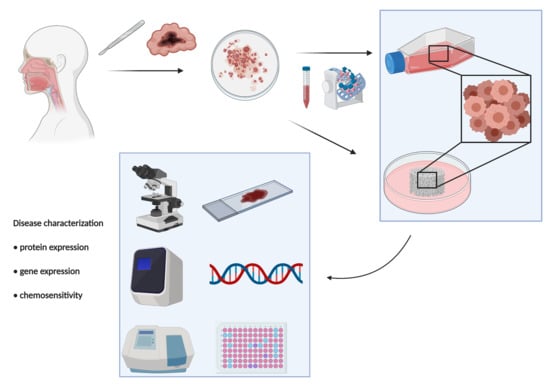
4.1. Ethical Statement and Case Series
4.2. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analyses
4.3. Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.4. Isolation of Patient-Derived RMS Primary Cells
4.5. Establishment of Sclerosing RMS Patient-Derived Primary Culture
4.6. Building of a Collagen-Based Scaffold 3D Culture Model
4.7. Chemobiogram Analysis
4.8. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
4.9. Evaluation of Microsatellite Instability (MSI) Status
4.10. In Silico Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hawkins, W.G.; Hoos, A.; Antonescu, C.R.; Urist, M.J.; Leung, D.H.; Gold, J.S.; Woodruff, J.M.; Lewis, J.J.; Brennan, M.F. Clinicopathologic analysis of patients with adult rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer 2001, 91, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, W.H.; Spunt, S.L. Soft tissue sarcomas of childhood. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Seibel, N.L.; Altekruse, S.F.; Ries, L.A.; Melbert, D.L.; O’Leary, M.; Smith, F.O.; Reaman, G.H. Outcomes for children and adolescents with cancer: Challenges for the twenty-first century. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboo, S.S.; Krajewski, K.M.; Zukotynski, K.; Howard, S.; Jagannathan, J.P.; Hornick, J.L.; Ramaiya, N. Imaging features of primary and secondary adult rhabdomyosarcoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, W694–W703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, D.; Sapkota, S.; Kapoor, R.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.C. Adult rhabdomyosarcoma: Clinical presentation, treatment, and outcome. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2015, 11, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberlin, O.; Rey, A.; Lyden, E.; Bisogno, G.; Stevens, M.C.; Meyer, W.H.; Carli, M.; Anderson, J.R. Prognostic factors in metastatic rhabdomyosarcomas: Results of a pooled analysis from United States and European cooperative groups. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO Classification of Tumours. In Soft Tissue and Bone, 5th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2020; Volume 3, p. 368. ISBN 978-92-832-4502-5.
- Elsebaie, M.; Amgad, M.; Elkashash, A.; Elgebaly, A.S.; Ashal, G.; Shash, E.; Elsayed, Z. Management of Low and Intermediate Risk Adult Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Pooled Survival Analysis of 553 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bompas, E.; Campion, L.; Italiano, A.; Le Cesne, A.; Chevreau, C.; Isambert, N.; Toulmonde, M.; Mir, O.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; et al. Outcome of 449 adult patients with rhabdomyosarcoma: An observational ambispective nationwide study. Cancer Med. 2018, 8, 4023–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, M.A.; Mentzel, T.; Fanburg-Smith, J.C. Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma in adults: A clinicopathologic study of 38 cases with emphasis on morphologic variants and recent skeletal muscle-specific markers. Mod. Pathol. 2001, 14, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freling, N.J.; Merks, J.H.; Saeed, P.; Balm, A.J.; Bras, J.; Pieters, B.R.; Adam, J.A.; van Rijn, R.R. Imaging findings in craniofacial childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatric Radiol. 2010, 40, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgenstern, D.A.; Rees, H.; Sebire, N.J.; Shipley, J.; Anderson, J. Rhabdomyosarcoma subtyping by immunohistochemical assessment of myogenin: Tissue array study and review of the literature. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2008, 14, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cessna, M.H.; Zhou, H.; Perkins, S.L.; Tripp, S.R.; Layfield, L.; Daines, C.; Coffin, C.M. Are myogenin and myoD1 expression specific for rhabdomyosarcoma? A study of 150 cases, with emphasis on spindle cell mimics. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2001, 25, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Dileo, P.; Casanova, M.; Bertulli, R.; Meazza, C.; Gandola, L.; Navarria, P.; Collini, P.; Gronchi, A.; Olmi, P.; et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma in adults. A retrospective analysis of 171 patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2003, 98, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crist, W.M.; Anderson, J.R.; Meza, J.L.; Fryer, C.; Raney, R.B.; Ruymann, F.B.; Breneman, J.; Qualman, S.J.; Wiener, E.; Wharam, M.; et al. Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma study-IV: Results for Patients with Nonmetastatic Disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3091–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skapek, S.X.; Ferrari, A.; Gupta, A.A.; Lupo, P.J.; Butler, E.; Shipley, J.; Barr, F.G.; Hawkins, D.S. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Yu, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Mao, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Ma, S. The survival benefit of radiotherapy in localized primary adult rhabdomyosarcoma. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 16, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noujaim, J.; Thway, K.; Jones, R.L.; Miah, A.; Khabra, K.; Langer, R.; Kasper, B.; Judson, I.; Benson, C.; Kollàr, A. Adult Pleomorphic Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Multicentre Retrospective Study. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 6213–6217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Bernasconi, A.; Bergamaschi, L.; Botta, L.; Andreano, A.; Castaing, M.; Rugge, M.; Bisogno, G.; Falcini, F.; Sacerdote, C.; et al. Impact of Rhabdomyosarcoma Treatment Modalities by Age in a Population-Based Setting. J. Adolesc. Young Adult Oncol. 2021, 10, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trans-Atlantic RPS Working Group. Management of Recurrent Retroperitoneal Sarcoma (RPS) in the Adult: A Consensus Approach from the Trans-Atlantic RPS Working Group. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 3531–3540, Erratum in: Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 688–689. [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Suurmeijer, A.; Agaram, N.P.; Zhang, L.; Antonescu, C.R. Head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma with TFCP2 fusions and ALK overexpression: A clinicopathological and molecular analysis of 11 cases. Histopathology 2021, 79, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaram, N.P.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Alaggio, R.; Zhang, L.; Fujisawa, Y.; Ladanyi, M.; Wexler, L.H.; Antonescu, C.R. MYOD1-mutant spindle cell and sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma: An aggressive subtype irrespective of age. A reappraisal for molecular classification and risk stratification. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, A.; Recine, F.; Mercatali, L.; Miserocchi, G.; Spadazzi, C.; Liverani, C.; Bongiovanni, A.; Pieri, F.; Casadei, R.; Riva, N.; et al. Primary Culture of Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma: Molecular Characterization and Response to Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Vita, A.; Recine, F.; Mercatali, L.; Miserocchi, G.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; Casadei, R.; Bongiovanni, A.; Pieri, F.; Riva, N.; et al. Myxofibrosarcoma primary cultures: Molecular and pharmacological profile. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2017, 9, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vita, A.; Ferrari, A.; Miserocchi, G.; Vanni, S.; Domizio, C.; Fonzi, E.; Fausti, V.; Recine, F.; Bassi, M.; Campobassi, A.; et al. Identification of a novel RAB3IP-HMGA2 fusion transcript in an adult head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma. Oral Dis. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shern, J.F.; Chen, L.; Chmielecki, J.; Wei, J.S.; Patidar, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Ambrogio, L.; Auclair, D.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.K.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of rhabdomyosarcoma reveals a landscape of alterations affecting a common genetic axis in fusion-positive and fusion-negative tumors. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polyak, K.; Weinberg, R.A. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marzo, A.M.; Knudsen, B.; Chan-Tack, K.; Epstein, J.I. E-cadherin expression as a marker of tumor aggressiveness in routinely processed radical prostatectomy specimens. Urology 1999, 53, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.L.; Shepard, C.R.; Wells, A. Breast carcinoma cells re-express E-cadherin during mesenchymal to epithelial reverting transition. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, K.M.; Parker, N.N.; Dai, Y.; Vieweg, J.; Siemann, D.W. E-cadherin plasticity in prostate cancer stem cell invasion. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abell, A.N.; Johnson, G.L. Implications of Mesenchymal Cells in Cancer Stem Cell Populations: Relevance to EMT. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2014, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emori, M.; Tsukahara, T.; Murata, K.; Sugita, S.; Sonoda, T.; Kaya, M.; Soma, T.; Sasaki, M.; Nagoya, S.; Hasegawa, T.; et al. Prognostic impact of CD109 expression in myxofibrosarcoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 111, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypek, K.; Kusienicka, A.; Trzyna, E.; Szewczyk, B.; Ulman, A.; Konieczny, P.; Adamus, T.; Badyra, B.; Kortylewski, M.; Majka, M. SNAIL is a key regulator of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma tumor growth and differentiation through repression of MYF5 and MYOD function. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vita, A.; Recine, F.; Miserocchi, G.; Pieri, F.; Spadazzi, C.; Cocchi, C.; Vanni, S.; Liverani, C.; Farnedi, A.; Fabbri, F.; et al. The potential role of the extracellular matrix in the activity of trabectedin in UPS and L-sarcoma: Evidences from a patient-derived primary culture case series in tridimensional and zebrafish models. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, A.; Mercatali, L.; Recine, F.; Pieri, F.; Riva, N.; Bongiovanni, A.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; Miserocchi, G.; Amadori, D.; et al. Current classification, treatment options, and new perspectives in the management of adipocytic sarcomas. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 6233–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouron-Dal Soglio, D.; Rougemont, A.L.; Absi, R.; Barrette, S.; Montpetit, A.; Fetni, R.; Fournet, J.C. SNP genotyping of a sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma: Reveals highly aneuploid profile and a specific MDM2/HMGA2 amplification. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K.; Wettach, G.R.; Ryan, C.W.; Hung, A.; Hooper, J.E.; Beadling, C.; Warrick, A.; Corless, C.L.; Olson, S.B.; Keller, C.; et al. MDM2 Amplification and PI3KCA Mutation in a Case of Sclerosing Rhabdomyosarcoma. Sarcoma 2013, 2013, 520858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Recine, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Riva, N.; Fausti, V.; De Vita, A.; Mercatali, L.; Liverani, C.; Miserocchi, G.; Amadori, D.; Ibrahim, T. Update on the role of trabectedin in the treatment of intractable soft tissue sarcomas. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tazzari, M.; Bergamaschi, L.; De Vita, A.; Collini, P.; Barisella, M.; Bertolotti, A.; Ibrahim, T.; Pasquali, S.; Castelli, C.; Vallacchi, V. Molecular Determinants of Soft Tissue Sarcoma Immunity: Targets for Immune Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonneville, R.; Krook, M.A.; Kautto, E.A.; Miya, J.; Wing, M.R.; Chen, H.Z.; Reeser, J.W.; Yu, L.; Roychowdhury, S. Landscape of Microsatellite Instability Across 39 Cancer Types. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, S. Deficient mismatch repair: Read all about it (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D.; et al. PD-1 BLOCKADE in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudley, J.C.; Lin, M.T.; Le, D.T.; Eshleman, J.R. Microsatellite Instability as a Biomarker for PD-1 Blockade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Overman, M.J.; McDermott, R.; Leach, J.L.; Lonardi, S.; Lenz, H.J.; Morse, M.A.; Desai, J.; Hill, A.; Axelson, M.; Moss, R.A.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): An open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; Lonardi, S.; Wong, K.; Lenz, H.J.; Gelsomino, F.; Aglietta, M.; Morse, M.A.; Van Cutsem, E.; McDermott, R.; Hill, A.; et al. Durable clinical benefit with nivolumab plus ipilimumab in DNA mismatch repair deficient microsatellite instability-high metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruma, T.; Nagasaka, T.; Nakamura, K.; Haraga, J.; Nyuya, A.; Nishida, T.; Goel, A.; Masuyama, H.; Hiramatsu, Y. Clinical impact of endometrial cancer stratified by genetic mutational profiles, POLE mutation, and microsatellite instability. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polom, K.; Das, K.; Marrelli, D.; Roviello, G.; Pascale, V.; Voglino, C.; Rho, H.; Tan, P.; Roviello, F. KRAS Mutation in Gastric Cancer and Prognostication Associated with Microsatellite Instability Status. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genutis, L.K.; Tomsic, J.; Bundschuh, R.A.; Brock, P.L.; Williams, M.D.; Roychowdhury, S.; Reeser, J.W.; Frankel, W.L.; Alsomali, M.; Routbort, M.J.; et al. Microsatellite Instability Occurs in a Subset of Follicular Thyroid Cancers. Thyroid 2019, 29, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalniz, Z.; Demokan, S.; Suoglu, Y.; Ulusan, M.; Dalay, N. Assessment of microsatellite instability in head and neck cancer using consensus markers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3541–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.P.; Mahoney, M.R.; Van Tine, B.A.; Atkins, J.; Milhem, M.M.; Jahagirdar, B.N.; Antonescu, C.R.; Horvath, E.; Tap, W.D.; Schwartz, G.K.; et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab treatment for metastatic sarcoma (Alliance A091401): Two open-label, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserocchi, G.; Mercatali, L.; Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Spadazzi, C.; Pieri, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Recine, F.; Amadori, D.; Ibrahim, T. Management and potentialities of primary cancer cultures in preclinical and translational studies. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Spadazzi, C.; Miserocchi, G.; Cocchi, C.; Bongiovanni, A.; De Lucia, A.; La Manna, F.; Fabbri, F.; Tebaldi, M.; et al. Lineage-specific mechanisms and drivers of breast cancer chemoresistance revealed by 3D biomimetic culture. Mol. Oncol. 2021. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liverani, C.; La Manna, F.; Groenewoud, A.; Mercatali, L.; Van Der Pluijm, G.; Pieri, F.; Cavaliere, D.; De Vita, A.; Spadazzi, C.; Miserocchi, G.; et al. CORRECTION: Innovative approaches to establish and characterize primary cultures: An ex vivo 3D system and the zebrafish model. Biol. Open 2017, 6, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miserocchi, G.; Cocchi, C.; De Vita, A.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; Calpona, S.; Di Menna, G.; Bassi, M.; Meccariello, G.; De Luca, G.; et al. Three-dimensional collagen-based scaffold model to study the microenvironment and drug-resistance mechanisms of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vita, A.; Mercatali, L.; Miserocchi, G.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; Recine, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Pieri, F.; Cavaliere, D.; Fausti, V.; et al. Establishment of a Primary Culture of Patient-derived Soft Tissue Sarcoma. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 134, 56767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Minardi, S.; Kang, Y.; Mercatali, L.; Amadori, D.; Bongiovanni, A.; La Manna, F.; Ibrahim, T.; Tasciotti, E. A biomimetic 3D model of hypoxia-driven cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Vita, A.; Liverani, C.; Molinaro, R.; Martinez, J.O.; Hartman, K.A.; Spadazzi, C.; Miserocchi, G.; Taraballi, F.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Pieri, F.; et al. Lysyl oxidase engineered lipid nanovesicles for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehn, C.F.; Boulikas, T.; Kourvetaris, A.; Possinger, K.; Lüftner, D. Pharmacokinetics of liposomal cisplatin (lipoplatin) in combination with 5-FU in patients with advanced head and neck cancer: First results of a phase III study. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- De Vita, A.; Miserocchi, G.; Recine, F.; Mercatali, L.; Pieri, F.; Medri, L.; Bongiovanni, A.; Cavaliere, D.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; et al. Activity of Eribulin in a Primary Culture of Well-Differentiated/Dedifferentiated Adipocytic Sarcoma. Molecules 2016, 21, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hande, K.R.; Wedlund, P.J.; Noone, R.M.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Greco, F.A.; Wolff, S.N. Pharmacokinetics of high-dose etoposide (VP-16-213) administered to cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 379–382. [Google Scholar]
- Boss, D.S.; Glen, H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Keesen, M.; Morrison, R.; Tait, B.; Copalu, W.; Mazur, A.; Wanders, J.; O’Brien, J.P.; et al. A phase I study of E7080, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Racanelli, D.; Brenca, M.; Baldazzi, D.; Goeman, F.; Casini, B.; De Angelis, B.; Guercio, M.; Milano, G.M.; Tamborini, E.; Busico, A.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Approaches for the Identification of Pathognomonic Fusion Transcripts in Sarcomas: The Experience of the Italian ACC Sarcoma Working Group. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Patient | Gender | Age at Surgery | Site | Size (cm) | Histological Subtype | IHC Analysis | Surgical Margins | Radiotherapy Post-Surgery | Chemotherapy Post-Surgery | Follow-up Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS1 | male | 74 | masseterine parotid region | 10 × 9 × 3 | Spindle cell/sclerosing RMS | VIM+ MyoD1+ CD56+ Desmin+ Myoglobin+ Myogenin+ SMA+ CD34+ AE1-AE3 cytokeratin+ MDM2+ S100– STAT6– P63– | R1 | adjuvant IMRT radiotherapy treatment 60 Gy | Doxorubicin4 cycles Gemcitabine 3 cycles | 11 |
| RMS2 | female | 72 | ethmoid-orbital region | 1.2 × 0.8 | Alveolar RMS | MyoD1+ Desmin+ Myogenin+ AE1-AE3 cytokeratin– MDM2– S100– Synaptophysin– CD99– CD 45– GFAP– | na | na | na | 7 |
| RMS3 | male | 77 | latissimus dorsi | 15 × 11.5 × 7.5 | Pleomorphic RMS | MyoD1+ Desmin+ Myogenin+ SMA+ CD34– AE1-AE3 cytokeratin– S100– | R0 | na | na | 1 |
| Patient | Response to Chemotherapy | Survival Data | In Vitro Chemosensitivity (Cell Survival %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMS1 | PD after Doxorubicin 4 cycles SD after Gemcitabine 3 cycles | deceased after 11 months of follow up | (2D) 33% Doxorubicin 31% Doxorubicin and Dacarbazine combination 26% Doxorubicin and Cisplatin combination 75% Etoposide 39% Lenvatinib (3D) 43% Doxorubicin 47% Doxorubicin and Dacarbazine combination 43% Doxorubicin and Cisplatin combination 100% Etoposide 99% Lenvatinib |
| RMS2 | na | alive after 7 months of follow up | na |
| RMS3 | na | alive after 1 month of follow up | na |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Vita, A.; Vanni, S.; Fausti, V.; Cocchi, C.; Recine, F.; Miserocchi, G.; Liverani, C.; Spadazzi, C.; Bassi, M.; Gessaroli, M.; et al. Deciphering the Genomic Landscape and Pharmacological Profile of Uncommon Entities of Adult Rhabdomyosarcomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111564
De Vita A, Vanni S, Fausti V, Cocchi C, Recine F, Miserocchi G, Liverani C, Spadazzi C, Bassi M, Gessaroli M, et al. Deciphering the Genomic Landscape and Pharmacological Profile of Uncommon Entities of Adult Rhabdomyosarcomas. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111564
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Vita, Alessandro, Silvia Vanni, Valentina Fausti, Claudia Cocchi, Federica Recine, Giacomo Miserocchi, Chiara Liverani, Chiara Spadazzi, Massimo Bassi, Manlio Gessaroli, and et al. 2021. "Deciphering the Genomic Landscape and Pharmacological Profile of Uncommon Entities of Adult Rhabdomyosarcomas" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111564
APA StyleDe Vita, A., Vanni, S., Fausti, V., Cocchi, C., Recine, F., Miserocchi, G., Liverani, C., Spadazzi, C., Bassi, M., Gessaroli, M., Campobassi, A., De Luca, G., Pieri, F., Farnedi, A., Franchini, E., Ferrari, A., Domizio, C., Cavagna, E., Gurrieri, L., ... Mercatali, L. (2021). Deciphering the Genomic Landscape and Pharmacological Profile of Uncommon Entities of Adult Rhabdomyosarcomas. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(21), 11564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111564