Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Novel 18F-Labeled Radiotracer for PET Imaging of the Adenosine A2A Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Structure–Activity Relationship Studies
2.3. Radiochemistry
2.4. Metabolite Analysis
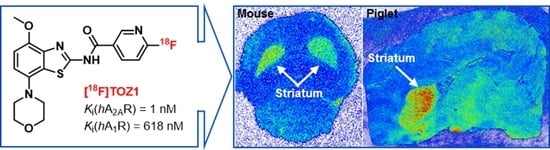
2.5. Autoradiography Study
2.6. PET Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Chemical Synthesis
3.3. Docking Stimulation
3.4. Manual Radiosynthesis
3.5. Automated Radiosynthesis
3.6. Quality Control
3.7. In Vitro stability And Lipophilicity (LogD7.4)
3.8. Biological Evaluation
3.9. In Vitro Binding Assays
3.10. In Vitro Autoradiography
3.11. In Vivo Metabolism
3.12. PET Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuxe, K.; Ferré, S.; Canals, M.; Torvinen, M.; Terasmaa, A.; Marcellino, D.; Goldberg, S.R.; Staines, W.; Jacobsen, K.X.; Lluis, C. Adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 heteromeric receptor complexes and their function. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2005, 26, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, S.; Karcz-Kubicha, M.; Hope, B.T.; Popoli, P.; Burgueño, J.; Gutiérrez, M.A.; Casadó, V.; Fuxe, K.; Goldberg, S.R.; Lluis, C. Synergistic interaction between adenosine A2A and glutamate mGlu5 receptors: Implications for striatal neuronal function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11940–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuxe, K.; Marcellino, D.; Guidolin, D.; Woods, A.S.; Agnati, L. Brain receptor mosaics and their intramembrane receptor-receptor interactions: Molecular integration in transmission and novel targets for drug development. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2009, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, S.; Quiroz, C.; Woods, A.; Cunha, R.; Popoli, P.; Ciruela, F.; Lluis, C.; Franco, R.; Azdad, K.; Schiffmann, S.N. An update on adenosine A2A-dopamine D2 receptor interactions: Implications for the function of G protein-coupled receptors. Cur. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenner, P. A2A antagonists as novel non-dopaminergic therapy for motor dysfunction in PD. Neurology 2003, 61, S32–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuxe, K.; Marcellino, D.; Genedani, S.; Agnati, L. Adenosine A2A receptors, dopamine D2 receptors and their interactions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1990–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, M.; Komoszynski, M.; Wojtczak, A. Adenosine A2A receptors in Parkinson’s disease treatment. Purinergic Signal. 2008, 4, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Japanese Istradefylline Study, G. A long-term study of istradefylline safety and efficacy in patients with Parkinson disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 38, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoritaka, A.; Hattori, N. Differences between Istradefylline responders and non-responders in Parkinson’s disease. Adv. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 06, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.F.; Cunha, R.A. The belated US FDA approval of the adenosine A2A receptor antagonist istradefylline for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Purinergic Signal. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, A.; Moreau, J.L.; Poli, S.; Riemer, C.; Steward, L. 4-Hydroxy-4-methyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic Acid (4-methoxy-7-morpholin-4-yl-benzothiazol-2-yl)-amide. U.S. Patent US20050261289A1, 24 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrinmayeh, H.; Territo, P.R. Purinergic receptors of the central nervous system: Biology, PET ligands, and their applications. Mol. Imaging 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuorimaa, A.; Rissanen, E.; Airas, L. In vivo PET imaging of adenosine 2A receptors in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disease. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2017, 2017, 6975841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barret, O.; Hannestad, J.; Vala, C.; Alagille, D.; Tavares, A.; Laruelle, M.; Jennings, D.; Marek, K.; Russell, D.; Seibyl, J.; et al. Characterization in humans of 18F-MNI-444, a PET radiotracer for brain adenosine 2A receptors. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharjee, A.K.; Lang, L.; Jacobson, O.; Shinkre, B.; Ma, Y.; Niu, G.; Trenkle, W.C.; Jacobson, K.A.; Chen, X.; Kiesewetter, D.O. Striatal adenosine A2A receptor-mediated positron emission tomographic imaging in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats using [18F]-MRS5425. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2011, 38, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khanapur, S.; Paul, S.; Shah, A.; Vatakuti, S.; Koole, M.J.; Zijlma, R.; Dierckx, R.A.; Luurtsema, G.; Garg, P.; van Waarde, A.; et al. Development of [18F]-labeled pyrazolo[4,3-e]-1,2,4- triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine (SCH442416) analogs for the imaging of cerebral adenosine A2A receptors with positron emission tomography. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6765–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, S.; Lai, T.H.; Toussaint, M.; Kranz, M.; Chovsepian, A.; Shang, Q.; Dukić-Stefanović, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Teodoro, R.; Wenzel, B. PET imaging of the adenosine A2A receptor in the rotenone-based mouse model of Parkinson’s disease with [18F]FESCH synthesized by a simplified two-step one-pot radiolabeling strategy. Molecules 2020, 25, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alanine, A.; Flohr, A.; Miller, A.K.; Norcross, R.D.; Riemer, C. Benzothiazole Derivatives. WIPO (PCT) Patent. WO2001097786A3, 27 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Flohr, A.; Jakob-Roetne, R.; Norcross, R.D.; Riemer, C. Ureas of 2-Aminobenzothiazoles as Adenosine Modulators. WIPO (PCT) Patent. WO2003049741A1, 19 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Flohr, A.; Jakob-Roetne, R.; Norcross, R.D.; Riemer, C. Urea Substituted Benzothiazoles. U.S. Patent US20040242576A1, 2 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Flohr, A.; Jakob-Roetne, R.; Norcross, R.D.; Riemer, C. Nicotin-or Isonicotin Benzothiazole Derivatives. WIPO (PCT) Patent. WO2003043636A1, 3 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Barawkar, D.A.; Thorat, S.; Shejul, Y.D.; Patel, M.; Naykodi, M.; Jain, V.; Salve, Y.; Prasad, V.; Chaudhary, S.; et al. Design, Synthesis of novel, potent, selective, orally bioavailable adenosine A2A receptor antagonists and their biological evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, V.T.; Riss, P.J. Radiosynthesis of [18F]trifluoroalkyl groups: Scope and limitations. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 380124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, O.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Chen, X. Fluorine-18 radiochemistry, labeling strategies and synthetic routes. Bioconjug Chem. 2015, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Rong, J.; Wang, L.; Vasdev, N.; Zhang, L.; Josephson, L.; Liang, S.H. Chemistry for positron emission tomography: Recent advances in 11C-, 18F-, 13N-, and 15O-labeling reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 2580–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakola, V.P.; Griffith, M.T.; Hanson, M.A.; Cherezov, V.; Chien, E.Y.; Lane, J.R.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Stevens, R.C. The 2.6 angstrom crystal structure of a human A2A adenosine receptor bound to an antagonist. Science 2008, 322, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, B.; Günther, R.; Brust, P.; Steinbach, J. A fluoro versus a nitro derivative-a high-performance liquid chromatography study of two basic analytes with different reversed phases and silica phases as basis for the separation of a positron emission tomography radiotracer. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1311, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, M.; Hinz, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Namasivayam, V.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Teodoro, R.; Toussaint, M.; Kranz, M.; Juhl, C.; Steinbach, J.; et al. Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of a fluorine-18 labeled pyrazine based radioligand for PET imaging of the adenosine A2B receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4650–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Teodoro, R.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Kranz, M.; Scheunemann, M.; Fischer, S.; Wenzel, B.; Egerland, U.; Hoefgen, N.; Steinbach, J.; et al. Radiosynthesis and biological evaluation of the new PDE10A radioligand [18F]AQ28A. J. Labelled Comp. Radiopharm. 2017, 60, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, P.; van den Hoff, J.; Steinbach, J. Development of 18F-labeled radiotracers for neuroreceptor imaging with positron emission tomography. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 777–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Bittner, G.C.; Ricq, E.L.; Hooker, J.M. A philosophy for CNS radiotracer design. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS Physicochemical property space shaped by a diverse set of molecules with experimentally determined exposure in the mouse brain. J. Med. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancel, V.; Mathy, F.X.; Boulanger, P.; English, S.; Croft, M.; Kenney, C.; Knott, T.; Stockis, A.; Bani, M. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of [14C]-tozadenant (SYN-115), a novel A2A receptor antagonist ligand, in healthy volunteers. Xenobiotica 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.E. 6-Hydroxynicotinic acid as an intermediate in the oxidation of nicotinic acid by pseudomonas fluorescens. Biochem. J. 1955, 60, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrman, E.; Stanier, R. Observations on the oxidation of halogenated nicotinic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 228, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, V.; Amici, A.; Mazzola, F.; Di Stefano, M.; Conforti, L.; Magni, G.; Ruggieri, S.; Raffaelli, N.; Orsomando, G. Metabolic profiling of alternative NAD biosynthetic routes in mouse tissues. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pike, V.W. Considerations in the development of reversibly binding PET radioligands for brain imaging. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1818–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albasanz, J.L.; Rodríguez, A.; Ferrer, I.; Martín, M. Adenosine A2A receptors are up-regulated in Pick’s disease frontal cortex. Brain Pathol 2006, 16, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Sutherland, G.; Geiger, J. Binding of the adenosine A2 receptor ligand [3H]CGS 21680 to human and rat brain: Evidence for multiple affinity sites. J. Neurochem. 1990, 55, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.E.; Jacobson, K.A. Recent developments in adenosine receptor ligands and their potential as novel drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011, 1808, 1290–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Witte, W.E.; Wong, Y.C.; Nederpelt, I.; Heitman, L.H.; Danhof, M.; van der Graaf, P.H.; Gilissen, R.A.; de Lange, E.C. Mechanistic models enable the rational use of in vitro drug-target binding kinetics for better drug effects in patients. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Wientjes, M.G.; Au, J.L.-S. Kinetics of P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of paclitaxel. J. Pharmacol Exp. Ther 2001, 298, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Pajouhesh, H.; Lenz, G.R. Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, M.A. Molecular biology of adenosine receptors. In Adenosine and Adenine Nucleotides: From Molecular Biology to Integrative Physiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, G.A.; Jarvis, M.F.; Sills, M.A.; Weeks, B.; Snowhill, E.W.; Williams, M. Species differences in high-affinity adenosine A2 binding sites in striatal membranes from mammalian brain. Drug Dev. Res. 1988, 15, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, R. Determination of lipophilicity and its use as a predictor of blood–brain barrier penetration of molecular imaging agents. Mol. Imag Biol. 2003, 5, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










 | R | Ki(hA2AR) in nM | Ki(hA1R) in nM |  | R | Ki(hA2AR) in nM | Ki(hA1R) in nM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tozadenant |  | 2.39 (2.04, 2.74) | 897 (841, 952) | TOZ4 |  | n.d. | n.d. |
| TOZ1 |  | 1.00 ± 0.16 | 618 ± 31 | TOZ5 (6a) |  | 1.04 (1.09, 1.03) | 336 (376, 271) |
| TOZ2 |  | 5.02 (5.57, 4.78) | 1398 (1547, 1294) | TOZ6 |  | 4.84 (4.96, 4.74) | 239 (488, 132) |
| TOZ3 |  | 2.56 ± 0.11 | 729 ± 22 | TOZ7 |  | 3.23 (3.47, 2.99) | 4278 (5069, 3487) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, T.H.; Toussaint, M.; Teodoro, R.; Dukić-Stefanović, S.; Kranz, M.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Moldovan, R.-P.; Brust, P. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Novel 18F-Labeled Radiotracer for PET Imaging of the Adenosine A2A Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031182
Lai TH, Toussaint M, Teodoro R, Dukić-Stefanović S, Kranz M, Deuther-Conrad W, Moldovan R-P, Brust P. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Novel 18F-Labeled Radiotracer for PET Imaging of the Adenosine A2A Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031182
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Thu Hang, Magali Toussaint, Rodrigo Teodoro, Sladjana Dukić-Stefanović, Mathias Kranz, Winnie Deuther-Conrad, Rareş-Petru Moldovan, and Peter Brust. 2021. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Novel 18F-Labeled Radiotracer for PET Imaging of the Adenosine A2A Receptor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031182
APA StyleLai, T. H., Toussaint, M., Teodoro, R., Dukić-Stefanović, S., Kranz, M., Deuther-Conrad, W., Moldovan, R. -P., & Brust, P. (2021). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Novel 18F-Labeled Radiotracer for PET Imaging of the Adenosine A2A Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031182