Mycobacterial and Human Ferrous Nitrobindins: Spectroscopic and Reactivity Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
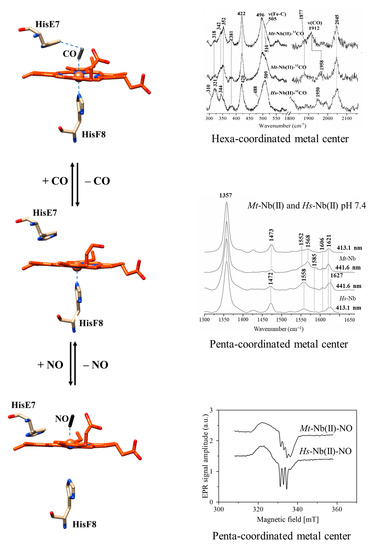
2.1. UV-Vis and RR Spectroscopic Properties of Mt-Nb(II) and Hs-Nb(II)
2.2. UV-Vis and RR Spectroscopic Properties of Mt-Nb(II)-CO and Hs-Nb(II)-CO
2.3. UV-Vis and EPR Spectroscopic Properties of Mt-Nb(II)-NO and Hs-Nb(II)-NO
2.4. Kinetics of CO Binding to Mt-Nb(II) and Hs-Nb(II)
2.4.1. Rapid-Mixing
2.4.2. Rebinding Kinetics
2.5. NO Binding to Mt-Nb(II) and Hs-Nb(II)
2.5.1. Rapid Mixing
2.5.2. Rebinding Kinetics
2.6. O2 Dissociation from Mt-Nb(II)-O2 and Hs-Nb(II)-O2
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Procedures
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy of Mt-Nb(II), Mt-Nb(II)-CO, Hs-Nb(II), and Hs-Nb(II)-CO
4.2.2. Resonance Raman Measurements of Mt-Nb(II), Mt-Nb(II)-CO, Hs-Nb(II), and Hs-Nb(II)-CO
4.2.3. UV-Vis Spectroscopy of Mt-Nb(II)-NO and Hs-Nb(II)-NO
4.2.4. EPR Spectroscopy of Mt-Nb(II)-NO and Hs-Nb(II)-NO
4.2.5. CO Binding to Mt-Nb(II) and Hs-Nb(II)
Rapid-Mixing Experiments
4.2.6. Laser Flash Photolysis Experiments
4.2.7. NO Binding to Mt-Nb(II) and Hs-Nb(II)
Rapid Mixing
4.2.8. Laser Flash Photolysis Experiments
4.2.9. NO Dissociation from Mt-Nb(II)-NO and Hs-Nb(II)-NO
4.2.10. O2 Dissociation from Mt-Nb(II)-O2, At-Nb(II)-O2, and Hs-Nb(II)-O2
4.3. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| At-Nb | Arabidopsis thaliana |
| Ec-Mb(II) | ferrous Equus caballus Mb |
| EPR spectra | electron paramagnetic resonance spectra |
| Hs-Nb | Homo sapiens Nb |
| Hs-Nb(II) | ferrous Hs-Nb |
| Hs-Nb(II)-CO | carbonylated Hs-Nb(II) |
| Hs-Nb(II)-NO | nitrosylated Hs-Nb(II) |
| Hs-Nb(III) | ferric Hs-Nb |
| Hs-Nb(III)-NO | nitrosylated Hs-Nb(III) |
| IPTG | isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactoside |
| Mb | myoglobin |
| Mt-Nb | Mycobacterium tuberculosis Nb |
| Mt-Nb(II) | ferrous Mt-Nb |
| Mt-Nb(II)-CO | carbonylated Mt-Nb(II) |
| Mt-Nb(II)-NO | nitrosylated Mt-Nb(II) |
| Mt-Nb(III) | ferric Mt-Nb |
| Mt-Nb(III)-NO | nitrosylated Mt-Nb(III) |
| Nb | nitrobindin |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| NP | nitrophorin |
| Pc-Mb(II) | ferrous Physeter catodon Mb |
| RR | Resonance Raman |
| UV-Vis spectra | UV-Visible spectra |
References
- Perutz, M.F. Regulation of oxygen affinity of hemoglobin: Influence of structure of the globin on the heme iron. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1979, 48, 327–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, H.F.; Forget, B.G. Hemoglobin: Molecular, Genetic and Clinical Aspects; Saunders WB Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi, M.; Bordo, D.; Rizzi, M.; Tarricone, C.; Ascenzi, P. Non-vertebrate hemoglobins: Structural bases for reactivity. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1997, 68, 29–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauenfelder, H.; McMahon, B.H.; Fenimore, P.W. Myoglobin: The hydrogen atom of biology and a paradigm of complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8615–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wittenberg, J.B.; Wittenberg, B.A. Myoglobin function reassessed. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Grubina, R.; Doyle, M.P. The new chemical biology of nitrite reactions with hemoglobin: R-state catalysis, oxidative denitrosylation, and nitrite reductase/anhydrase. Acc Chem Res. 2009, 4, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.J.; Kahraman, A.; Thornton, J.M. Heme proteins-diversity in structural characteristics, function, and folding. Proteins 2010, 78, 2349–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girvan, H.M.; Munro, A.W. Heme sensor proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13194–13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ascenzi, P.; Brunori, M. A molecule for all seasons: The heme. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2016, 20, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, A.; Couture, M.; Dewilde, S.; Guertin, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ascenzi, P.; Moens, L.; Bolognesi, M. A novel two-over-two α-helical sandwich fold is characteristic of the truncated hemoglobin family. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pesce, A.; Bolognesi, M.; Nardini, M. The diversity of 2/2 (truncated) globins. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2013, 63, 49–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, T.; Ondrias, M.R.; Rousseau, D.L.; Ikeda-Saito, M.; Yonetani, T. Evidence for hydrogen bonding of bound dioxygen to the distal histidine of oxycobalt myoglobin and haemoglobin. Nature 1982, 298, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S.; Mathews, A.J.; Rohlfs, R.J.; Springer, B.A.; Egeberg, K.D.; Sligar, S.G.; Tame, J.; Renaud, J.P.; Nagai, K. The role of the distal histidine in myoglobin and haemoglobin. Nature 1988, 336, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perutz, M.F. Myoglobin and haemoglobin: Role of distal residues in reactions with haem ligands. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1989, 14, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlfs, R.J.; Mathews, A.J.; Carver, T.E.; Olson, J.S.; Springer, B.A.; Egeberg, K.D.; Sligar, S.G. The effects of amino acid substitution at position E7 (residue 64) on the kinetics of ligand binding to sperm whale myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 3168–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, R.E., Jr.; Smerdon, S.J.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Singleton, E.W.; Olson, J.S. The mechanism of autooxidation of myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 6995–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S.; Phillips, G.N., Jr. Kinetic pathways and barriers for ligand binding to myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17593–17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenzuela, J.G.; Walker, F.A.; Ribeiro, J.M. A salivary nitrophorin (nitric-oxide-carrying hemoprotein) in the bedbug Cimex lectularius. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Weichsel, A.; Andersen, J.F.; Champagne, D.E.; Walker, F.A.; Montfort, W.R. Crystal structures of a nitric oxide transport protein from a blood-sucking insect. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, J.F.; Montfort, W.R. The crystal structure of nitrophorin 2. A trifunctional antihemostatic protein from the saliva of Rhodnius prolixus. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30496–30503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weichsel, A.; Maes, E.M.; Andersen, J.F.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Shokhireva, T.K.; Walker, F.A.; Montfort, W.R. Heme-assisted S-nitrosation of a proximal thiolate in a nitric oxide transport protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersen, J.F. Structure and mechanism in salivary proteins from blood-feeding arthropods. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knipp, M.; Ogata, H.; Soavi, G.; Cerullo, G.; Allegri, A.; Abbruzzetti, S.; Bruno, S.; Viappiani, C.; Bidon-Chanal, A.; Luque, F.J. Structure and dynamics of the membrane attaching nitric oxide transporter nitrophorin 7. F1000Res 2015, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Simone, G.; Ascenzi, P.; Polticelli, F. Nitrobindin: An ubiquitous family of all β-barrel heme-proteins. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Simone, G.; Ascenzi, P.; di Masi, A.; Polticelli, F. Nitrophorins and nitrobindins: Structure and function. Biomol. Concepts 2017, 8, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, G.; di Masi, A.; Vita, G.M.; Polticelli, F.; Pesce, A.; Nardini, M.; Bolognesi, M.; Ciaccio, C.; Coletta, M.; Turilli, E.S.; et al. Mycobacterial and human nitrobindins: Structure and function. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichsel, A.; Andersen, J.F.; Roberts, S.A.; Montfort, W.R. Nitric oxide binding to nitrophorin 4 induces complete distal pocket burial. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 551–554. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, S.A.; Weichsel, A.; Qiu, Y.; Shelnutt, J.A.; Walker, F.A.; Montfort, W.R. Ligand-induced heme ruffling and bent no geometry in ultra-high-resolution structures of nitrophorin 4. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 11327–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, C.M.; Blouin, G.C.; Bitto, E.; Olson, J.S.; Phillips, G.N., Jr. The structure and NO binding properties of the nitrophorin-like heme-binding protein from Arabidopsis thaliana gene locus At1g79260.1. Proteins 2010, 78, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bianchetti, C.M.; Bingman, C.A.; Phillips, G.N., Jr. Structure of the C-terminal heme-binding domain of THAP domain containing protein 4 from Homo sapiens. Proteins 2011, 79, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Simone, G.; di Masi, A.; Polticelli, F.; Ascenzi, P. Human nitrobindin: The first example of an all-β-barrel ferric heme-protein that catalyzes peroxynitrite detoxification. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, T.G.; Li, X.Y. Biological Applications of Raman Spectroscopy; Spiro, T.G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Smulevich, G.; Feis, A.; Howes, B.D.; Ivancich, A. Handbook of Porphyrin Science; Kadish, K.M., Smith, K.M., Guilard, R., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, T.; Nagai, K.; Tsubaki, M. Assignment of the Fe-Nε (His F8) stretching band in the Resonance Raman spectra of deoxy myoglobin. FEBS Lett. 1979, 104, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smulevich, G.; Mantini, A.R.; Paoli, M.; Coletta, M.; Geraci, G. Resonance Raman studies of the heme active site of the homodimeric myoglobin from Nassa mutabilis: A peculiar case. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 7507–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiro, T.G.; Wasbotten, I.H. CO as a vibrational probe of heme protein active sites. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, G.N.; Teodoro, M.L.; Li, T.; Smith, B.; Olson, J.S. Bound CO is a molecular probe of electrostatic potential in the distal pocket of myoglobin. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1999, 103, 8817–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Spiro, T.G. Is bound carbonyl linear or bent in heme proteins? Evidence from resonance Raman and infrared spectroscopic data. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 6024–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, F.P.; Howes, B.D.; Fittipaldi, M.; Fanali, G.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Smulevich, G. Ibuprofen induces an allosteric conformational transition in the heme complex of human serum albumin with significant effects on heme ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11677–11688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayland, B.B.; Olson, L.W. Spectroscopic studies and bonding model for nitric oxide complexes of iron porphyrins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 6037–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, A.; Perutz, M.F. Equilibrium between six- and five-coordinated hemes in nitrosylhemoglobin: Interpretation of electron spin resonance spectra. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 4427–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, W.E. The study of hemoglobin by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Meth. Enzym. 1981, 76, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ascenzi, P.; Giacometti, G.M.; Antonini, E.; Rotilio, G.; Brunori, M. Equilibrium and kinetic evidence for a transition between six- and five-coordinate ferrous heme in the nitric oxide derivative of Aplysia myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 5383–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Coletta, M.; Desideri, A.; Polizio, F.; Condò, S.G.; Giardina, B. Effect of inositol hexakisphosphate on the spectroscopic properties of the nitric oxide derivative of ferrous horse and bovine hemoglobin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1990, 40, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Coletta, M.; Desideri, A.; Petruzzelli, R.; Polizio, F.; Bolognesi, M.; Condò, S.G.; Giardina, B. Spectroscopic properties of the nitric oxide derivative of ferrous man, horse, and ruminant hemoglobins: A comparative study. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1992, 45, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorslaer, S. Probing the structure-function relationship of heme proteins using multifrequency pulse EPR techniques. In High Resolution EPR: Applications to Metalloenzymes and Metals in Medicine; Hanson, G., Berliner, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Luchsinger, B.P.; Walter, E.D.; Lee, L.J.; Stamler, J.S.; Singel, D.J. EPR studies of the chemical dynamics of NO and hemoglobin. In High Resolution EPR: Applications to Metalloenzymes and Metals in Medicine; Hanson, G., Berliner, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Duprat, A.F.; Traylor, T.G.; Wu, G.-Z.; Coletta, M.; Sharma, V.S.; Walda, K.N.; Magde, D. Myoglobin-NO at low pH: Free four-coordinated heme in the protein pocket. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 2634–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Coletta, M.; Desideri, A.; Brunori, M. pH-induced cleavage of the proximal histidine to iron bond in the nitric oxide derivative of ferrous monomeric hemoproteins and of the “chelated” protoheme model compound. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 829, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbruzzetti, S.; He, C.; Ogata, H.; Bruno, S.; Viappiani, C.; Knipp, M. Heterogeneous kinetics of the carbon monoxide association and dissociation reaction to nitrophorin 4 and 7 coincide with structural heterogeneity of the gate-loop. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9986–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, E.; Brunori, M. Hemoglobin and Myoglobin in their Reactions with Ligands; North Holland Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Watanabe, M.; Hisaeda, Y.; Hayashi, T. Unusual ligand discrimination by a myoglobin reconstituted with a hydrophobic domain-linked heme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eich, R.F.; Li, T.; Lemon, D.D.; Doherty, D.H.; Curry, S.R.; Aitken, J.F.; Mathews, A.J.; Johnson, K.A.; Smith, R.D.; Phillips, G.N., Jr.; et al. Mechanism of NO-induced oxidation of myoglobin and hemoglobin. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 6976–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.G.; Gibson, Q.H. Cooperativity in the dissociation of nitric oxide from hemoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 2788–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunori, M.; Schuster, T.M. Kinetic studies of ligand binding to hemoglobin and its isolated subunits by the temperature jump relaxation method. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 4046–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Traylor, T.G.; Brunori, M. Kinetics of carbon monoxide binding to monomeric hemoproteins. Role of the proximal histidine. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 4151–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalakis, V.; Varotsis, C. Binding and docking interactions of NO, CO and O2 in heme proteins as probed by density functional theory. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kharitonov, V.G.; Sharma, V.S.; Pilz, R.B.; Magde, D.; Koesling, D. Basis of guanylate cyclase activation by carbon monoxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2568–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liebl, U.; Lambry, J.C.; Vos, M.H. Primary processes in heme-based sensor proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geibel, J.; Chang, C.K.; Traylor, T.G. Coordination of myoglobin active site models in aqueous solution as studied by kinetic methods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 5924–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacometti, G.M.; Traylor, T.G.; Ascenzi, P.; Brunori, M.; Antonini, E. Reactivity of ferrous myoglobin at low pH. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 7447–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traylor, T.G.; Deardurff, L.A.; Coletta, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Antonini, E.; Brunori, M. Reactivity of ferrous heme proteins at low pH. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 12147–12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Brunori, M. Kinetic evidence for a role of heme geometry on the modulation of carbon monoxide reactivity in human hemoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 18286–18289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, M.; Boffi, A.; Ascenzi, P.; Brunori, M.; Chiancone, E. A novel mechanism of heme-heme interaction in the homodimeric hemoglobin from Scapharca inaequivalvis as manifested upon cleavage of the proximal Fe-Nε bond at low pH. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 4828–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Smulevich, G.; Mantini, A.R.; Del Gaudio, R.; Piscopo, M.; Geraci, G. Alteration of the proximal bond energy in the unliganded form of the homodimeric myoglobin from Nassa mutabilis. Kinetic and spectroscopic evidence. FEBS Lett. 1992, 296, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coletta, M.; Ascenzi, P.; D’Avino, R.; Di Prisco, G. Proton-linked subunit kinetic heterogeneity for carbon monoxide binding to hemoglobin from Chelidonichtys kumu. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 29859–29864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coletta, M.; Costa, H.; De Sanctis, G.; Neri, F.; Smulevich, G.; Turner, D.L.; Santos, H. pH-dependence of structural and functional properties of oxidized cytochrome c” from Methylophilus methylotrophus. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24800–24804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ansari, A.; Jones, C.M.; Henry, E.R.; Hofrichter, J.; Eaton, W.A. Conformational relaxation and ligand binding in myoglobin. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5128–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbruzzetti, S.; Tilleman, L.; Bruno, S.; Viappiani, C.; Desmet, F.; Van Doorslaer, S.; Coletta, M.; Ciaccio, C.; Ascenzi, P.; Nardini, M.; et al. Ligation tunes protein reactivity in an ancient haemoglobin: Kinetic evidence for an allosteric mechanism in Methanosarcina acetivorans protoglobin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, T.Y.; Srajer, V.; Moffat, K. Photolysis-induced structural changes in single crystals of carbonmonoxy myoglobin at 40 K. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1994, 1, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Vojtechovsky, J.; Mcmahon, B.H.; Sweet, R.M.; Berendzen, J.; Schlichting, I. Crystal structure of a new ligand binding intermediate in wildtype carbonmonoxy myoglobin. Nature 2000, 403, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, R.M.; Lopes Jesus, A.J.; Santos, R.M.; Pereira, C.L.; Marques, C.F.; Rocha, B.S.; Ferreira, N.R.; Ledo, A.; Laranjin, J. Preparation, standardization, and measurement of nitric oxide solutions. Glob. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 2, 272–284. [Google Scholar]
- Tognaccini, L.; Ciaccio, C.; D’Oria, V.; Cervelli, M.; Howes, B.D.; Coletta, M.; Mariottini, P.; Smulevich, G.; Fiorucci, L. Structure-function relationships in human cytochrome c: The role of Tyr67. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 155, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, S.; Schweiger, A. EasySpin, a comprehensive software package for spectral simulation and analysis in EPR. J. Magn. Reson. 2006, 178, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Coletta, A.; Cao, Y.; Trezza, V.; Leboffe, L.; Fanali, G.; Fasano, M.; Pesce, A.; Ciaccio, C.; Marini, S.; et al. Isoniazid inhibits the heme-based reactivity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis truncated hemoglobin N. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbruzzetti, S.; Bruno, S.; Faggiano, S.; Grandi, E.; Mozzarelli, A.; Viappiani, C. Time-resolved methods in Biophysics 2. Monitoring haem proteins at work with nanosecond laser flash photolysis. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2006, 5, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; De Simone, G.; Polticelli, F.; Gioia, M.; Coletta, M. Reductive nitrosylation of ferric human hemoglobin bound to human haptoglobin 1-1 and 2-2. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 23, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

















| Heme-Protein | Ligand | kon (M−1 s−1) | koff (s−1) | K (=koff/kon; M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At-Nb(II) b | CO | 2.3 × 105 | 5.0 × 10−2 | 2.2 × 10−7 |
| Mt-Nb(II) c | CO | 5.5 × 104 1.6 × 105 (~40%) 8.3 × 104 (~60%) | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 6.3 × 10−5 |
| Hs-Nb(II) c | CO | 1.0 × 105 3.9 × 106 (~15%) 1.7 × 105 (~85%) | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 3.8 × 10−5 |
| Rp-NP4(II) d | CO | 4.5 × 107 (77%) 1.9 × 107 (23%) | 9.7 × 10−3 (77%) 4.1 × 10−3 (23%) | 2.2 × 10−10 2.2 × 10−10 |
| Rp-NP7(II) d | CO | 5.0 × 107 | 4.4 × 10−3 (30%) 7.6 × 10−4 (70%) | 8.8 × 10−11 1.5 × 10−11 |
| Ec-Mb(II) | CO | 5.0 × 105 e 6.1 × 105 f | 3.5 × 10−2 | 5.7 × 10−8 |
| Pc-Mb(II) g | CO | 5.1 × 105 | 1.9 × 10−2 | 3.7 × 10−8 |
| At-Nb(II) b | NO | 8.1 × 107 | ~8 × 10−2 | ~1 × 10−9 |
| Mt-Nb(II) c | NO | 1.7 × 106 | 6.8 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−8 |
| Hs-Nb(II) c | NO | 9.3 × 105 1.5 × 107 (12%) 8.5 × 105 (88%) | 2.1 × 10−2 | 2.3 × 10−8 1.4 × 10−9 2.5 × 10−8 |
| Rp-NP(II) | NO | |||
| Ec-Mb(II) | NO | |||
| Pc-Mb(II) | NO | 2.2 × 107h | 1.2 × 10−4 h,i | 5.5 × 10−12 |
| At-Nb(II) c | O2 | − | 6.8 | − |
| Mt-Nb(II) c | O2 | − | 1.1 × 101 | − |
| Hs-Nb(II) c | O2 | − | 1.9 × 101 | − |
| Rp-NP(II) | O2 | − | − | |
| Ec-Mb(II) j | O2 | − | 1.0 × 101 | − |
| Pc-Mb(II) k | O2 | − | 1.0 × 101 | − |
| Mt-Nb(II) | Hs-Nb(II) | |
|---|---|---|
| ΔH1‡ (kJ/mol) | 32 ± 2 | 38 ± 4 |
| ΔS1‡ (kJ/(mol·K)) | −33 ± 4 | 0 ± 10 |
| ΔG1‡ (kJ/mol) at 20.0 °C | 42 ± 3 | 35 ± 12 |
| ΔH2‡ (kJ/mol) | 36 ± 4 | 38 ± 4 |
| ΔS2‡ (kJ/mol·K) | −29 ± 8 | ‒21 ± 8 |
| ΔG2‡ (kJ/mol) at 20.0 °C | 44 ± 4 | 42 ± 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Simone, G.; di Masi, A.; Pesce, A.; Bolognesi, M.; Ciaccio, C.; Tognaccini, L.; Smulevich, G.; Abbruzzetti, S.; Viappiani, C.; Bruno, S.; et al. Mycobacterial and Human Ferrous Nitrobindins: Spectroscopic and Reactivity Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041674
De Simone G, di Masi A, Pesce A, Bolognesi M, Ciaccio C, Tognaccini L, Smulevich G, Abbruzzetti S, Viappiani C, Bruno S, et al. Mycobacterial and Human Ferrous Nitrobindins: Spectroscopic and Reactivity Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041674
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Simone, Giovanna, Alessandra di Masi, Alessandra Pesce, Martino Bolognesi, Chiara Ciaccio, Lorenzo Tognaccini, Giulietta Smulevich, Stefania Abbruzzetti, Cristiano Viappiani, Stefano Bruno, and et al. 2021. "Mycobacterial and Human Ferrous Nitrobindins: Spectroscopic and Reactivity Properties" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041674
APA StyleDe Simone, G., di Masi, A., Pesce, A., Bolognesi, M., Ciaccio, C., Tognaccini, L., Smulevich, G., Abbruzzetti, S., Viappiani, C., Bruno, S., Monaca, S. D., Pietraforte, D., Fattibene, P., Coletta, M., & Ascenzi, P. (2021). Mycobacterial and Human Ferrous Nitrobindins: Spectroscopic and Reactivity Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041674