The Role of Collagen Triple Helix Repeat-Containing 1 Protein (CTHRC1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
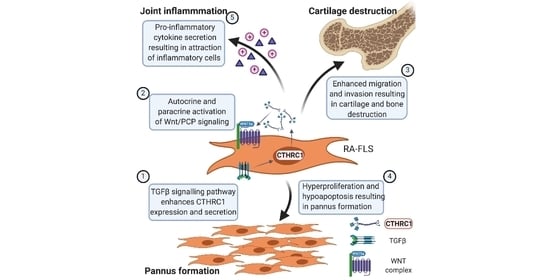
:1. Introduction
2. CTHRC1 Domain Structure
3. Identification and Physiological Function of CTHRC1
4. Expression of CTHRC1
5. Signaling Roles of CTHRC1
5.1. Role of CTHRC1 in the TGF-β Pathway
5.2. CTHRC1 Is a Component of Canonical and Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathways
6. CTHRC1 Is Associated with RA Development and Disease Severity
7. Invasive Synoviocytes Are Key Drivers of Joint Destruction in RA
8. RA-FLS Are One Source of CTHRC1
9. CTHRC1 Plays a Central Role in Bone Remodeling
10. Sex Disparity and CTHRC1
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACPA | Anti-citrullinated protein antibody |
| ADAMTs12 | A disintegrin and metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 12 |
| Ang2 | angiopoietin 2 |
| BMP2/4 | Bone morphogenetic protein 2/4 |
| CAIA | Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis |
| CCL2 | C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 |
| CD34, CD90 | Cluster of differentiation 34/90 |
| CDH11 | cadherin 11 |
| COMP | cartilage oligomeric matrix protein |
| C1qtnf3 | Complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 3 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CSF-1 | Colony stimulating factor 1 |
| CTHRC1 | Collagen triple helix repeat-containing 1 protein |
| CXCL12 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 12 |
| Daam2 | Dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis |
| DPAGT 1 | Dolichyl-Phosphate N-Acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase 1 |
| Dvl | Dishevelled |
| FZD | Frizzled |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta |
| IL-1/6/8/11/15 | Interleukin 1/6/8/11/15 |
| INF-γ | Interferon gamma |
| LRP | Lipoprotein receptor-related protein |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| OPG | Osteoprotegerin |
| PCP Pathway | Planar cell polarity pathway |
| Pgia8 | Proteoglycan induced arthritis 8 |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RA-FLS | Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast like synoviocyte |
| RANKL | Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B ligand |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| ROR2 | Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 |
| RSPO2 | R-spondin 2 |
| Sdc2 | Syndecan 2 |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SMAD 2/3/4 | The abbreviation refers to the homologies to the Caenorhabditis elegans “small” worm phenotype and Drosophila MAD (“Mothers Against Decapentaplegic”) family of genes |
| SOST | Sclerostin |
| TPBG | trophoblast glycoprotein |
| TCF | T cell factor |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| THY1 | Thy-1 Cell Surface Antigen |
| VANGL2 | VANGL planar cell polarity protein 2 |
| WAIF1 | Wnt-activated inhibitory factor 1 |
| Wnt | Wingless and Int-1 |
References
- Gibofsky, A. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: A Synopsis. Am. J. Manag. Care 2014, 20, S128–S135. [Google Scholar]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, M. Development of anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, P.; Mueller, R.B. Treatment with Biologicals in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Rheumatol. Ther. 2017, 4, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brzustewicz, E.; Bryl, E. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis--Practical and potential application of cytokines as biomarkers and targets of personalized therapy. Cytokine 2015, 76, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Delft, M.A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myngbay, A.; Bexeitov, Y.; Adilbayeva, A.; Assylbekov, Z.; Yevstratenko, B.P.; Aitzhanova, R.M.; Matkarimov, B.; Adarichev, V.A.; Kunz, J. CTHRC1: A New Candidate Biomarker for Improved Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, T.; Liu, Y.; Tan, L.; Huang, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Song, L.; et al. Value of serum collagen triple helix repeat containing-1(CTHRC1) and 14-3-3eta protein compared to anti-CCP antibodies and anti-MCV antibodies in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, F.; Slowikowski, K.; Wei, K.; Marshall, J.L.; Rao, D.A.; Chang, S.K.; Nguyen, H.N.; Noss, E.H.; Turner, J.D.; Earp, B.E.; et al. Functionally distinct disease-associated fibroblast subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Kwan, K.M.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, J.M.; Darnay, B.G.; Behringer, R.R.; Nakamura, T.; de Crombrugghe, B.; Akiyama, H. Cthrc1 is a positive regulator of osteoblastic bone formation. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, S.; Fumoto, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Park, K.A.; Aburatani, H.; Kato, S.; Ito, M.; Ikeda, K. Osteoclast-secreted CTHRC1 in the coupling of bone resorption to formation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyagay, P.; Heroult, M.; Wang, Q.; Lehnert, W.; Belden, J.; Liaw, L.; Friesel, R.E.; Lindner, V. Collagen triple helix repeat containing 1, a novel secreted protein in injured and diseased arteries, inhibits collagen expression and promotes cell migration. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclere, L.; Nir, T.S.; Bazarsky, M.; Braitbard, M.; Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Gat, U. Dynamic Evolution of the Cthrc1 Genes, a Newly Defined Collagen-Like Family. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 3957–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, U.; Gaboriaud, C.; Waters, P.; Shrive, A.K.; Greenhough, T.J.; Reid, K.B.; Sim, R.B.; Arlaud, G.J. C1q and tumor necrosis factor superfamily: Modularity and versatility. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Nishimura, O.; Misaki, K.; Nishita, M.; Minami, Y.; Yonemura, S.; Tarui, H.; Sasaki, H. Cthrc1 selectively activates the planar cell polarity pathway of Wnt signaling by stabilizing the Wnt-receptor complex. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeClair, R.; Lindner, V. The role of collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 in injured arteries, collagen expression, and transforming growth factor beta signaling. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Togo, S.; Kadoya, K.; Tulafu, M.; Namba, Y.; Iwai, M.; Watanabe, J.; Nagahama, K.; Okabe, T.; Hidayat, M.; et al. Pirfenidone attenuates lung fibrotic fibroblast responses to transforming growth factor-beta1. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, Y.; Tedrow, J.; de Bernard, S.; Birker-Robaczewska, M.; Gibson, K.F.; Guardela, B.J.; Hess, P.; Klenk, A.; Lindell, K.O.; Poirey, S.; et al. A novel genomic signature with translational significance for human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, C.; Tian, G.; Li, Q.; et al. Autocrine CTHRC1 activates hepatic stellate cells and promotes liver fibrosis by activating TGF-beta signaling. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.K.; Li, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.R.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; You, Z.R.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B.Y.; Miao, Q.; et al. CTHRC1 expression in primary biliary cholangitis. J. Dig. Dis. 2019, 20, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Miao, Q.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, C.; Shen, L.; Yang, F.; et al. Treatment of cholestatic fibrosis by altering gene expression of Cthrc1: Implications for autoimmune and non-autoimmune liver disease. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 63, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binks, A.P.; Beyer, M.; Miller, R.; LeClair, R.J. Cthrc1 lowers pulmonary collagen associated with bleomycin-induced fibrosis and protects lung function. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukui, T.; Sun, K.H.; Wetter, J.B.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Hazelwood, L.A.; Henderson, N.C.; Adams, T.S.; Schupp, J.C.; Poli, S.D.; Rosas, I.O.; et al. Collagen-producing lung cell atlas identifies multiple subsets with distinct localization and relevance to fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Villalba, A.; Romero, J.P.; Hernandez, S.C.; Vilas-Zornoza, A.; Fortelny, N.; Castro-Labrador, L.; San Martin-Uriz, P.; Lorenzo-Vivas, E.; Garcia-Olloqui, P.; Palacio, M.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis Reveals a Crucial Role for CTHRC1 (Collagen Triple Helix Repeat Containing 1) Cardiac Fibroblasts After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2020, 142, 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhang, W.; Tan, L.; Yang, H.; Ge, M.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, R.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Luo, Z.; et al. Hepatitis B virus hijacks CTHRC1 to evade host immunity and maintain replication. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 7, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Cao, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhu, C.; Li, R.; He, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, F.; Wu, J. The collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 facilitates hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating multiple cellular factors and signal cascades. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Sun, H. Role of collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 in tumor and inflammatory diseases. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 13, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Yang, Z.; Ke, Z. Multidimensional Roles of Collagen Triple Helix Repeat Containing 1 (CTHRC1) in Malignant Cancers. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durmus, T.; LeClair, R.J.; Park, K.S.; Terzic, A.; Yoon, J.K.; Lindner, V. Expression analysis of the novel gene collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 (Cthrc1). Gene Expr. Patterns 2006, 6, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclair, R.J.; Wang, Q.; Benson, M.A.; Prudovsky, I.; Lindner, V. Intracellular localization of Cthrc1 characterizes differentiated smooth muscle. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, C.W.; Stohn, J.P.; Wang, Q.; Emery, I.F.; Prueser, A.; Lindner, V. Elevated plasma levels of the pituitary hormone Cthrc1 in individuals with red hair but not in patients with solid tumors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derynck, R.; Budi, E.H. Specificity, versatility, and control of TGF-beta family signaling. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaav5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzavlaki, K.; Moustakas, A. TGF-beta Signaling. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vander Ark, A.; Cao, J.; Li, X. TGF-beta receptors: In and beyond TGF-beta signaling. Cell Signal. 2018, 52, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, X.Y.; Shen, Z.Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yu, J.; Zhu, J.D.; Lu, Y.Y.; Fang, J.Y. CTHRC1 is upregulated by promoter demethylation and transforming growth factor-beta1 and may be associated with metastasis in human gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeClair, R.J.; Durmus, T.; Wang, Q.; Pyagay, P.; Terzic, A.; Lindner, V. Cthrc1 is a novel inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling and neointimal lesion formation. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, K.; Kubo, M.; Sato, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Tamaki, K. Serum tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1995, 33, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, C.G.; Yang, Y.Y.; He, X.; Li, X.F.; Huang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Jin, Y.; Li, J. Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Sengupta, P.K.; Jamal, B.; Yang, H.Y.; Bouchie, M.P.; Lindner, V.; Varelas, X.; Kukuruzinska, M.A. N-glycosylation induces the CTHRC1 protein and drives oral cancer cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20217–20227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, P.K.; Bouchie, M.P.; Kukuruzinska, M.A. N-glycosylation gene DPAGT1 is a target of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31164–31173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, C.Y.; Pan, Y.F.; Guo, X.H.; Wu, Y.Q.; Gu, J.R.; Cai, D.Z. Expression of beta-catenin in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 40, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Vold, S.; Olvera-Jaramillo, C.; Chang, H. Functional redundancy of frizzled 3 and frizzled 6 in planar cell polarity control of mouse hair follicles. Development 2018, 145, dev168468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kagermeier-Schenk, B.; Wehner, D.; Ozhan-Kizil, G.; Yamamoto, H.; Li, J.; Kirchner, K.; Hoffmann, C.; Stern, P.; Kikuchi, A.; Schambony, A.; et al. Waif1/5T4 inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and activates noncanonical Wnt pathways by modifying LRP6 subcellular localization. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adarichev, V.A.; Nesterovitch, A.B.; Bardos, T.; Biesczat, D.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Vermes, C.; Mikecz, K.; Finnegan, A.; Glant, T.T. Sex effect on clinical and immunologic quantitative trait loci in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtseva, E.; Forde, T.S.; Pucker, A.D.; Adarichev, V.A. Wnt signaling genes of murine chromosome 15 are involved in sex-affected pathways of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adarichev, V.A.; Vegvari, A.; Szabo, Z.; Kis-Toth, K.; Mikecz, K.; Glant, T.T. Congenic strains displaying similar clinical phenotype of arthritis represent different immunologic models of inflammation. Genes Immun. 2008, 9, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glant, T.T.; Szanto, S.; Vegvari, A.; Szabo, Z.; Kis-Toth, K.; Mikecz, K.; Adarichev, V.A. Two loci on chromosome 15 control experimentally induced arthritis through the differential regulation of IL-6 and lymphocyte proliferation. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Libioulle, C.; Louis, E.; Hansoul, S.; Sandor, C.; Farnir, F.; Franchimont, D.; Vermeire, S.; Dewit, O.; de Vos, M.; Dixon, A.; et al. Novel Crohn disease locus identified by genome-wide association maps to a gene desert on 5p13.1 and modulates expression of PTGER4. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, T.; Hoffjan, S.; Hayes, M.G.; Schneider, D.; Nicolae, R.; Heinzmann, A.; Jerkic, S.P.; Parry, R.; Cox, N.J.; Deichmann, K.A.; et al. Fine mapping and positional candidate studies on chromosome 5p13 identify multiple asthma susceptibility loci. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Kong, W.; Xu, K.; Luan, Y.; Ilalov, K.; Sehgal, B.; Yu, S.; Howell, R.D.; Di Cesare, P.E. ADAMTS-12 associates with and degrades cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15800–15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wright, G.L.; Peterson, J.M. C1q/TNF-Related Protein 3 (CTRP3) Function and Regulation. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Min, J.Y.; Baek, J.M.; Ahn, S.J.; Jun, H.Y.; Yoon, K.H.; Choi, M.K.; Lee, M.S.; Oh, J. CTRP3 acts as a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis through AMPK-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling in vitro and RANKL-induced calvarial bone destruction in vivo. Bone 2015, 79, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, M.A.; Kakuta, S.; Maruhashi, T.; Shimizu, K.; Seno, A.; Kubo, S.; Sato, N.; Saijo, S.; Hattori, M.; Iwakura, Y. CTRP3 plays an important role in the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Li, M. Genome-wide linkage and association analysis of rheumatoid arthritis in a Canadian population. BMC Proc. 2007, 1 (Suppl. 1), S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jawaheer, D.; Seldin, M.F.; Amos, C.I.; Chen, W.V.; Shigeta, R.; Etzel, C.; Damle, A.; Xiao, X.; Chen, D.; Lum, R.F.; et al. Screening the genome for rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility genes: A replication study and combined analysis of 512 multicase families. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.; Halder, I.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Weeks, D.E. Two-dimensional linkage analyses of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Proc. 2007, 1 (Suppl. 1), S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plant, D.; Bowes, J.; Potter, C.; Hyrich, K.L.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register; Barton, A. Genome-wide association study of genetic predictors of anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis identifies associations with polymorphisms at seven loci. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Sun, H. Collagen triple helix repeat containing-1: A novel biomarker associated with disease activity in Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2018, 27, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvaifler, N.J.; Firestein, G.S. Pannus and pannocytes. Alternative models of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravallese, E.M. Bone destruction in arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61 (Suppl. 2), ii84–ii86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G. Synovitis--an inflammation of joints destroying the bone. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2012, 142, w13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R.; Gravallese, E.M. Pathogenesis of bone lesions in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2002, 4, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartok, B.; Firestein, G.S. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, S.; Mima, T.; Sasai, M.; Nishioka, K.; Shimizu, M.; Murata, N.; Yoshikawa, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Suemura, M.; McCloskey, R.V.; et al. Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) interferes with Fas-mediated apoptotic cell death on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial cells: A possible mechanism of rheumatoid synovial hyperplasia and a clinical benefit of anti-TNF-alpha therapy for RA. Cytokine 2000, 12, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhani, M.T.; Forde, T.S.; Adilbayeva, A.; Ramez, M.; Myngbay, A.; Bexeitov, Y.; Lindner, V.; Adarichev, V.A. Collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 is a new promigratory marker of arthritic pannus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindqvist, E.; Jonsson, K.; Saxne, T.; Eberhardt, K. Course of radiographic damage over 10 years in a cohort with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machold, K.P.; Stamm, T.A.; Nell, V.P.; Pflugbeil, S.; Aletaha, D.; Steiner, G.; Uffmann, M.; Smolen, J.S. Very recent onset rheumatoid arthritis: Clinical and serological patient characteristics associated with radiographic progression over the first years of disease. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abuwarwar, M.H.; Knoblich, K.; Fletcher, A.L. A pathogenic hierarchy for synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, H.; Boyle, D.L.; Firestein, G.S. Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein-3 regulation and microsatellite structure in arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 2106–2114. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Nawata, M.; Wakitani, S. Expression profiles and functional analyses of Wnt-related genes in human joint disorders. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sen, M.; Lauterbach, K.; El-Gabalawy, H.; Firestein, G.S.; Corr, M.; Carson, D.A. Expression and function of wingless and frizzled homologs in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D.W.; Ha, Y.; Ihm, M.H.; Kim, H.; Song, K.; Lee, I. Wnt5a induces endothelial inflammation via beta-catenin-independent signaling. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauner, M.; Stein, N.; Winzer, M.; Goettsch, C.; Zwerina, J.; Schett, G.; Distler, J.H.; Albers, J.; Schulze, J.; Schinke, T.; et al. WNT5A is induced by inflammatory mediators in bone marrow stromal cells and regulates cytokine and chemokine production. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, M.; Chamorro, M.; Reifert, J.; Corr, M.; Carson, D.A. Blockade of Wnt-5A/frizzled 5 signaling inhibits rheumatoid synoviocyte activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.; Oronsky, B.; Carter, C.A.; Oronsky, A.; Knox, S.J.; Sher, D.; Reid, T.R. TGF-beta: A master immune regulator. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, H.; Yu, S.J.; Yoo, D.H.; Chae, I.J.; Song, G.G.; Sohn, J. Increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and metalloproteinase-1 by TGF-beta1 in synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis and normal individuals. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 127, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schett, G.; Gravallese, E. Bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.Y.; Yoshida, H.; Sarosi, I.; Tan, H.L.; Timms, E.; Capparelli, C.; Morony, S.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J.; Van, G.; Itie, A.; et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature 1999, 397, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geusens, P. The role of RANK ligand/osteoprotegerin in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2012, 4, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jann, J.; Gascon, S.; Roux, S.; Faucheux, N. Influence of the TGF-beta Superfamily on Osteoclasts/Osteoblasts Balance in Physiological and Pathological Bone Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gu, W.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Xu, X.; Wen, Y. CTHRC1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells by regulating TAZ. J. Mol. Histol. 2017, 48, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.; Kohara, Y.; Naoe, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Ito, M.; Ikeda, K.; Takeshita, S. WAIF1 Is a Cell-Surface CTHRC1 Binding Protein Coupling Bone Resorption and Formation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.R.; Stohn, J.P.; Wang, Q.; Nagano, K.; Baron, R.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Rosen, C.J.; Adarichev, V.A.; Lindner, V. Inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and collagen antibody-induced arthritis by CTHRC1. Bone 2017, 97, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ohira, T. Mechanisms and therapeutic targets for bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis, in particular the RANK-RANKL system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 40, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Calle, J.; Sato, A.Y.; Bellido, T. Role and mechanism of action of sclerostin in bone. Bone 2017, 96, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldring, S.R.; Purdue, P.E.; Crotti, T.N.; Shen, Z.; Flannery, M.R.; Binder, N.B.; Ross, F.P.; McHugh, K.P. Bone remodelling in inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72 (Suppl. 2), ii52–ii55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Pluchino, N.; Canny, G.; Gabay, C.; Finckh, A. The role of female hormonal factors in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taneja, V. Sex Hormones Determine Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islander, U.; Jochems, C.; Lagerquist, M.K.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Carlsten, H. Estrogens in rheumatoid arthritis; the immune system and bone. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Cell Type | Potential Effect on Cells | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS) | Proliferation, migration, initiation of cartilage destruction | [66] |
| Osteoclasts | Inhibition of osteoblast differentiation and osteoblast driven bone formation; | [10,11,82,83] |
| activates WAIF1/PKCδ/ERK pathway necessary for RANKL expression leading to reduced bone resorption and formation | [83] | |
| Osteoblasts | Inhibition of monocyte-osteoclast differentiation and osteoclast-driven bone resorption in trabecular bone, inhibition of NFκB-dependent signaling; CTHRC1 may additionally suppress RANKL expression | [84] |
| Osteocytes | Inhibition of monocyte-osteoclast differentiation and osteoclast driven bone resorption in trabecular bone, inhibition of NFκB-dependent signaling; CTHRC1 may additionally suppress RANKL expression | [84] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Myngbay, A.; Manarbek, L.; Ludbrook, S.; Kunz, J. The Role of Collagen Triple Helix Repeat-Containing 1 Protein (CTHRC1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052426
Myngbay A, Manarbek L, Ludbrook S, Kunz J. The Role of Collagen Triple Helix Repeat-Containing 1 Protein (CTHRC1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052426
Chicago/Turabian StyleMyngbay, Askhat, Limara Manarbek, Steve Ludbrook, and Jeannette Kunz. 2021. "The Role of Collagen Triple Helix Repeat-Containing 1 Protein (CTHRC1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052426
APA StyleMyngbay, A., Manarbek, L., Ludbrook, S., & Kunz, J. (2021). The Role of Collagen Triple Helix Repeat-Containing 1 Protein (CTHRC1) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052426