Berberine Delays Onset of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through T Cell Suppression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Berberine delays the onset of collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice.
- Berberine treatment reduces splenic and lymph node CXCR5+ follicular T helper (Tfh) cell populations.
- Berberine polarizes splenic and lymph node T cells toward a CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory (Treg) phenotype.
2. Results
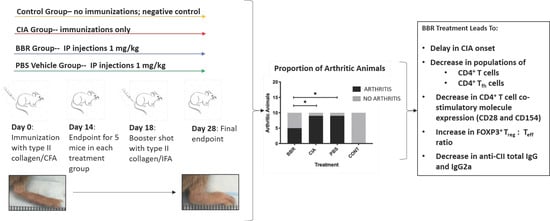
2.1. Berberine Treatment Delays Onset of CIA
2.2. The Effect of Berberine on Circulating Anti-CII IgG in the CIA Model
2.3. Key CD4+T Cell Population and Co-Stimulatory Molecule Characteristics in Response to Berberine Treatment
2.4. Berberine Treatment Leads to Increased Proportion of Foxp3+CD4+CD25+ T Cells
2.5. Key CD19+B Cell Population and Co-Stimulatory Molecule Characteristics in Response to Berberine Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Reagents
4.2. Berberine Solution
4.3. Antibodies
4.4. Mice
4.5. CIA Induction and Assessment
4.6. ELISA
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Katiyar, S.; Singh, A.; Misra, R.; Aggarwal, A. CD39 positive regulatory T cell frequency as a biomarker of treatment response to methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, V.C.; Vital, E.M.; Fonseca, J.E.; Buch, M.H. Right drug, right patient, right time: Aspiration or future promise for biologics in rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Nies, J.A.B.; Tsonaka, R.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Fautrel, B.; Van Der Helm-Van Mil, A.H.M. Evaluating relationships between symptom duration and persistence of rheumatoid arthritis: Does a window of opportunity exist? Results on the Leiden Early Arthritis Clinic and ESPOIR cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saevarsdottir, S.; Wallin, H.; Seddighzadeh, M.; Ernestam, S.; Geborek, P.; Petersson, I.F.; Bratt, J.; Van Vollenhoven, R.F. Predictors of response to methotrexate in early DMARD naïve rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the initial open-label phase of the SWEFOT trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steenbergen, H.W.; Da Silva, J.A.P.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Van Der Helm-Van Mil, A.H.M. Preventing progression from arthralgia to arthritis: Targeting the right patients. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Effectiveness profiles and dose dependent retention of traditional disease modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. An observational study. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebina, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamamoto, W.; Ohnishi, A.; Kabata, D.; Hirano, T.; Hara, R.; Katayama, M.; Yoshida, S.; Nagai, K.; et al. Drug retention and discontinuation reasons between seven biologics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—The ANSWER cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebina, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamamoto, W.; Hirano, T.; Hara, R.; Katayama, M.; Onishi, A.; Nagai, K.; Son, Y.; Amuro, H.; et al. Correction to: Drug tolerability and reasons for discontinuation of seven biologics in 4466 treatment courses of rheumatoid arthritis—The ANSWER cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonafede, M.; Johnson, B.H.; Tang, D.H.; Harrison, D.J.; Stolshek, B.S. Compliance and cost of biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Pharm. Benefits 2017, 9, e1–e7. [Google Scholar]
- Niewold, T.B.; Harrison, M.J.; Paget, S.A. Anti-CCP antibody testing as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. QJM Int. J. Med. 2007, 100, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deane, K.D.; Striebich, C.C.; Holers, V.M. Editorial: Prevention of rheumatoid arthritis: Now is the time, but how to proceed? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deane, K.D. Preclinical rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis prevention. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, K.D.; Norris, J.M.; Holers, V.M. Preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: Identification, evaluation, and future directions for investigation. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 36, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Guan, Y.; Lu, M. The use of berberine for women with polycystic ovary syndrome undergoing IVF treatment. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kuang, H.; Ng, E.H.Y.; Hou, L.; Wu, X. Effect of berberine on insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Study protocol for a randomized multicenter controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Xue, R.; Wu, J.D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, S.K.; Zhou, Z.X.; Song, D.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 2010, 59, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Xing, H.; Ye, J. Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2008, 57, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Tao, C.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Pan, Q.; Zheng, L.; Li, Q.; Song, Z.; Fichna, J. A Randomized clinical trial of berberine hydrochloride in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Phyther. Res. 2015, 29, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeczek, M.; Moy, L.; Lake, E.P.; Swan, J. Review of the efficacy and safety of topical mahonia aquifolium for the treatment of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2018, 11, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Oben, J.; Enonchong, E.; Kothari, S.; Chambliss, W.; Garrison, R.; Dolnick, D. Phellodendron and citrus extracts benefit joint health in osteoarthritis patients: A pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr. J. 2009, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.-H.; Zeng, X.-J.; Li, Y.-Y. Efficacy and safety of berberine for congestive heart failure secondary to ischemic or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 92, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.-M.; Xia, M.-F.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X.-X.; Yao, X.-Z.; Rao, S.-X.; Zeng, M.-S.; Tu, Y.-F.; Feng, R.; Jia, W.-P.; et al. Efficacy of berberine in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Jiao, Q.; Ding, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, R.; Shan, L.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Berberine induces dendritic cell apoptosis and has therapeutic potential for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Gao, J.; Tu, S.; Rao, Z. Berberine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in rats associated with anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic effects. Inflammation 2014, 37, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, C.-F.; Guo, C.-R.; Wang, C.-Z.; Yuan, C.-S. Anti-arthritic effect of berberine on adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Xia, Y.; Shi, C.; Guan, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Wei, Z.; Dai, Y. Berberine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in rats by suppressing Th17 cell responses via inducing cortistatin in the gut. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 2786–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Geng, Y.-N.; Jiang, J.-D.; Kong, W.-J. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory activities of berberine in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 289264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, L.; Washington, M.K.; Chaturvedi, R.; Israel, D.A.; Cao, H.; Wang, B.; et al. Berberine promotes recovery of colitis and inhibits inflammatory responses in colonic macrophages and epithelial cells in DSS-treated mice. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G504–G514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, H.; Hu, D.; Fatima, S.; Lin, C.; Mu, H.; Lee, N.P.; Bian, Z. Berberine ameliorates chronic relapsing dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in C57BL/6 mice by suppressing Th17 responses. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 110, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, A.; Zhu, C.; Pi, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, D.; Chen, X. The protective effect of berberine against neuronal damage by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-9 and laminin degradation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurol. Res. 2013, 35, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tu, S.; Yang, S.; Shen, P.; Huang, Y.; Ba, X.; Lin, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, K.; et al. Berberine modulates LPA function to inhibit the proliferation and inflammation of FLS-RA via p38/ERK MAPK pathway mediated by LPA1. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinesh, P.; Rasool, M.K. Berberine mitigates IL-21/IL-21R mediated autophagic influx in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and regulates Th17/Treg imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis. Apoptosis 2019, 24, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; He, R.; Pei, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; et al. Anti-arthritis effect of berberine associated with regulating energy metabolism of macrophages through AMPK/ HIF-1α pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Jiao, Y.; Miao, L.; Chen, J.-h.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A. Immunomodulatory effects of berberine on the inflamed joint reveal new therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis management. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12234–12245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschovakis, G.L.; Bubke, A.; Friedrichsen, M.; Falk, C.S.; Feederle, R.; Förster, R. T cell specific Cxcr5 deficiency prevents rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; He, J.; Han, Y.; Jie, H.; He, Y.; Sun, E. Novel function of hydroxychloroquine: Down regulation of T follicular helper cells in collagen-induced arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, S. T follicular helper cell differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity 2014, 41, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dekkers, J.S.; Schoones, J.W.; Huizinga, T.W.; Toes, R.E.; Van Der Helm-Van Mil, A.H. Possibilities for preventive treatment in rheumatoid arthritis? Lessons from experimental animal models of arthritis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podojil, J.R.; Miller, S.D. Molecular mechanisms of T-cell receptor and costimulatory molecule ligation/blockade in autoimmune disease therapy. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, M.E.; Flierman, R.; Van Duivenvoorde, L.M.; Witteveen, H.J.; Van Ewijk, W.; Van Laar, J.M.; De Vries, R.R.P.; Toes, R.E.M. Effective treatment of collagen-induced arthritis by adoptive transfer of CD25+ regulatory T cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.E.; Sutmuller, R.P.M.; Witteveen, H.J.; van Duivenvoorde, L.M.; Zanelli, E.; Melief, C.J.M.; Snijders, A.; Offringa, R.; de Vries, R.R.P.; Toes, R.E.M. CD25+ cell depletion hastens the onset of severe disease in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.; Siepmann, K.; Wohlleben, G. CD40 ligation in B cell activation, isotype switching and memory development. Semin. Immunol. 1994, 6, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.A.; Hostager, B.S. The CD40–CD154 interaction in B cell–T cell liaisons. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durie, F.H.; Foy, T.M.; Masters, S.R.; Laman, J.D.; Noelle, R.J. The role of CD40 in the regulation of humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Immunol. Today 1994, 15, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durie, F.; Fava, R.; Foy, T.; Aruffo, A.; Ledbetter, J.; Noelle, R. Prevention of collagen-induced arthritis with an antibody to gp39, the ligand for CD40. Science 1993, 261, 1328–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, L.M.C.; Walmsley, M.J.; Feldmann, M. Prevention and amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis by blockade of the CD28 co-stimulatory pathway: Requirement for both B7-1 and B7-2. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellander, A.C.; Pettersson, U.; Runström, A.; Andersson, M.; Michaëlsson, E. Interference with CD28, CD80, CD86 or CD152 in collagen-induced arthritis. Limited role of IFN-γ in Anti-B7-mediated suppression of disease. J. Autoimmun. 2001, 17, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.W.; Lee, K.W.; Park, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Song, J.W.; Yang, J.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, T.M.; Park, J.B.; et al. Therapeutic effects of anti-CD154 antibody in cynomolgus monkeys with advanced rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vierboom, M.P.M.; Breedveld, E.; Kap, Y.S.; Mary, C.; Poirier, N.; ’t Hart, B.A.; Vanhove, B. Clinical efficacy of a new CD28-targeting antagonist of T cell co-stimulation in a non-human primate model of collagen-induced arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 183, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.-G.; Cho, M.-L.; Min, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-Y. Type II collagen autoimmunity in a mouse model of human rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 7, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, R.T.; Thornton, S.; Finkelman, F.D. Cγ1 deficiency exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hietala, M.A.; Jonsson, I.-M.; Tarkowski, A.; Kleinau, S.; Pekna, M. Complement deficiency ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Kristan, J.; Hao, L.; Lenkoski, C.S.; Shen, Y.; Matis, L.A. A role for complement in antibody-mediated inflammation: C5-Deficient DBA/1 mice are resistant to collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4340–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeuws, S.; Jacques, P.; Van Praet, J.; Drennan, M.; Coudenys, J.; Decruy, T.; Deschepper, E.; Lepescheux, L.; Pujuguet, P.; Oste, L.; et al. A multiparameter approach to monitor disease activity in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikulowska, A.; Metz, C.N.; Bucala, R.; Holmdahl, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is involved in the pathogenesis of collagen type II-induced arthritis in mice. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 5514–5517. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, K.W.; Shuster, D.J.; Gillooly, K.M.; Warrier, R.R.; Connaughton, S.E.; Hall, L.B.; Arp, L.H.; Gately, M.K.; Magram, J. Reduced incidence and severity of collagen-induced arthritis in interleukin-12-deficient mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 2933–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.L.W.; Deng, L.; Lepore, J.; Cutler, C.; Cannon-Carlson, S.; Wang, Y.; Voloch, M. Improvement of monoclonal antibody production in hybridoma cells by dimethyl sulfoxide. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Miao, Y.-Q.; Fan, D.-J.; Yang, S.-S.; Lin, X.; Meng, L.-K.; Tang, X. Bioavailability study of berberine and the enhancing effects of TPGS on intestinal absorption in rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Hao, H.-P.; Xie, H.-G.; Lai, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.-X.; Wang, G.-J. Extensive intestinal first-pass elimination and predominant hepatic distribution of berberine explain its low plasma levels in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-S.; Zheng, Y.-R.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Long, X.-Y. Research progress on berberine with a special focus on its oral bioavailability. Fitoterapia 2016, 109, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooke Laboratories. CIA Induction in DBA/1 Mice. Available online: https://hookelabs.com/protocols/ciaInduction_DBA1.html (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Chondrex Inc. Mouse Anti-Type I and Type II Collagen IgG Assay Kit with TMB Standard ELISA Kit; Chondrex Inc.: Woodinville, WA, USA, 2011; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chondrex Inc. Mouse Anti-Type II Collagen IgG Subtype Antibody Assay Kit with TMB. Available online: https://www.chondrex.com/documents/Mouse ELISA Subtype TMB.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2019).






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vita, A.A.; Aljobaily, H.; Lyons, D.O.; Pullen, N.A. Berberine Delays Onset of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through T Cell Suppression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073522
Vita AA, Aljobaily H, Lyons DO, Pullen NA. Berberine Delays Onset of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through T Cell Suppression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073522
Chicago/Turabian StyleVita, Alexandra A., Hend Aljobaily, David O. Lyons, and Nicholas A. Pullen. 2021. "Berberine Delays Onset of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through T Cell Suppression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073522
APA StyleVita, A. A., Aljobaily, H., Lyons, D. O., & Pullen, N. A. (2021). Berberine Delays Onset of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through T Cell Suppression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073522