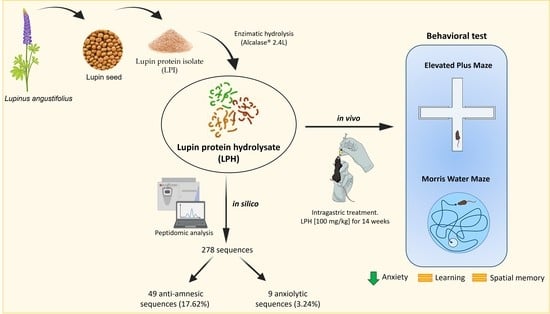
A Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Protein Hydrolysate Exerts Anxiolytic-Like Effects in Western Diet-Fed ApoE−/− Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of LPH
2.1.1. Chemical Analysis of LPH
2.1.2. LPH Contains Peptides with Anxiolytic and Antiamnesic Effects
2.2. In Vivo Experiments
2.2.1. LPH Treatment Does Not Alter the Body Weight of Mice
2.2.2. LPH Palliates the Anxious Effects Induced by WD Ingestion
2.2.3. LPH Treatment Does Not Improve Spatial Memory but Modulates WD-Induced Thigmotaxis, an Anxiety-Related Behavior
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. LPH Preparation
4.2. Purification and Concentration of Peptides
4.3. Peptides’ Analysis and Identification by Mass Spectrometry
4.4. Bioactivities Peptide Analysis
4.5. Animals and Experimental Design
4.6. Behavioral Tests
4.6.1. Elevated Plus Maze
4.6.2. Morris Water Maze
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otte, C. Cognitive behavioral therapy in anxiety disorders: Current state of the evidence. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 13, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perna, G.; Alciati, A.; Sangiorgio, E.; Caldirola, D.; Nemeroff, C.B. Personalized clinical approaches to anxiety disorders. Anxiety Disord. 2020, 1191, 489–521. [Google Scholar]
- Canuto, A.; Weber, K.; Baertschi, M.; Andreas, S.; Volkert, J.; Dehoust, M.C.; Sehner, S.; Suling, A.; Wegscheider, K.; Ausín, B. Anxiety disorders in old age: Psychiatric comorbidities, quality of life, and prevalence according to age, gender, and country. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gainey, S.J.; Kwakwa, K.A.; Bray, J.K.; Pillote, M.M.; Tir, V.L.; Towers, A.E.; Freund, G.G. Short-term high-fat diet (HFD) induced anxiety-like behaviors and cognitive impairment are improved with treatment by glyburide. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.D.; Crean, A.J.; Senior, A.M. Obesogenic diets induce anxiety in rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13399. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, D.M.; Currie, K.C. Depression, anxiety and their relationship with chronic diseases: A review of the epidemiology, risk and treatment evidence. Med. J. Aust. 2009, 190, S54–S60. [Google Scholar]
- Gerontoukou, E.-I.; Michaelidoy, S.; Rekleiti, M.; Saridi, M.; Souliotis, K. Investigation of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic diseases. Health Psychol. Res. 2015, 3, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.; Sutradhar, R.; Yao, Z.; Wodchis, W.P.; Rosella, L.C. Smoking, drinking, diet and physical activity—modifiable lifestyle risk factors and their associations with age to first chronic disease. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 113–130. [Google Scholar]
- Scoditti, E.; Massaro, M.; Garbarino, S.; Toraldo, D.M. Role of diet in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease prevention and treatment. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1357. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Bu, X.; Liu, J.; Wei, L.; Ma, A.; Wang, T. Cardiovascular disease burden attributable to dietary risk factors from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 897–907. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, K.; Li, D. Dietary fat intake and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 869–876. [Google Scholar]
- Celano, C.M.; Daunis, D.J.; Lokko, H.N.; Campbell, K.A.; Huffman, J.C. Anxiety disorders and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2016, 18, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Naicker, K.; Johnson, J.A.; Skogen, J.C.; Manuel, D.; Øverland, S.; Sivertsen, B.; Colman, I. Type 2 diabetes and comorbid symptoms of depression and anxiety: Longitudinal associations with mortality risk. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmeijer-Sevink, M.K.; Batelaan, N.M.; van Megen, H.J.G.M.; Penninx, B.W.; Cath, D.C.; van den Hout, M.A.; van Balkom, A.J.L.M. Clinical relevance of comorbidity in anxiety disorders: A report from the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA). J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 137, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, G.S.; Sazma, M.A.; McCullough, A.M.; Yonelinas, A.P. The effects of acute stress on episodic memory: A meta-analysis and integrative review. Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 636. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, S.; Schwabe, L. Learning and memory under stress: Implications for the classroom. Npj Sci. Learn. 2016, 1, 16011. [Google Scholar]
- Who, J.; Consultation, F.E. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2003, 916, 1–149. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Zhao, N.; Caulfield, T.R.; Liu, C.-C.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 501–518. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, S.; Anton, F.; Solle, D.; Neumann, M.; Hitzmann, B.; Scheper, T.; Liese, A. Fluorescence spectroscopy as a novel method for on-line analysis of biocatalytic C–C bond formations. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 66, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Aucoin, M.; LaChance, L.; Naidoo, U.; Remy, D.; Shekdar, T.; Sayar, N.; Cardozo, V.; Rawana, T.; Chan, I.; Cooley, K. Diet and Anxiety: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4418. [Google Scholar]
- Panes, A.; Verdoux, H.; Fourrier-Réglat, A.; Berdaï, D.; Pariente, A.; Tournier, M. Misuse of benzodiazepines: Prevalence and impact in an inpatient population with psychiatric disorders. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 601–610. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-derived bioactive peptides in human health: Challenges and opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar]
- Daliri, E.B.-M.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, B.H. Bioactive peptides. Foods 2017, 6, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Ulug, S.K.; Jahandideh, F.; Wu, J. Novel technologies for the production of bioactive peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Giannetto, A.; Esposito, E.; Lanza, M.; Oliva, S.; Riolo, K.; Di Pietro, S.; Abbate, J.M.; Briguglio, G.; Cassata, G.; Cicero, L. Protein hydrolysates from anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) waste: In vitro and in vivo biological activities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Abbate, J.M.; Macrì, F.; Arfuso, F.; Iaria, C.; Capparucci, F.; Anfuso, C.; Ieni, A.; Cicero, L.; Briguglio, G.; Lanteri, G. Anti-atherogenic effect of 10% supplementation of anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) waste protein hydrolysates in ApoE-deficient mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2137. [Google Scholar]
- Abbate, J.M.; Macrì, F.; Capparucci, F.; Iaria, C.; Briguglio, G.; Cicero, L.; Salvo, A.; Arfuso, F.; Ieni, A.; Piccione, G. Administration of protein hydrolysates from anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) waste for twelve weeks decreases metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease severity in ApoE−/−mice. Animals 2020, 10, 2303. [Google Scholar]
- Hafeez, Z.; Benoit, S.; Cakir-Kiefer, C.; Dary, A.; Miclo, L. Food protein-derived anxiolytic peptides: Their potential role in anxiety management. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Ohinata, K.; Agui, S.; Yoshikawa, M. Soymorphins, novel μ opioid peptides derived from soy β-conglycinin β-subunit, have anxiolytic activities. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 2618–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sonada, S.; Yoshikawa, A.; Ohinata, K.; Yoshikawa, M. Rubimetide, humanin, and MMK1 exert anxiolytic-like activities via the formyl peptide receptor 2 in mice followed by the successive activation of DP1, A2A, and GABAA receptors. Peptides 2016, 83, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, H.; Sonoda, S.; Agui, S.; Yoshida, M.; Ohinata, K.; Yoshikawa, M. Rubiscolin-6, a δ opioid peptide derived from spinach Rubisco, has anxiolytic effect via activating σ1 and dopamine D1 receptors. Peptides 2007, 28, 1998–2003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oda, A.; Kaneko, K.; Mizushige, T.; Lazarus, M.; Urade, Y.; Ohinata, K. Characterization of ovolin, an orally active tryptic peptide released from ovalbumin with anxiolytic-like activity. J. Neurochem. 2012, 122, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- dela Pena, I.J.I.; Kim, H.J.; de la Pena, J.B.; Kim, M.; Botanas, C.J.; You, K.Y.; Woo, T.; Lee, Y.S.; Jung, J.-C.; Kim, K.-M. A tryptic hydrolysate from bovine milk αs1-casein enhances pentobarbital-induced sleep in mice via the GABAA receptor. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 313, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Mizushige, T.; Sawashi, Y.; Yamada, A.; Kanamoto, R.; Ohinata, K. Characterization of Tyr-Leu-Gly, a novel anxiolytic-like peptide released from bovine αS-casein. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, A.; Mizushige, T.; Kanamoto, R.; Ohinata, K. Identification of novel β-lactoglobulin-derived peptides, wheylin-1 and-2, having anxiolytic-like activity in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohinata, K.; Sonoda, S.; Inoue, N.; Yamauchi, R.; Wada, K.; Yoshikawa, M. β-Lactotensin, a neurotensin agonist peptide derived from bovine β-lactoglobulin, enhances memory consolidation in mice. Peptides 2007, 28, 1470–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Chu, C.; Shi, R.; Cui, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Hui, Y.; Pan, J.; Qian, R. ApoE-Dependent Protective Effects of Sesamol on High-Fat Diet-Induced Behavioral Disorders: Regulation of the Microbiome-Gut–Brain Axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6190–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yuan, R.; Geng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, T.; Kowalski, E.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Toll-interacting protein deficiency promotes neurodegeneration via impeding autophagy completion in high-fat diet-fed ApoE−/−mouse model. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 59, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
- Raber, J. Role of apolipoprotein E in anxiety. Neural Plast. 2007, 2007, 091236. [Google Scholar]
- Raber, J.; Akana, S.F.; Bhatnagar, S.; Dallman, M.F.; Wong, D.; Mucke, L. Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Dysfunction inApoe−/−Mice: Possible Role in Behavioral and Metabolic Alterations. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Strekalova, T.; Evans, M.; Costa-Nunes, J.; Bachurin, S.; Yeritsyan, N.; Couch, Y.; Steinbusch, H.M.; Köhler, S.E.; Lesch, K.-P.; Anthony, D.C. Tlr4 upregulation in the brain accompanies depression-and anxiety-like behaviors induced by a high-cholesterol diet. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felger, J.C. Imaging the role of inflammation in mood and anxiety-related disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 533–558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fedoce, A.d.G.; Ferreira, F.; Bota, R.G.; Bonet-Costa, V.; Sun, P.Y.; Davies, K.J. The role of oxidative stress in anxiety disorder: Cause or consequence? Free. Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, S.S.; Sandrini, L.; Musazzi, L.; Popoli, M.; Ieraci, A. Apocynin prevents anxiety-like behavior and histone deacetylases overexpression induced by sub-chronic stress in mice. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 885. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; del Carmen Millán-Linares, M.; del Mar Yust, M.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F.; Lardone, P.J.; Carrera-Sánchez, C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Carrillo-Vico, A. Lupine protein hydrolysates decrease the inflammatory response and improve the oxidative status in human peripheral lymphocytes. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108585. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Álvarez-Ríos, A.I.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F.; Sánchez, C.C.; Fernández-Pachón, M.S.; Millán-Linares, M.C.; Martínez-López, A. Safety and Efficacy of a Beverage Containing Lupine Protein Hydrolysates on the Immune, Oxidative and Lipid Status in Healthy Subjects: An Intervention Study (the Lupine-1 Trial). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2100139. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Sánchez, G.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Álvarez-Ríos, A.I.; Fernández-Santos, J.M.; Vázquez-Román, M.V.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, B.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Álvarez-López, A.I.; Millán-Linares, M.d.C.; Millán, F. Lupinus angustifolius protein hydrolysates reduce abdominal adiposity and ameliorate metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in Western diet fed-ApoE−/−mice. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, S.; Ohmori, T.; Nakagami, T. Prolylendopeptidase inhibitory activity of a glial fibrillary acidic protein fragment and other proline-rich peptides. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 358–359. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmarin, I.; Karazeeva, E.; Lyapina, L.; Samonina, G. The simplest proline-containing peptides PG, GP, PGP, and GPGG: Regulatory activity and possible sources of biosynthesis. Biochem. Biokhimiia 1998, 63, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kanegawa, N.; Suzuki, C.; Ohinata, K. Dipeptide Tyr-Leu (YL) exhibits anxiolytic-like activity after oral administration via activating serotonin 5-HT1A, dopamine D1 and GABAA receptors in mice. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 599–604. [Google Scholar]
- Parish, D.; Smyth, D.; Normanton, J.; Wolstencroft, J. Glycyl glutamine, an inhibitory neuropeptide derived from β-endorphin. Nature 1983, 306, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Database of Bioactive Peptides: Current Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar]
- Burgos-Díaz, C.; Opazo-Navarrete, M.; Wandersleben, T.; Soto-Añual, M.; Barahona, T.; Bustamante, M. Chemical and nutritional evaluation of protein-rich ingredients obtained through a technological process from yellow lupin seeds (Lupinus luteus). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaky, A.A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Eun, J.-B.; Shim, J.-H.; Abd El-Aty, A. Bioactivities, applications, safety, and health benefits of bioactive peptides from food and by-products: A review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 815640. [Google Scholar]
- Norwitz, N.G.; Naidoo, U. Nutrition as Metabolic Treatment for Anxiety. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 598119. [Google Scholar]
- Ljungberg, T.; Bondza, E.; Lethin, C. Evidence of the importance of dietary habits regarding depressive symptoms and depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1616. [Google Scholar]
- Qubty, D.; Schreiber, S.; Rubovitch, V.; Boag, A.; Pick, C.G. No Significant Effects of Cellphone Electromagnetic Radiation on Mice Memory or Anxiety: Some Mixed Effects on Traumatic Brain Injured Mice. Neurotrauma Rep. 2021, 2, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, R.; Dalvi, A. Anxiety, defence and the elevated plus-maze. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 801–810. [Google Scholar]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Scott, B.W.; Burnham, W.M. Effects of cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the elevated plus maze in mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2022, 33, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Grahn, R.E.; Kalman, B.A.; Vlasaty, J.A.; Perna, J.A.; Nevins-Herbert, C.; Patton, S.M.; Barison, L.K. Effects of plus-maze experience and chlordiazepoxide on anxiety-like behavior and serotonin neural activity in the dorsal raphe nucleus in rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.D.; Loughman, A.; Spencer, S.J.; Reichelt, A.C. The impact of obesity and hypercaloric diet consumption on anxiety and emotional behavior across the lifespan. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 83, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dutheil, S.; Ota, K.T.; Wohleb, E.S.; Rasmussen, K.; Duman, R.S. High-fat diet induced anxiety and anhedonia: Impact on brain homeostasis and inflammation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1874–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, C.I.; Jansen, D.; Mutsaers, M.P.; Dederen, P.J.; Geenen, B.; Mulder, M.T.; Kiliaan, A.J. The Effect of a High-Fat Diet on Brain Plasticity, Inflammation and Cognition in Female ApoE4-Knockin and ApoE-Knockout Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, D.; Dupuy, J.-B.; Rochford, J.; Poirier, J. Apolipoprotein E knockout mice display procedural deficits in the Morris water maze: Analysis of learning strategies in three versions of the task. Neuroscience 2002, 114, 641–654. [Google Scholar]
- Belviranli, M.; Atalik, K.; Okudan, N.; Gökbel, H. Age and sex affect spatial and emotional behaviors in rats: The role of repeated elevated plus maze test. Neuroscience 2012, 227, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrelli, A.; Lopez-Costa, J.; Goñi, R.; Brusco, A.; Basso, N. Aerobic exercise prevents age-dependent cognitive decline and reduces anxiety-related behaviors in middle-aged and old rats. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 252–266. [Google Scholar]
- Alveal-Mellado, D.; Giménez-Llort, L. Thigmotaxis helps to differentiate normal and pathological aging processes in a mice model for Alzheimer’s Disease. Med. Sci. Forum 2021, 8, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mayagoitia, K.; Shin, S.D.; Rubini, M.; Siebold, L.; Wilson, C.G.; Bellinger, D.L.; Figueroa, J.D.; Soriano, S. Short-term exposure to dietary cholesterol is associated with downregulation of interleukin-15, reduced thigmotaxis and memory impairment in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 393, 112779. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J. Anxiolytic effects of ACE inhibitory peptides on the behavior of rats in an elevated plus-maze. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Belhaj, N.; Desor, F.; Gleizes, C.; Denis, F.M.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Soulimani, R.; Linder, M. Anxiolytic-like effect of a salmon phospholipopeptidic complex composed of polyunsaturated fatty acids and bioactive peptides. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4294–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclo, L.; Perrin, E.; Driou, A.; Papadopoulos, V.; Boujrad, N.; Vanderesse, R.; Boudier, J.-F.; Desor, D.; Linden, G.; Gaillard, J.-L. Characterization of α-casozepine, a tryptic peptide from bovine αs1-casein with benzodiazepine-like activity. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1780–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Sánchez, G.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Bollati, C.; Bartolomei, M.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F.; Millán-Linares, M.d.C.; Capriotti, A.; Cerrato, A.; Laganà, A.; et al. A Lupinus angustifolius protein hydrolysate exerts hypocholesterolemic effect in western diet-fed-ApoE−/−mice through the modulation of LDLR and PCSK9 pathways. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4158–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fercha, A.; Capriotti, A.L.; Caruso, G.; Cavaliere, C.; Samperi, R.; Stampachiacchiere, S.; Laganà, A. Comparative analysis of metabolic proteome variation in ascorbate-primed and unprimed wheat seeds during germination under salt stress. J. Proteom. 2014, 108, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Springer Protocols Handbooks; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: Common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tecniplast. Sealsafe® 1285L Cage. Available online: https://www.tecniplast.it/uk/product/sealsafe.html (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- ENVIGO. Teklad Global 14% Protein Rodent Maintenance Diet. Available online: https://insights.envigo.com/hubfs/resources/data-sheets/2014s-datasheet-0915.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- TestDiet. 58V8-45 kcal % Fat. Available online: https://www.testdiet.com/Diets/High-Fat-DIO/index.html (accessed on 1 July 2022).






| Amino Acid | No. | % |
|---|---|---|
| Glu (E) | 493 | 12.9 |
| Leu (L) | 396 | 10.3 |
| Ile (I) | 307 | 8.0 |
| Pro (P) | 307 | 8.0 |
| Arg (R) | 287 | 7.5 |
| Asp (D) | 275 | 7.2 |
| Val (V) | 249 | 6.5 |
| Gly (G) | 224 | 5.8 |
| Ser (S) | 202 | 5.3 |
| Gln (Q) | 196 | 5.1 |
| Asn (N) | 185 | 4.8 |
| Lys (K) | 151 | 3.9 |
| Ala (A) | 130 | 3.4 |
| Thr (T) | 130 | 3.4 |
| Phe (F) | 122 | 3.2 |
| Tyr (Y) | 84 | 2.2 |
| His (H) | 60 | 1.6 |
| Trp (W) | 19 | 0.5 |
| Met (M) | 16 | 0.4 |
| Cys (C) | 0 | 0.0 |
| Effect | Bioactive Peptide Motif a | BIOPEP-UWM ID b | Origin Protein c | Accession Number c | N. Peptides | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-amnesic | VPL | 3166 | Non-conglutin proteins | 1 | [48] | |
| PGP | 3459 | α-Conglutin | F5B8V7 | 3 | [49] | |
| PG | 3460 | |||||
| GP | 3461 | |||||
| β-Conglutin | F5B8W1 | 14 | ||||
| F5B8W2 | ||||||
| F5B8W3 | ||||||
| Non-conglutin proteins | 31 | |||||
| anxiolytic | YL | 8310 | α-Conglutin | F5B8V6 | 4 | [50] |
| Non-conglutin proteins | 1 | |||||
| GQ | 2890 | α-Conglutin | F5B8V6 | 3 | [51] | |
| F5B8V7 | ||||||
| Non-conglutin proteins | 1 | |||||
| TOTAL | 58 |
| Parameter (g) | Experimental Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SD | WD | WD + LPH | |
| BBW | 20.35 ± 0.41 | 20.98 ± 0.36 | 20.88 ± 0.49 |
| FBW | 26.20 ± 0.87 | 26.50 ± 0.54 | 27.15 ± 0.69 |
| BWG | 5.85 ± 1.18 | 5.53 ± 0.65 | 6.28 ± 1.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos-Sánchez, G.; Ponce-España, E.; López, J.C.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Álvarez-López, A.I.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F.; Millán-Linares, M.C.; Lardone, P.J.; Bejarano, I.; et al. A Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Protein Hydrolysate Exerts Anxiolytic-Like Effects in Western Diet-Fed ApoE−/− Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179828
Santos-Sánchez G, Ponce-España E, López JC, Álvarez-Sánchez N, Álvarez-López AI, Pedroche J, Millán F, Millán-Linares MC, Lardone PJ, Bejarano I, et al. A Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Protein Hydrolysate Exerts Anxiolytic-Like Effects in Western Diet-Fed ApoE−/− Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):9828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179828
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos-Sánchez, Guillermo, Eduardo Ponce-España, Juan Carlos López, Nuria Álvarez-Sánchez, Ana Isabel Álvarez-López, Justo Pedroche, Francisco Millán, María Carmen Millán-Linares, Patricia Judith Lardone, Ignacio Bejarano, and et al. 2022. "A Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Protein Hydrolysate Exerts Anxiolytic-Like Effects in Western Diet-Fed ApoE−/− Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 9828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179828
APA StyleSantos-Sánchez, G., Ponce-España, E., López, J. C., Álvarez-Sánchez, N., Álvarez-López, A. I., Pedroche, J., Millán, F., Millán-Linares, M. C., Lardone, P. J., Bejarano, I., Cruz-Chamorro, I., & Carrillo-Vico, A. (2022). A Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) Protein Hydrolysate Exerts Anxiolytic-Like Effects in Western Diet-Fed ApoE−/− Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 9828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179828