Manganese-Induced Toxicity in C. elegans: What Can We Learn from the Transcriptome?
Abstract
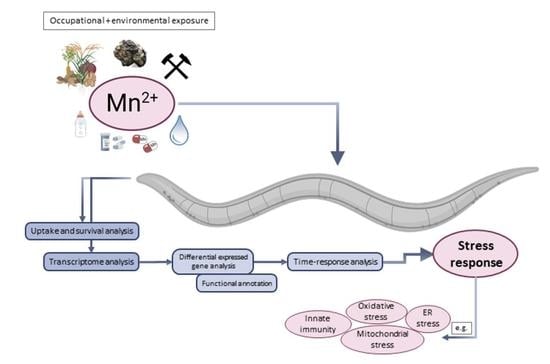
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Time-Dependent Uptake and Toxicity of Mn
2.2. Time Series Transcriptomics during Mn Exposure
2.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) and GO Annotation/Grouping
2.4. GO Annotation Identified Oxidative RNA Damage, Unfolded Protein Response and Innate Immunity As Major Pathways in Mn Toxicity
2.5. The Transcriptional Response to Mn Overexposure Increases with Time and Bioavailability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. C. elegans Cultivation, Mn Treatment and Assessment of Toxicity
3.2. Measurement of Mn Bioavailability
3.3. Sample Preparation for RNA Sequencing
3.4. Transcriptome Analysis
3.5. DEG Analysis of Time Course Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neal, S.L.; Zheng, W. Manganese Toxicity Upon Overexposure: A Decade in Review. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Todd, G.D.; Roney, N.; Crawford, J.; Coles, C.; McClure, P.R.; Garey, J.D.; Zaccaria, K.; Citra, M. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) Toxicological Profiles. In Toxicological Profile for Manganese; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- SCoF, E. Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for Vitamins and Minerals. Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies; Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food; European Food Safety Authority: Parma, Italy, 2006.
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for manganese. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3419. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Bornhorst, J.; Aschner, M. Manganese metabolism in humans. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 1655–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattison, D.R.; Milton, B.; Krewski, D.; Levy, L.; Dorman, D.C.; Aggett, P.J.; Roels, H.A.; Andersen, M.E.; Karyakina, N.A.; Shilnikova, N.; et al. Severity scoring of manganese health effects for categorical regression. Neurotoxicology 2017, 58, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollin, H.B.; Nogueira, C.M.C.A. Manganese: Environmental Pollution and Health Effects 2011; Elsevier: Burligton, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 617–629. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, P.D.; Malcolm, H.M.; Dobson, S.; World Health, O.; International Programme on Chemical, S. Manganese and Its Compounds: Environmental Aspects; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Fitzgerald, K.; Mikalunas, V.; Rubin, H.; McCarthey, R.; Vanagunas, A.; Craig, R.M. Hypermanganesemia in patients receiving total parenteral nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 1999, 23, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalian, R.; Saqui, O.; Fernandes, G.; Allard, J.P. Effects of manganese from a commercial multi-trace element supplement in a population sample of Canadian patients on long-term parenteral nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2013, 37, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, D.P.; Goeden, H.M.; Klos, K.S. Potential for Manganese-Induced Neurologic Harm to Formula-Fed Infants: A Risk Assessment of Total Oral Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 47011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, J.L.; Aschner, M. Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Colon-Perez, L.M.; Sambo, D.O.; Miller, D.R.; Lebowitz, J.J.; Jimenez-Rondan, F.; Cousins, R.J.; Horenstein, N.; Aydemir, T.B.; Febo, M.; et al. Mechanism of Manganese Dysregulation of Dopamine Neuronal Activity. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 5871–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, M.M.; Weishaupt, A.K.; Baesler, J.; Brinkmann, V.; Wellenberg, A.; Winkelbeiner, N.; Gremme, A.; Aschner, M.; Fritz, G.; Schwerdtle, T.; et al. Effects of Manganese on Genomic Integrity in the Multicellular Model Organism Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, M.M.; Witt, B.; Friese, S.; Michaelis, V.; Hölz-Armstrong, L.; Martin, M.; Ebert, F.; Schwerdtle, T.; Bornhorst, J. Mechanistic studies on the adverse effects of manganese overexposure in differentiated LUHMES cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 161, 112822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erikson, K.M.; Dobson, A.W.; Dorman, D.C.; Aschner, M. Manganese exposure and induced oxidative stress in the rat brain. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 334–335, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudgalvyte, M.; Peltonen, J.; Lakso, M.; Nass, R.; Wong, G. RNA-Seq Reveals Acute Manganese Exposure Increases Endoplasmic Reticulum Related and Lipocalin mRNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletta, T.; Hengartner, M.O. Finding function in novel targets: C. elegans as a model organism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.; Benedetto, A.; Anderson, J.; Labrousse, A.; Erikson, K.; Ewbank, J.J.; Aschner, M. SMF-1, SMF-2 and SMF-3 DMT1 orthologues regulate and are regulated differentially by manganese levels in C. elegans. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Chen, P.; Bornhorst, J.; Schwerdtle, T.; Schumacher, F.; Kleuser, B.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Loss of pdr-1/parkin influences Mn homeostasis through altered ferroportin expression in C. elegans. Metallomics 2015, 7, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, A.K.; Wightman, B.; Chalfie, M. A Transparent Window into Biology: A Primer on Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2015, 200, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.H.; Chou, C.Y.; Ch’ang, L.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Lin, W. Identification of novel human genes evolutionarily conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans by comparative proteomics. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.R. The C. elegans model in toxicity testing. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, J.C. Venny. An Interactive Tool for Comparing Lists with Venn’s Diagrams. 2007–2015. Available online: https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Neumann, C.; Baesler, J.; Steffen, G.; Nicolai, M.M.; Zubel, T.; Aschner, M.; Burkle, A.; Mangerich, A.; Schwerdtle, T.; Bornhorst, J. The role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases in manganese exposed Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 57, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecki, E.A. Manganese toxicity is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA fragmentation in rat primary striatal neurons. Brain Res. Bull. 2001, 55, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvani, P.; Fumagalli, P.; Santagostino, A. Vulnerability of mitochondrial complex I in PC12 cells exposed to manganese. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 293, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, M.; Canini, A.; Mattioli, P.; Sorge, R.P.; Alimonti, A.; Bocca, B.; Forte, G.; Martorana, A.; Bernardi, G.; Sancesario, G. Sub-cellular localization of manganese in the basal ganglia of normal and manganese-treated rats An electron spectroscopy imaging and electron energy-loss spectroscopy study. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, R.C.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; McBride, D.; Veevers, J.; Harrison, F.E.; Aschner, M.; Haynes, E.N.; Bowman, A.B. Brain manganese and the balance between essential roles and neurotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6312–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhorst, J.; Chakraborty, S.; Meyer, S.; Lohren, H.; Große Brinkhaus, S.; Knight, A.L.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A.; Karst, U.; Schwerdtle, T.; et al. The effects of pdr1, djr1.1 and pink1 loss in manganese-induced toxicity and the role of α-synuclein in C. elegans. Metallomics 2013, 6, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirin-Stricker, C.; Mauvais, C.; Schmitt, M. Transcriptional activation of human choline acetyltransferase by AP2- and NGF-induced factors. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 49, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wang, Y.; Paudel, H.K. Early Growth Response 1 (Egr-1) Is a Transcriptional Activator of β-Secretase 1 (BACE-1) in the Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22276–22287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassar, R.; Kovacs, D.M.; Yan, R.; Wong, P.C. The beta-secretase enzyme BACE in health and Alzheimer’s disease: Regulation, cell biology, function, and therapeutic potential. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12787–12794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, N.; Zheng, W. Manganese Exposure Aggravates β-Amyloid Pathology by Microglial Activation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 556008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Yang, H.; Tian, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, T.; Fan, D.; Guo, X.; et al. High manganese, a risk for Alzheimer’s disease: High manganese induces amyloid-β related cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakad, R.; Schumacher, B. DNA Damage Response and Immune Defense: Links and Mechanisms. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiin, S.-J.; Lin, T.-H.; Shih, T.-S. Lipid peroxidation in workers exposed to manganese. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 1996, 22, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Yao, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, K.; Chen, J.; Luo, W. Proteasome inhibition is associated with manganese-induced oxidative injury in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 2007, 1185, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Pappolla, M.A.; Wade, R.; Hirai, K.; Chiba, S.; Smith, M.A. RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Kong, Q.; Shan, X.; Tian, G.; Ilieva, H.; Cleveland, D.W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Borchelt, D.R.; Wong, P.C.; Lin, C.-L.G. Messenger RNA oxidation occurs early in disease pathogenesis and promotes motor neuron degeneration in ALS. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Chiba, S.; Kosaka, K.; Takeda, A.; Castellani, R.J.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G. Neuronal RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Lin, C.-L.G. Oxidative damage to RNA: Mechanisms, consequences, and diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Dimayuga, E.; Keller, J.N. Oxidative stress alters neuronal RNA- and protein-synthesis: Implications for neural viability. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Chang, Y.; Lin, C.G. Messenger RNA oxidation is an early event preceding cell death and causes reduced protein expression. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2753–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Chock, P.B.; Stadtman, E.R. Oxidized messenger RNA induces translation errors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, A.Y.; Potapova, E.V.; Dremin, V.V.; Dunaev, A.V. Interaction of Oxidative Stress and Misfolded Proteins in the Mechanism of Neurodegeneration. Life 2020, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Conza, G.; Ho, P.-C. ER Stress Responses: An Emerging Modulator for Innate Immunity. Cells 2020, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irazoqui, J.E.; Urbach, J.M.; Ausubel, F.M. Evolution of host innate defence: Insights from Caenorhabditis elegans and primitive invertebrates. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukkila-Worley, R.; Ausubel, F.M. Immune defense mechanisms in the Caenorhabditis elegans intestinal epithelium. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mills, C.; Albou, L.-P.; Mushayamaha, T.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 16: A revised family classification, tree-based classification tool, enhancer regions and extensive API. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D394–D403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Kejariwal, A.; Guo, N.; Mi, H.; Campbell, M.J.; Muruganujan, A.; Lazareva-Ulitsky, B. Applications for protein sequence-function evolution data: mRNA/protein expression analysis and coding SNP scoring tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W645–W650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolai, M.M.; Pirritano, M.; Gasparoni, G.; Aschner, M.; Simon, M.; Bornhorst, J. Manganese-Induced Toxicity in C. elegans: What Can We Learn from the Transcriptome? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810748
Nicolai MM, Pirritano M, Gasparoni G, Aschner M, Simon M, Bornhorst J. Manganese-Induced Toxicity in C. elegans: What Can We Learn from the Transcriptome? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810748
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolai, Merle M., Marcello Pirritano, Gilles Gasparoni, Michael Aschner, Martin Simon, and Julia Bornhorst. 2022. "Manganese-Induced Toxicity in C. elegans: What Can We Learn from the Transcriptome?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810748
APA StyleNicolai, M. M., Pirritano, M., Gasparoni, G., Aschner, M., Simon, M., & Bornhorst, J. (2022). Manganese-Induced Toxicity in C. elegans: What Can We Learn from the Transcriptome? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810748