Brown Adipose Tissue Sheds Extracellular Vesicles That Carry Potential Biomarkers of Metabolic and Thermogenesis Activity Which Are Affected by High Fat Diet Intervention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. White and Brown Adipose Tissues Shed EVs Which Change Their Tetraspanins Profile after High Fat Diet (HFD) Intervention
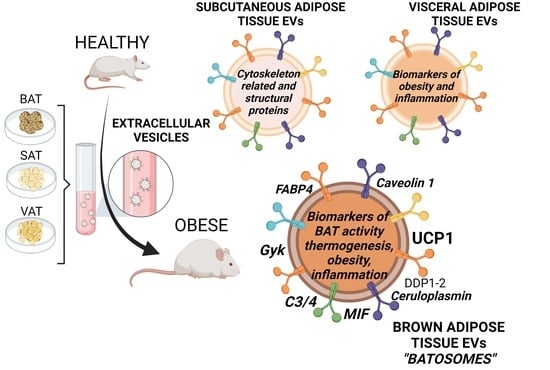
2.2. Proteome Content of White and Brown Adipose Tissue Shed EVs Shows Depot-Specific Protein Profiles That Reflect Metabolic Deregulation in Those Animals with HFD Intervention
2.3. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Brown Adipose Tissue Carry UCP1, Mitochondrial Components and Enzymes, and Proteins Associated with Obesity-Related Deregulated Metabolism in Obese Animals
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Lean and DIO Model
4.2. Rat Adipose Tissue Explants Culture
4.3. Secretome Collection
4.4. Isolation of EVs by Differential Ultracentrifugation
4.5. Immunoblotting
4.6. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
4.7. ExoView Analysis
4.8. Mass Spectrometric DDA Qualitative Analysis and Protein Quantification by DIA-SWATH (Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Mass Spectra)
4.9. Protein Functional Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Chi, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. Obesity and Diabetes as High-Risk Factors for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, F.; Villalobos-Labra, R.; Sobrevia, B.; Toledo, F.; Sobrevia, L. Extracellular Vesicles in Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 60, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Cicero, A.; Stahl, P.D.; Raposo, G. Extracellular Vesicles Shuffling Intercellular Messages: For Good or for Bad. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, I.K.H.; Lucas, C.D.; Rossi, A.G.; Ravichandran, K.S. Apoptotic Cell Clearance: Basic Biology and Therapeutic Potential. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, T.; Lago-Baameiro, N.; Martis-Sueiro, A.; Couto, I.; Santos, F.; Baltar, J.; Pardo, M. Molecular Sciences Deciphering Adipose Tissue Extracellular Vesicles Protein Cargo and Its Role in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, A. Adipose Extracellular Vesicles in Intercellular and Inter-Organ Crosstalk in Metabolic Health and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 608680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamara, C.; Nerea, L.-B.; Belén, B.; Aurelio, S.; Iván, C.; Fernando, S.; Javier, B.; Felipe, C.; María, P. Vesicles Shed by Pathological Murine Adipocytes Spread Pathology: Characterization and Functional Role of Insulin Resistant/Hypertrophied Adiposomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-J.; Fang, Q.-H.; Liu, M.-L.; Lin, J.-N. Current Understanding of the Role of Adipose-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Homeostasis and Diseases: Communication from the Distance between Cells/Tissues. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7422–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, T.; Lago-Baameiro, N.; Bravo, S.B.; Molares-Vila, A.; Sueiro, A.; Couto, I.; Baltar, J.; Casanueva, E.F.; Pardo, M. Human Obese White Adipose Tissue Sheds Depot-Specific Extracellular Vesicles and Reveals Candidate Biomarkers for Monitoring Obesity and Its Comorbidities. Transl. Res. 2022, 239, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Poliakov, A.; Hardy, R.W.; Clements, R.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, X.; et al. Adipose Tissue Exosome-like Vesicles Mediate Activation of Macrophage-Induced Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartwig, S.; De Filippo, E.; Göddeke, S.; Knebel, B.; Kotzka, J.; Al-Hasani, H.; Roden, M.; Lehr, S.; Sell, H. Exosomal Proteins Constitute an Essential Part of the Human Adipose Tissue Secretome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 140172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, I.; Clement, E.; Dauvillier, S.; Milhas, D.; Ducoux-Petit, M.; LeGonidec, S.; Moro, C.; Soldan, V.; Dalle, S.; Balor, S.; et al. Adipocyte Exosomes Promote Melanoma Aggressiveness through Fatty Acid Oxidation: A Novel Mechanism Linking Obesity and Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4051–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcin, M.; Fleury, A.; Taillebois, E.; Hilairet, G.; Krupova, Z.; Henry, C.; Truchet, S.; Trötzmüller, M.; Köfeler, H.; Mabilleau, G.; et al. Characterisation of Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes Identifies Distinct Protein and Lipid Signatures for Large and Small Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1305677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, I.; Vidal-Puig, A.J. Fed-EXosome: Extracellular Vesicles and Cell–Cell Communication in Metabolic Regulation. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang-Doran, I.; Zhang, C.Y.; Vidal-Puig, A. Extracellular Vesicles: Novel Mediators of Cell Communication In Metabolic Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranendonk, M.E.G.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Nolte-‘T Hoen, E.N.M.; Van Herwaarden, J.A.; De Jager, W.; Schipper, H.S.; Brenkman, A.B.; Verhaar, M.C.; Wauben, M.H.M.; et al. Human Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicles in Reciprocal Signaling between Adipocytes and Macrophages. Obesity 2014, 22, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, P.; Wagner, D.; McGann, P.; Joshi, M. Did Hospital Engagement Networks Actually Improve Care? N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2040–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Salomon, C.; Freeman, D.J. Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose Tissue—A Potential Role in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes? Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeck, E.S.; Iordanskaia, T.; Sevilla, S.; Ferrante, S.C.; Hubal, M.J.; Freishtat, R.J.; Nadler, E.P. Adipocyte Exosomes Induce Transforming Growth Factor Beta Pathway Dysregulation in Hepatocytes: A Novel Paradigm for Obesity-Related Liver Disease. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 192, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, S.E.; Grijalva, A.; Xu, X.; Ables, E.; Nomani, A.; Ferrante, A.W. A Lipase-Independent Pathway of Lipid Release and Immune Modulation by Adipocytes. Science 2019, 363, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, F.; Cereijo, R.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Brown Adipose Tissue as a Secretory Organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 13, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Buyel, J.J.; Hanssen, M.J.W.; Siegel, F.; Pan, R.; Naumann, J.; Schell, M.; Van Der Lans, A.; Schlein, C.; Froehlich, H.; et al. Exosomal MicroRNA MiR-92a Concentration in Serum Reflects Human Brown Fat Activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdikari, A.; Leparc, G.G.; Balaz, M.; Pires, N.D.; Lidell, M.E.; Sun, W.; Fernandez-Albert, F.; Müller, S.; Akchiche, N.; Dong, H.; et al. BATLAS: Deconvoluting Brown Adipose Tissue. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 784–797.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goody, D.; Pfeifer, A. BAT Exosomes: Metabolic Crosstalk with Other Organs and Biomarkers for BAT Activity. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer New York LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 251, pp. 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Villarroya, F.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Peyrou, M.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Brown Adipokines. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer New York LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 251, pp. 239–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Eguchi, A.; Tempaku, M.; Honda, T.; Togashi, K.; Iwasa, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Takei, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Taguchi, O. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Are Associated with Lipid and Insulin Metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E574–E582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, A.; Lazic, M.; Armando, A.M.; Phillips, S.A.; Katebian, R.; Maraka, S.; Quehenberger, O.; Sears, D.D.; Feldstein, A.E. Circulating Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are Novel Markers of Metabolic Stress. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yao, D.; Sun, L.; Qin, L.; Qiu, H.; Zhan, X. Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Appetite and Weight through MTOR Signalling in the Hypothalamus. Acta Physiol. 2020, 228, e13339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-S.; Park, H.-S.; Kawada, T.; Kim, J.-H.; Lim, D.; Hubbard, N.E.; Kwon, B.-S.; Erickson, K.L.; Yu, R. Circulating Levels of MCP-1 and IL-8 Are Elevated in Human Obese Subjects and Associated with Obesity-Related Parameters. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, O.K. Potential Roles of Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle-Derived MiRNAs in Obesity-Mediated Insulin Resistance. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, R.; Tanaka, C.; Sato, M.; Nagasaki, H.; Sugimura, K.; Okumura, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Aoki, N. Adipocyte-Derived Microvesicles Contain RNA That Is Transported into Macrophages and Might Be Secreted into Blood Circulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown Adipose Tissue: Function and Physiological Significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Villarroya, J.; Cereijo, R.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F. The Endocrine Role of Brown Adipose Tissue: An Update on Actors and Actions. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 23, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matteis, R.; Solinas, G.; Giralt, M.; Trayhurn, P. Article 1672 Citation: Trayhurn P (2018) Brown Adipose Tissue-A Therapeutic Target in Obesity? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amosse, J.; Durcin, M.; Malloci, M.; Vergori, L.; Fleury, A.; Gagnadoux, F.; Dubois, S.; Simard, G.; Boursier, J.; Hue, O.; et al. Phenotyping of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) in Obesity Identifies Large EVs as Functional Conveyors of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor. Mol. Metab. 2018, 18, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachurski, D.; Schuldner, M.; Nguyen, P.H.; Malz, A.; Reiners, K.S.; Grenzi, P.C.; Babatz, F.; Schauss, A.C.; Hansen, H.P.; Hallek, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle Measurements with Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis—An Accuracy and Repeatability Comparison between NanoSight NS300 and ZetaView. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1596016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizenko, R.R.; Brostoff, T.; Rojalin, T.; Koster, H.J.; Swindell, H.S.; Leiserowitz, G.S.; Wang, A.; Carney, R.P. Tetraspanins Are Unevenly Distributed across Single Extracellular Vesicles and Bias Sensitivity to Multiplexed Cancer Biomarkers. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, J.; Cereijo, R.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Peyrou, M.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F. New Insights into the Secretory Functions of Brown Adipose Tissue. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 243, R19–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Khan, A.; Hansson, J.; Weber, P.; Foehr, S.; Krijgsveld, J.; Herzig, S.; Scheideler, M. Comparative Secretome Analyses of Primary Murine White and Brown Adipocytes Reveal Novel Adipokines. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 2358–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.S.; Peijs, L.; Beaudry, J.L.; Jespersen, N.Z.; Nielsen, C.H.; Ma, T.; Brunner, A.D.; Larsen, T.J.; Bayarri-Olmos, R.; Prabhakar, B.S.; et al. Proteomics-Based Comparative Mapping of the Secretomes of Human Brown and White Adipocytes Reveals EPDR1 as a Novel Batokine. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 963–975.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariba, Y.; Yoshizawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Tsuyama, T.; Araki, E.; Yamagata, K. Brown Adipocyte-Derived Exosomal MiR-132-3p Suppress Hepatic Srebf1 Expression and Thereby Attenuate Expression of Lipogenic Genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya, F.; Cereijo, R.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Villarroya, J.; Giralt, M. Inflammation of Brown/Beige Adipose Tissues in Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldmann, H.M.; Golozoubova, V.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. UCP1 Ablation Induces Obesity and Abolishes Diet-Induced Thermogenesis in Mice Exempt from Thermal Stress by Living at Thermoneutrality. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, M.; Calderon-Dominguez, M.; Bustos, E.; Ramos, P.; Casals, N.; Serra, D.; Viana, M.; Herrero, L. Increased Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Respiration in Brown Adipose Tissue from Obese Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Park, H.S.; Kim, J.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Heo, Y. Depot-Specific UCP1 Expression in Human White Adipose Tissue and Its Association with Obesity-Related Markers. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Choi, C.; Saha, A.; Park, J.H.; Im, H.; Cho, Y.K.; Seong, J.K.; Burl, R.B.; Rondini, E.A.; Granneman, J.G.; et al. REEP6 Knockout Leads to Defective β-Adrenergic Signaling in Adipocytes and Promotes Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction. Metabolism 2022, 130, 155159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franckhauser, S.; Muñoz, S.; Elias, I.; Ferre, T.; Bosch, F. Adipose Overexpression of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase Leads to High Susceptibility to Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Obesity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iffiú-Soltész, Z.; Mercader, J.; Daviaud, D.; Boucher, J.; Carpéné, C. Increased Primary Amine Oxidase Expression and Activity in White Adipose Tissue of Obese and Diabetic Db−/− Mice. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Norris, D.M.; Humphrey, S.J.; Yang, P.; Cooke, K.C.; Bultitude, W.P.; Parker, B.L.; Conway, O.J.; Burchfield, J.G.; Krycer, J.R.; et al. Trafficking Regulator of GLUT4-1 (TRARG1) Is a GSK3 Substrate. Biochem. J. 2022, 479, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwase, M.; Tokiwa, S.; Seno, S.; Mukai, T.; Yeh, Y.S.; Takahashi, H.; Nomura, W.; Jheng, H.F.; Matsumura, S.; Kusudo, T.; et al. Glycerol Kinase Stimulates Uncoupling Protein 1 Expression by Regulating Fatty Acid Metabolism in Beige Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7033–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.S.; Hirsch, J.; Drewnowski, A.; Sullivan, A.C.; Johnson, P.R.; Cohn, C.K. Glycerol Kinase Activity in Adipose Tissue of Obese Rats and Mice: Effects of Diet Composition. J. Nutr. 1983, 113, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, M.; Weber, L.W.D.; Stampfl, A. Nutritional Regulation of the Activities of Lipogenic Enzymes of Rat Liver and Brown Adipose Tissue. Z. Naturforsch. C. 1996, 51, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.E.; Hodgson, L.R.; Song, S.; May, M.T.; Kelly, E.E.; McCaffrey, M.W.; Mastick, C.C.; Verkade, P.; Tavare, J.M. A Role for Rab14 in the Endocytic Trafficking of GLUT4 in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gurmaches, J.; Tang, Y.; Jespersen, N.Z.; Wallace, M.; Martinez Calejman, C.; Gujja, S.; Li, H.; Edwards, Y.J.K.; Wolfrum, C.; Metallo, C.M.; et al. Brown Fat AKT2 Is a Cold-Induced Kinase That Stimulates ChREBP-Mediated De Novo Lipogenesis to Optimize Fuel Storage and Thermogenesis. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 195–209.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrani, N.T.; Ferreira, C.N.; Rodrigues, K.F.; Perucci, L.O.; Carneiro, F.S.; Bosco, A.A.; Oliveira, M.C.; Pereira, S.S.; Teixeira, A.L.; Alvarez-Leite, J.I.; et al. Proresolving Protein Annexin A1: The Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa Rodrigues, C.; Chatterjee, A.; Wiese, M.; Stehle, T.; Szymanski, W.; Shvedunova, M.; Akhtar, A. Histone H4 Lysine 16 Acetylation Controls Central Carbon Metabolism and Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crewe, C.; Joffin, N.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Kim, M.; Zhang, F.; Towler, D.A.; Gordillo, R.; Scherer, P.E. An Endothelial-to-Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle Axis Governed by Metabolic State. Cell 2018, 175, 695–708.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.E.; Ordovás, J.M. Update on Perilipin Polymorphisms and Obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwosu, Z.C.; Ebert, M.P.; Dooley, S.; Meyer, C. Caveolin-1 in the Regulation of Cell Metabolism: A Cancer Perspective. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, K.J.; Saksi, J.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Adipokine FABP4 Integrates Energy Stores and Counterregulatory Metabolic Responses. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M.; Klöting, N.; Wueest, S.; Schoenle, E.J.; Schön, M.R.; Dietrich, A.; Fasshauer, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Konrad, D. Fas and FasL Expression in Human Adipose Tissue Is Related to Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E36–E44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, D.; Famulla, S.; Wronkowitz, N.; Hartwig, S.; Lehr, S.; Ouwens, D.M.; Eckardt, K.; Kaufman, J.M.; Ryden, M.; Müller, S.; et al. Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Is a Novel Adipokine Potentially Linking Obesity to the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, O.Y.; Shin, M.J.; Moon, J.; Chung, J.H. Plasma Ceruloplasmin as a Biomarker for Obesity: A Proteomic Approach. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curat, C.A.; Wegner, V.; Sengenès, C.; Miranville, A.; Tonus, C.; Busse, R.; Bouloumié, A. Macrophages in Human Visceral Adipose Tissue: Increased Accumulation in Obesity and a Source of Resistin and Visfatin. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, I.; Cho, W.; Oh, G.T.; Park, Y.M. Vimentin Deficiency Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Rivada, A.; Bravo, S.B.; Pérez-Sotelo, D.; Alonso, J.; Castro, A.I.; Baamonde, I.; Baltar, J.; Casanueva, F.F.; Pardo, M. CILAIR-Based Secretome Analysis of Obese Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissues Reveals Distinctive ECM Remodeling and Inflammation Mediators. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.F.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Möller, A. Optimized Exosome Isolation Protocol for Cell Culture Supernatant and Human Plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Proteomic Comparison Defines Novel Markers to Characterize Heterogeneous Populations of Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Ang, C.S.; Gangoda, L.; Quek, C.Y.J.; Williamson, N.A.; Mouradov, D.; Sieber, O.M.; Simpson, R.J.; Salim, A.; et al. FunRich: An Open Access Standalone Functional Enrichment and Interaction Network Analysis Tool. Proteomics 2015, 15, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Casagrande, J.T.; Thomas, P.D. Large-Scale Gene Function Analysis with the PANTHER Classification System. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, A.; Jupe, S.; Matthews, L.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Gillespie, M.; Garapati, P.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Korninger, F.; May, B.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D649–D655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Jensen, O.N.; Podtelejnikov, A.V.; Neubauer, G.; Shevchenko, A.; Mortensen, P.; Mann, M. A Strategy for Identifying Gel-Separated Proteins in Sequence Databases by MS Alone. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1996, 24, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| DIA-SWATH Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevated in Lean SAT EVs | ||||
| UNIPROT | PROT ID | Protein Name | p-Value | Fold |
| KACB_RAT | P01835 | Ig kappa chain C region, B allele | 0.026 | 4.44 |
| PDK1_RAT | Q63065 | [Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring)] kinase isozyme 1 | 0.021 | 3.50 |
| PSME1_RAT | Q63797 | Proteasome activator complex subunit 1 | 0.006 | 2.13 |
| KPYM_RAT | P119802 | Isoform M2 of pyruvate kinase PKM | 0.026 | 2.11 |
| FBLN5_RAT | Q9WVH8 | Fibulin-5 | 0.011 | 2.07 |
| Elevated in Obese SAT EVs | ||||
| PAIRB_RAT | Q6AXS5 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 RNA-binding protein | 0.027 | 3.24 |
| CLIC1_RAT | Q6MG61 | Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 | 0.021 | 3.06 |
| SGPL1_RAT | Q8CHN6 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 | 0.003 | 2.64 |
| MGLL_RAT | Q8R431 | Monoglyceride lipase | 0.004 | 2.54 |
| CAV1_RAT | P41350 | Caveolin-1 | 0.011 | 2.53 |
| LPPRC_RAT | Q5SGE0 | Leucine-rich PPR motif-containing protein, mitochondrial | 0.000 | 2.53 |
| VAMP2_RAT | P63045 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 | 0.025 | 2.27 |
| NAGAB_RAT | Q66H12 | Alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase | 0.000 | 2.18 |
| OST48_RAT | Q641Y0 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase 48 kDa sub | 0.034 | 2.12 |
| Elevated in Lean VAT EVs | ||||
| PTPRC_RAT | P04157 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C | 0.002 | 2.82 |
| PROF1_RAT | P62963 | Profilin-1 | 0.047 | 2.67 |
| PLST_RAT | Q63598 | Plastin-3 | 0.050 | 2.46 |
| TCPA_RAT | P28480 | T-complex protein 1 subunit alpha | 0.037 | 2.46 |
| LETM1_RAT | Q5XIN6 | Mitochondrial proton/calcium exchanger protein | 0.030 | 2.30 |
| RL8_RAT | P62919 | 60S ribosomal protein L8 | 0.055 | 2.27 |
| NEDD4_RAT | Q62940 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 | 0.049 | 2.24 |
| DEST_RAT | Q7M0E3 | Destrin | 0.026 | 2.13 |
| PP2AB_RAT | P62716 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit beta isoform | 0.018 | 2.09 |
| FIS1_RAT | P84817 | Isoform 2 of mitochondrial fission 1 protein | 0.007 | 2.09 |
| PGRC1_RAT | P70580 | Membrane-associated progesterone receptor component 1 | 0.032 | 2.08 |
| FUCO_RAT | P17164 | Tissue alpha-L-fucosidase | 0.004 | 2.07 |
| SAHH_RAT | P10760 | Adenosylhomocysteinase | 0.053 | 2.04 |
| ATPB_RAT | P10719 | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | 0.053 | 2.03 |
| PUR9_RAT | O35567 | Bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein ATIC | 0.043 | 1.98 |
| Elevated in Obese VAT EVs | ||||
| NHRF2_RAT | Q920G2 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF2 | 0.034 | 9.64 |
| K2C7_RAT | Q6IG12 | Keratin type II cytoskeletal 7 | 0.035 | 4.41 |
| S10A4_RAT | P05942 | Protein S100-A4 | 0.001 | 3.70 |
| PEBP1_RAT | P31044 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | 0.027 | 3.49 |
| VDAC2_RAT | P81155 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 | 0.030 | 3.00 |
| S10A6_RAT | P05964 | Protein S100-A6 | 0.003 | 2.93 |
| ISOC1_RAT | Q6I7R3 | Isochorismatase domain-containing protein 1 | 0.017 | 2.87 |
| S100B_RAT | P04631 | Protein S100-B | 0.018 | 2.78 |
| CLYBL_RAT | Q5I0K3 | Citramalyl-CoA lyase. mitochondrial | 0.019 | 2.67 |
| DRS7B_RAT | Q5RJY4 | Dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 7B | 0.027 | 2.65 |
| UCP1_RAT | P04633 | Mitochondrial brown fat uncoupling protein 1 | 0.053 | 2.64 |
| ALBU_RAT | P02770 | Albumin | 0.038 | 2.59 |
| ODBB_RAT | P35738 | 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase subunit beta, mitochondrial | 0.029 | 2.39 |
| ILEUA_RAT | Q4G075 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor A | 0.016 | 2.33 |
| CBPQ_RAT | Q6IRK9 | Carboxypeptidase Q | 0.049 | 2.29 |
| S10AB_RAT | Q6B345 | Protein S100-A11 | 0.030 | 2.15 |
| VTDB_RAT | P04276 | Vitamin D-binding protein | 0.031 | 2.08 |
| PURA_RAT | P86252 | Transcriptional activator protein Pur-alpha (fragments) | 0.021 | 2.07 |
| K2C8_RAT | Q10758 | Keratin type II cytoskeletal 8 | 0.005 | 2.05 |
| HIBCH_RAT | Q5XIE6 | 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase mitochondrial | 0.025 | 2.02 |
| Elevated in Lean BAT EVs | ||||
| RAB14_RAT | P61107 | Ras-related protein Rab-14 | 0.018 | 4.19 |
| QCR6_RAT | Q5M9I5 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 6, mitochondrial | 0.014 | 3.21 |
| DX39A_RAT | Q5U216 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX39A | 0.039 | 2.90 |
| MMSA_RAT | Q02253 | Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (acylating), mitochondrial | 0.019 | 2.69 |
| ARP3_RAT | Q4V7C7 | Actin-related protein 3 | 0.011 | 2.46 |
| RS12_RAT | P63324 | 40S ribosomal protein S12 | 0.053 | 2.44 |
| ACLY_RAT | P16638 | ATP-citrate synthase | 0.010 | 2.34 |
| CPT2_RAT | P18886 | Carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase 2, mitochondrial | 0.008 | 2.31 |
| ACADM_RAT | P08503 | Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 0.047 | 2.13 |
| THIL_RAT | P17764 | Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, mitochondrial | 0.006 | 2.12 |
| PYC_RAT | P52873 | Pyruvate carboxylase, mitochondrial | 0.003 | 2.10 |
| IDH3A_RAT | Q99NA5 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit Alpha, mitochondrial | 0.027 | 2.07 |
| HSP74_RAT | O88600 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 | 0.044 | 2.04 |
| FETA_RAT | P02773 | Alpha-fetoprotein | 0.029 | 2.01 |
| DECR_RAT | Q64591 | 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase [(3E)-enoyl-CoA-producing], mitochondrial | 0.033 | 2.00 |
| ODP2_RAT | P08461 | Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial | 0.010 | 1.99 |
| Elevated in Obese BAT EVs | ||||
| UCP1_RAT | P04633 | Mitochondrial brown fat uncoupling protein 1 | 0.012 | 4.38 |
| DPEP1_RAT | P31430 | Dipeptidase 1 | 0.003 | 3.71 |
| PCKGC_RAT | P07379 | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, cytosolic [GTP] | 0.055 | 3.42 |
| FAHD1_RAT | Q6AYQ8 | Acylpyruvase FAHD1, mitochondrial | 0.001 | 3.26 |
| FUCO_RAT | P17164 | Tissue alpha-L-fucosidase | 0.009 | 3.18 |
| REEP5_RAT | B2RZ37 | Receptor expression-enhancing protein 5 | 0.002 | 3.07 |
| CD9_RAT | P40241 | CD9 antigen | 0.014 | 3.03 |
| UCRI_RAT | P20788 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit Rieske, mitochondrial | 0.027 | 2.89 |
| TERA_RAT | P46462 | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase | 0.002 | 2.75 |
| 2|RTN3_RA | Q6RJR6 | Isoform 2 of reticulon-3 | 0.004 | 2.72 |
| SEC13_RAT | Q5XFW8 | Protein SEC13 homolog | 0.040 | 2.72 |
| AOC3_RAT | O08590 | Membrane primary amine oxidase | 0.035 | 2.69 |
| TARG1_RAT | Q2MHH0 | Trafficking regulator of GLUT4 1 | 0.021 | 2.68 |
| LEG5_RAT | P47967 | Galectin-5 | 0.007 | 2.59 |
| GLPK_RAT | Q63060 | Glycerol kinase | 0.002 | 2.59 |
| CLH1_RAT | P11442 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 | 0.004 | 2.56 |
| ECI1_RAT | P23965 | Enoyl-CoA delta isomerase 1, mitochondrial | 0.017 | 2.54 |
| PARVA_RAT | Q9HB97 | Alpha-parvin | 0.005 | 2.43 |
| AT1B3_RAT | Q63377 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit beta-3 | 0.006 | 2.41 |
| PP2AB_RAT | P62716 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit beta isoform | 0.006 | 2.40 |
| SUOX_RAT | Q07116 | Sulfite oxidase, mitochondrial | 0.016 | 2.39 |
| CD36_RAT | Q07969 | Platelet glycoprotein 4 | 0.003 | 2.38 |
| FAAA_RAT | P25093 | Fumarylacetoacetase | 0.001 | 2.35 |
| MVP_RAT | Q62667 | Major vault protein | 0.004 | 2.31 |
| HYEP_RAT | P07687 | Epoxide hydrolase 1 | 0.011 | 2.30 |
| NIT2_RAT | Q497B0 | Omega-amidase NIT2 | 0.012 | 2.30 |
| GRIFN_RAT | O88644 | Grifin | 0.006 | 2.29 |
| SAP_RAT | P10960 | Prosaposin | 0.009 | 2.29 |
| 5NTD_RAT | P21588 | 5′-Nucleotidase | 0.019 | 2.27 |
| PGAM1_RAT | P25113 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | 0.001 | 2.24 |
| DPP2_RAT | Q9EPB1 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 2 | 0.000 | 2.24 |
| MDHM_RAT | P04636 | Malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 0.047 | 2.22 |
| PLPP3_RAT | P97544 | Phospholipid phosphatase 3 | 0.030 | 2.20 |
| ACOC_RAT | Q63270 | Cytoplasmic aconitate hydratase | 0.004 | 2.19 |
| SBP1_RAT | Q8VIF7 | Methanethiol oxidase | 0.041 | 2.19 |
| PLBL1_RAT | Q5U2V4 | Phospholipase B-like 1 | 0.005 | 2.16 |
| LDHB_RAT | P42123 | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain | 0.000 | 2.15 |
| AP1B1_RAT | P52303 | AP-1 complex subunit beta-1 | 0.031 | 1.97 |
| GPDA_RAT | O35077 | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [NAD(+)], cytoplasmic | 0.008 | 1.97 |
| RAC1_RAT | Q6RUV5 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 | 0.016 | 1.97 |
| RL10A_RAT | P62907 | 60S ribosomal protein L10a | 0.003 | 1.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camino, T.; Lago-Baameiro, N.; Sueiro, A.; Bravo, S.B.; Couto, I.; Santos, F.F.; Baltar, J.; Casanueva, F.F.; Pardo, M. Brown Adipose Tissue Sheds Extracellular Vesicles That Carry Potential Biomarkers of Metabolic and Thermogenesis Activity Which Are Affected by High Fat Diet Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810826
Camino T, Lago-Baameiro N, Sueiro A, Bravo SB, Couto I, Santos FF, Baltar J, Casanueva FF, Pardo M. Brown Adipose Tissue Sheds Extracellular Vesicles That Carry Potential Biomarkers of Metabolic and Thermogenesis Activity Which Are Affected by High Fat Diet Intervention. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810826
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamino, Tamara, Nerea Lago-Baameiro, Aurelio Sueiro, Susana Belén Bravo, Iván Couto, Francisco Fernando Santos, Javier Baltar, Felipe F. Casanueva, and María Pardo. 2022. "Brown Adipose Tissue Sheds Extracellular Vesicles That Carry Potential Biomarkers of Metabolic and Thermogenesis Activity Which Are Affected by High Fat Diet Intervention" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810826
APA StyleCamino, T., Lago-Baameiro, N., Sueiro, A., Bravo, S. B., Couto, I., Santos, F. F., Baltar, J., Casanueva, F. F., & Pardo, M. (2022). Brown Adipose Tissue Sheds Extracellular Vesicles That Carry Potential Biomarkers of Metabolic and Thermogenesis Activity Which Are Affected by High Fat Diet Intervention. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810826