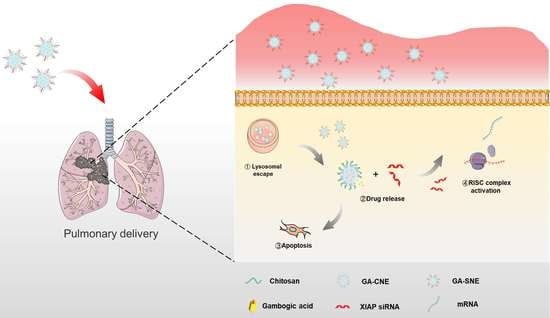
Nanoemulsion Co-Loaded with XIAP siRNA and Gambogic Acid for Inhalation Therapy of Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Nanoemulsions
2.2. Cellular Uptake
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Analysis of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Biodistribution
2.7. The Codelivery System’s In Vivo Therapeutic Effectiveness
2.8. Histopathological Examination
2.9. TUNEL Assay and Immunohistochemistry

3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Animal Care
4.3. Preparation and Characterization of Nanoemulsions
4.4. Preparation and Characterization of GA-SNE
4.5. Cellular Uptake
4.5.1. Quantitative Cell Uptake
4.5.2. Endosomal Scape
4.6. Cell Viability
4.7. Evaluation of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Lung Cancer Induction in BALB/c Mice
4.10. Biodistribution
4.11. In Vivo Antitumor Therapy
4.12. Histological Examination
4.13. TUNEL Assay
4.14. Immunohistochemistry
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNE | Cationic nano-emulsion |
| C6 | Coumarin 6 |
| CS | Chitosan |
| CS-CNE | Chitosan-Cationic nano-emulsion |
| CS-SNE | Chitosan-siRNA nano-emulsion |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| GA | Gambogic acid |
| GA-CNE | Gambogic acid-Cationic nano-emulsion |
| GA-SNE | Gambogic acid-siRNA nano-emulsion |
| PDI | Polymer dispersity index |
| XIAP | X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein |
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, J.N.; Sorensen, J.B. Intratumor heterogeneity and chemotherapy-induced changes in EGFR status in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J., Jr.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; Hassan, O.U.; Yang, Y.W.; Buchanan, P. Lung cancer: Biology and treatment options. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.; Mishima, M. Maintenance chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Leng, D.; Cun, D.; Foged, C.; Yang, M. Advances in combination therapy of lung cancer: Rationales, delivery technologies and dosage regimens. J. Control. Release 2017, 260, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Loo, C.Y.; Ghadiri, M.; Leong, C.R.; Young, P.M.; Traini, D. The potential to treat lung cancer via inhalation of repurposed drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 133, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Brugger, A.; Khare, A.; Chaubal, M.; Papadopoulos, P.; Rabinow, B.; Kipp, J.; Ning, J. Suspensions for intravenous (IV) injection: A review of development, preclinical and clinical aspects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanki, K.; van Eetvelde, D.; Geyer, A.; Fraire, J.; Hendrix, R.; Van Eygen, H.; Putteman, E.; Sami, H.; de Souza Carvalho-Wodarz, C.; Franzyk, H.; et al. Mechanistic profiling of the release kinetics of siRNA from lipidoid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo after pulmonary administration. J. Control. Release 2019, 310, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qian, C.; Oupicky, D.; Sun, M. Targeting pulmonary tumor microenvironment with CXCR4-inhibiting nanocomplex to enhance anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmov, A.; Minko, T. Nanotechnology approaches for inhalation treatment of lung diseases. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banik, K.; Harsha, C.; Bordoloi, D.; Lalduhsaki Sailo, B.; Sethi, G.; Leong, H.C.; Arfuso, F.; Mishra, S.; Wang, L.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Therapeutic potential of gambogic acid, a caged xanthone, to target cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 416, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Mondal, R.; Tuli, H.S.; Kumar, G.; Sharma, A.K. Molecular targets of gambogic acid in cancer: Recent trends and advancements. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 12915–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, H. Gambogic Acid as a Candidate for Cancer Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10385–10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, M.M.; Liu, F.L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, R.J.; Huan, X.X.; Han, L.F.; Zhang, Z.T.; Feng, F.; Qu, W.; Liu, W.; et al. A novel redox/pH dual-responsive and hyaluronic acid-decorated multifunctional magnetic complex micelle for targeted gambogic acid delivery for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, R.; Sang, M.; Liu, B.; Sun, M.; Qu, W.; Feng, F.; Liu, W. Tumor-specific activated photodynamic therapy with an oxidation-regulated strategy for enhancing anti-tumor efficacy. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5059–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danson, S.; Dean, E.; Dive, C.; Ranson, M. IAPs as a target for anticancer therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2007, 7, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.H.A.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Cheng, S.M.; Leung, E. Anti-apoptotic proteins in the autophagic world: An update on functions of XIAP, Survivin, and BRUCE. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Larisch, S. Targeting XIAP for Promoting Cancer Cell Death-The Story of ARTS and SMAC. Cells 2020, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Ren, P. Combined treatment of XIAP-targeting shRNA and celecoxib synergistically inhibits the tumor growth of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Yi, X.P.; Shen, H.; Li, Y.X. Targeting X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth through p-Akt depletion. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2956–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.J.; Chen, B.L.; Xin, X.Y. XIAP gene downregulation by small interfering RNA inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and reverses the cisplatin resistance of ovarian carcinoma. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2009, 146, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.Q.; Chen, W.L.; You, B.G.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.D.; Li, J.Z.; Zhu, W.J.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.N. Multifunctional nanoparticles co-delivering EZH2 siRNA and etoposide for synergistic therapy of orthotopic non-small-cell lung tumor. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, P.; Motasadizadeh, H.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R.; Gholami, M.; Farokhi, M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Mottaghitalab, F. Combination Therapy of Breast Cancer by Codelivery of Doxorubicin and Survivin siRNA Using Polyethylenimine Modified Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Cho, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; Ahn, H.J. KSP siRNA/paclitaxel-loaded PEGylated cationic liposomes for overcoming resistance to KSP inhibitors: Synergistic antitumor effects in drug-resistant ovarian cancer. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Jiang, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, D.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Z. Combination of gambogic acid with cisplatin enhances the antitumor effects on cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells by downregulating MRP2 and LRP expression. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Gui, Q. Exosomal Circ-XIAP Promotes Docetaxel Resistance in Prostate Cancer by Regulating miR-1182/TPD52 Axis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Nanoparticles | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS-CNE | 183.81 ± 1.15 | 0.210 ± 0.013 | 12.37 ± 0.75 | N |
| GA-CNE | 174.53 ± 0.78 | 0.262 ± 0.014 | 9.93 ± 0.58 | 91.51 ± 3.732 |
| C6-CNE | 174.26 ± 1.15 | 0.280 ± 0.011 | 15.57 ± 0.37 | N |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Bai, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B.; Kuang, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, C.; et al. Nanoemulsion Co-Loaded with XIAP siRNA and Gambogic Acid for Inhalation Therapy of Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214294
Xu M, Zhang L, Guo Y, Bai L, Luo Y, Wang B, Kuang M, Liu X, Sun M, Wang C, et al. Nanoemulsion Co-Loaded with XIAP siRNA and Gambogic Acid for Inhalation Therapy of Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(22):14294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214294
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Minhao, Lanfang Zhang, Yue Guo, Lu Bai, Yi Luo, Ben Wang, Meiyan Kuang, Xingyou Liu, Meng Sun, Chenhui Wang, and et al. 2022. "Nanoemulsion Co-Loaded with XIAP siRNA and Gambogic Acid for Inhalation Therapy of Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 22: 14294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214294
APA StyleXu, M., Zhang, L., Guo, Y., Bai, L., Luo, Y., Wang, B., Kuang, M., Liu, X., Sun, M., Wang, C., & Xie, J. (2022). Nanoemulsion Co-Loaded with XIAP siRNA and Gambogic Acid for Inhalation Therapy of Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(22), 14294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214294