Characterization of Endogenous Levels of Brassinosteroids and Related Genes in Grapevines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
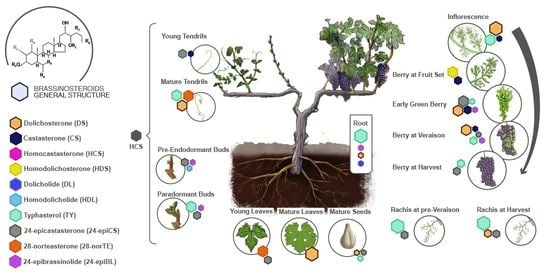
2.1. Quantification of the Levels of Brassinosteroids during the Development of Grapevines
2.2. Gene Expression Analysis of the Brassinosteroid Pathways in Grapevines
3. Discussion
3.1. Endogenous Levels of Brassinosteroids in Grapevines
3.2. Tissue- and Development-Specific Expression Profile of Genes Involved in the Brassinosteroid Pathway in Grapevines
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Brassinosteroid Measurements
4.3. Bioinformatic Search of Genes in Grapevine Databases and Primer Design
4.4. qRT-PCR Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 24-epiBL | 24-epibrassinolide |
| 24-epiCS | 24-epicastasterone |
| 28-norTE | 28-norteasterone |
| BES1 | BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR1 |
| BIN2 | BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE2 |
| BR6OX | BRASSINOSTEROID-6-OXIDASE |
| BRI1 | BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE1 |
| BRs | Brassinosteroids |
| BZR1 | BRASSINAZOLE RESISTANT |
| CS | Castasterone |
| CT | Cathasterone |
| CPD | CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC DWARF |
| CYP90D1 | CYTOCHROME P450 90D1 |
| DET2 | DEETIOLATED2 |
| DL | Dolicholide |
| DS | Dolichosterone |
| DWF4 | DWARF4 |
| HDL | Homodolicholide |
| HCS | Homocastasterone |
| HDS | Homodolichosterone |
| ROT3 | ROTUNDIFOLIA 3 |
| TE | Teasterone |
| TY | Typhasterol |
References
- Gladstone, E.A.; Dokoozlian, N.K. Influence of leaf area density and trellis/training system on the light microclimate within grapevine canopies. Vitis 2003, 42, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, M. The Science of Grapevines: Anatomy and Physiology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- Fenn, M.A.; Giovannoni, J.J. Phytohormones in fruit development and maturation. Plant J. 2021, 105, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogawat, A.; Yadav, B.; Chhaya; Lakra, N.; Singh, A.K.; Narayan, O.P. Crosstalk between phytohormones and secondary metabolites in the drought stress tolerance of crop plants: A review. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 172, 1106–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, Q.; Wang, B.; Yuan, F. Roles of Phytohormones and Their Signaling Pathways in Leaf Development and Stress Responses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3566–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajguz, A.; Tretyn, A. The chemical characteristic and distribution of brassinosteroids in plants. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklestkova, J.; Tarkowská, D.; Eyer, L.; Elbert, T.; Marek, A.; Smržová, Z.; Novák, O.; Fránek, M.; Zhabinskii, V.N.; Strnad, M. Immunoaffinity chromatography combined with tandem mass spectrometry: A new tool for the selective capture and analysis of brassinosteroid plant hormones. Talanta 2017, 170, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkowská, D.; Novák, O.; Oklestkova, J.; Strnad, M. The determination of 22 natural brassinosteroids in a minute sample of plant tissue by UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6799–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Nitta, T.; Asami, T.; Fujioka, S.; Arai, Y.; Sekimata, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yamaguchi, I.; Yoshida, S. Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. Plant J. 2003, 33, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furio, R.N.; Albornoz, P.L.; Coll, Y.; Martínez Zamora, G.M.; Salazar, S.M.; Martos, G.G.; Díaz Ricci, J.C. Effect of natural and synthetic Brassinosteroids on strawberry immune response against Colletotrichum acutatum. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 153, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, G.J.; Li, X.; Liu, A.; Chen, S. Brassinosteroids in Plant Tolerance to Abiotic Stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.M.; Vukasinovic, N.; Liu, D.; Russinova, E.; Yin, Y. Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional Regulators of Plant Growth, Development, and Stress Responses. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anwar, A.; Liu, Y.; Dong, R.; Bai, L.; Yu, X.; Li, Y. The physiological and molecular mechanism of brassinosteroid in response to stress: A review. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clouse, S.D. Brassinosteroids. Arab. Book 2011, 9, e0151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Sae-seaw, J.; Wang, Z. Brassinosteroid signalling. Development 2013, 140, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azpiroz, R.; Wu, Y.; LoCascio, J.C.; Feldmann, K.A. An Arabidopsis Brassinosteroid-Dependent Mutant Is Blocked in Cell Elongation. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goda, H.; Sawa, S.; Asami, T.; Fujioka, S.; Shimada, Y.; Yoshida, S. Comprehensive Comparison of Auxin-Regulated and Brassinosteroid-Regulated Genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1555–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Bao, F.; Li, J. Promotive effect of brassinosteroids on cell division involves a distinct CycD3-induction pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2000, 24, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Netto, A.B. Genomic and non-genomic events involved in the brassinosteroid promoted plant cell growth. In Brassinosteroids: A Class of Plant Hormone; Hayat, S., Ahmad, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordercht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clouse, S.D. Brassinosteroids Plant Counterparts to animals steroid hormones? Vitam. Horm. 2002, 65, 195–223. [Google Scholar]
- Brosa, C.; Capdevila, J.M.; Zamora, I. Brassinosteroids: A new way to define the structural requirements. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 2435–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Sun, X.; Ding, T.; Lei, B.; Zhang, C. Structure-activity relationship of brassinosteroids and their agricultural practical usages. Steroids 2017, 124, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuto, S.; Ikekawa, N.; Morishita, T.; Abe, H. Structure-Activity Relationship of Brassinosteroids with Respect to the A/B-Ring Functional Groups. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takatsuto, S.; Yazawa, N. Structure-activity relationship of brassinosteroids. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Chang, S.C.; Choo, J.; Watanabe, T.; Takatsuto, S.; Yokota, T.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.K. Brassinolide and [26, 28–2H6] brassinolide are differently demethylated by loss of C-26 and C-28, respectively, in Marchantia polymorpha. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000, 41, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wada, K.; Marumo, S.; Mori, K.; Morisaki, M.; Ikekawa, N.; Takatsuto, S. The Rice Lamina Inclination-promoting Activity of Synthetic Brassinolide Analogues with a Modified Side Chain. Agr. Biol. Chem. 1983, 47, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Noguchi, T.; Yokota, T.; Shibata, K.; Koshino, H.; Seto, H.; Kim, S.; Takatsuto, S. Synthesis and biological activity of 26-norbrassinolide, 26-norcastasterone and 26-nor-6-deoxocastasterone. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullo MA, T.; Bajguz, A. The Brassinosteroids Family-Structural Diversity of Natural Compounds and Their Precursors. In Brassinosteroids: Plant Growth and Development; Hayat, S., Yusuf, M., Bhardwaj, R., Bajguz, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, T.; Kushiro, T.; Yokota, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Bishop, G.J.; Yamaguchi, S. The last reaction producing brassinolide is catalyzed by cytochrome P-450s, CYP85A3 in tomato and CYP85A2 in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17873–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, A.; Fujioka, S.; Sunohara, H.; Kamiya, N.; Hong, Z.; Inukai, Y.; Miura, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; et al. The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamuro, C.; Ihara, Y.; Wu, X.; Noguchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zullo MA, T.; Adam, G. Brassinosteroid phytohormones—Structure, bioactivity and applications. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 14, 143–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajguz, A.; Chmur, M.; Gruszka, D. Comprehensive overview of the brassinosteroid biosynthesis pathways: Substrates, products, inhibitors, and connnections. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, S.; Yokota, T. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Brassinosteroids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Jang, M.S.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.K. Biosynthetic relationship between C28-brassinosteroids and C29-brassinosteroids in rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Phytochemistry 2015, 111, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMorris, T.C.; Patil, P.A.; Chavez, R.G.; Baker, M.E.; Clouse, S.D. Synthesis and biological activity of 28-homobrassinolide and analogues. Phytochemistry 1994, 36, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Sato, T.; Bishop, G.J.; Kamiya, Y.; Takatsuto, S.; Yokota, T. Accumulation of 6-deoxocathasterone and 6-deoxocastasterone in Arabidopsis, pea and tomato is suggestive of common rate-limiting steps in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, G.M.; Davies, C.; Shavrukov, Y.; Dry, I.B.; Reid, J.B.; Thomas, M.R. Grapes on steroids. Brassinosteroids are involved in grape berry ripening. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Champa WA, H.; Gill MI, S.; Mahajan, B.V.C.; Aror, N.K.; Bedi, S. Brassinosteroids Improve Quality of Table Grapes (Vitis vinifera L.) cv. Flame Seedless. Trop. Agric. Res. 2015, 26, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xi, Z.; Huo, S.; Ma, L. Brassinosteroids Regulate Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in the Ripening of Grape Berries. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2013, 34, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huo, S.S.; Luan, L.Y.; Gao, X.; Ma, L.N.; Fang, Y.L. Regulating the secondary metabolism in grape berry using exogenous 24-epibrassinolide for enhanced phenolics content and antioxidant capacity. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Xi, Z.-M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.-J.; Zhang, Z.-W. Brassinosteroids are involved in controlling sugar unloading in Vitis vinifera “Cabernet Sauvignon” berries during véraison. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalık, Z.; Demirci, T.; Aşcı, Ö.A.; Baydar, N.G. Brassinosteroids Modify Yield, Quality, and Antioxidant Components in Grapes (Vitis vinifera cv. Alphonse Lavallée). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 39, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichsen, D.M.; Joazeiro, C.A.P.; Li, J.; Hunter, T.; Chory, J. Brassinosteroid-Insensitive-1 Is a Ubiquitously Expressed Leucine-Rich Repeat Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinase. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Nam, K.H.; Vafeados, D.; Chory, J. BIN2, a new brassinosteroid -insensitive locus in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimada, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Miyauchi, N.; Kushiro, M.; Takatsuto, S.; Nomura, T.; Yokota, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Bishop, G.J.; Yoshida, S. Brassinosteroid-6-Oxidases from Arabidopsis and Tomato Catalyze Multiple C-6 Oxidations in Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, M.-Y.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Zhu, S.-W.; Song, W.-Y.; Chong, K.; Wang, Z.-Y. Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13839–13844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holton, N.; Can, A.; Bishop, G.J. Tomato BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE1 Is Required for Systemin-Induced Root Elongation in Solanum pimpinellifolium but Is Not Essential for Wound Signaling. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corvalán, C.; Choe, S. Identification of brassinosteroid genes in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasoli, M.; Dal Santo, S.; Zenoni, S.; Tornielli, G.B.; Farina, L.; Zamboni, A.; Porceddu, A.; Venturini, L.; Bicego, M.; Murino, V.; et al. The grapevine expression atlas reveals a deep transcriptome shift driving the entire plant into a maturation program. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3489–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joo, S.H.; Kim, T.W.; Son, S.H.; Lee, W.S.; Yokota, T.; Kim, S.K. Biosynthesis of a cholesterol-derived brassinosteroid, 28-norcastasterone, in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Hwang, J.Y.; Joo, S.H.; Son, S.H.; Youn, J.H.; Kim, S.K. Biosynthesis and metabolism of dolichosterone in Arabidopsis thaliana. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 3475–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youn, J.H.; Kim, T.W.; Joo, S.H.; Son, S.H.; Roh, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, S.K. Function and molecular regulation of DWARF1 as a C-24 reductase in brassinosteroid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Xu, H.; Li, B.; Shang, Y.; Wei, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Qin, R.; Cui, F.; Wu, Y. The brassinosteroid biosynthesis gene, ZmD11, increases seed size and quality in rice and maize. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, S.; Ashikari, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; et al. A Novel Cytochrome P450 Is Implicated in Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis via the Characterization of a Rice Dwarf Mutant, dwarf11, with Reduced Seed Length. Plant Cell. 2005, 17, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohnishi, T.; Godza, B.; Watanabe, B.; Fujioka, S.; Hategan, L.; Ide, K.; Shibata, K.; Yokota, T.; Szekeres, M.; Mizutani, M. CYP90A1/CPD, a brassinosteroid biosynthetic cytochrome P450 of Arabidopsis, catalyzes C-3 oxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 87, 31551–31560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Biswas, M.G.; Chao, A.; Russell, D.W.; Chory, J. Conservation of function between mammalian and plant steroid 5alpha-reductases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3554–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choe, S.; Dilkes, B.P.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Sakurai, A.; Feldmann, K.A. The DWF4 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a cytochrome P450 that mediates multiple 22α-hydroxylation steps in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Watanabe, B.; Yokota, T.; Takatsuto, S.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Sakata, K.; Mizutani, M. Arabidopsis CYP90B1 catalyses the early C-22 hydroxylation of C27,C28 and C29 sterols. Plant J. 2006, 45, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.T.; Fujioka, S.; Kozuka, T.; Tax, F.E.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Tsukaya, H. CYP90C1 and CYP90D1 are involved in different steps in the brassinosteroid biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2005, 41, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Goda, H.; Nakamura, A.; Takatsuto, S.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S. Organ-Specific Expression of Brassinosteroid-Biosynthetic Genes and Distribution of Endogenous Brassinosteroids in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belkhadir, Y.; Jaillais, Y. The molecular circuitry of brassinosteroids Signaling. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 522–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, P. Biosynthesis and Accumulation of Sterols. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajguz, A. Brassinosteroids-occurence and chemical structures in plants. In Brassinosteroids: A Class of Plant Hormone; Hayat, S., Ahmad, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka, S.; Noguchi, T.; Yokota, T.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S. Brassinosteroids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Fujioka, S.; Yokota, T.; Murofushi, N.; Sakurai, A. Identification of Brassinolide, Castasterone, Typhasterol, and Teasterone from the Pollen of Lilium elegans. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 2075–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Ueno, M.; Yamada, Y.; Takatsuto, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yokota, T. Roles of Brassinosteroids and Related mRNAs in Pea Seed Growth and Germination. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokota, T.; Baba, J.; Takahashi, N. A new steroidal lactone with plant growth-regulatory activity from Dolichos lablab seed. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 4965–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancoş, S.; Nomura, T.; Sato, T.; Molnár, G.; Bishop, G.J.; Koncz, C.; Yokota, T.; Nagy, F.; Szekeres, M. Regulation of Transcript Levels of the Arabidopsis Cytochrome P450 Genes Involved in Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikekawa, N.; Nishiyama, F.; Fujimoto, Y. Identification of 24-epibrassinolide in bee pollen of the broad bean, Vicia faba L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Symons, G.M.; Ross, J.J.; Jager, C.E.; Reid, J.B. Brassinosteroid transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Li, J. Regulation of Brassinosteroid Homeostasis in Higher Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 583622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, G.M.; Reid, J.B. Brassinosteroids Do Not Undergo Long-Distance Transport in Pea. Implications for the Regulation of Endogenous Brassinosteroid Levels. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 2196–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montoya, T.; Nomura, T.; Yokota, T.; Farrar, K.; Harrison, K.; Jones, J.G.D.; Kaneta, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Szekeres, M.; Bishop, G.J. Patterns of Dwarf expression and brassinosteroid accumulation in tomato reveal the importance of brassinosteroid synthesis during fruit development. Plant J. 2005, 42, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, M.; Németh, K.; Koncz-Kálmán, Z.; Mathur, J.; Kauschmann, A.; Altmann, T.; Rédei, G.P.; Nagy, F.; Schell, J.; Koncz, C. Brassinosteroids Rescue the Deficiency of CYP90, a Cytochrome P450, Controlling Cell Elongation and De-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Cell 1996, 85, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panchy, N.; Lehti-Shiu, M.; Shiu, S.-H. Evolution of Gene Duplication in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohnishi, T.; Szatmari, A.-M.; Watanabe, B.; Fujita, S.; Bancos, S.; Koncz, C.; Lafos, M.; Shibata, K.; Yokota, T.; Sakata, K.; et al. C-23 Hydroxylation by Arabidopsis CYP90C1 and CYP90D1 Reveals a Novel Shortcut in Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3275–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.-T.; Tsukaya, H.; Saito, Y.; Uchimiya, H. Changes in the shapes of leaves and flowers upon overexpression of cytochrome P450 in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9433–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castle, J.; Szekeres, M.; Jenkins, G.; Bishop, G.J. Unique and overlapping expression patterns of Arabidopsis CYP85 genes involved in brassinosteroid C-6 oxidation. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 57, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hategan, L.; Godza, B.; Szekeres, M. Regulation of brassinosteroid metabolism. In Brassinosteroids: A Class of Plant Hormone; Hayat, S., Ahmad, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordercht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Codreanu, M.C.; Russinova, E. Regulatory mechanisms of brassinosteroid signaling in plants. In Brassinosteroids: A Class of Plant Hormone; Hayat, S., Ahmad, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordercht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Coombe, B.G. Growth Stages of the Grapevine: Adoption of a system for identifying grapevine growth stages. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 1995, 1, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar]
- Loyola, R.; Herrera, D.; Mas, A.; Chern, D.; Wong, J.; Höll, J.; Cavallini, E.; Amato, A.; Azuma, A.; Ziegler, T.; et al. The photomorphogenic factors UV-B RECEPTOR 1, ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5, and HY5 HOMOLOGUE are part of the UV-B signalling pathway in grapevine and mediate flavonol accumulation in response to the environment. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5429–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, C.; Gomez-Talquenca, S.; Chialva, C.; Ibáñez, J.; Martinez-Zapater, J.M.; Peña-Neira, Á.; Lijavetzky, D. Relationships among gene expression and anthocyanin composition of malbec grapevine clones. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6716–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parada, F.; Oklestkova, J.; Arce-Johnson, P. Characterization of Endogenous Levels of Brassinosteroids and Related Genes in Grapevines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031827
Parada F, Oklestkova J, Arce-Johnson P. Characterization of Endogenous Levels of Brassinosteroids and Related Genes in Grapevines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031827
Chicago/Turabian StyleParada, Francisca, Jana Oklestkova, and Patricio Arce-Johnson. 2022. "Characterization of Endogenous Levels of Brassinosteroids and Related Genes in Grapevines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031827
APA StyleParada, F., Oklestkova, J., & Arce-Johnson, P. (2022). Characterization of Endogenous Levels of Brassinosteroids and Related Genes in Grapevines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031827