Phytoglobin Expression Alters the Na+/K+ Balance and Antioxidant Responses in Soybean Plants Exposed to Na2SO4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
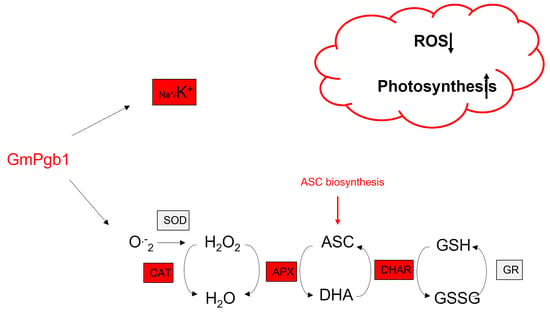
2.1. Overexpression of GmPgb1 Augments Tolerance to Salinity Stress
2.2. Na+ and K+ Accumulation during Salinity Stress Is Influenced by GmPgb1
2.3. Na2SO4 Accumulation of Foliar H2O2 and Lipid Peroxidation Are Mitigated by the Overexpression of GmPgb1
2.4. Antioxidant Responses in Leaves of Salt-Stressed Plants Are Induced by GmPgb1
2.5. GmPgb1 Expression in Commercial Soybean Cultivars
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. Determination of Morphophysiological Parameters
4.3. Measurements of K+ and Na+
4.4. Stomata Measurements
4.5. Measurements of Transcript Levels
4.6. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Quantification of Ascorbic Acid and Glutathione
4.7. Lipid Peroxidation and H2O2 Measurements
4.8. Nitric Oxide (NO) Localization
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartels, D.; Sunkar, R. Drought and salt tolerance in plants. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2005, 24, 23–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, P.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Effect of salinity stress on plants and its tolerance strategies, a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4056–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Blumwald, E. Developing salt-tolerant crop plants, challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.Z.; Chen, Y.W.; Shao, G.H.; Wan, C.W. Effect of salt stress on agronomic characteristics and chemical quality of seeds in soybean. Soybean Sci. 1994, 13, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Phang, T.H.; Shao, G.; Lam, H.M. Salt tolerance in soybean. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 1196–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabot, C.; Sibole, J.V.; Barceló, J.; Poschenrieder, C. Lessons from crop plants struggling with salinity. Plant Sci. 2014, 226, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, J.; Rodrigo-Moreno, A.; Shabala, S. ROS homeostasis in halophytes in the context of salinity stress tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Termaat, A. Whole-plant responses to salinity. Funct. Plant Biol. 1986, 13, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.; Tester, M.; Roy, S.J. Quantifying the three main components of salinity tolerance in cereals. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayenkov, S.V.; Maathuis, F.J. Plant salinity stress, many unanswered questions remain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isayenkov, S.V. Physiological and molecular aspects of salt stress in plants. Cytol. Genet. 2012, 46, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.; Jajoo, A.; Mathur, S.; Bharti, S. Chlorophyll a fluorescence study revealing effects of high salt stress on Photosystem II in wheat leaves. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaji, H.M.; Rastogi, A.; Živčák, M.; Brestic, M.; Daszkowska-Golec, A.; Sitko, K.; Alsharafa, K.Y.; Lotfi, R.; Stypiński, P.; Samborska, I.A.; et al. Prompt chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool for crop phenotyping, an example of barley landraces exposed to various abiotic stress factors. Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, G. Responses of leaf stomatal density to water status and its relationship with photosynthesis in a grass. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 3317–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assaha, D.V.; Ueda, A.; Saneoka, H.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Yaish, M.W. The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in Glycophytes. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidchik, V.; Straltsova, D.; Medvedev, S.S.; Pozhvanov, G.A.; Sokolik, A.; Yurin, V. Stress-induced electrolyte leakage, the role of K+-permeable channels and involvement in programmed cell death and metabolic adjustment. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabala, S.; Pottosin, I. Regulation of potassium transport in plants under hostile conditions, implications for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 151, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Ishitani, M.; Kim, C.; Zhu, J.K. The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6896–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintero, F.J.; Ohta, M.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J.-H.; Pardo, J.M. Reconstitution in yeast of the Arabidopss SOS signaling pathway for Na+ homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9061–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feki, K.; Quintero, F.J.; Khoudi, H.; Leidi, E.O.; Masmoudi, K.; Pardo, J.M.; Brini, F. A constitutively active form of a durum wheat Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 confers high salt tolerance to transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, P.; Liu, Z.; Yu, B.; Shi, H. Soybean Na+/K+ antiporter GmSOS1 enhances antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces Na+ accumulation in Arabidopsis cells under stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Stress-triggered redox signalling, what’s in pROSpect? Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, A.M.; Hunter, M.I.S.; Crawford, R.M. Contrasting effects of anoxia on rhizome lipids in Iris species. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.M.M.; Walton, J.C.; Wollenweber-Ratzer, B. Similarities between post-ischaemic injury to animal tissues and post-anoxic injury in plants. Proc. Royal Soc. B 1994, 102, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ullah, F.; Zhou, D.X.; Yi, M.; Zhao, Y. Mechanisms of ROS regulation of plant development and stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, A.; Yadav, S.; Bhatla, S.C. Sodium chloride stress induces nitric oxide accumulation in root tips and oil body surface accompanying slower oleosin degradation in sunflower seedlings. Plant Physiol. 2010, 140, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C. Regulation of programmed cell death by phytoglobins. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5901–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.M.; Huang, S.; Kapoor, K.; Hammond, C.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C. Expression of Arabidopsis class 1 phytoglobin (AtPgb1) delays death and degradation of the root apical meristem during severe PEG-induced water deficit. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5653–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mira, M.M.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C. Phytoglobins improve hypoxic root growth by alleviating apical meristem cell death. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Xiong, D.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Hu, W.J.; Simon, M.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, D.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Hu, W.H.; et al. Nitric oxide mediates root K+/Na+ balance in a mangrove plant, Kandelia obovata, by enhancing the expression of AKT1-Type K+ channel and Na+/H+ antiporter under high salinity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Kong, D.; Xue, S.; Tian, W.; Li, N.; Bao, F.; Hu, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; et al. Nitric oxide negatively regulates AKT1-mediated potassium uptake through modulating vitamin B6 homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16196–16201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nabi, R.B.S.; Tayade, R.; Hussain, A.; Kulkarni, K.P.; Imran, Q.M.; Mun, B.G.; Yun, B.W. Nitric oxide regulates plant responses to drought, salinity, and heavy metal stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.D. Non-symbiotic haemoglobins—What’s happening beyond nitric oxide scavenging? AoB Plants 2012, 2012, pls004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva-Cardenas, R.I.; Ricard, B.; Saglio, P.; Hill, R.D. Hemoglobin and hypoxic acclimation in maize root tips. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 50, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.S.; Mira, M.M.; Renault, S.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C. Phytoglobin expression influences soil flooding response of corn plants. Ann. Bot. 2016, 118, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mira, M.M.; Huang, S.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C. Tolerance to excess moisture in soybean is enhanced by over-expression of the Glycine max Phytoglobin (GmPgb1). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, C.R.; Jensen, E.O.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Dennis, E.S.; Peacock, W.J. A new hemoglobin gene from soybean, a role for hemoglobin in all plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5682–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Morita, R.; Katsuma, S.; Nishimura, M.; Tanaka, A.; Kusaba, M. Two short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases, NON-YELLOW COLORING 1 and NYC1-LIKE, are required for chlorophyll b and light-harvesting complex II degradation during senescence in rice. Plant J. 2009, 57, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Q.; Chang, X.; Sun, M.; Li, W.; Li, Y. GmAKT1 is involved in K+ uptake and Na+/K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis and soybean plants. Plant Sci. 2021, 304, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, H. Non-destructive determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) distribution in oilseed rape leaves by laboratory scale NIR hyperspectral imaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi, M.; Fluhr, R. Production of reactive oxygen species by plant NADPH oxidases. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blokhina, O.; Fagerstedt, K.V. Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in plant mitochondria, origin and redundant regulatory systems. Physiol. Plant. 2010, 138, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelsaad, I.; Relault, S. Enhanced oxidative stress in jasmonic acid-deficient tomato mutant def-1 exposed to NaCl stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 226, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Wu, G.; Cai, Q. Puccinella tenuiflora mantains a low Na+ level under salinity by limiting unidirectional Na+ influx resulting in a high selectivity for K+ over Na+. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.K.; Das, A.B. Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants, a review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 324–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Suzuki, N.; Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.X.; Yuan, H.J.; Hu, J.; Wei, L.; Bao, A.K.; Zheng, J.L.; Wang, S.M. ZxSOS1 is essential for limiting long-distance transport and special distribution of Na+ in Zygophyllum. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.H.; Leidi, E.; Zhang, Q.; Hwang, S.M.; Li, Y.; Quintero, F.J.; Bohnert, H.J. Loss of halophytism by interference with SOS1 expression. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormick, S.D.; Sundell, K.; Björnsson, B.T.; Brown, C.L.; Hiroi, J. Influence of salinity on the localization of Na+/K+-ATPase, Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter (NKCC) and CFTR anion channel in chloride cells of the Hawaiian goby (Stenogobius hawaiiensis). J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 4575–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begara-Morales, J.C.; Sánchez-Calvo, B.; Chaki, M.; Valderrama, R.; Mata-Pérez, C.; López-Jaramillo, J.; Padilla, M.N.; Carreras, A.; Corpas, F.C.; Barroso, J.B. Dual regulation of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (APX) by tyrosine nitration and S-nitrosylation. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seminario, A.; Song, L.; Zulet, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; González, E.M.; Larrainzar, E. Drought stress causes a reduction in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid in soybean plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez, J.M.; Hernandez, J.A.; Jimenez, A.; Del Rio, L.A.; Sevilla, F. Differential response of antioxidative enzymes of chloroplasts and mitochondria to long-term NaCl stress of pea plants. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciolla, C.; Fortunato, S.; Dipierro, N.; Paradiso, A.; De Leonardis, S.; Mastropasqua, L.; De Pinto, M.C. Vitamin C in plants, from functions to biofortification. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youssef, M.S.; Renault, S.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C. The soybean Phytoglobin1 (GmPgb1) is involved in water deficit responses through changes in ABA metabolism. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 267, 153538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, C.; Sun, S.; Wu, C.; Hou, W. Soybean hairy roots produced in vitro by Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation. Crop J. 2018, 6, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Hussain, S.; Raza, M.A.; Yang, C.Q.; Safdar, M.E.; Brestic, M.; Liu, J. Drought tolerance of soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) by improved photosynthetic characteristics and an efficient antioxidant enzyme activities under a split-root system. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kirkham, M.B. Antioxidant responses to drought in sunflower and sorghum seedlings. New Phytol. 1996, 132, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts, I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.P. Ferrous ion oxidation in presence of ferric ion indicator xylenol orange for measurement of hydroperoxides. Meth. Enzymol. 1994, 233, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, Z.X.; Wei, J.P.; Shen, C.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.P.; Han, W.Y. Nitric oxide mediates brassinosteroid-induced flavonoid biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis L. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 214, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Kim, H.J.; Chen, H.; Lu, Y.; Lu, X.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Zhou, B.Y. Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide induce senescence of rudimentary leaves and the expression profiles of the related genes in Litchi chinensis. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youssef, M.S.; Mira, M.M.; Renault, S.; Hill, R.D.; Stasolla, C. Phytoglobin Expression Alters the Na+/K+ Balance and Antioxidant Responses in Soybean Plants Exposed to Na2SO4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084072
Youssef MS, Mira MM, Renault S, Hill RD, Stasolla C. Phytoglobin Expression Alters the Na+/K+ Balance and Antioxidant Responses in Soybean Plants Exposed to Na2SO4. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(8):4072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084072
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoussef, Mohamed S., Mohammed M. Mira, Sylvie Renault, Robert D. Hill, and Claudio Stasolla. 2022. "Phytoglobin Expression Alters the Na+/K+ Balance and Antioxidant Responses in Soybean Plants Exposed to Na2SO4" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 8: 4072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084072
APA StyleYoussef, M. S., Mira, M. M., Renault, S., Hill, R. D., & Stasolla, C. (2022). Phytoglobin Expression Alters the Na+/K+ Balance and Antioxidant Responses in Soybean Plants Exposed to Na2SO4. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(8), 4072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084072