Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EPAC2 Is Expressed in Rod Inner Segments and Perikaryonal Regions
2.2. EPAC2 Is Overexpressed upon Retinal Degeneration
2.3. Both cGMP and cAMP Levels Increase in Degenerating Photoreceptors
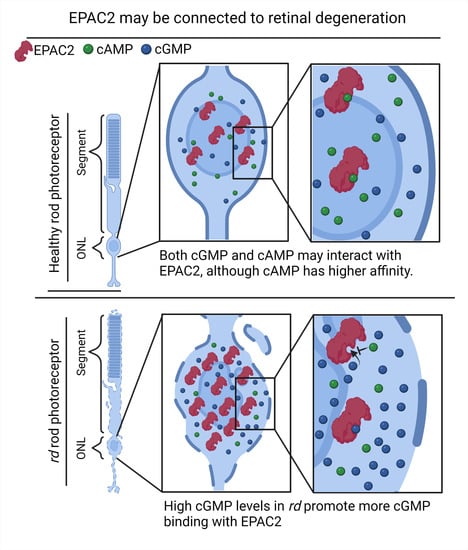
2.4. EPAC2 Shows Increased Interaction with cGMP during Retinal Degeneration
2.5. Inhibiting EPAC2 Activity Reduces ONL Thickness in the rd10 Model
3. Discussion
3.1. EPAC2 Is Expressed in Rod Inner Segments and Perikaryonal Regions
3.2. EPAC2 Is Overexpressed upon Retinal Degeneration
3.3. The EPAC2 Interactors cGMP and cAMP Accumulate during Degeneration
3.4. Inhibiting EPAC2 Activity Reduces ONL Thickness in the rd10 Model
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Organotypic Retinal Explant Culture
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
4.6. Rap1-GTP Activity Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahim, A.T.; Daiger, S.P.; Weleber, R.G. Nonsyndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa Overview. GeneReviews®. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301590 (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Chang, S.; Vaccarella, L.; Olatunji, S.; Cebulla, C.; Christoforidis, J. Diagnostic Challenges in Retinitis Pigmentosa: Genotypic Multiplicity and Phenotypic Variability. Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfeiffer, R.L.; Marc, R.E.; Jones, B.W. Persistent remodeling and neurodegeneration in late-stage retinal degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 74, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.; Yücel, Y.H.; Zhou, X.; Mathieu, E.; Paczka-Giorgi, L.A.; Gupta, N. Progressive loss of retinal blood vessels in a live model of retinitis pigmentosa. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 53, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petit, L.; Lhériteau, E.; Weber, M.; Le Meur, G.; Deschamps, J.Y.; Provost, N.; Mendes-Madeira, A.; Libeau, L.; Guihal, C.; Colle, M.A.; et al. Restoration of vision in the PDE6β-deficient dog, a large animal model of rod-cone dystrophy. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haim, M. The epidemiology of retinitis pigmentosa in Denmark. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. Suppl. 2002, 80, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichard, V.; Provost, N.; Mendes-Madeira, A.; Libeau, L.; Hulin, P.; Tshilenge, K.T.; Biget, M.; Ameline, B.; Deschamps, J.Y.; Weber, M.; et al. AAV-mediated gene therapy halts retinal degeneration in PDE6β-deficient dogs. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, S.; Bennett, J.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; McCague, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.; Das, S.; Schütze, K.; Marigo, V.; Ekström, P.; Paquet-Durand, F. Cellular mechanisms of hereditary photoreceptor degeneration—Focus on cGMP. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 74, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, D.B.; Lolley, R.N. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate: Elevation in degenerating photoreceptor cells of the C3H mouse retina. Science 1974, 186, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet-Durand, F.; Hauck, S.M.; Van Veen, T.; Ueffing, M.; Ekström, P. PKG activity causes photoreceptor cell death in two retinitis pigmentosa models. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahaboglu, A.; Paquet-Durand, O.; Dietter, J.; Dengler, K.; Bernhard-Kurz, S.; Ekström, P.A.R.; Hitzmann, B.; Ueffing, M.; Paquet-Durand, F. Retinitis pigmentosa: Rapid neurodegeneration is governed by slow cell death mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango-Gonzalez, B.; Trifunović, D.; Sahaboglu, A.; Kranz, K.; Michalakis, S.; Farinelli, P.; Koch, S.; Koch, F.; Cottet, S.; Janssen-Bienhold, U.; et al. Identification of a common non-apoptotic cell death mechanism in hereditary retinal degeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, E.; Burgers, P.P.; Plank, M.; Heck, A.J.R.; Scholten, A. Huntingtin-Associated Protein 1 (HAP1) is a cGMP-dependent Kinase Anchoring Protein (GKAP) specific for the cGMP-dependent protein kinase Iβ isoform. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 7887–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francis, S.H.; Corbin, J.D. Cyclic Nucleotide-Dependent Protein Kinases. Encycl. Biol. Chem. Second Ed. 2013, 50, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.H.; Blount, M.A.; Zoraghi, R.; Corbin, J.D. Molecular properties of mammalian proteins that interact with cGMP: Protein kinases, cation channels, phosphodiesterases, and multi-drug anion transporters. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2097–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzolini, M.; Arcangeletti, M.; Marchesi, A.; Napolitano, L.M.R.; Grosa, D.; Maity, S.; Anselmi, C.; Torre, V. The gating mechanism in cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vighi, E.; Trifunović, D.; Veiga-Crespo, P.; Rentsch, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Sahaboglu, A.; Strasser, T.; Kulkarni, M.; Bertolotti, E.; Van Den Heuvel, A.; et al. Combination of cGMP analogue and drug delivery system provides functional protection in hereditary retinal degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2997–E3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehmann, H.; Arias-Palomo, E.; Hadders, M.A.; Schwede, F.; Llorca, O.; Bos, J.L. Structure of Epac2 in complex with a cyclic AMP analogue and RAP1B. Nature 2008, 455, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.; Welinder, C.; Schwede, F.; Ekström, P. The cGMP system in normal and degenerating mouse neuroretina: New proteins with cGMP interaction potential identified by a proteomics approach. J. Neurochem. 2020, 157, 2173–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmann, H.; Schwede, F.; Doøskeland, S.O.; Wittinghofer, A.; Bos, J.L. Ligand-mediated activation of the cAMP-responsive guanine nucleotide exchange factor Epac. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38548–38556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, A.E.; Selheim, F.; De Rooij, J.; Dremier, S.; Schwede, F.; Dao, K.K.; Martinez, A.; Maenhaut, C.; Bos, J.L.; Genieser, H.G.; et al. cAMP analog mapping of Epac1 and cAMP kinase: Discriminating analogs demonstrate that Epac and cAMP kinase act synergistically to promote PC-12 cell neurite extension. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35394–35402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Takahashi, M.; Li, Y.; Dillon, T.J.; Kaech, S.; Stork, P.J.S. The Interaction of Epac1 and Ran Promotes Rap1 Activation at the Nuclear Envelope. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 3956–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Yokoyama, U.; Abe, T.; Kiyonari, H.; Yamashita, N.; Kato, Y.; Kurotani, R.; Sato, M.; Okumura, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Differential roles of Epac in regulating cell death in neuronal and myocardial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24248–24259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shim, M.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Bu, J.H.; Nam, H.S.; Jeong, S.W.; Park, T.L.; Ellisman, M.H.; Weinreb, R.N.; Ju, W.K. Elevated intracellular cAMP exacerbates vulnerability to oxidative stress in optic nerve head astrocytes article. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Chowdhury, S.; Mazhab-Jafari, M.T.; SilDas, S.; Selvaratnam, R.; Melacini, G. Dynamically driven ligand selectivity in cyclic nucleotide binding domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23682–23696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitaker, C.M.; Cooper, N.G.F. Differential distribution of exchange proteins directly activated by cyclic AMP within the adult rat retina. Neuroscience 2010, 165, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Ha, Y.; Xia, F.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, S.; Mei, F.C.; Merkley, K.; Vizzeri, G.; Motamedi, M.; et al. Neuronal Epac1 mediates retinal neurodegeneration in mouse models of ocular hypertension. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.J.; Lin, C.; Liu, X.; Antonetti, D.A. The EPAC-Rap1 pathway prevents and reverses cytokineinduced retinal vascular permeability. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Gao, R. Inhibition of Epac2 Attenuates Neural Cell Apoptosis and Improves Neurological Deficits in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro-Belmar, A.; Domanski, D.M.; Bo, X.; Shewan, D.; Huang, W. The therapeutic potential of targeting exchange protein directly activated by cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (Epac) for central nervous system trauma. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanks, J.C.; Johnson, L.V. Specific binding of peanut lectin to a class of retinal photoreceptor cells. A species comparison. IOVS 1984, 25, 546–557. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.V.; Hageman, G.S.; Blanks, J.C. Interphotoreceptor matrix domains ensheath vertebrate cone photoreceptor cells. IOVS 1986, 27, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Molday, L.L.; Cheng, C.L.; Molday, R.S. Cell-Specific Markers for the Identification of Retinal Cells and Subcellular Organelles by Immunofluorescence Microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1834, 293–310. [Google Scholar]
- Traverso, V.; Bush, R.A.; Sieving, P.A.; Deretic, D. Retinal cAMP levels during the progression of retinal degeneration in rhodopsin P23H and S334ter transgenic rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Bowes, C.; Li, T.; Danciger, M.; Baxter, L.C.; Applebury, M.L.; Farber, D.B. Retinal degeneration in the rd mouse is caused by a defect in the β subunit of rod cGMP-phosphodiesterase. Nature 1990, 347, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter-Dawson, L.D.; LaVail, M.M.; Sidman, R.L. Differential effect of the rd mutation on rods and cones in the mouse retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1978, 17, 489–498. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.; Hawes, N.L.; Pardue, M.T.; German, A.M.; Hurd, R.E.; Davisson, M.T.; Nusinowitz, S.; Rengarajan, K.; Boyd, A.P.; Sidney, S.S.; et al. Two mouse retinal degenerations caused by missense mutations in the β-subunit of rod cGMP phosphodiesterase gene. Vision Res. 2007, 47, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanyal, S.; Jansen, H.G. Absence of receptor outer segments in the retina of rds mutant mice. Neurosci. Lett. 1981, 21, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tsang, S.H.; Chen, J. Two pathways of rod photoreceptor cell death induced by elevated cGMP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, C.; Miller, C.L.; Abe, J.I. Regulation of Phosphodiesterase 3 and Inducible cAMP Early Repressor in the Heart. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakao, T.; Tsujikawa, M.; Notomi, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Nishida, K. The Role of Mislocalized Phototransduction in Photoreceptor Cell Death of Retinitis Pigmentosa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, J.; Van Ittersum, M.M.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; De Vente, J. Nitric oxide-mediated cGMP synthesis in oligodendrocytes in the developing rat brain. Glia 1997, 19, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.; Bal, A.K. Comparative light and electron microscopic study of retinal histogenesis in normal and rd mutant mice. Z. Anat. Entwicklungsgesch. 1973, 142, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.; Zeilmaker, G.H. Development and degeneration of retina in rds mutant mice: Light and electron microscopic observations in experimental chimaeras. Exp. Eye Res. 1984, 39, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj, S.; Tolone, A.; Christensen, G.; Das, S.; Chen, Y.; Paquet-Durand, F. Long-Term, Serum-Free Cultivation of Organotypic Mouse Retina Explants with Intact Retinal Pigment Epithelium. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 2020, e61868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffé, A.R.; Ahuja, P.; Holmqvist, B.; Azadi, S.; Forsell, J.; Holmqvist, I.; Söderpalm, A.K.; Van Veen, T. Mouse retina explants after long-term culture in serum free medium. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2002, 22, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Antibody | Provider | Cat. No. | Dilution IF/PLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep anti-cGMP | Provided by Harry W.M. Steinbusch, Maastrich University, the Netherlands [43] | Not applicable | 1:500 |
| Rabbit anti-EPAC2 | Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA) | ABN492 | 1:300 |
| Mouse-anti Rhodopsin | Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA) | Mab5316 | 1:300 |
| Rabbit-anti cAMP | Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA) | 07-1497 | 1:300 |
| Lectin PNA Alexa Fluor™ 594 Conjugate | Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) | L32459 | 1:1000 |
| Mouse-anti ATP1A3 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | Ab2826 | 1:300 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasmussen, M.; Zhou, J.; Schwede, F.; Ekström, P. Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094619
Rasmussen M, Zhou J, Schwede F, Ekström P. Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094619
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasmussen, Michel, Jiaming Zhou, Frank Schwede, and Per Ekström. 2022. "Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094619
APA StyleRasmussen, M., Zhou, J., Schwede, F., & Ekström, P. (2022). Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094619