Enhancer RNA AL928768.3 from the IGH Locus Regulates MYC Expression and Controls the Proliferation and Chemoresistance of Burkitt Lymphoma Cells with IGH/MYC Translocation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Search for Potential eRNAs from the IGH Locus
2.2. Analysis of AL928768.3 eRNA Expression in Human Blood Cells
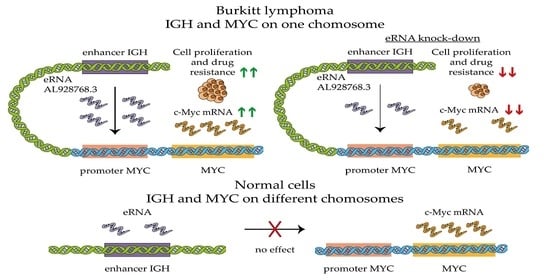
2.3. Effect of eRNA Knockdown on MYC Expression, Cell Proliferation and Chemoresistance
2.4. Effect of eRNA Overexpression on MYC Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Search for eRNAs for Functional Analysis
4.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.3. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay and Chemoresistance
4.5. Correlational Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nambiar, M.; Kari, V.; Raghavan, S.C. Chromosomal translocations in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2008, 1786, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardi, T.; Vicente, C.; Cools, J.; De Keersmaecker, K. The genetics and molecular biology of T-ALL. Blood 2017, 129, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangazio, M.; Pasqualucci, L.; Dalla-Favera, R. Chromosomal Translocations in B Cell Lymphomas. In Chromosomal Translocations and Genome Rearrangements in Cancer; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2015; pp. 157–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J. Oncogenic chromosomal translocations and human cancer (review). Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burmeister, T.; Molkentin, M.; Schwartz, S.; Gökbuget, N.; Hoelzer, D.; Thiel, E.; Reinhardt, R. Erroneous class switching and false VDJ recombination: Molecular dissection of t(8;14)/MYC-IGH translocations in Burkitt-type lymphoblastic leukemia/B-cell lymphoma. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernheim, A.; Berger, R.; Lenoir, G. Cytogenetic studies on African Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines: T(8;14), t(2;8) and t(8;22) translocations. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1981, 3, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, G.; MacArthur, G.J.; Farrell, P.J. Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt lymphoma. Postgrad. Med. J. 2008, 84, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, B.; Liebermann, D.A. Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6462–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dang, C. V MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stasevich, E.M.; Murashko, M.M.; Zinevich, L.S.; Demin, D.E.; Schwartz, A.M. The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of the Proto-Oncogene MYC in Different Types of Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wu, Q.; Lathia, J.D.; McLendon, R.E.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Rich, J.N. c-Myc Is Required for Maintenance of Glioma Cancer Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Curet, I.; Perkins, R.S.; Bennett, R.; Feidler, K.L.; Dunn, S.P.; Krueger, L.J. c-Myc inhibition negatively impacts lymphoma growth. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Gan, Y.; Xu, S.; Gu, Y.; Huang, W. Alternative approaches to target Myc for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, P.A.; Freie, B.W.; Mathsyaraja, H.; Eisenman, R.N. The MYC transcription factor network: Balancing metabolism, proliferation and oncogenesis. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, P.-F.; Dell’Orso, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Vivanco, K.O.; Ko, K.-D.; Jiang, K.; Juan, A.H.; Sarshad, A.A.; Vian, L.; Tran, M.; et al. A Muscle-Specific Enhancer RNA Mediates Cohesin Recruitment and Regulates Transcription In trans. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 129–141.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo, C.A.; Drost, J.; Wijchers, P.J.; van de Werken, H.; de Wit, E.; Oude Vrielink, J.A.F.; Elkon, R.; Melo, S.A.; Léveillé, N.; Kalluri, R.; et al. eRNAs are required for p53-dependent enhancer activity and gene transcription. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Xie, P.; Cao, L.; Zhang, M.Q.; Kim, T.H. Global transcriptional activity dynamics reveal functional enhancer RNAs. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, P.R.; Wells, A.D.; Li, X.C. Diversity and Emerging Roles of Enhancer RNA in Regulation of Gene Expression and Cell Fate. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, M.T.Y.; Li, W.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Glass, C.K. Enhancer RNAs and regulated transcriptional programs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, G.; Wang, T.; Xue, F.; Qi, Y.; Wang, R.; Yuan, H. Identification of enhancer RNAs for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 3820–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Shen, H.; Ma, G.; Cong, L.; Du, J. Gender specific eRNA TBX5-AS1 as the immunological biomarker for male patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma in pan-cancer screening. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.Y.; Kraus, W.L. Spirits in the Material World: Enhancer RNAs in Transcriptional Regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaukowitch, K.; Joo, J.-Y.; Liu, X.; Watts, J.K.; Martinez, C.; Kim, T.-K. Enhancer RNA facilitates NELF release from immediate early genes. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Ren, S.; Wang, L.; Blackburn, P.R.; McNulty, M.S.; Gao, X.; Qiao, M.; Vessella, R.L.; Kohli, M.; et al. Activation of P-TEFb by Androgen Receptor-Regulated Enhancer RNAs in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Notani, D.; Ma, Q.; Tanasa, B.; Nunez, E.; Chen, A.Y.; Merkurjev, D.; Zhang, J.; Ohgi, K.; Song, X.; et al. Functional roles of enhancer RNAs for oestrogen-dependent transcriptional activation. Nature 2013, 498, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahnamoun, H.; Lee, J.; Sun, Z.; Lu, H.; Ramsey, K.M.; Komives, E.A.; Lauberth, S.M. RNAs interact with BRD4 to promote enhanced chromatin engagement and transcription activation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Yuan, J.; Sun, K.; Chen, X.; Bao, X.; Esteban, M.A.; Sun, H.; et al. MyoD induced enhancer RNA interacts with hnRNPL to activate target gene transcription during myogenic differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, D.A.; Donahue, G.; Reinberg, D.; Shiekhattar, R.; Bonasio, R.; Berger, S.L. RNA Binding to CBP Stimulates Histone Acetylation and Transcription. Cell 2017, 168, 135–149.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sartorelli, V.; Lauberth, S.M. Enhancer RNAs are an important regulatory layer of the epigenome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.-H.; Ruan, H.; Ye, Y.; Krakowiak, J.; Hu, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhou, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Transcriptional landscape and clinical utility of enhancer RNAs for eRNA-targeted therapy in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eraslan, G.; Drokhlyansky, E.; Anand, S.; Subramanian, A.; Fiskin, E.; Slyper, M.; Wang, J.; Wittenberghe, N.; Van Rouhana, J.M.; Waldman, J.; et al. Single-nucleus cross-tissue molecular reference maps to decipher disease gene function. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.M.; Anastasi, J.; Cohen, K.S.; Godley, L.A. The impact of MYC expression in lymphoma biology: Beyond Burkitt lymphoma. Blood Cells. Mol. Dis. 2010, 45, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rihawi, K.; Alfieri, R.; Fiorentino, M.; Fontana, F.; Capizzi, E.; Cavazzoni, A.; Terracciano, M.; La Monica, S.; Ferrarini, A.; Buson, G.; et al. MYC Amplification as a Potential Mechanism of Primary Resistance to Crizotinib in ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Brief Report. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilling, A.B.; Kim, J.; Estrada-Bernal, A.; Zhou, Q.; Le, A.T.; Singleton, K.R.; Heasley, L.E.; Tan, A.C.; DeGregori, J.; Doebele, R.C. ALK is a critical regulator of the MYC-signaling axis in ALK positive lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8823–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, C.; Hassan, B.; Haque, M.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Lipke, E.; Chen, W.; Giuriato, S.; Lai, R. Crizotinib Resistance Mediated by Autophagy Is Higher in the Stem-Like Cell Subset in ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, and This Effect Is MYC-Dependent. Cancers 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Tu, J.; Liu, C.; Pan, A.; Xia, X.; Chen, X. Analysis of lncRNA expression profiles by sequencing reveals that lnc-AL928768.3 and lnc-AC091493.1 are novel biomarkers for disease risk and activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Zorca, C.E.; Traboulsi, T.; Noutahi, E.; Krause, M.R.; Mader, S.; Zenklusen, D. Single-cell profiling reveals that eRNA accumulation at enhancer-promoter loops is not required to sustain transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhaylichenko, O.; Bondarenko, V.; Harnett, D.; Schor, I.E.; Males, M.; Viales, R.R.; Furlong, E.E.M. The degree of enhancer or promoter activity is reflected by the levels and directionality of eRNA transcription. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristjánsdóttir, K.; Dziubek, A.; Kang, H.M.; Kwak, H. Population-scale study of eRNA transcription reveals bipartite functional enhancer architecture. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Trivedi, P.; Jain, N.K. Advances in siRNA delivery in cancer therapy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ruan, Y.; Tan, Y.; Reed-Maldonado, A.B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Peng, D.; Banie, L.; et al. Regenerating Urethral Striated Muscle by CRISPRi/dCas9-KRAB-Mediated Myostatin Silencing for Obesity-Associated Stress Urinary Incontinence. Cris. J. 2020, 3, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logunov, D.Y.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; Tukhvatulin, A.I.; Zubkova, O.V.; Dzharullaeva, A.S.; Kovyrshina, A.V.; Lubenets, N.L.; Grousova, D.M.; Erokhova, A.S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: An interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. Lancet 2021, 397, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenforde, M.W.; Self, W.H.; Naioti, E.A.; Ginde, A.A.; Douin, D.J.; Olson, S.M.; Talbot, H.K.; Casey, J.D.; Mohr, N.M.; Zepeski, A.; et al. Sustained Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines Against COVID-19 Associated Hospitalizations Among Adults-United States, March–July 2021. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Oehm, P.; Derhovanessian, E.; Jabulowsky, R.A.; Vormehr, M.; Gold, M.; Maurus, D.; Schwarck-Kokarakis, D.; Kuhn, A.N.; Omokoko, T.; et al. An RNA vaccine drives immunity in checkpoint-inhibitor-treated melanoma. Nature 2020, 585, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, A.M.; Flotte, T.R. Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy in Light of Luxturna (and Zolgensma and Glybera): Where Are We, and How Did We Get Here? Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 601–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistillo, M.P.; Tanigaki, N.; Mazzoleni, O.; Ciccone, E.; Hämmerling, U.; Park, M.; Terasaki, P.I.; Ferrara, G.B. Human lymphoblastoid cell lines secreting antibodies with restricted HLA specificity. Immunogenetics 1987, 25, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagapova, E.; Kozlov, M.; Lebedev, T.; Ivanenko, K.; Leonova, O.; Popenko, V.; Spirin, P.; Kochetkov, S.; Prassolov, V. Selective Inhibition of HDAC Class I Sensitizes Leukemia and Neuroblastoma Cells to Anticancer Drugs. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Oligonucleotides | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| siRNA AL928768.3 F | UCUGCAACACAGCAAGAGCdTdT |
| siRNA AL928768.3 R | GCUCUUGCUGUGUUGCAGAdTdT |
| scRNA AL928768.3 F | GGAGAAUAGCCCCAACACUdTdT |
| scRNA AL928768.3 R | AGUGUUGGGGCUAUUCUCCdTdT |
| AL928768.3_qPCR F | CACAGGGAGGAAGTGTGGAG |
| AL928768.3_qPCR R | GGGCCACTTTATTGCACCTG |
| c-Myc_qPCR F | AGCCCCGAGCCCCTGGTG |
| c-Myc_qPCR R | GGCGCTGCGTAGTTGTGCTGATGT |
| GAPDH_qPCR F | CAAGGTCATCCATGACAACTTTG |
| GAPDH_qPCR R | GGCCATCCACAGTCTTCTGG |
| IGHA1 qPCR F | ACATGCCACGTGAAGCACT |
| IGHA1 qPCR R | GCACGTGAGGTTCGCTTCT |
| IGHG1 qPCR F | CAGGACTCTACTCCCTCAGCA |
| IGHG1 qPCR R | ATGAGGGTGTCCTTGGGTTT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stasevich, E.M.; Uvarova, A.N.; Murashko, M.M.; Khabusheva, E.R.; Sheetikov, S.A.; Prassolov, V.S.; Kuprash, D.V.; Demin, D.E.; Schwartz, A.M. Enhancer RNA AL928768.3 from the IGH Locus Regulates MYC Expression and Controls the Proliferation and Chemoresistance of Burkitt Lymphoma Cells with IGH/MYC Translocation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094624
Stasevich EM, Uvarova AN, Murashko MM, Khabusheva ER, Sheetikov SA, Prassolov VS, Kuprash DV, Demin DE, Schwartz AM. Enhancer RNA AL928768.3 from the IGH Locus Regulates MYC Expression and Controls the Proliferation and Chemoresistance of Burkitt Lymphoma Cells with IGH/MYC Translocation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094624
Chicago/Turabian StyleStasevich, Ekaterina Mikhailovna, Aksinya Nicolaevna Uvarova, Matvey Mikhailovich Murashko, Elmira Ramilevna Khabusheva, Saveliy Andreevich Sheetikov, Vladimir Sergeyevich Prassolov, Dmitriy Vladimirovich Kuprash, Denis Eriksonovich Demin, and Anton Markovich Schwartz. 2022. "Enhancer RNA AL928768.3 from the IGH Locus Regulates MYC Expression and Controls the Proliferation and Chemoresistance of Burkitt Lymphoma Cells with IGH/MYC Translocation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094624
APA StyleStasevich, E. M., Uvarova, A. N., Murashko, M. M., Khabusheva, E. R., Sheetikov, S. A., Prassolov, V. S., Kuprash, D. V., Demin, D. E., & Schwartz, A. M. (2022). Enhancer RNA AL928768.3 from the IGH Locus Regulates MYC Expression and Controls the Proliferation and Chemoresistance of Burkitt Lymphoma Cells with IGH/MYC Translocation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094624