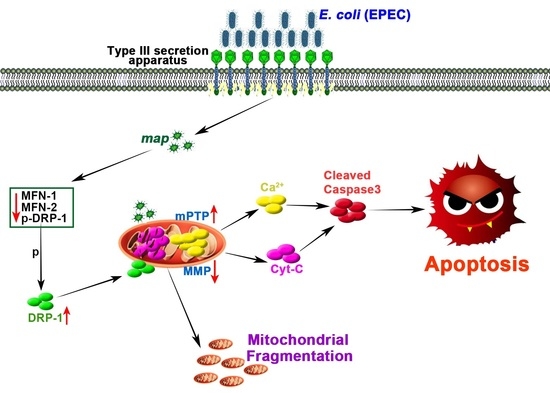
Map of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Targets Mitochondria and Triggers DRP-1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Cell Apoptosis in Bovine Mastitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. E. Coli (EPEC) Induces Increased Mitochondrial Fission, Decreased Fusion, Cyt-C Release, and Decreased MMP, Eventually Leading to Apoptosis
2.2. E. Coli (EPEC) Mediates DRP-1-Dependent Apoptosis
2.3. E. Coli (EPEC) Evokes the Continuous Opening of mPTP and Mitochondrial Cyt-C and Ca2+ Release
2.4. E. Coli (EPEC)-Map Induces Mitochondrial Fragmentation
2.5. E. Coli (EPEC)-Map Results in Sustained mPTP Opening, Cyt-C Release, Low MMP, and Apoptosis
2.6. Map, as a Virulence Factor of E. Coli (EPEC), Is Sufficient to Induce Mitochondrial Fission and Apoptosis
2.7. Map Is Required for E. Coli (EPEC)-Induced Apoptosis In Vivo
3. Discussion and Conclusions
3.1. EPEC Leads to DRP-1-Dependent Endogenous Apoptosis in Bovine Mastitis
3.2. The Map Virulence Factor Induces Mitochondrial Fission and Mitochondrial Apoptosis in EPEC-Induced Bovine Mastitis
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Mitochondrial Imaging
4.6. MMP and mPTP Measurements
4.7. Calcium (Ca2+) Concentration Detection
4.8. Flow Cytometry Assessment of Apoptosis
4.9. Localization of the Map Effector-Protein
4.10. Animals
4.11. Mouse Mastitis Model
4.12. Histopathology, TUNEL, and Transmission Electron Microscopy Assay (TEM)
4.13. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cvetnic, L.; Samardzija, M.; Duvnjak, S.; Habrun, B.; Cvetnic, M.; Jaki Tkalec, V.; Duricic, D.; Benic, M. Multi locus sequence typing and spa typing of staphylococcus aureus isolated from the milk of cows with subclinical mastitis in croatia. Microoganisms 2021, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaas, I.C.; Zadoks, R.N. An update on environmental mastitis: Challenging perceptions. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65 (Suppl. 1), 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burvenich, C.; Van Merris, V.; Mehrzad, J.; Diez-Fraile, A.; Duchateau, L. Severity of E. coli mastitis is mainly determined by cow factors. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 521–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nemeth, J.; Muckle, C.A.; Gyles, C.L. In vitro comparison of bovine mastitis and fecal Escherichia coli isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 1994, 40, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidar-Ugrinovich, L.; Blanco, J.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Leomil, L.; Dahbi, G.; Mora, A.; Onuma, D.L.; Silveira, W.D.; Pestana de Castro, A.F. Serotypes, virulence genes, and intimin types of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) isolated from calves in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2007, 115, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, D.J.; Ennis, C.; McDowell, D. Occurrence, virulence genes and antibiotic resistance of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) from twelve bovine farms in the North-East of Ireland. Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovski, K.R.; Trajcev, M.; Buneski, G. A review of the factors affecting the costs of bovine mastitis. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2006, 77, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaytan, M.O.; Martinez-Santos, V.I.; Soto, E.; Gonzalez-Pedrajo, B. Type Three Secretion System in attaching and effacing pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinaud, L.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Phalipon, A. Host cell targeting by Enteropathogenic bacteria T3SS effectors. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.; Kenny, B. The effector repertoire of enteropathogenic E. coli: Ganging up on the host cell. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, P.; Maresca, M.; Kenny, B. EPEC’s weapons of mass subversion. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, B.; Jepson, M. Targeting of an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) effector protein to host mitochondria. Cell Microbiol. 2000, 2, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, J.A.; Li, Y.; Wickham, M.E.; Deng, W.; Vogl, A.W.; Finlay, B.B. Attaching and effacing pathogen-induced tight junction disruption in vivo. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.; Scott, J.A.; Knox, A.A.; Quitard, S.; Watkins, N.J.; Kenny, B. The enteropathogenic E. coli effector EspF targets and disrupts the nucleolus by a process regulated by mitochondrial dysfunction. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quitard, S.; Dean, P.; Maresca, M.; Kenny, B. The enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF effector molecule inhibits PI-3 kinase-mediated uptake independently of mitochondrial targeting. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenny, B. Mechanism of action of EPEC type III effector molecules. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 291, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Ghochani, M.; McCaffery, J.M.; Frey, T.G.; Chan, D.C. Mitofusins and OPA1 mediate sequential steps in mitochondrial membrane fusion. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 3525–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Chan, D.C. Mitochondrial dynamics and inheritance during cell division, development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Duan, H.; Wang, H.; Pei, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L. Activation of mitophagy in inflamed odontoblasts. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudel, T.; Kepp, O.; Kozjak-Pavlovic, V. Interactions between bacterial pathogens and mitochondrial cell death pathways. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montessuit, S.; Somasekharan, S.P.; Terrones, O.; Lucken-Ardjomande, S.; Herzig, S.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Manstein, D.J.; Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Basanez, G.; Meda, P.; et al. Membrane remodeling induced by the dynamin-related protein Drp1 stimulates Bax oligomerization. Cell 2010, 142, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Syed, G.H.; Khan, M.; Chiu, W.W.; Sohail, M.A.; Gish, R.G.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis C virus triggers mitochondrial fission and attenuates apoptosis to promote viral persistence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6413–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.G.; Park, J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, D.S. Iron overload-induced calcium signals modulate mitochondrial fragmentation in HT-22 hippocampal neuron cells. Toxicology 2016, 365, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.B.; Kalkhoran, S.B.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Hausenloy, D.J. Mitochondrial fusion and fission proteins as novel therapeutic targets for treating cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 763 Pt A, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Z.K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, D.B.; Liu, Z.P.; Wang, L. Mitochondrial permeability transition and its regulatory components are implicated in apoptosis of primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1193–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinthong, W.; Pumipuntu, N.; Santajit, S.; Kulpeanprasit, S.; Buranasinsup, S.; Sookrung, N.; Chaicumpa, W.; Aiumurai, P.; Indrawattana, N. Detection and drug resistance profile of Escherichia coli from subclinical mastitis cows and water supply in dairy farms in Saraburi Province, Thailand. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baggiolini, M.; Walz, A.; Kunkel, S.L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, J.A.; Rosen, A. Apoptosis and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behar, S.M.; Briken, V. Apoptosis inhibition by intracellular bacteria and its consequence on host immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2019, 60, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, A.N.; Wang, A.; McKay, D.M.; Buret, A.G. Apoptosis-inducing factor contributes to epithelial cell apoptosis induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 89, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, A.; Scorrano, L. Mitochondria: From cell death executioners to regulators of cell differentiation. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.J.; Goldufsky, J.W.; Bello, D.; Masood, S.; Shafikhani, S.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoT induces mitochondrial apoptosis in target host cells in a manner that depends on its GTPase-activating protein (GAP) domain activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29063–29073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, P.; Luo, Z.Q.; Blanke, S.R. Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA) engages the mitochondrial fission machinery to induce host cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16032–16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escoll, P.; Song, O.R.; Viana, F.; Steiner, B.; Lagache, T.; Olivo-Marin, J.C.; Impens, F.; Brodin, P.; Hilbi, H.; Buchrieser, C. Legionella pneumophila modulates mitochondrial dynamics to trigger metabolic repurposing of infected macrophages. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 302–316.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nougayrede, J.P.; Donnenberg, M.S. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF is targeted to mitochondria and is required to initiate the mitochondrial death pathway. Cell. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.K.; McNamara, B.P.; Donnenberg, M.S. Role of EspF in host cell death induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Cell. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.P.; Spiegel, C.; Keren, Y.; Danieli, T.; Melamed-Book, N.; Pal, R.R.; Zlotkin-Rivkin, E.; Rosenshine, I.; Aroeti, B. Mitochondrial targeting of the Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Map triggers Calcium mobilization, ADAM10-MAP Kinase signaling, and host cell apoptosis. mBio 2020, 11, e01397-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samba-Louaka, A.; Nougayrede, J.P.; Watrin, C.; Oswald, E.; Taieb, F. The enteropathogenic Escherichia coli effector Cif induces delayed apoptosis in epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 5471–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papatheodorou, P.; Domanska, G.; Oxle, M.; Mathieu, J.; Selchow, O.; Kenny, B.; Rassow, J. The enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) Map effector is imported into the mitochondrial matrix by the TOM/Hsp70 system and alters organelle morphology. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Abe, A.; Sasakawa, C. Targeting of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF to host mitochondria is essential for bacterial pathogenesis: Critical role of the 16th leucine residue in EspF. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2998–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Wickham, M.E.; Guttman, J.A.; Deng, W.; Walker, J.; Madsen, K.L.; Jacobson, K.; Vogl, W.A.; Finlay, B.B.; Vallance, B.A. Citrobacter rodentium infection causes both mitochondrial dysfunction and intestinal epithelial barrier disruption in vivo: Role of mitochondrial associated protein (Map). Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1669–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, B.; Duan, C.; Sun, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, S. Multigene editing in the Escherichia coli genome via the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2506–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valente, A.J.; Maddalena, L.A.; Robb, E.L.; Moradi, F.; Stuart, J.A. A simple ImageJ macro tool for analyzing mitochondrial network morphology in mammalian cell culture. Acta Histochem. 2017, 119, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, P.; Maimai, T.; Yanyi, L.; Cao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N. The gut microbiota contributes to the development of Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chu, B.; Liu, N.; Chen, S.; Wang, J. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 prevents Escherichia coli-induced apoptosis through PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in bovine mastitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 715098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, S. Lactobacillus casei Zhang counteracts blood-milk barrier disruption and moderates the inflammatory response in Escherichia coli-induced mastitis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 675492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chu, B.; Liu, N.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y. Map of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Targets Mitochondria and Triggers DRP-1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Cell Apoptosis in Bovine Mastitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094907
Li Y, Zhu Y, Chu B, Liu N, Chen S, Wang J, Zou Y. Map of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Targets Mitochondria and Triggers DRP-1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Cell Apoptosis in Bovine Mastitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094907
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanan, Yaohong Zhu, Bingxin Chu, Ning Liu, Shiyan Chen, Jiufeng Wang, and Yunjing Zou. 2022. "Map of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Targets Mitochondria and Triggers DRP-1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Cell Apoptosis in Bovine Mastitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094907
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhu, Y., Chu, B., Liu, N., Chen, S., Wang, J., & Zou, Y. (2022). Map of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Targets Mitochondria and Triggers DRP-1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and Cell Apoptosis in Bovine Mastitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094907