Impact of Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupter DDT on Adrenal Medulla Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Changes in Epinephrine Plasma Levels
2.2. Changes in Histology of Adrenal Medulla
2.3. Changes in Fine Structure of Adrenal Chromaffin Cells
2.4. Changes in Tyrosine Hydroxylase Production
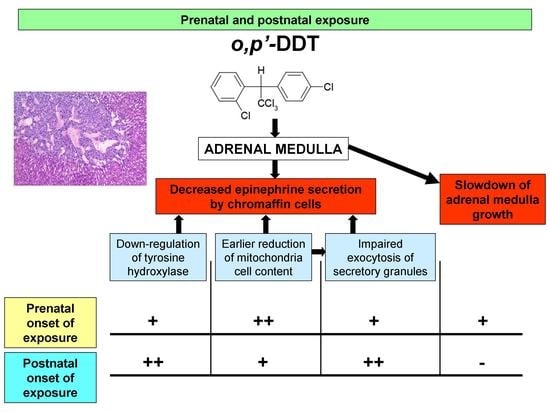
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2. Epinephrine Assay
4.3. Adrenal Histology
4.4. Electron Microscopy
4.5. Computer Histo- and Cytomorphometry
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Street, M.E.; Angelini, S.; Bernasconi, S.; Burgio, E.; Cassio, A.; Catellani, C.; Cirillo, F.; Deodati, A.; Fabbrizi, E.; Fanos, V.; et al. Current knowledge on endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) from animal biology to humans, from pregnancy to adulthood: Highlights from a national Italian meeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Merrill, M.A.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Smith, M.T.; Goodson, W.; Browne, P.; Patisaul, H.B.; Guyton, K.Z.; Kortenkamp, A.; Cogliano, V.J.; Woodruff, T.J.; et al. Consensus on the key characteristics of endocrine-disrupting chemicals as a basis for hazard identification. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 18, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansouri, A.; Cregut, M.; Abbes, C.; Durand, M.-J.; Landoulsi, A.; Thouand, G. The environmental issues of DDT pollution and bioremediation: A multidisciplinary review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 309–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The Use of DDT in Malaria Vector Control; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Neto, E.B.; Azevedo-Silva, C.E.; Bisi, T.L.; Santos, J.; Meirelles, A.C.O.; Carvalho, V.L.; Lailson-Brito, J. Organochlorine concentrations (PCBs, DDTs, HCHs, HCB and MIREX) in delphinids stranded at northeastern Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.C.; Chen, S.J.; Zheng, J.; Tian, M.; Feng, A.H.; Luo, X.J.; Mai, B.X. The occurrence of brominated flame retardants (BFRs), organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in agricultural soils in a BFR-manufacturing region of North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munschy, C.; Bodin, N.; Potier, M.; Héas-Moisan, K.; Pollono, C.; Degroote, M.; Nikolic, N. Persistent organic pollutants in albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga) from Reunion Island (Southwest Indian Ocean) and South Africa in relation to biological and trophic characteristics. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Faiz, P.; Aamir, M.; Sabir, M.; Mahmood, Q. Occurrence and spatio-vertical distribution of DDT in soils of abandoned DDT factory area, Amangarh, Pakistan. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haug, L.S.; Sakhi, A.K.; Cequier, E.; Casas, M.; Maitre, L.; Basagana, X.; Andrusaityte, S.; Chalkiadaki, G.; Chatzi, L.; Coen, M.; et al. In-utero and childhood chemical exposome in six European mother-child cohorts. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2, The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, D.M.; Beckman, B.S.; Hill, S.M.; McLachlan, J.A.; Walters, M.R.; Arnold, S.F. Identification of environmental chemicals with estrogenic activity using a combination of in vitro assays. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Lemmen, J.G.; Carlsson, B.; Corton, J.C.; Safe, S.H.; van der Saag, P.T.; van der Burg, B.; Gustafsson, J.A. Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4252–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Tsomartova, D.A.; Yaglov, V.V. Differences in production of adrenal steroid hormones in pubertal rats exposed to low doses of the endocrine disrupter DDT during prenatal and postnatal development. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2018, 12, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Vizcaino, E.; Murcia, M.; Llop, S.; Espada, M.; Seco, V.; Marco, A.; Rebagliato, M.; Grimalt, J.O.; Ballester, F. Association between thyroid hormone levels and 4,40-DDE concentrations in pregnant women (Valencia, Spain). Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Mechanisms of disruptive action of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) on the function of thyroid follicular epitheliocytes. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 160, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calsolaro, V.; Pasqualetti, G.; Niccolai, F.; Caraccio, N.; Monzani, F. Thyroid disrupting chemicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Codru, N.; Schymura, M.J.; Negoita, S.; Rej, R.; Carpenter, D.O. Diabetes in relation to serum levels of polychlorinated biphenyls and chlorinated pesticides in adult Native Americans. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tank, A.W.; Lee Wong, D. Peripheral and central effects of circulating catecholamines. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.; Tsomartova, D.; Yaglov, V. Effect of prenatal and postnatal exposure to low doses of DDT on catecholamine secretion in rats in different period of ontogeny. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 163, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Pesticide Residues in Food—2018. Toxicological Evaluations. World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; p. 780. [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli, D.; Xiao, F.; Gouvtia, A.; Ferreira, J.; Vinson, G. Adrenarche in the rat. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 191, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbins, I.L. Peripheral Autonomic Pathways; in The Human Nervous System; Mai, J.K., Paxinos, G., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 141–186. [Google Scholar]
- Daubner, S.C.; Le, T.; Wang, S. Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmichael, S.W.; Brooks, J.C.; Malhotra, R.K.; Wakade, T.D.; Wakade, A.R. Ultrastructural demonstration of exocytosis in the intact rat adrenal medulla. J. Electron. Microsc. Technol. 1989, 12, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupland, R.E. Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the rat adrenal medulla. I. The ultrastructure and organization of chromaffin cells in the normal adrenal medulla. J. Anat. 1965, 99, 31–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgoyne, R.D.; Morgan, A.; Robinson, I.; Pender, N.; Cheek, T.R. Exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J. Anat. 1993, 183, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montero, M.; Alonso, M.T.; Carnicero, E.; Cuchillo-Ibanez, I.; Albillos, A.; Garcıa, A.G.; Garcıa-Sancho, J.; Alvarez, J. Chromaffin-cell stimulation triggers fast millimolar mitochondrial Ca2+ transients that modulate secretion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa, A.G.; Garcıa-De-Diego, A.M.; Gandıa, L.; Borges, R.; Garcıa-Sancho, J. Calcium signaling and exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1093–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcıa-Sancho, J.; de Diego, A.M.; Garcıa, A.G. Mitochondria and chromaffin cell function. Pflugers Arch. 2012, 464, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, C.; Nuñez, L.; Montero, M.; Garcıa, A.; Alonso, M.T.; Chamero, P.; Alvarez, J.; Garcia-Sancho, J. Redistribution of Ca2+ among cytosol and organella during stimulation of bovine chromaffin cells. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, J.F.; Baris, O.R.; Kittelmann, A.; Becker, K.; Rothschild, M.A.; Wiesner, R.J. Catecholamine Metabolism Induces Mitochondrial DNA Deletions and Leads to Severe Adrenal Degeneration during Aging. Neuroendocrinology 2017, 104, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, J.; Viniegra, S.; Gimenez-Molina, Y.; Garcia-Martinez, V.; Exposito-Romero, G.; del Mar Frances, M.; Garcia-Sancho, J.; Guttierez, L. The position of mitochondria and ER in relation to that of the secretory sites in chromaffin cells. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 5105–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvorak, A.M. A role for vesicles in human basophil secretion. Cell. Tissue Res. 1998, 293, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivellato, E.; Belloni, A.; Nico, B.; Nussdorfer, G.G.; Ribatti, D. Chromaffin granules in the rat adrenal medulla release their secretory content in a particulate fashion. Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2004, 277, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Biology of mast cells secretion. Clin. Exp. Morphol. 2012, 4, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Ultrastructural characteristics of molecular release of secretory products from thyroid mast cells induced by lipopolysaccharide. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 155, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheel, H.; Vicario, M.; Boesmans, W.; Salvo-Romero, E.; Tack, J.; Farre, R. Activation of Eosinophils and Mast Cells in Functional Dyspepsia: An Ultrastructural Evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Obernikhin, S.S.; Tsomartova, D.A.; Nazimova, S.V.; Yaglov, V.V.; Tsomartova, E.S.; Chereshneva, E.V.; Ivanova, M.Y.; Lomanovskaya, T.A. Impaired Morphogenesis and Function of Rat Adrenal Zona Glomerulosa by Developmental Low-Dose Exposure to DDT Is Associated with Altered Oct4 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Obernikhin, S.S.; Yaglov, V.V.; Nazimova, S.V.; Timokhina, E.P.; Tsomartova, D.A. Low-Dose Exposure to Endocrine Disrupter Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) Affects Transcriptional Regulation of Adrenal Zona Reticularis in Male Rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 170, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.; Kalcheim, C.; Unsicker, K. The development of the chromaffin cell lineage from the neural crest. Auton. Neurosci. 2009, 151, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhofstad, A.N.; Coupland, R.E.; Parker, T.R.; Goldstein, M. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study on the development of the noradrenaline and adrenaline-storing cells of the adrenal medulla of the rat. Cell Tis. Res. 1985, 242, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, A.; Durbin, J.; Coupland, R.E. A quantitative analysis of rat adrenal chromaffin tissue. Morphometric analysis at tissue and cellular level correlated with catecholamine content. Neuroscience 1987, 20, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Central Role of the Brain in Stress and Adaptation; in Stress: Concepts, Cognition, Emotion, and Behavior; Fink, J., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; p. 487. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, H.; Takano, R.; Shimizu, M.; Murayama, N.; Kitajima, M.; Shono, M. Human blood concentrations of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) extrapolated from metabolism in rats and humans and physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. J. Health Sci. 2010, 56, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaglova, N.V.; Obernikhin, S.S.; Tsomartova, D.A.; Yaglov, V.V.; Nazimova, S.V.; Tsomartova, E.S.; Timokhina, E.P.; Chereshneva, E.V.; Ivanova, M.Y.; Lomanovskaya, T.A. Impact of Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupter DDT on Adrenal Medulla Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094912
Yaglova NV, Obernikhin SS, Tsomartova DA, Yaglov VV, Nazimova SV, Tsomartova ES, Timokhina EP, Chereshneva EV, Ivanova MY, Lomanovskaya TA. Impact of Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupter DDT on Adrenal Medulla Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094912
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaglova, Nataliya V., Sergey S. Obernikhin, Dibakhan A. Tsomartova, Valentin V. Yaglov, Svetlana V. Nazimova, Elina S. Tsomartova, Ekaterina P. Timokhina, Elizaveta V. Chereshneva, Marina Y. Ivanova, and Tatiana A. Lomanovskaya. 2022. "Impact of Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupter DDT on Adrenal Medulla Function" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 9: 4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094912
APA StyleYaglova, N. V., Obernikhin, S. S., Tsomartova, D. A., Yaglov, V. V., Nazimova, S. V., Tsomartova, E. S., Timokhina, E. P., Chereshneva, E. V., Ivanova, M. Y., & Lomanovskaya, T. A. (2022). Impact of Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Endocrine Disrupter DDT on Adrenal Medulla Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(9), 4912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094912